Aquatic Biomes
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what is an aquatic biome?
an aquatic region characterized by a particular combination of salinity, depth, and water flow
what are the two domains of an aquatic biome?
fresh water and marine
what are the fresh water domains?
streams and rivers, lakes and ponds, freshwater wetlands
what are the marine domains?
salt marsh, mangrove, swamp, intertidal zone, coral reefs, and the open ocean
what are difference between streams and rivers?
- streams are more narrow and carry small amounts of water
- rivers are more wide and carry larger amounts of water
- streams have a rapid flow that support little plants/algar
- rivers have a slower flow so sediments/organic material accumulate and root plants/algae grow
where do streams and river originate as?
underground springs and runoff from rain or melting snow
what are 4 zones of the lakes and ponds?
littoral zone, limnetic zone, profundal zone, and benthic zone
what is the different between lakes and ponds?
- lakes are usually larger than ponds
- no clear distinction though between the two
what are lakes/ponds?
standing water with different depths which decide whether they are too deep or not to support emergent vegetation
what is the littoral zone?
the shallow zone of soil and water where algae and emergent plants usually grow
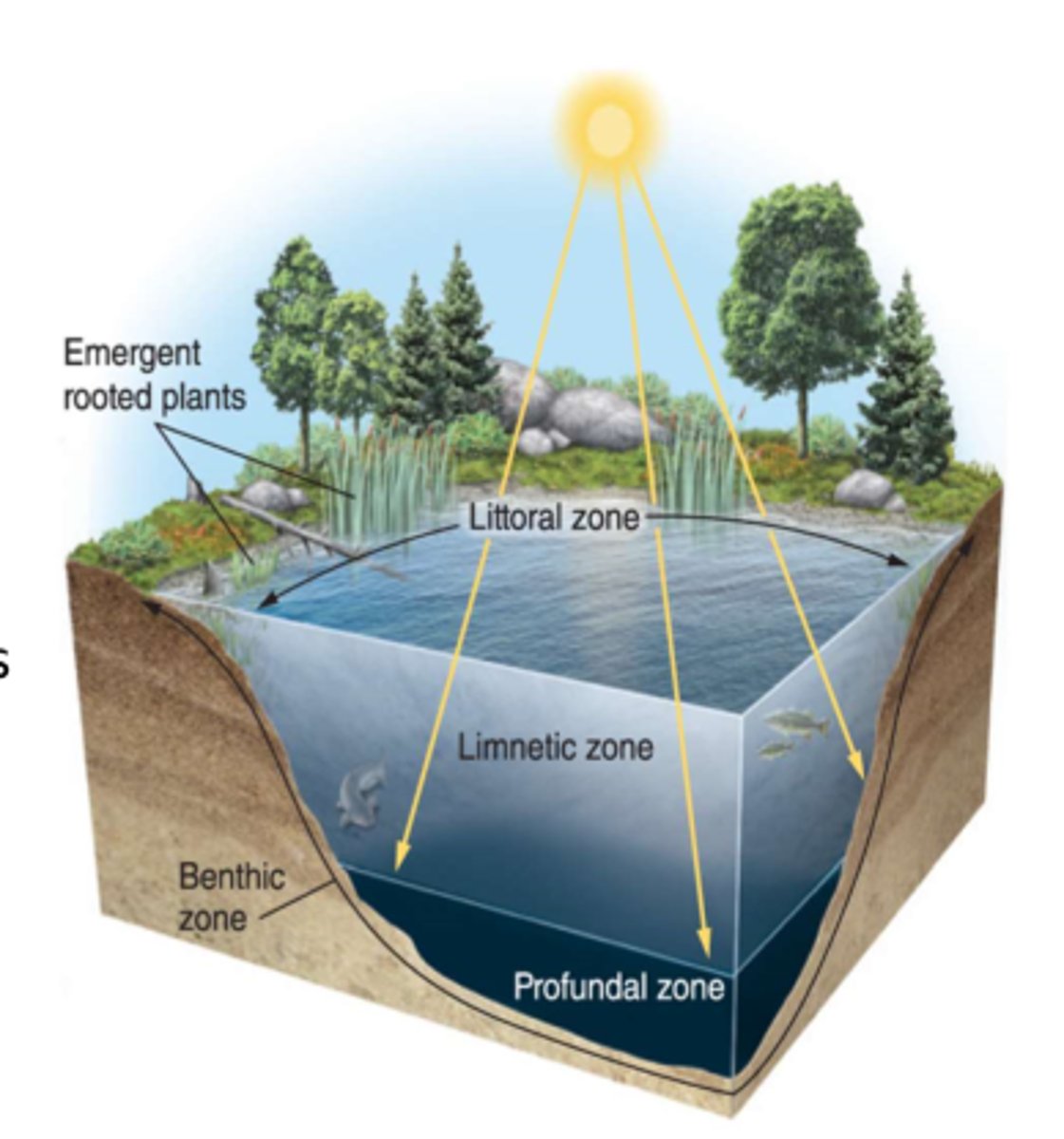
what is the limnetic zone?
