Dual Credit US History Semester Final Review (Final on 12/12/2023)
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
What were the "separate spheres of influence" for women vs. men in the early 19th century?
Men exercise influence in the public spheres of politics and business.
Women maintain the private, domestic, sphere of the home.
The intersection between these nineteenth-century ideas of appropriate femininity forms the groundwork for many female characters in realist novels of the period.
What was the First Great Awakening?
A time of religious fervor during the 1730s and 1740s.
Arose in reaction to the rise of skepticism and the waning of religious faith brought about by the Enlightenment.
Protestant ministers held revivals throughout the English colonies in America, stressing the need for individuals to repent and urging a personal understanding of truth.term-47
What was the Embargo Act?
Legislation by Congress in 1807 that closed U.S. ports to all exports and restricted imports from Britain.
Response to British and French interference (impressment of American sailors) with neutral U.S. merchant ships during the Napoleonic Wars.
Smugglers easily circumvented the embargo, and it was repealed two years later.
What was the National Road?
First road in U.S. history funded by the federal government.
Promoted westward expansion
Opened the Ohio River Valley and the Midwest for settlement and commerce.
620 miles finished in 1837 from Maryland to Illinois
What is Manifest Destiny?
Phrase first used in 1845 to urge annexation of Texas
Used thereafter to encourage American settlement of European colonial and Indian lands in the Great Plains and the West and, more generally, as a justification for American empire.
What was the Louisiana Purchase?
President Thomas Jefferson's 1803 purchase from France of the important port of New Orleans and 828,000 square miles west of the Mississippi River to the Rocky Mountains
More than doubled the territory of the United States at a cost of only $15 million.
What was significant about the Textile Industry in Lowell, Massachusetts (Lowell Mills)?
The largest industrial complex in the United States in the 1850s.
Wove cotton produced in the Southern United States.
Many workers - "Mill Girls",
What was Alexander Hamilton's financial plan/economic program?
To solve the debt problem of $80 million:
Fund the debt at par, Assume all state debts, Create a National Bank (Print money, give loans, interest rates), and tax whiskey (for revenue)
Favored the wealthy and utilized public credit and businesses to stabilize the central government.
Tell me about the presidential election of 1840.
Whig General William Henry Harrison defeated Democratic President Martin Van Buren.
Represented a major shift in political campaigns.
Whig Party candidate William Henry Harrison and his running mate, John Tyler, were the first candidates to campaign actively for office.
What was the Tariff of Abominations?
Passed in 1828 by Parliament that taxed imported goods at a very high rate
Aroused strong opposition in the South
What were the differences/strengths between the North and the South at the beginning of the Civil War?
South: Superior Military Leadership (More farms, less cities, lower population, more cotton, donkeys, and mules)
North: More Resources (Less farms, more cities, higher population, more factories, banks, horses, railroads, food crops, workers, produced goods, textiles, firearms, pig iron, men present for duty)
What were changes and developments in America between 1815-1830?
Second Bank of the United States 1816 (dealt with debt from war of 1812)
Tariff of 1816 (tax on foreign goods to encourage )
Erie Canal 1817-1825 (reduced the time and cost of shipping goods and fostered a population surge)
Adams-Onis Treaty 1819 (Spain ceded Florida to the United States)
Missouri Compromise 1820 (Maine is a free state, Missouri is a Slave state, latitude line)
Era Of Good Feelings 1817-1825 (aligned with Monroe's presidency, Good relationships between U.S. & Britain after war)
Second Great Awakening 1820s-40s (Religious revival throughout the country, emphasis on the purification of society)
Tariff of Abominations 1828 (increased the tax on imported manufactured goods)
Indian Removal Act (Pres. Jackson authorized aggression towards Native Americans in their land, forced many to move, Trail of Tears)
What were the Lincoln-Douglas Debates?
7 debates during the 1858 Illinois senatorial campaign largely concerning the issue of slavery extension into the territories.
