MUSCULOSKELETAL EXAMINATON OF THE KNEE (P2: special tests)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Tests for ligamentous stability
Anterior Drawer Test
Jerk Test of Hughston
Lachman Test
Lelli Test
Pivot Shift Test
Posterior Drawer Sign
Posterior Sag Sign
Reverse Lachman Test
Slocum Test
Valgus Stress Test
Varus Stress Test
Identify
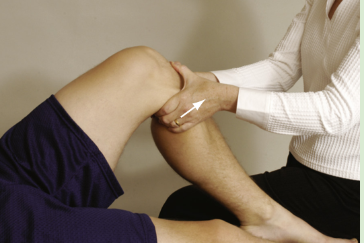
Anterior Drawers Test:
Pt knees flexed to 90o, hip flexed to 45o (ACL is parallel to tibial plateau), pt foot is held to the table (neutral position)
PT ensures HS mm are relaxed then draw tibia forward on the femur
(+) if tibia moves more than 6 mm on the femur
Structures injured in a (+) Anterior Drawers Test:
Structures injured to some degree:
Anterior cruciate ligament (especially the anteromedial bundle)
Posterolateral capsule
Posteromedial capsule
Medial collateral ligament (deep fibers)
Iliotibial band
Posterior oblique ligament
Arcuate-popliteus complex
Identify
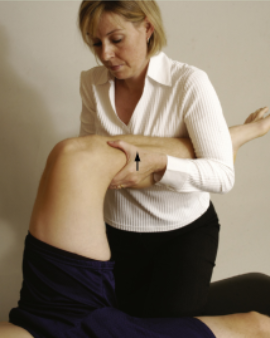
90-90 Anterior Drawer
Pt in supine with hips and knees flexed to 90o
PT places hand around the tibia and applies sufficient force to slowly lift the pt’s buttocks off the table
(+) excessive anterior translation of tibia
Sign shown when there is an audible snap or palpable jerk when doing the ant. drawers test
Finochietto Jumping Sign
Identify
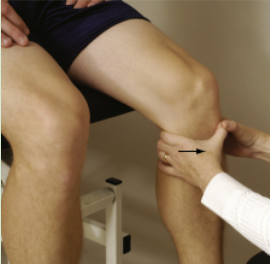
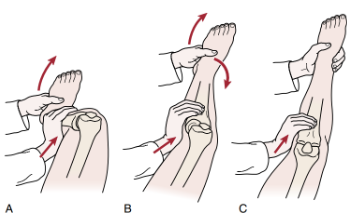
Sitting Anterior Drawer Test
Pt short-sitting on bed (posterior sag is eliminated d/t gravity)
PT places hands with standardized test and draws tibia forward then backward (anterior and posterior drawer)
(+) excessive tibial plateau movement
Identify
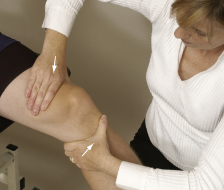
Jerk Test of Hughston
Pt in supine with hip flexed 90 degs and abducted 45 degs and slight IR (same with pivot shift manuever)
Leg is extended, maintain IR and valgus stress
(+) if at 20-30 degs flexion tibia shifts forward cause a subluxation of tibial plateau with jerk; ALRI
Identify
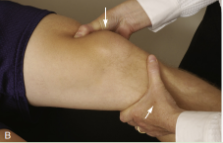
Lachman Test
AKA Ritchie, Trillat Test, Gold standard for ACL Tests
Pt supine then PT flexes knee between 30 degs to full extension
Stabilize the femur ,then apply force pulling the tibia anteriorly (apply force in posteriomedial aspect)
(+) if mushy or soft endfeel and disappearance of infrapatellar slope
(+) Lachman test affected structures:
Anterior cruciate ligament (especially the posterolateral bundle)
Posterior oblique ligament
Arcuate-popliteus complex
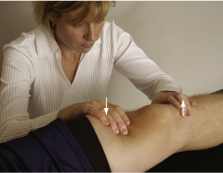
Modifications of Lachman:
Pt sitting dangling then rest foot on PT thigh so the knee is flexed to 30 degs
PT stabilize the thigh then pulls tibia forward with other hand
(+) if excessive forward motion
Modification 1
Modifications of Lachman:
Pt in supine
PT looks at knee eye level
PT holds femur then pulls tibia upward
Modification 5
Modifications of Lachman:
Pt in supine with hip abducted with knee flexed to 25 degs
PT stabilize the thigh then holds the foot between the knees
Apply anterior force to tibia
Modification 3
drop leg lachman test
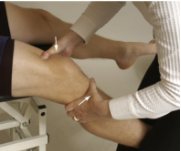
Modifications of Lachman:
Pt in supine with knee on top of PT forearm so knee is flexed 30 degs
Pt is asked to extend knee, PT watches for anterior displacement of tibia
Modification 7:
no touch lacman test
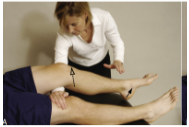
Modifications of Lachman:
Pt in supine with knee on top of PT knee
PT stabilize thigh then apply anterior force on the tibia
Modification 2
stable lachman test FOR PT c small hands
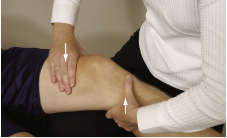
Modifications of Lachman:
Basically modification 7 but PT stabilizes the foot to increase pull of quads
Make sure no posterior sag prior to doing test
Modification 8:
maximum quads test
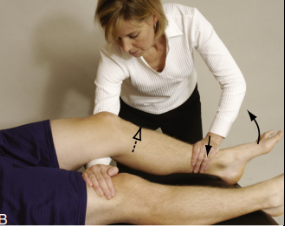
Modifications of Lachman:
Pt in prone with leg in between PT thorax and arm
Knee is flexed around 30 degs
Stabilize femur then push tibia downard
HARD TO ASSESS ENDFEEL
Modification 6:
prone lachman test
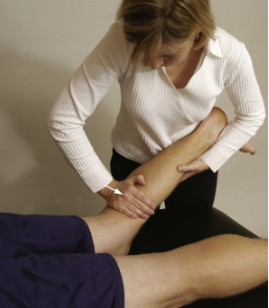
Modifications of Lachman:
Pt in supine with leg in between thorax and arm of PT
Knee is flexed to 30 degs
Put both hands on tibia and apply anterior drawer
Modification 4:
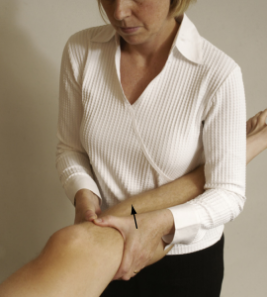
Grading of Lacman with stress radiograph:
grade 1 =
grade 2 =
grade 3 =
grade 4 =
Grading of Lacman with stress radiograph:
grade 1 = 3-6 mm
grade 2 = 6-9 mm
grade 3 =10-16 mm
grade 4 =16-20 mm
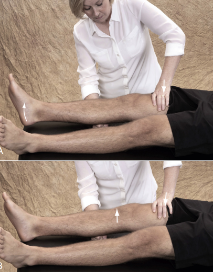
Identify
Lelli Test
Pt in supine knee extended
PT place fist on proximal ⅓ of calf then apply pressure on distal ⅓ of quads
(+) if heel does not lift of bed
(-) if heel lifts off (first pic)
cannot be used in isolation to dx ACL tear
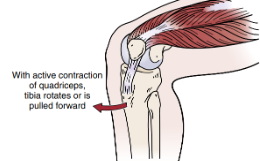
Identify
Pivot Shift Test
Pt sits with foot on floor with knee flexed 80-90 degs
Pt has to isom contract quads while PT stabilize foot
(+) if anterolateral subluxation of lateral tibia plateau
indicative of ALRI
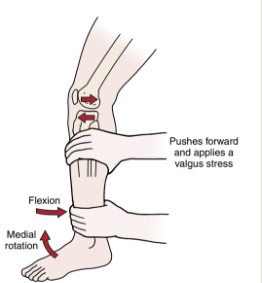
Identify
Lateral Pivot Shift Maneuver
Pt in supine with hip flexed and abducted 30 degs and slight IR
PT stabilizes foot and holds knee (fibula) with other hand
PT applies anterior force as you put knee into extension
Test for ALRI and ACL tears (3rd degree)
Dynamic Subluxation
Posterior Drawer Sign
Same position with anterior drawer test
PT pushes tibia postreriorly to femur
(+) if excessive tibial translation
Structures injured if (+) or Posterior Sag sign is (+)
Posterior cruciate ligament
Arcuate-popliteus complex