- a zone of open water in lakes and ponds where no plants break the surface
- usually no plants break the surface as rooted plants cant survive

what is phytoplankton?
primary producers like floating algae seen in the limnetic zone of lakes/ponds
what is the profundal zone?
the deepest part of water where oxygen can be limiting because little sunlight penetrates for photosynthesis

what is the benthic zone?
the muddy bottom of a lake, pond, or ocean
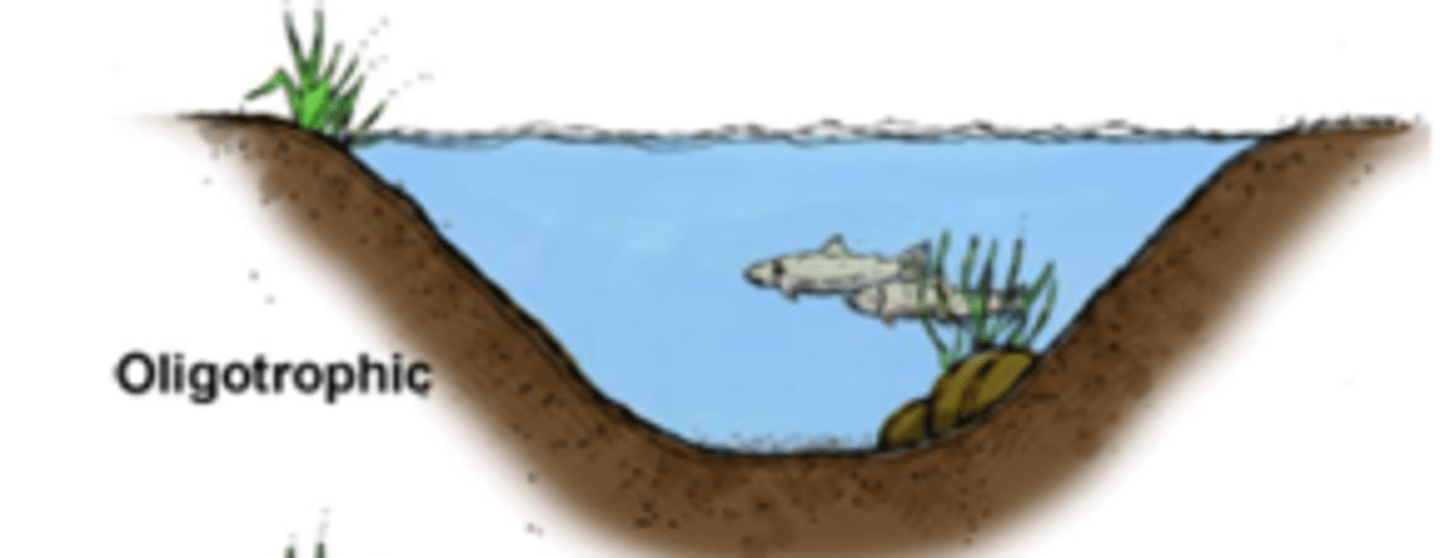
how are lakes classified for by their level of primary productivity?
oligotrophic, mesotrophic, and eutropic
what are oligotrophic lakes?
