Human Body Systems; Unit 4 Review
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Fibrous joints
made of fibrous tissue, little or no movement
Fibrous joints (examples)
skull sutures, pelvic bone and sacrum fusions
Cartilaginous joints
made of cartilage, some movement
Cartilaginous joints (examples)
between bones of vertebral column, joining of the 2 coxal bones (pubic symphasis)
Synovial joints
have synovial fluid pocket between bones, freely moveable
Synovial joints (examples)
between bones that are easily moved (like appendicular skeleton), fingers, wrist bones, knees, hips, etc
What type of joint has the biggest role in movement?
synovial joint
Name the 6 types of synovial joints
pivot
ball-and-socket
saddle
ellipsoid/condyloid
hinge
planar/gliding
What does a goniometer do?
It measures angles. One arm stays with the nonmoving bone, but the other moves with the bone to measure the amount of "bend" the joint is capable of.
Name the 3 types of muscle tissue
skeletal
smooth
cardiac
What do the 3 types of muscle tissue have in common?
They all contract, but in different ways.
Where is cardiac muscle found?
only in the ♡
Is cardiac muscle:
striated or not striated?
voluntary or involuntary?
striated
involuntary
Where is smooth muscle found?
lining of hollow organs and blood vessels
Is smooth muscle:
striated or not striated?
voluntary or involuntary?
not striated
involuntary
Where is skeletal muscle fiber found?
in muscles attached to bone
Is skeletal muscle:
striated or not striated?
voluntary or involuntary?
striated
voluntary