Posterior oblique ligament
Anterior cruciate ligament
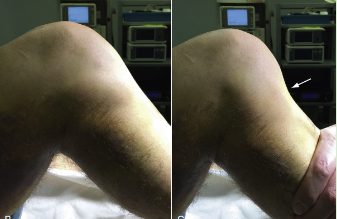
Identify
Gravity Drawer Test
Posterior Sag Sign
Pt in supine with hip flexed to 45 degs and knee flexes to 90 degs = tibia will sag back or “drops back”
(+) PCL tear
If medial tibial plateau does not extends 1cm anteriorly during 90 degs knee flexion this sign is present d/t torn meniscus
(+) Step-off test or Thumb sign
Structures that may be involved with a (+) Posterior Sag Sign:
Posterior cruciate ligament
Arcuate-popliteus complex
Posterior oblique ligament
Anterior cruciate ligament
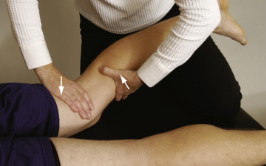
Idenitfy
Reverse Lachman Test
Pt prone with knee flexed to 30 degs then stabilize thigh
Pt then pulls tibia superiorly then check endfeel and movement
(+) PCL tear if excessive translation
Posterior drawer test better since greatest displacement is at 90 degs knee flexion
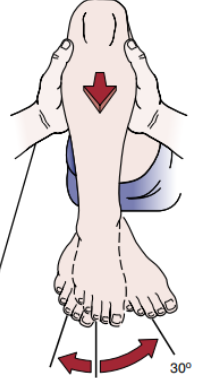
Identify
Slocum Test
For ALRI
Pt in supine flex knee to 80-90 degs and hip flexed to 45 degs
IR foot to 30 degs then draw tibia forward
If (+) most of movement comes from lateral side of knee also indicates ALRI
For AMRI
Lemaire’s T drawer Test
Foot is placed in 15o of ER, tibia is drawn forward by PT
(+) if movement occurs primarily on the medial side of the knee
Possible Affected structures (+) Slocum test (for ALRI):
Possible affected structures:
Anterior cruciate ligament
Posterolateral capsule
Arcuate-popliteus complex
Lateral collateral ligament
Posterior cruciate ligament
Iliotibial band
Possible Affected structures (+) Slocum test (for AMRI):
Possible affected structures:
Medial collateral ligament
Posterior oblique ligament
Posteromedial capsule
Anterior cruciate ligament
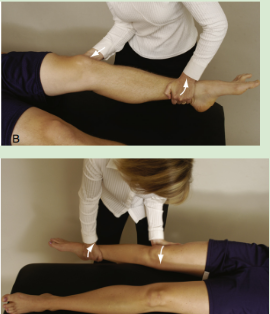
Idenify
Valgus Stress Test
Pt in supine
Apply valgus stress on knee (push it medially) with stabilized ankle in ER
From flexion, knee is slightly flexed (20-30o) = “unlocked”
(+) excessive ROM

Identify
Hughston’s Valgus Test
Same position as valgus stress test
But apply valgus stress by holding the big toe, allow natural rotation of tibia
(+) excessive ROM
For medial instability
Injury in the following If valgus stress test is (+) in extension:
Medial collateral ligament (superficial and deep fibers)
Posterior oblique ligament
Posteromedial capsule
Anterior cruciate ligament
Posterior cruciate ligament
Medial quadriceps expansion
Semimembranosus muscle
If (+) valgus stress test in 20-30 deg flexion:
Medial collateral ligament
Posterior oblique ligament
Posterior cruciate ligament
Posteromedial capsule
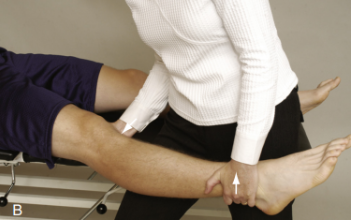
Identify
Varus stress test
Pt in supine
PT apply varus stress
Done in 30 deg knee flexion and full extension
Where do you apply varus stress in the Hughston’s varus test?