- lakes with less nutrient content and clean water
- low BOD
- high penetration of sunlight
- high DO
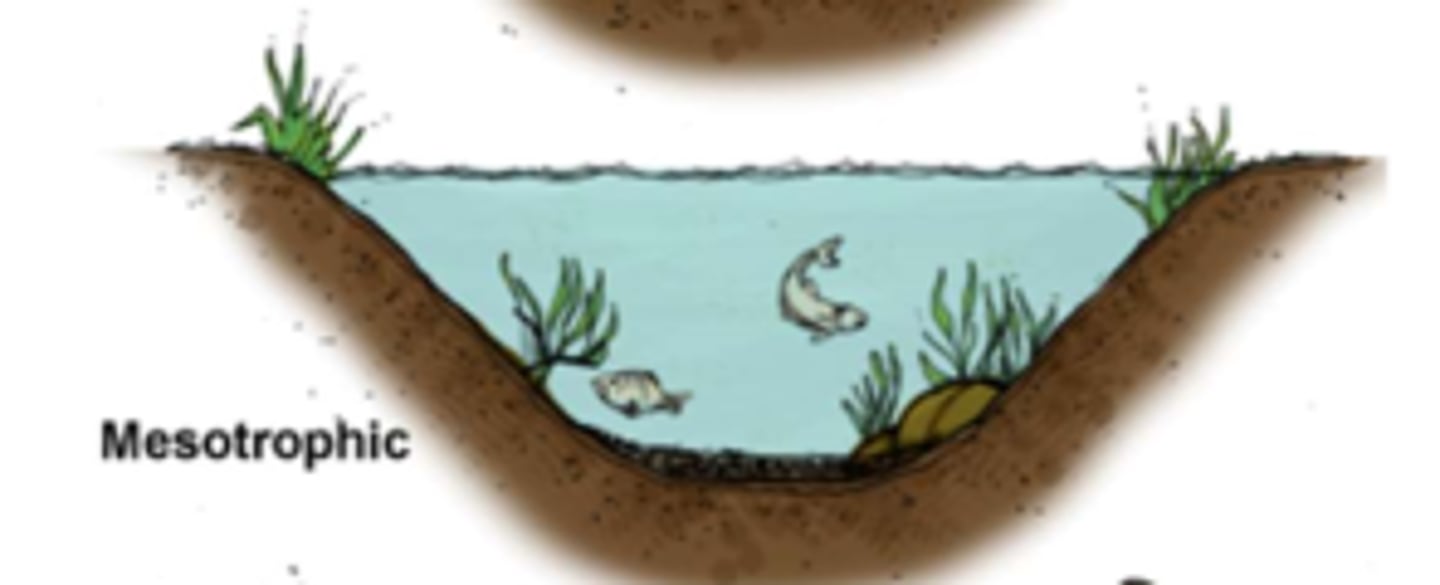
what are mesotrophic lakes?
- lakes with a moderate level of productivity
- most healthiest

what are eutrophic lakes?
- lakes with high level of productivity
- lots of nutrients so water is not clear and sunlight not penetrable
- high BOD and low DO
what are freshwater wetlands?
- an aquatic biome that is submerged or saturated by water (for at least part of an year) which is shallow enough to support emergent vegetation
- the most productive biome on Earth
what are some threats against freshwater wetlands?
agriculture, development, and ground removal due to mosquito breeding
what is a salt marsh?
a marsh containing nonwoody emergent vegetation found along the coast in temperate climates
where are salt marshes found
within estuaries which are an area along the coast where the fresh water of rivers mixes with salt water from the ocean
what are some threats against salt marshes?
development and pollution
what is a mangrove swamp?
a swamp that occurs along tropical and subtropical coasts and contains salt tolerant trees with roots submerged in water
what do mangrove swamps do for the environment?
due to the trees in the swamp being salt tolerant, they help protect coastlines from erosion and storm damage
what are some threats against mangrove swamps?
development and agriculture
what are intertidal zones?