Describe cardiac muscle contraction
cardiac muscle contraction occurs in the ♡ and propels blood through the blood vessels
Describe smooth muscle contraction
smooth muscle contraction move fluids and solids along the digestive tract and regulate the diameters of small arteries
Describe skeletal muscle contraction
skeletal muscle contraction moves the body by pulling on bones of the skeleton
How many muscles rule are there that apply to all skeletal muscles?
6
T or F? Muscles have at least TWO attachments and must cross at least ONE joint.
T
T or F? Muscles always "PUSH" and get shorter.
F, they always "PULL"
T or F? The attachment that REMAINS STATIONARY is known as the INSERTION and the attachment that MOVES is known as the ORIGIN.
F, The attachment that MOVES is known as the INSERTION and the attachment that REMAINS STATIONARY is known as the ORIGIN.
T o F? Muscles that DECREASE the angle between ventral surfaces of the body are known as FLEXORS.
T
T or F? Muscles that INCREASE the angle between ventral surfaces of the body are known as EXTENSORS.
T
T or F? Muscles work INDIVIDUALLY.
F, Muscles work in opposing PAIRS.
T or F? Muscle STRIATIONS point to the attachments and show the DIRECTION OF PULL.
T
Epimysium
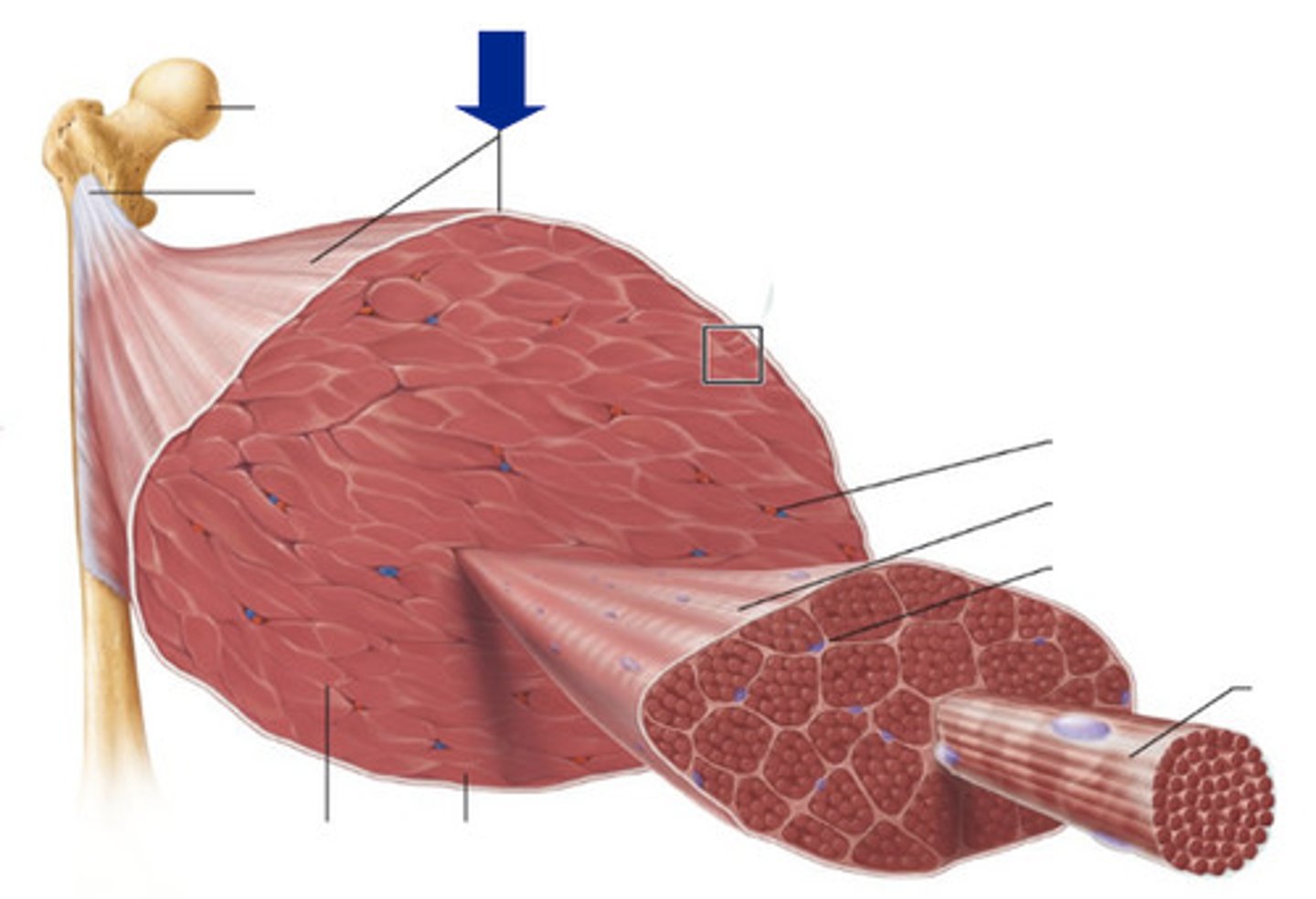
Fascicles
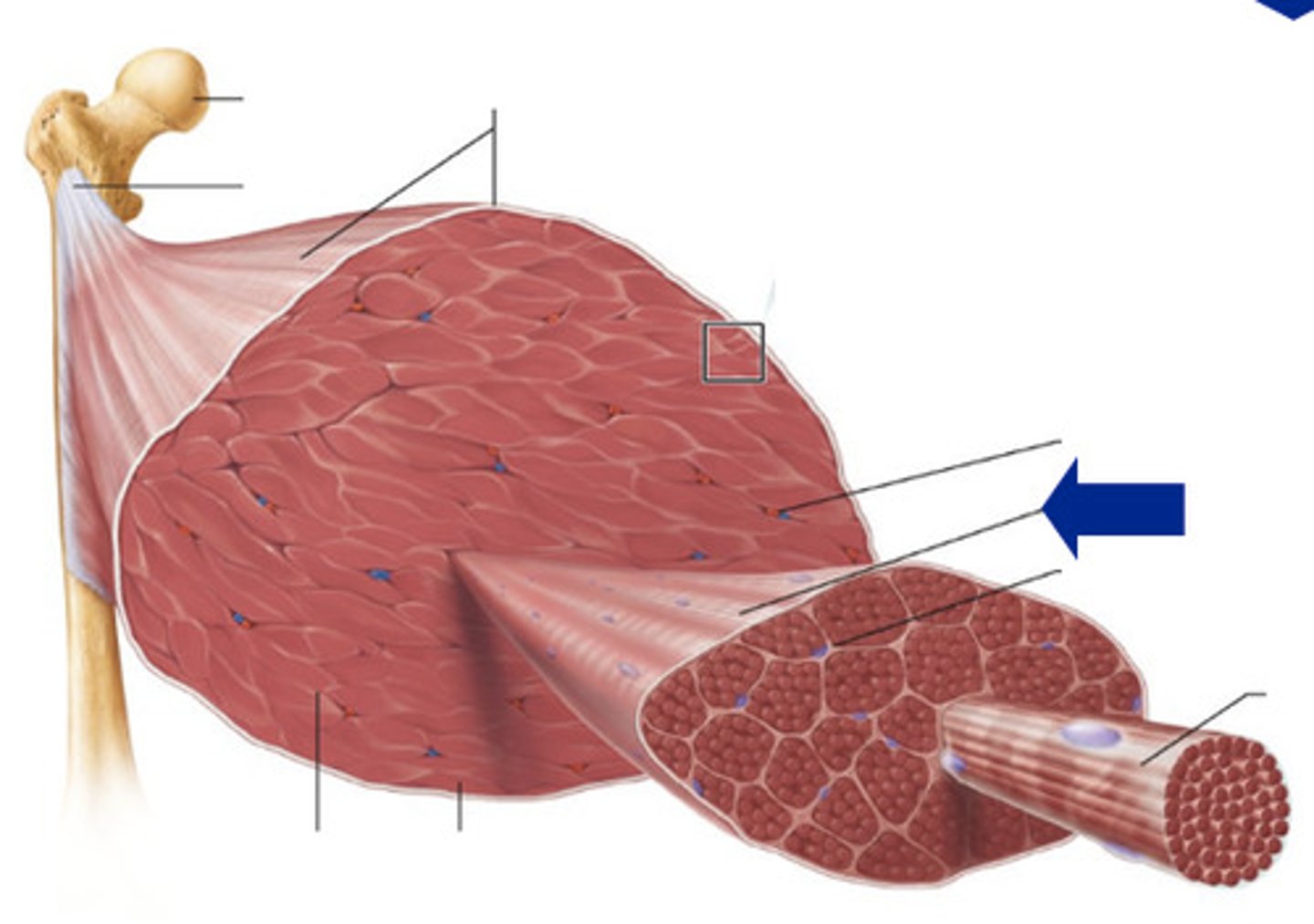
Perimysium
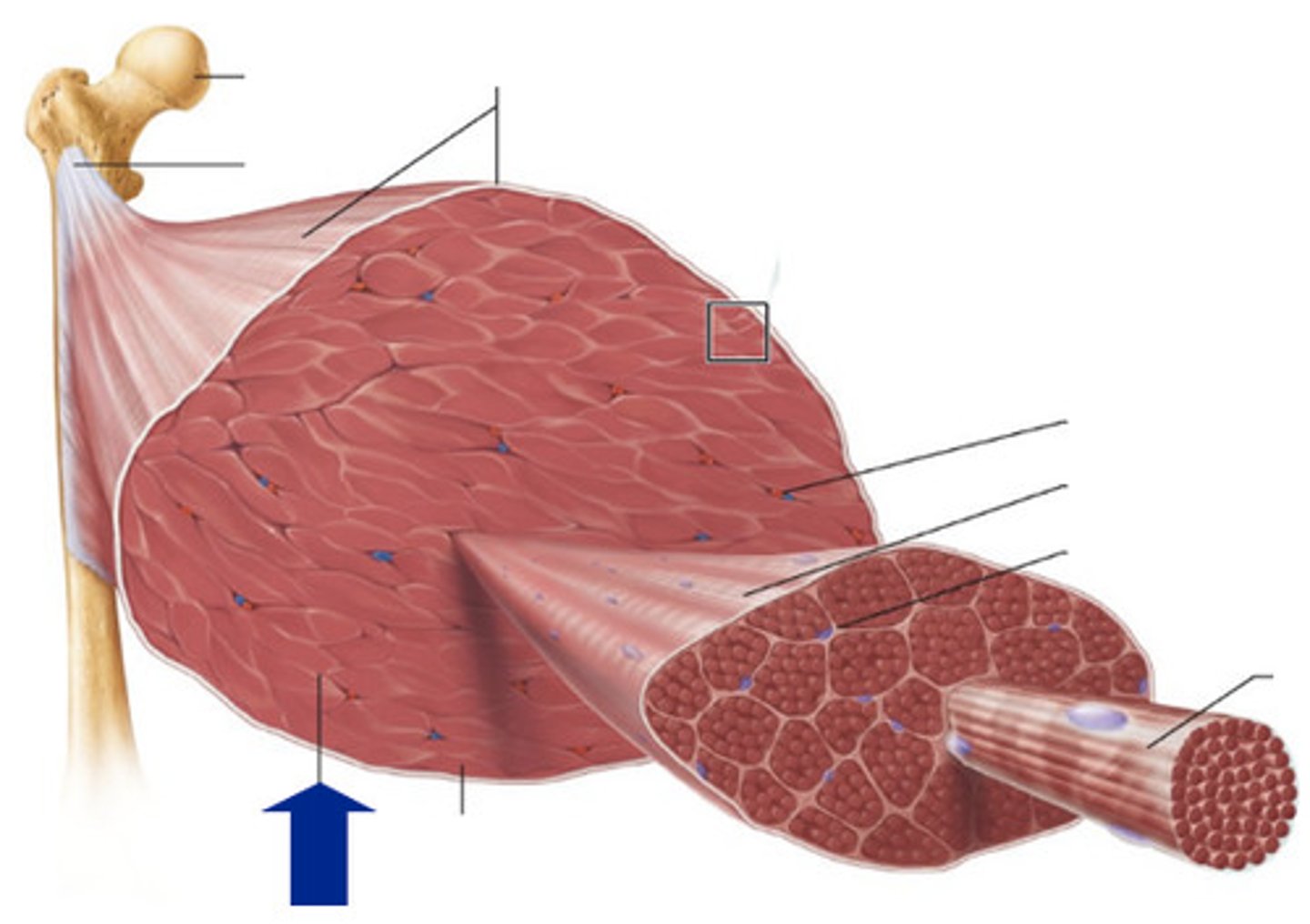
Muscle cells
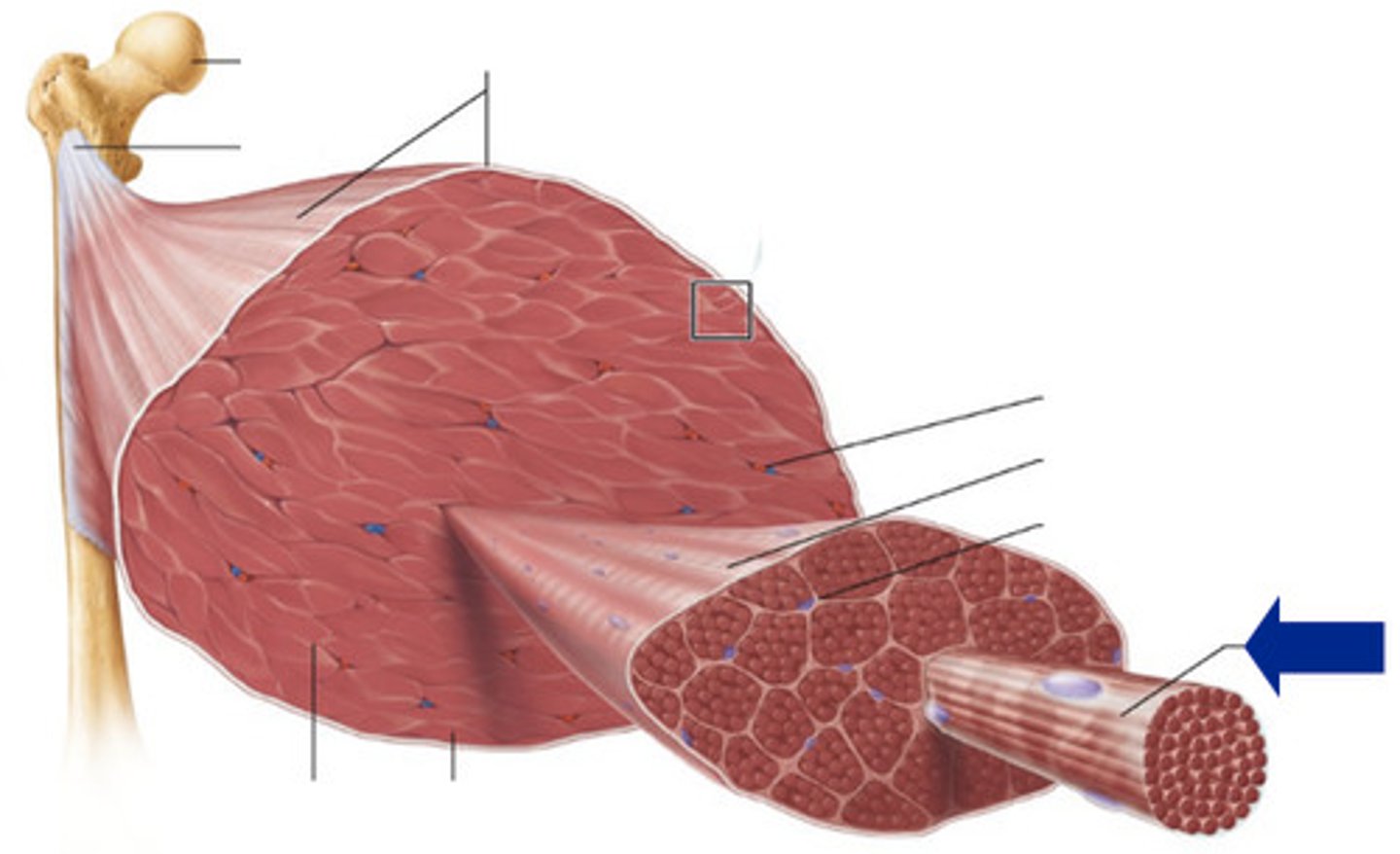
Endomysium
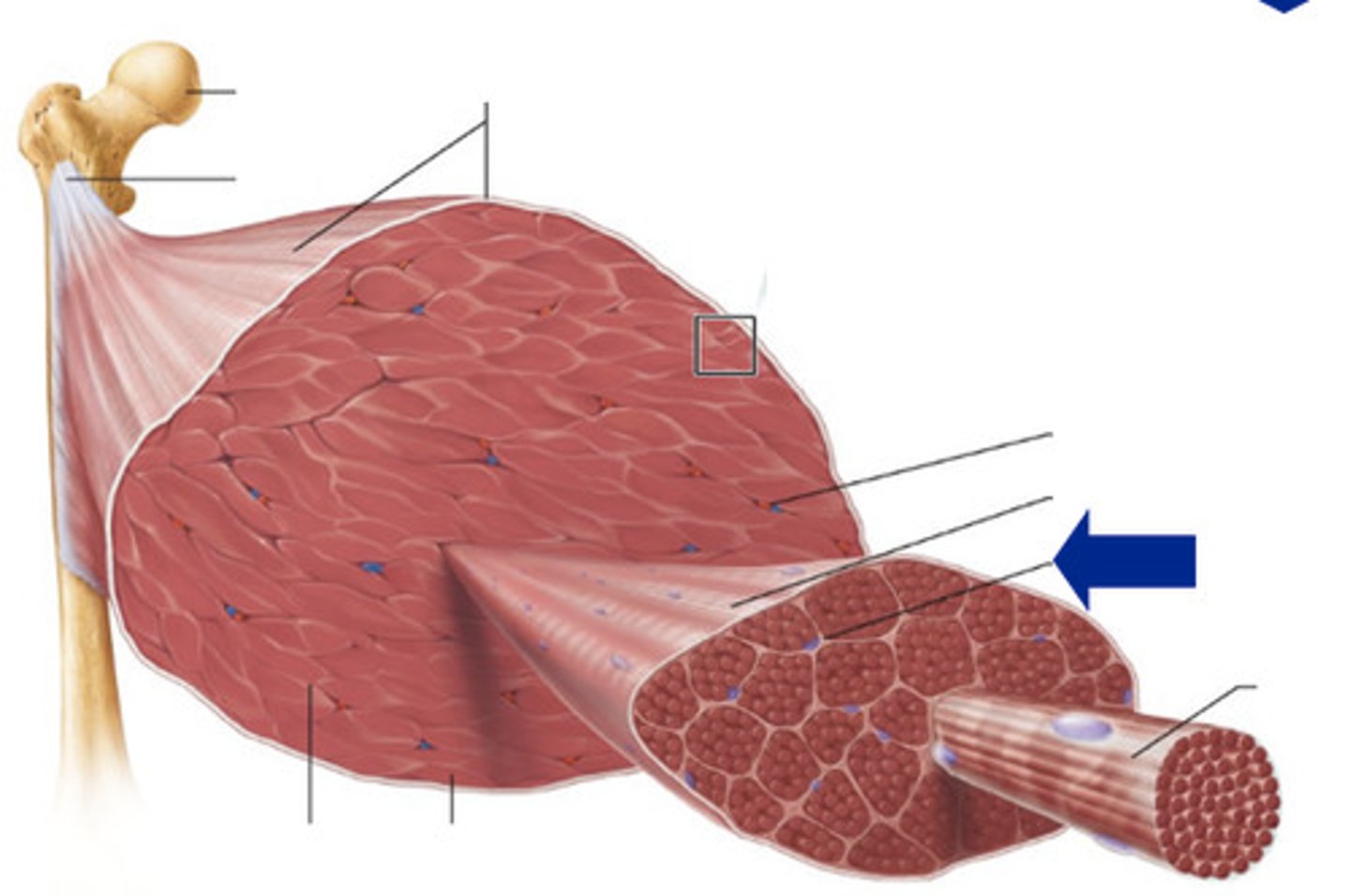
Myofiber
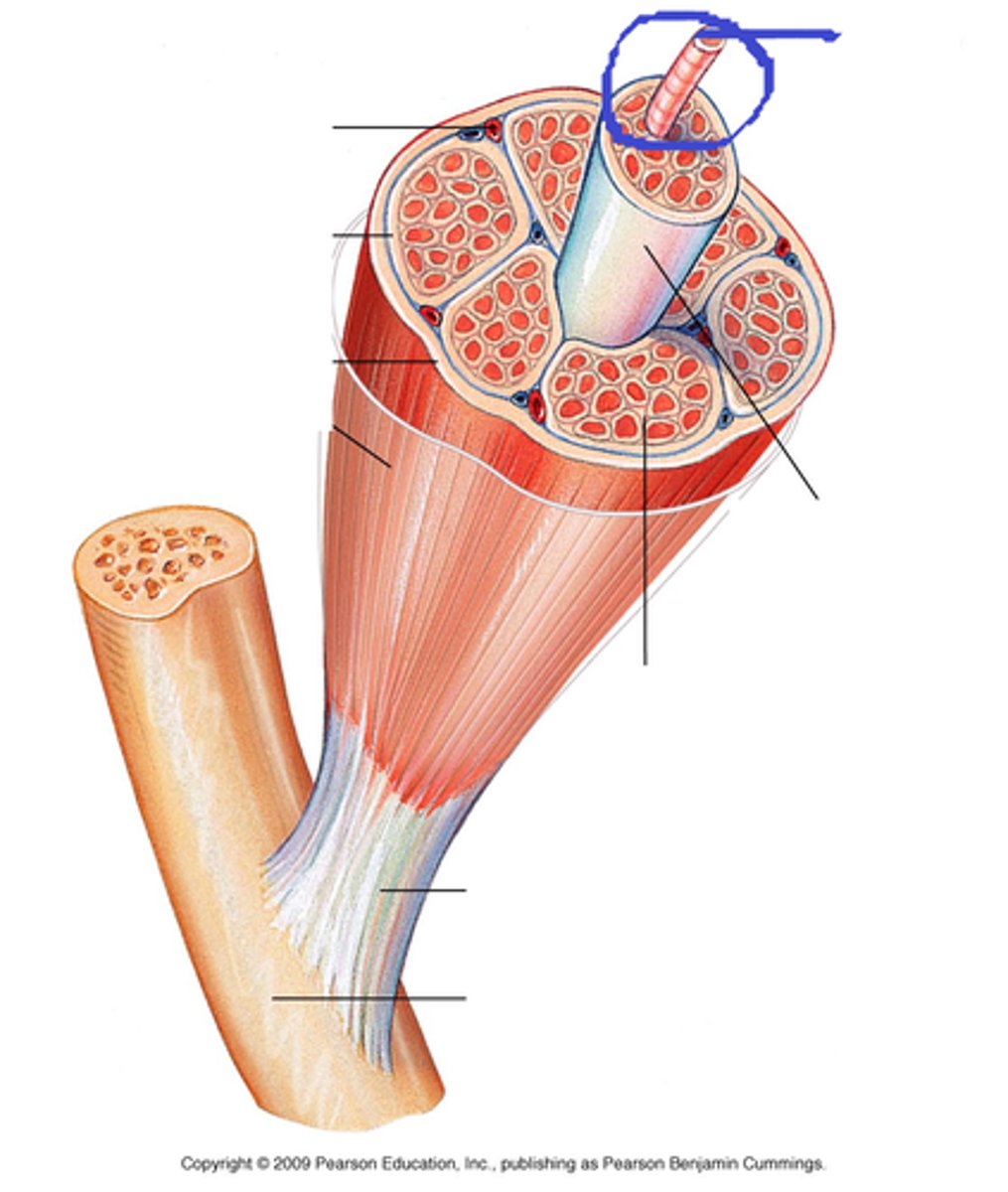
What small structure do myofibers contain?