Douglas emphasized popular sovereignty, supported the Dred Scott Decision, and branded Lincoln as a radical who advocated racial equality and disruption of the Union.
Lincoln emphasized the moral iniquity of slavery and attacked popular sovereignty for the bloody results it had produced in Kansas.
Many people listened to these debates and they established Lincoln's reputation.
What was the Preston Brooks/Charles Sumner Confrontation (Brooks-Sumner Affair)?
Pro-Slavery Democrat South Carolina Senator Preston Brooks attacked Abolitionist Republican Massachusetts Senator Charles Sumner with a walking cane in 1856
(Senator caning another senator)
What were Abraham Lincoln's Objectives and Actions during the Civil War?
Objectives:
Primary goal was to save the Union, regardless of slavery.
Morally opposed slavery but avoided any public comments connecting the war and the rights of slaves
Later saw that in order to save the Union, slaves should be emancipated.
Actions:
Built the Republican Party into a strong national organization.
Rallied most of the northern Democrats to the Union cause.
Issued the Emancipation Proclamation that declared forever free those slaves within the Confederacy.
What is Popular Sovereignty?
Government based on the consent of the people.
Tell me about President James Buchanan.
Historians condemn him for not forestalling the secession of southern states or addressing the issue of slavery.
Consistently ranked as one of the worst presidents in American history, often being ranked as the wterm-56orst president.
What was the impact of the novel "Uncle Tom's Cabin"?
VERY Best-Selling Novel by Harriet Beecher Stowe
Stowe's honest portrayal of slavery encouraged others to speak out, further eroding the already precarious relations between northern and southern states and advancing the nation's march toward the Civil War.
Demonstrated that many white abolitionists believed that slavery was unjust while also believing that white people were intellectually, physically, and spiritually superior to black people.
Synopsis: Slaves Tom and 4yo Harry, are sold to pay Shelby family debts. Tom, is a strong, religious man living with his wife, three young children, and Eliza, Harry's mother. The book ends when Eliza escapes slavery in Canada and Tom is whipped to death.
What was the Homestead Act of 1862?
Gave 160 acres of land to any settler who would farm the land for VERY cheap.
Enacted during the Civil War.
Encouraged westward migration.
Freedom opportunity for many, but also resulted in the massive displacement of Native Americans and the growth of big railroad empires.
Who were American military leaders during the Mexican-American War?
Robert E. Lee (Also a Confederate General in the Civil War)
George Pickett (Also a Confederate General in the Civil War)
Thomas "Stonewall" Jackson (Also a Confederate General in the Civil War)
Ulysses S. Grant (Also a Union General for the Civil War and the 18th President)
George Meade (Also a Union General in the Civil War)
What was John Brown's Raid at Harper's Ferry?
A failed effort to initiate a slave revolt in Southern states by taking over the United States arsenal in Virginia.
The Arsenal was a representation of American success, progress, and innovation.
What was Zachary Taylor's role in the Compromise of 1850?
Encouraged California and New Mexico to become free states.
President Zachary Taylor died suddenly before the Compromise was passed.
Goal: To avoid a long debate in Congress / compromise.
What was the Economic Crisis of 1857 (Panic of 1857)?
New York Banks collapsed and the word spread quickly through telegraph, scaring people throughout the country.
Caused by the declining international economy and over-expansion of the domestic economy.
Created business and factory failures, railroads went bankrupt, and crop prices fell.
Lasted 3 years.
What was the rise of the Republican Party before the Civil War?
Mid-1850s
Main goal of the party was to keep slavery out of the western territories.
Lincoln became a national figure because of the Lincoln-Douglas debates.
Raid on Harper's Ferry drove the North and South apart.
Northerners admired Brown's dignity shown during trial.
Southerners outraged at Northerners responses and Brown's attempt to lead a slave revolt.
Which US President served 1829-1837?
Andrew Jackson
Which US President served 1837-1841?