the narrow band of coastline between the levels of high tide and low tide
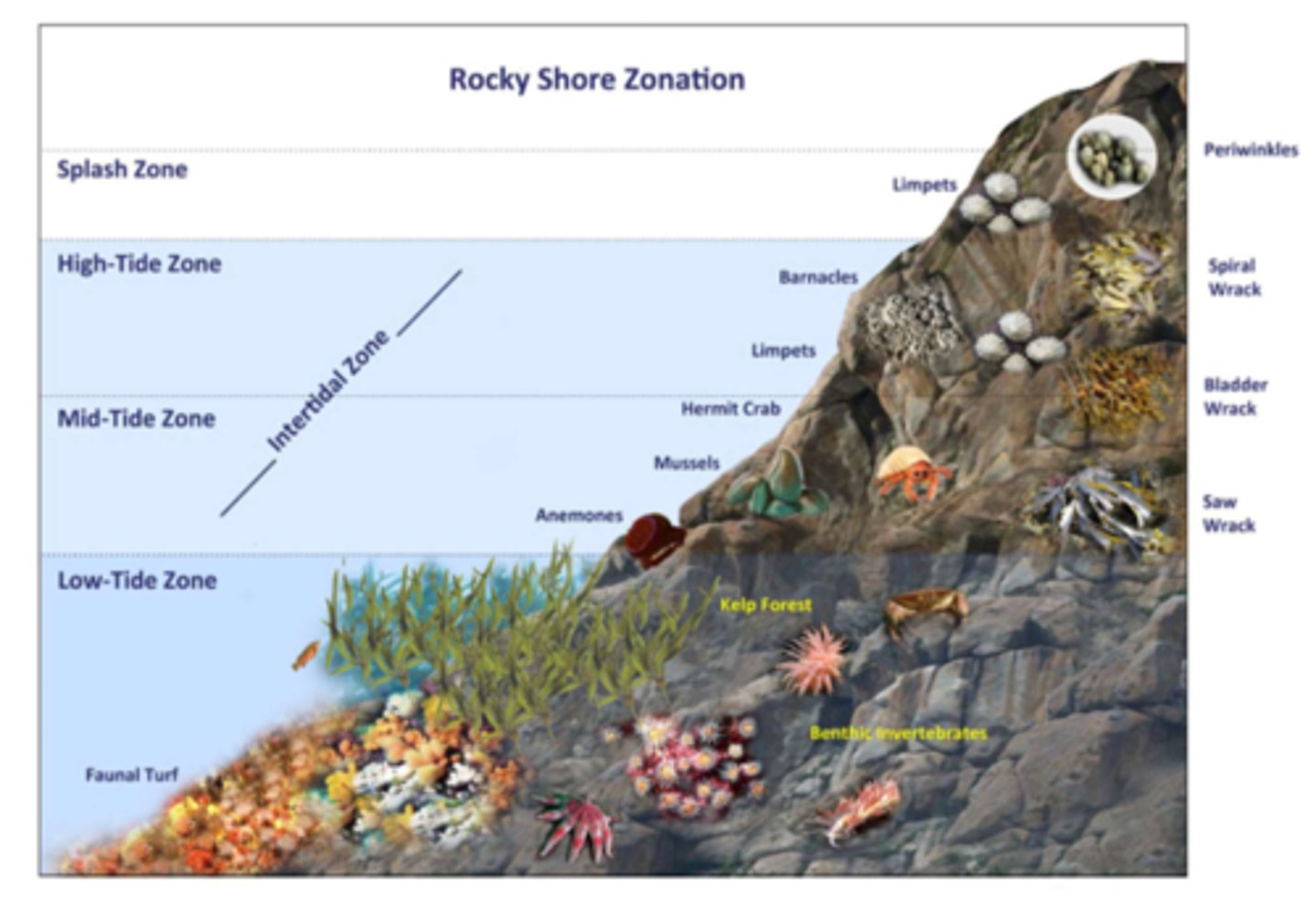
what is a threat against intertidal zones?
