Understanding Suicide: Prevention and Epidemiology
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Suicide
Intentional act of ending one's own life.
Suicide attempt
An act of trying to end one's life.
Suicidal behavior
Actions indicating intent to harm oneself.
Terminology to avoid
Language that misrepresents suicide's nature.
Commit suicide
Outdated term; suicide is not a crime
Successful suicide/failed attempt
Misleading term; completion is not success or is someone surviving a failure
Preventable
Suicides can be stopped with proper intervention.
Epidemiology
suicide impacts on the most vulnerable of the world's population and is highly prevalent in already marginalized and discriminated groups of society.
Global suicide rate
804,000 deaths annually; 11.4 per 100,000.
2nd Leading cause of death globally
Suicide for ages 15-29.
Common suicide methods
Pesticide ingestion, hanging, and firearms.
Canadian suicide rate
11.4 per 100,000; ~4000 annually.
in richer countries, what's the ratio of men and women dying to suicide?
3x as many men die then women attempt.
in low to middle class countries, the male-to female ratio is
much lower at 1.5 men to each women
suicide accounts for ____% of all violent deaths in men and _____% in women
50%, 71%
what age is the highest rate of suicide ?
70 years or over
Local BC suicide statistics
500 suicides annually in BC, Canada.
CACUSS, 2016 canada cohort NCHA survey gathered what were the main causes of suicide?
- overwhelming anxiety
- self harm
-depression
- attempted once already
what are the three main risk factors
1. health system and societal risk factors
2. community and relationship risk factors
3. individual risk factors
Health system risk factors
- Barriers to accessing care
-access to means
- inappropriate media reporting and use
- stigma in seeking help.
Community risk factors
-disaster, war, conflict
- stresses of acculturation
- discrimination
- trauma or abuse
- isolation/lack of social support
- relationship conflicts.
Individual risk factors
- Previous attempts
-mental disorders
- harmful use of alcohol and other substances
- job or financial loss
- hopelessness.
- chronic pain and illness
-family history of suicide
- genetic and biological factors
Cues and warning signs
verbal, behaviour, situational
Verbal cues
Direct or indirect statements about self-harm.
Behavioral cues
Changes in mood, performance, or social interaction, exit strategies, or getting a gun, giving personal items away, getting affairs sorted, interest or disinterest in religion, drug/alcohol abuse or relapse, visits local bridge
Situational cues
- being fired or expelled, unwanted move, death of a loved one, serious or terminal illness, loss of freedom, loss of financial security, lack of support, tragic event
Protective factors
- strong relationships
- religious or spiritual beliefs
- positive coping strategies
Prevention strategies
Research, policy, and practice to reduce suicides.
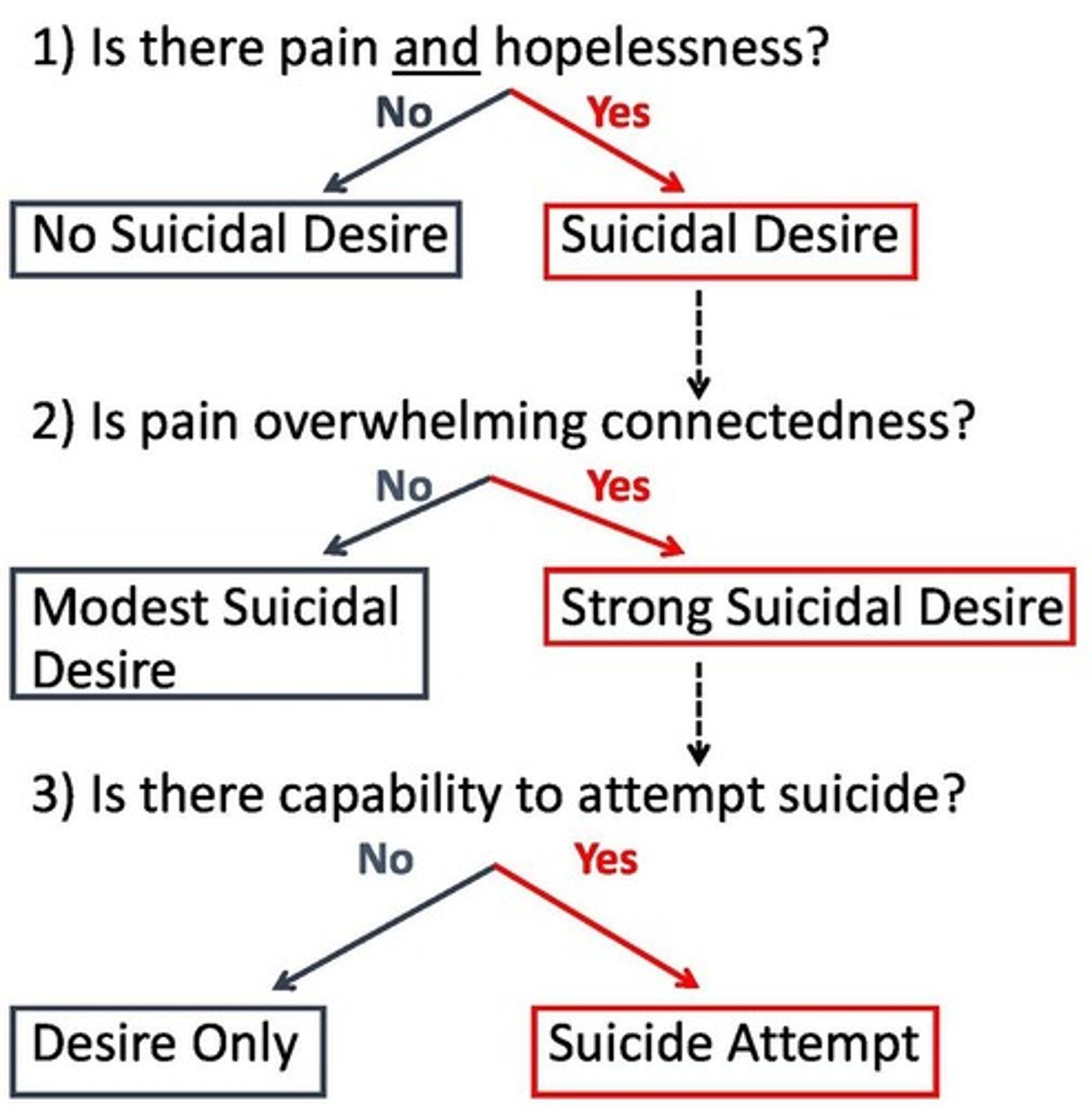
Three Step Theory (3ST)
Model explaining the progression to suicidal behavior.
World Suicide Prevention Day
Annual event promoting awareness and prevention efforts.
QPR
Question, Persuade, Refer; suicide prevention training.