Martin Van Buren
Which US President served 1841?
William Henry Harrison
Which US President served 1841-1845?
John Tyler
Which US President served 1845-1849?
James K. Polk
Which US President served 1849-1850?
Zachary Taylor
Which US President served 1797-1801?
John Adams
Which US President served 1850-1853?
Millard Fillmore
What was the significance of the Telegraph?
Used Morse Code to revolutionize long-distance communication
What is the basis of the American Constitution?
Creates a national government of legislative, executive, and judicial branches with a system of checks and balances
Divides power between the federal government and the states
Protects various freedoms of American citizens
Which US President served 1861-1865?
Abraham Lincoln

What was the Battle of New Orleans?
A battle during the War of 1812 - American victory forced the British to ratify the Treaty of Ghent (which ended the war). The US achieved its greatest land victory of the war. Elevated Andrew Jackson to fame. Incorporated Louisiana into the Union.
What did the 14th Amendment do?
Provided a constitutional guarantee of the rights and security of freed people. Prevented southern states from denying the right to vote to black US citizens.
Ratified July 1868
Granted citizenship to former slaves.
What was "The American System/Plan"?
Henry Clay's plan for economic growth to establish a protective tariff, establish a national bank, and improve the country's transportation system.
What was the Marbury v. Madison case and what did it declare?
James Madison, secretary of state, was supposed to make William Marbury's hire as a midnight judge official, but he didn't, so Marbury sued. The Supreme Court refused to grant Marbury his position because a portion of the Judiciary Act of 1789 was unconstitutional.
It was voided by Chief Justice John Marshall.
Established judicial review.
What was the significance of John Marshall's supreme court?
From 1801-1835.
Shaped interpretation of Constitution (loose).
Strengthened judicial branch.
Increased power of federal government over state.
Supported economic activity.
What was the Missouri Compromise of 1820?
Missouri's admission as a slave state, Maine was carved out of Massachusetts and admitted as a free state, the latitude line of 36° 30' across the Louisiana Purchase was drawn so slavery would not be permitted north of that boundary, except for Missouri.
What was the Jeffersonian-Republican Party?
Political Party that believed in Rule by the People, desired more power for the states, distrusted central government, and supported middle class, poor farmers, and the South.
Beginning in the 1820s, National Republicans favored a national bank and internal improvement. Old Republicans support states' rights and a smaller federal government.
What was the Federalist Party?
Political Party that believed the elite should make decisions, distrusted the public's ability to govern, desired a strong national government, and wanted to support, NOT regulate economics.
What was the Whig Party?
Political Party active in the period 1834-54 that espoused a program of national development but was founded on sectional antagonism.
What was the Republican Party? (Civil War era)
Political Party that rose in the 1850s, opposed slavery.
What was the Democratic Party? (Civil War era)
Political Party, mostly White men living in the South who believed in Jacksonian democracy
Defended slavery in the United States, and promoted its expansion into the Western United States against the Free Soil opposition in the Northern United States.
Who were the Tories?
Political Party consisting of American colonists who supported the British side during the American Revolution.
Who were the Copperheads?
Political Party during the Civil War of Radical Peace Democrats who opposed the draft and emancipation.
What is Nativism?
Anti-immigrant and anti-Catholic feeling especially prominent from the 1830s through the 1850s; the largest group of its proponents was New York's Order of the Star-Spangled Banner, which expanded into the American (Know-Nothing) Party in 1854.
What was the Know-Nothing Party?
Nativist, anti-Catholic third party organized in 1854 in reaction to large-scale German and Irish immigration; the party's only presidential candidate was Millard Fillmore in 1856.
Who was Harriet Tubman?
Abolitionist who was born a slave, escaped to the North, and then returned to the South nineteen times and guided 300 slaves to freedom on the Underground Railroad.
What was Freedmen's Bureau?