- waves crashing onto shore make it a challenge for organisms to hold on and not get washed away
- high tides have more stability though
- low tides however are more prone to desiccating due to sunlight exposure and high temps
what is the coral reef?
the most diverse marine biome on Earth with warm, shallow waters beyond the shoreline
what are some threats against coral reefs?
coral bleaching and low nutrients/food even though super diverse
what is coral bleaching?
a phenomenon in which algae inside corals die, causing the corals to turn white
what is ocean acidification?
the decreasing pH levels of the earth's oceans
what is the open ocean?
deep ocean water, located away from the shoreline where sunlight cannot reach the ocean bottom
what are the zones in open oceans?
photic zone and aphotic zone
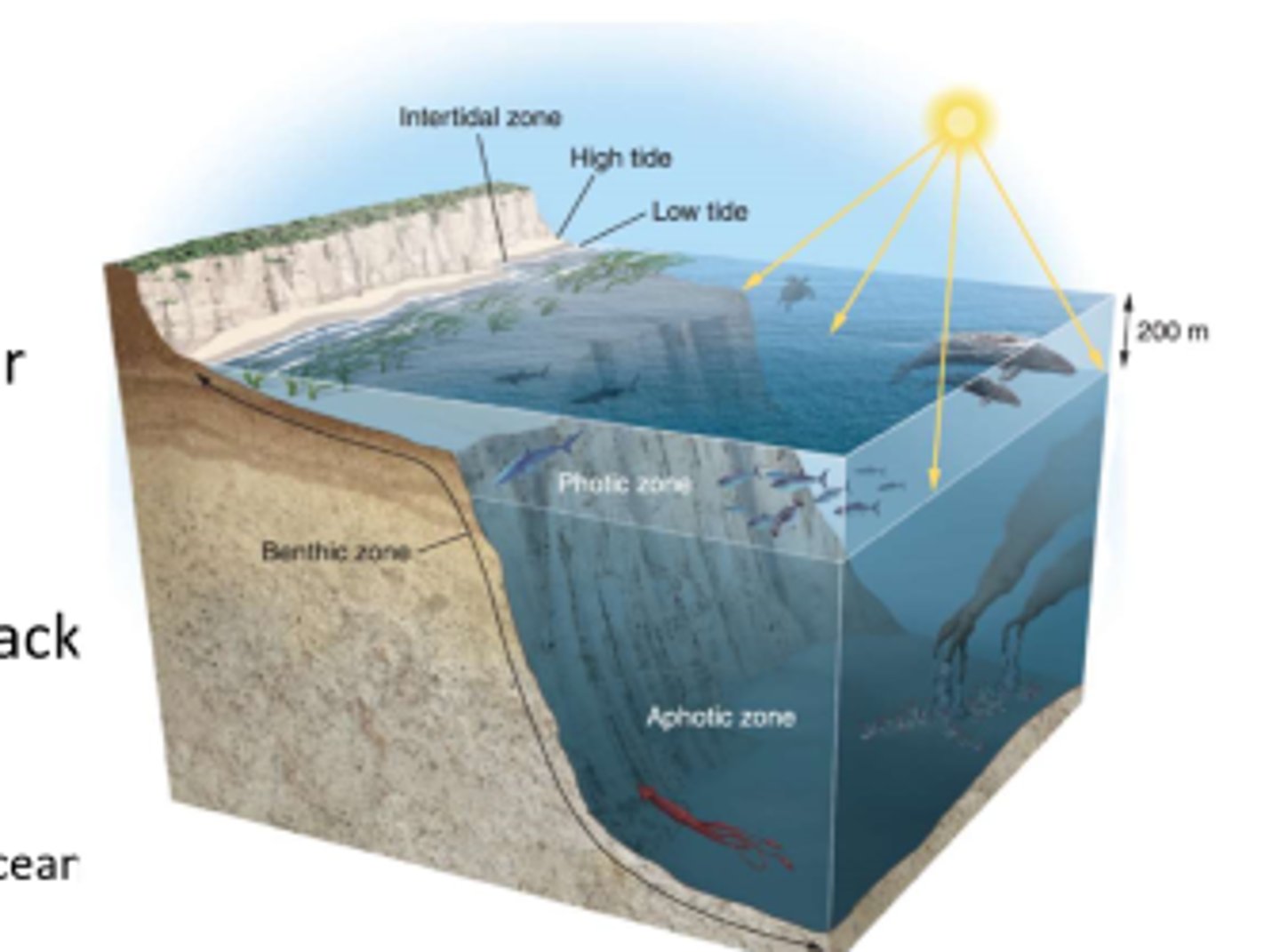
what is the photic zone?