Apply varus stress on the 4th and 5th toes
Injury in the following structures if (+) Varus stress test in extension:
Fibular or lateral collateral ligament
Posterolateral capsule
Arcuate-popliteus complex
Biceps femoris tendon
Posterior cruciate ligament
Anterior cruciate ligament
Lateral gastrocnemius muscle
Iliotibial band
Injury in the following structures if (+) Varus stress test in 20-30 degs flexion with ER of tibia :
Lateral collateral ligament
Posterolateral capsule
Arcuate-popliteus complex
Iliotibial band
Biceps femoris tendon
Tests for swelling
Brush Test
Patellar Tap Test
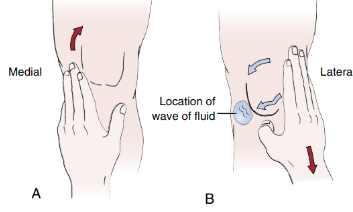
Identify
Brush, Stroke, or Bulge Test
AKA wipe test
For minimal effusion
Start at the jt line on the medial side of patella then stroke proximally toward hip for 2-3 times (suprapatellar pouch)
Use the other hand to stroke the lateral jt line of patella downward
there will be a bulge of fluid around 4-8 ml in 2 secs
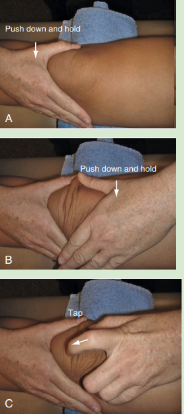
Idenitfy
Patellar Tap Test
“Ballotable patella”
Pt positions knee to position of discomfort (flex or ext)
PT applies slight pressure or taps the patella
(+) if floating of patella (aka Dancing Patella sign)
Modification:
PT applies thumb and forefinger of one hand lightly on both sides of patella
Using other hand, PT then strokes down on the suprapatellar pouch
(+) separation of thumb and forefinger
Detects up to 40-50mL of swelling in the knee
Tests for Plica lesions
Hughston’s Plica Test
Plica “Stutter” Test
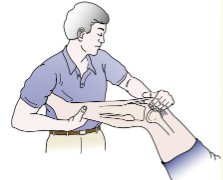
Identify
Hughston’s Plica Test
Pt in supine while PT flexes knee and IR tibia while pushing patella medially and palpating the medial condyle
Passively flex and extend knee
(+) if popping
What test is described?
Pt on the edge of table with knee flexed to 90 degs while palpating patella
Pt has to extend the knee slowly
(+) if patella stutters or jumps somewhere between 60o and 45o
test is only effective when there is no swelling
Plica “Stutter” Test
Tests for Meniscal Injuries
Apley’s Test
Bounce Home Test
Childress’ sign
Ege’s Test
McMurray Test
Thessaly Test
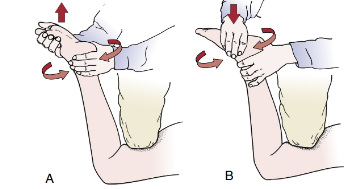
Identify
Apley’s Test
Pt in prone with knee flexed to 90 degs
Anchor pt’s thigh using PT knee
Distract the tibia from the knee jt then apply IR and ER
Next do the same thing except using compression instead of distraction
If IR and ER more painful with distraction or increased rotation to one side = (+) ligemental affectation
If IR and ER more painful with compression or decreased rotation = (+) meniscal affectation
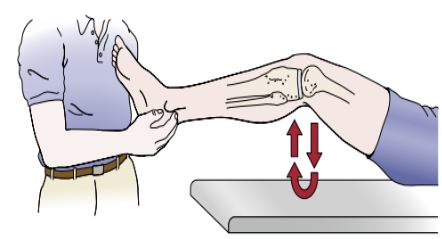
Identify
Bounce Home Test
Pt in supine, then PT cups foot
Pt’s knee is flexed and then passively extended
Note for incomplete ROM and springy block end feel
If something is blocking full extension = most likely torn meniscus (springy block)

Identify
Childress Test
AKA Squat and Duck Walk test
Ask pt to squat then walk or waddle forward in the squatting position
(+) if pain in joint line or painful clicking = posterior horn lesion of meniscus
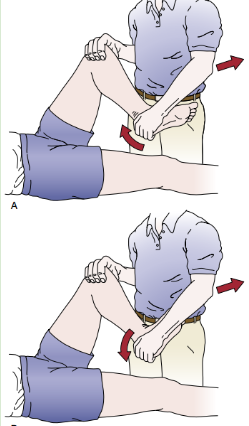
Idenitfy
McMurray’s Test
Pt in supine with knee maximally flexed (heel to ass)
PT IR tibia then extends knee to asses lateral meniscus
PT ER tibia then extends knee to assess medial lemniscus