Agency established by Congress - Had a very daunting task
Bureau agents were supposed to establish schools, provide aid to the poor and aged, settle disputes between whites and blacks and among the freedpeople, and secure for former slaves and white Unionists equal treatment before the courts.
Successful in Education: coordinated and helped to finance the activities of northern societies committed to black education - 3000 schools in the South.
Provided medical care to both black and white southerners.
NOT as successful in economic relations.
Lasted from 1865 to 1870.
What are the 3 kinds of Reconstruction?
Wartime, Presidential, and Radical/Congressional
Tell me about President Andrew Johnson.
Jacksonian Democrat.
Blames the wealthy for the Civil War.
White Supremacist.
Agreed with Lincoln that the Southern States never left a Union.
Presidency - pardoned 13000 people,
What are the Black Codes?
Guaranteed stable labor supply even though blacks were emancipated
To restore pre-emancipation system of race relations.
Example: Forced many blacks to become Sharecroppers (Tenant Farmers)//Prison Labor
What was the Wilmot Proviso?
Proposal to prohibit slavery in any land acquired in the Mexican War.
Defeated by Southern senators.
Introduced by David Wilmot
Does the 13th Amendment still affect the US today?
Connections can be drawn from the loophole "except for criminals" found in the amendment and the prison boom that came soon after the amendment was passed.
What is the 15th Amendment?
The right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude.
Ratified in 1870
Congress shall have the power to enforce this article by appropriate legislation.
Upset Women - rights groups were furious that they were not granted the vote!
ESCAPE -
ES = Ending Slavery (13th)
C = Citizenship (14th)
APE = [black men are] Allowed to Participate in Elections (15th)
Pneumonic for Amendments
What is the Military Reconstruction Act of 1867?
Divided 10 southern states (that did not ratify the 14th amendment) into 5 military districts
"Unreconstructed States"
Troops patrolled - making sure stores were open to people of all colors, everyone could vote, etc.
Only through the Military that some of these things are possible.
What is the Tenure of Office Act?
Designed to protect radical members of Lincoln's government.
The President could only remove Cabinet members/officials with the Senate's consent.
Johnson removed Edwin Stanton from office (Secretary of War) because he didn't like him in 1868. The House impeached him. Johnson acquitted.
What was the Compromise of 1850?
Amended the The Fugitive Slave Act.
Abolished Slave Trade in Washington D.C.
California entered the Union as a free state.
Territorial government created in Utah.
Goal: to preserve the Union by appeasing both sides on the slavery issue.
What was the California Gold Rush of 1849?
Gold discovered in Sacramento Valley prompted one of the largest migrations in U.S. history.
Led to the establishment of boomtowns, rapid economic growth and prosperity, and the building of railroads, churches and banks.
Significant increase in population and infrastructure allowed California to qualify for statehood in 1850.
What was the Dred Scott decision?
Very famous and impactful Supreme Court decision:
A slave sued for freedom - It was decided that he had no right to sue because blacks could not be citizens and therefore could not enjoy the rights American citizens were granted.
What was the Kansas-Nebraska Act?
Repealed the Missouri Compromise.
Created two new territories.
Allowed for popular sovereignty.
Stephen Douglas signed the act to peacefully settle national issues (didn't really work)
Consequences:
Violent uprising known as "Bleeding Kansas."
Creation of the new Republican Party.
Violence that was a precursor to the Civil War.
What was the Trent Affair?
Diplomatic crisis between the United States and Great Britain in late 1861 during the U.S. Civil War.
U.S. Navy seized a British neutral ship to get British support for the South.
Angered British - Claimed the Navy violated international law.
President Abraham Lincoln's administration averted an armed conflict with Britain by releasing the envoys who were arrested.
Tell me about President Zachary Taylor.
Major General in the U.S. Army
Became a National Hero for his victories in the Mexican-American War.
12th president of the United States from 1849 until his sudden death in 1850.
What were the specifics and results of the 1860 election?
Slavery was the central issue.