the upper layer of ocean water in the open ocean that receives enough sunlight for photosynthesis
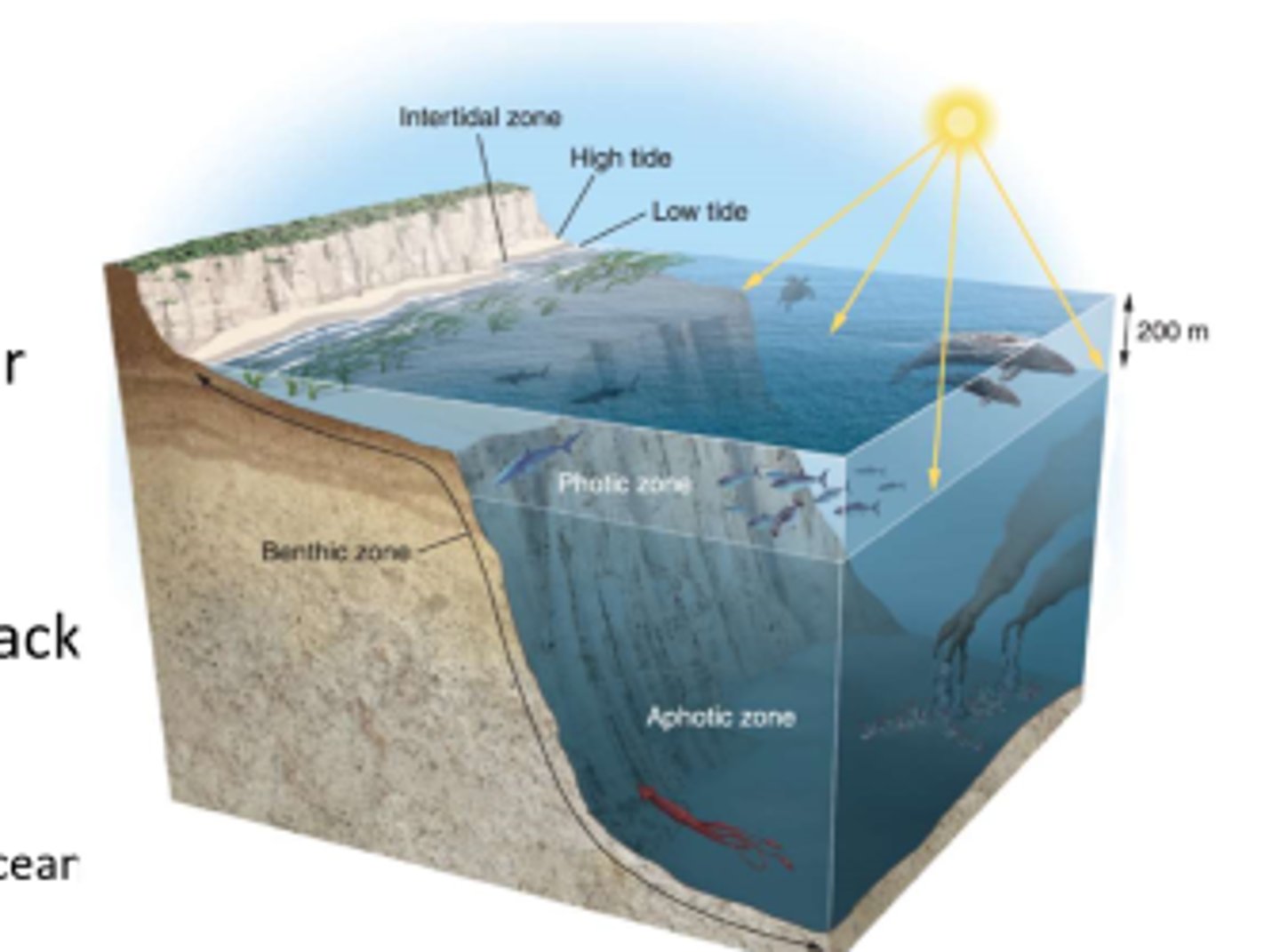
what is the aphotic zone?
the deepest layer of ocean water that lack sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis
what is chemosynthesis?
a process used by some bacteria in the open ocean to generate energy with methane and hydrogen sulfide