if accompanied by pain and snapping = indicative of loose bodies
Identify
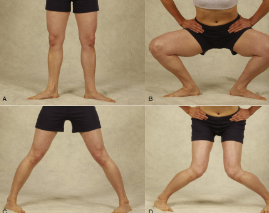
Ege’s Test
Basically a WB McMurray’s test
Pt stands with feet 30-40cm (11-15 inches) apart
Testing for medial meniscus
Pt ER tibia then squats then slowly stand up
Testing for lat meniscus
Pt IR tibia then squats then slowly stand up
(+) if pain along jt. line and clicking sounds
not accurate in acute cases <6 wks
squatting with IR is difficult even in healthy individuals
Identify
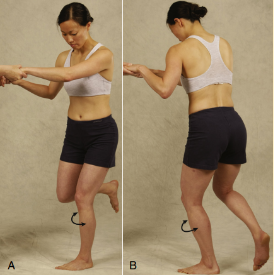
Thessaly’s Test
Pt stands on one leg, PT can help balance
Pt flexes knee 5 degs (then 20 deg) then IR and ER femur on tibia 3 times
(+) if jt. line discomfort; May have locking or catching
Contraindicated for ACL injury
Tests for Patellar Affectation:
Clarke’s Sign
Eccentric Step Test
Fairbank’s Apprehension test
Noble Compression Test
Step up Test
Waldron Test
Identify
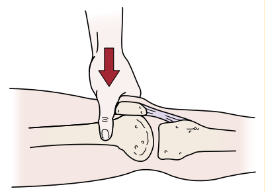
Clarke’s Sign or Patellar Grind Test
For articulation problem between the patella and femoral condyles
Pt in supine knees extended
PT presses down on superior pole of patella using web of hand
Push down on the patella while pt contracts quads
(+) if pt cant maintain contraction or pain on patella
better if test is repeated in many different ROMS of knee flexion (30, 60, 90) and increasing pressure
Identify
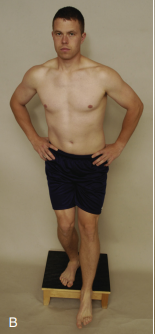
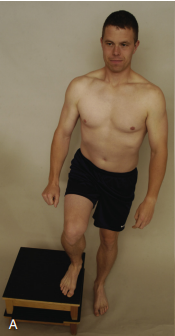
Eccentric Step Test or Lateral Step Down Test
Pt stands on a 15 cm-high step with hands on hip (6 inches)
Pt steps down slowly using the injured leg first, while PT watches
(+) if pain
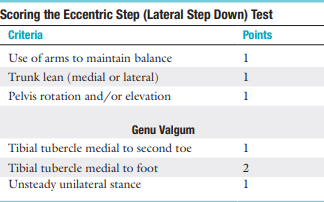
Eccentric Step Test or Lateral Step Down Test scoring:
Score range for good quality of movement?
Score range for medium quality of movement?
Score range for poor movement?
Eccentric Step Test or Lateral Step Down Test scoring:
0-1
2-3
4+
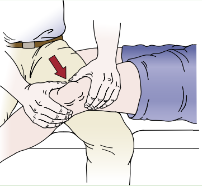
Identify
Fairbank’s Apprehension Test
Pt in supine with knees flexed to 30 degs, quads relaxed
PT then pushes patella laterally and distally
(+) if pt feels apprehension seen by the contraction of quads
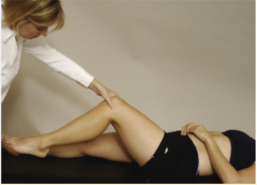
Identify
Noble Compression Test
For checking if pt has ITB friction syndrome near knee (chronic inflammation of ITB near insertion/ femoral condyles)
Pt in supine with knee flexed to 90 degs with hip flexion
PT extends the knee while applying pressure on lateral femoral condyle
(+) if at 30 degs knee flexion, pt feels pain on lateral femoral condyle; Same pain pt feels when running
Identify
Step up Test
Pt stands beside stool 25 cm high
Pt is instructed to step up laterally using good leg then the injured leg
(+) may indicate patellofemoral arthralgia, weak quads, or inability to stabilize pelvis

Identify
Waldron Test
Palpate patella while pt performs slow deep knee bends (squats)
PT has note for crepitus throughout ROM
(+) if pain and crepitus in ROM
Tests for Muscle Dysfunction:
90–90 straight leg raise test
Trendelenburg test
Ely’s Test
Ober’s Test
Thomas Test
Noble Compression Test
Adductor Squeeze Test
Hip Lag Sign
Phelps’ Test
Piriformis Test
Sign of the Buttock
Tripod Sign
(read hip special tests we finished dis alr)
THAT FEELING WHEN KNEE SURGERY IS TOMORROW