Abraham Lincoln (Republican) won over Stephen Douglas (Democrat), John Breckinridge (Democrat), and John Bell (Constitutional Union Party).
Lincoln won 40% of the popular vote but won a large majority of electoral votes.
Lincoln's victory led the South to secede.
Which states were Southern States in the Civil War?
Texas, Arkansas, Louisiana, Tennessee, Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, Florida, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Virginia.
Jefferson Davis - President
Which states were Northern States in the Civil War?
Maine, New York, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Kansas, Michigan, Wisconsin, Minnesota, Iowa, California, Nevada, and Oregon.
Abraham Lincoln - President
Which states were Border States in the Civil War?
Maryland, Delaware, West Virginia, Kentucky, and Missouri.
What was the Gadsden Purchase?
30,000 square miles of land purchased from Mexican government in 1853
Present-day Arizona and New Mexico
Purchased for $10 million
Established present American/Mexican Border
What was the Abolition Movement?
A social reform effort to abolish slavery in the United States.
Started in the mid-eighteenth century and lasted until 1865, when slavery was abolished (13th Amendment).
Famous Abolitionists:
William Lloyd Garrison (published "The Liberator")
Elijah Lovejoy (started a religious newspaper "The St. Louis Observer")
Frances Harper (traveling lecturer for the American Anti-Slavery Society)
Fredrick Douglass (born a slave but escaped and wrote about his life in "Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass")
Sojourner Truth (female escaped slave who wrote "The Narrative of Sojourner Truth: A Northern Slave."
Harriet Tubman (went by "Moses" and helped over 300 slaves on the Underground Railroad)
Who was Thomas "Stonewall" Jackson?
Confederate general in the American Civil War,
Skillful tactician.
Nicknamed because of he stationed his brigade in a strong line, withholding the enemy against overwhelming odds at the First Battle of Bull Run (AKA Battle of Manassas).
What were the New York City Draft Riots?
Sparked by laws that made thousands of male New Yorkers eligible to be drafted into the Union Army.
Violent disturbances in Lower Manhattan.
Crowds of white workers marched through the city, destroying buildings, factories, streetcar lines, and homes.
Deadliest riots in U.S. history as well as millions of dollars in property damage.
What was the order of seceding states from the Union?
1. South Carolina (December 20, 1860)
2. Mississippi (January 9, 1861)
3. Florida (January 10, 1861)
4. Alabama (January 11, 1861)
5. Georgia (January 19, 1861)
6. Louisiana (January 26, 1861)
7. Texas (February 1, 1861)
8. Virginia (April 17, 1861)
9. Arkansas (May 6, 1861)
10. North Carolina (May 20, 1861)
11. Tennessee (June 8, 1861)
What was the Battle of Fort Sumter (April 12, 1861)?
Site of the opening engagement of the Civil War.
North maintained this fort and planned to send supplies but Confederate General Beauregard demanded surrender (refused).
Confederates bombarded the fort, which surrendered on April 14th.
Congress declared war on the Confederacy the next day.
What was the First Battle of Bull Run AKA Battle of Manassas (July 1861)?
First major conflict of the Civil War.
Southern victory led to overconfidence.
What was the Seven Days Battle (June 1862)?
Series of attacks on McClellan's forces in Virginia near the C.S.A. capital.
The South succeeded in driving back the North; however, both sides suffered major losses
What was the Battle of the Ironclads (March 1862)?
Naval battle between Confederate ship "the Virginia" vs. Union ship "the Monitor"
Ended in a draw.
What was the Battle of Shiloh (April 1862)?
Bloody Civil War battle on the Tennessee-Mississippi border.
More than 23,000 soldiers dead.
Ended in a marginal Union victory.
General Grant lost popularity despite victory.What was the
What was the Battle of Antietam (September 1862)?
7000 deaths and over 25,000 casualties - "Bloodiest day in US History."
Landmark battle in the Civil War.
General Lee's orders were found in a cigarette box, but General McClellan didn't do anything about it/didn't act quickly enough.