sarcomeres
What do sarcomeres contain?
actin and myosin, troponin and tropmyosin
What is actin, myosinm troponin, and tropomyosin responsible for?
contraction in the presence of ATP and calcium
What are the main proteins of the sarcomere?
actin (thin filament) and myosin (thick filament)
What are the steps of muscle contraction
1) calcium binds to troponin
2) tropomyosin moves out of way
3) myosin grabs actin
4) myosin pulls actin
5) actin is yanked toward middle of sarcomere
6) muscle gets shorter
7) myosin stuck on actin until ATP comes in to give it the energy to let it go
Why is calcium critical for muscle contraction?
Calcium has to bind to the troponin so the tropomyosin moves out of the way, freeing up the actin. This allows the myosin to grab onto the actin and pull.
T or F? A lot of ATP needs to be present in order for a whole muscle to relax.
T
Arteries take blood _______ from the heart
Away
Veins take blood ______ the heart
Toward
Which have thicker walls, veins or arteries?
Arteries
What do veins have to keep blood flowing in one direction?
Valves
What causes a varicose veins?
Blood pooling in a vein due to damaged or dysfunctional valve. When too much blood pools there it can become painful
What connects arteries to capillaries?
Aterioles
What connects veins to capillaries?
Venules
What is the flow of blood?
Superior/inferior vena cava --> Right atrium --> Tricuspid valve --> Pulmonary artery -->lungs --> Pulmonary arteriole --> Capillaries around aveoli --> Pulmonary venules --> Pulmonary veins --> Left atrium -->Bicuspid valve --> Left ventricle --> aortic valve --> aorta --> body--> body arteries --> body arterioles --> capillaries --> body venules --> body veins --> superior/inferior vena cava
What is pulmonary circulation?
Blood flow between the heart and lungs
What is systemic circulation?
Blood flow between the body and the heart
What is cardiac output?
The amount of blood your heart pumps out of the left ventricle in one minute
What happens if cardiac output is too high?
Extra blood is pooling and being ejected from the heart
What happens if cardiac output is too low?
Muscle contractions are weak or blood volume is decreased
What is blood pressure?
The amount of force upon the walls of blood vessels
What is peripheral vascular disease?
Occluded vessels in the limbs cause poor circulation
How is PVD detected?
PVD is detected by comparing blood pressure in all four extremities. If blood pressure is lower in one arm/leg over the other body parts its a clue that something is wrong in that body part.
What is the leading cause of PVD?
Smoking
What are the three major pathway that your body uses to make ATP?
Aerobic respiration, Anaerobic respiration, and the phosphagen system
What is ATP?
Adenosine Triphosphate; also is a form of energy for muscle
What is the fastest way for ATP to get made?
Using creatine-phosphate stored in those skeletal muscle
How long during exercise does the phosphagen system get used?
The first 10 seconds
After your creatine-phosphate system is exhausted what does your body turn to?
To Anaerobic respiration
What energy source does anaerobic respiration?
Glycolysis
How long during exercise does anaerobic respiration get used?
For about 2 minuets. It can make a lot of ATP at once.
Aerobic respiration uses what in a steady and efficient manner?
Oxygen and sugar to make ATP
What does your sympathetic nervous system do during exercise?
Increased "fight or flight" responses, allowing your pupils to dilate, pumping out adrenaline for extra energy, increasing heart rate to meet the demands of the body, shuts down non-essential system like your urinary and digestive sysetem
What does your parasympathetic nervous system do during exercise?
kinda shuts off and does nothing
Can muscles become so tired no matter how much signal is sent the muscles lose strength?
Yes
After ATP is used what byproduct is produced?
Lactic acid