Bloody Lane - lots of dead people.
Gave Lincoln the opportunity to issue the Emancipation Proclamation
What was the Battle of Fredericksburg (December 1862)?
General Burnside attacked Lee and lost.
It was a reckless attack by the Union.
The Union had 12,000 casualties compared to the Confederacy's 5,000 casualties.
(Burnside was quickly replaced afterwards cause he was being stupid lol)
What was the Battle of Chancellorsville (May 1863)?
Southern Victory.
General Hooker planned to drive Lee from Fredericksburg by surprise.
General Stonewall Jackson attacked from the rear while Hooker held them. Stonewall ended up getting shot on accident and died, replaced by Gen. Ewel. (The Union never recovered they kinda needed him tbh)
What was the Battle of Gettysburg (July 1863)?
Accidental meeting of two great armies.
Major Union victory (But Lincoln was mad about it).
Turning Point in the war: Confederacy never again managed to invade the North.
20,000 Union Losses; 30,000 Confederacy Losses
Little Round Top.
What was the Battle of the Crater (July 1864)?
Part of the Siege of Petersburg.
The Union dug under the Confederate troops and planted a bunch of dynamite, which exploded and created a gap in the enemy line.
Union troops fell in the hole in created and couldn't get out, and the Confederates were firing at them.
Became a massacre of the Union soldiers.
What was the Surrender at Appomattox Courthouse (April 9th, 1865)?
Lee chose to meet Grant at Wilbur McClean's house in ACH
Grant gave very generous terms and got Southerners to sign parole papers promising not to fight anymore and were fed.
Grants would not let his army celebrate their victory and humiliate the Confederates further.
Instead they were saluted and national healing
began...
What was the North's Civil War Strategy?
Anaconda Plan (Use the Navy to surround the Southern coast and the West to block any imports and exports from reaching the South).
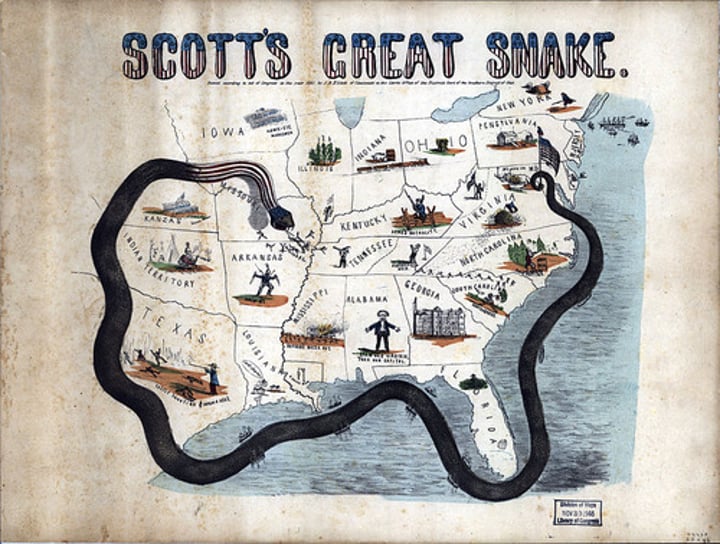
What was the South's Civil War Strategy?
Outlast the North.
The North had more resources, but the South had superior military leadership.
Why did the Southern states secede from the Union?
Many Southerners felt that with Lincoln's election, the South did not have a voice in the national government.
Protect their property and way of life. (They wanted to keep slavery).
Who invented the Telegraph and when?
Samuel Morse; 1830s and 40s
Which US President served 1789-1797?
George Washington
Which US President served 1801-1809?
Thomas Jefferson
Which US President served 1809-1817?
James Madison
Which US President served 1817-1825?
James Monroe
Which US President served 1825-1829?
John Quincy Adams
Which US President served 1853-1857?
Franklin Pierce
Which US President served 1857-1861?
James Buchanan