Hearing Science: Middle Ear Anatomy
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
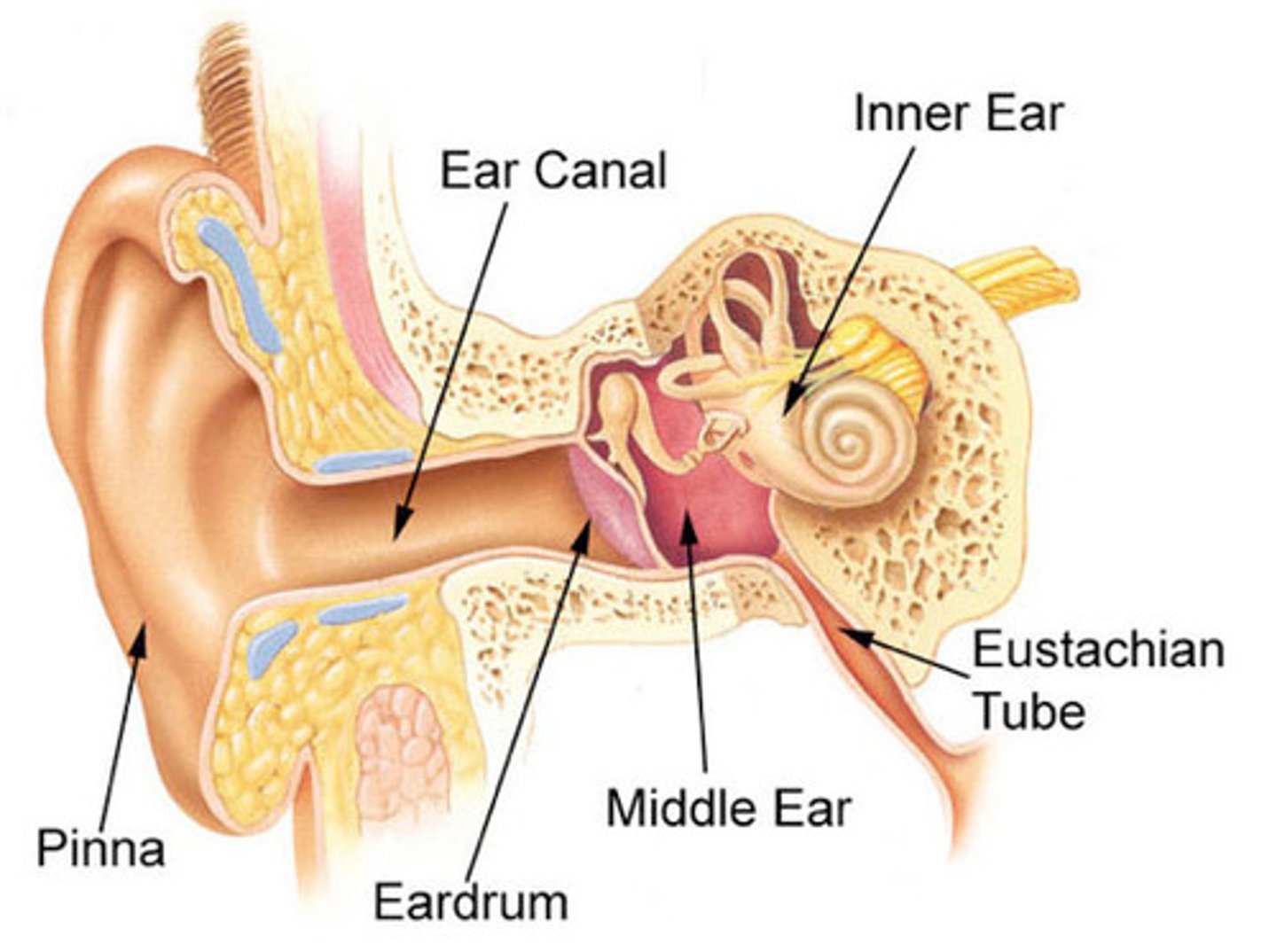
What does the middle ear occupy?
the tympanic cavity (tympanum) in the temporal bone
-bounded by the tympanic membrane (laterally) and inner ear (medially)
What is the volume of the middle ear?
about 2 cc (air filled)
What are the six surfaces of the middle ear?
lateral, medial, superior, inferior, anterior, posterior
What surface is the tympanic membrane located on in the ear box?
lateral
-ear drum
What surface is the cochlea located on in the ear box?
medial
The posterior wall is...
toward the back of the head
The anterior wall is...
toward the nose/face
What is above the superior wall of the middle ear?
the brain
What is the medial wall going towards?
the inner ear
What is inside the middle ear?
mucus
What causes negative pressure within the middle ear?
when the mucus in the walls gets sucked out, into the ear
-caused by the eustachian tube not opening and closing
What makes up the lateral surface?
tympanic membrane
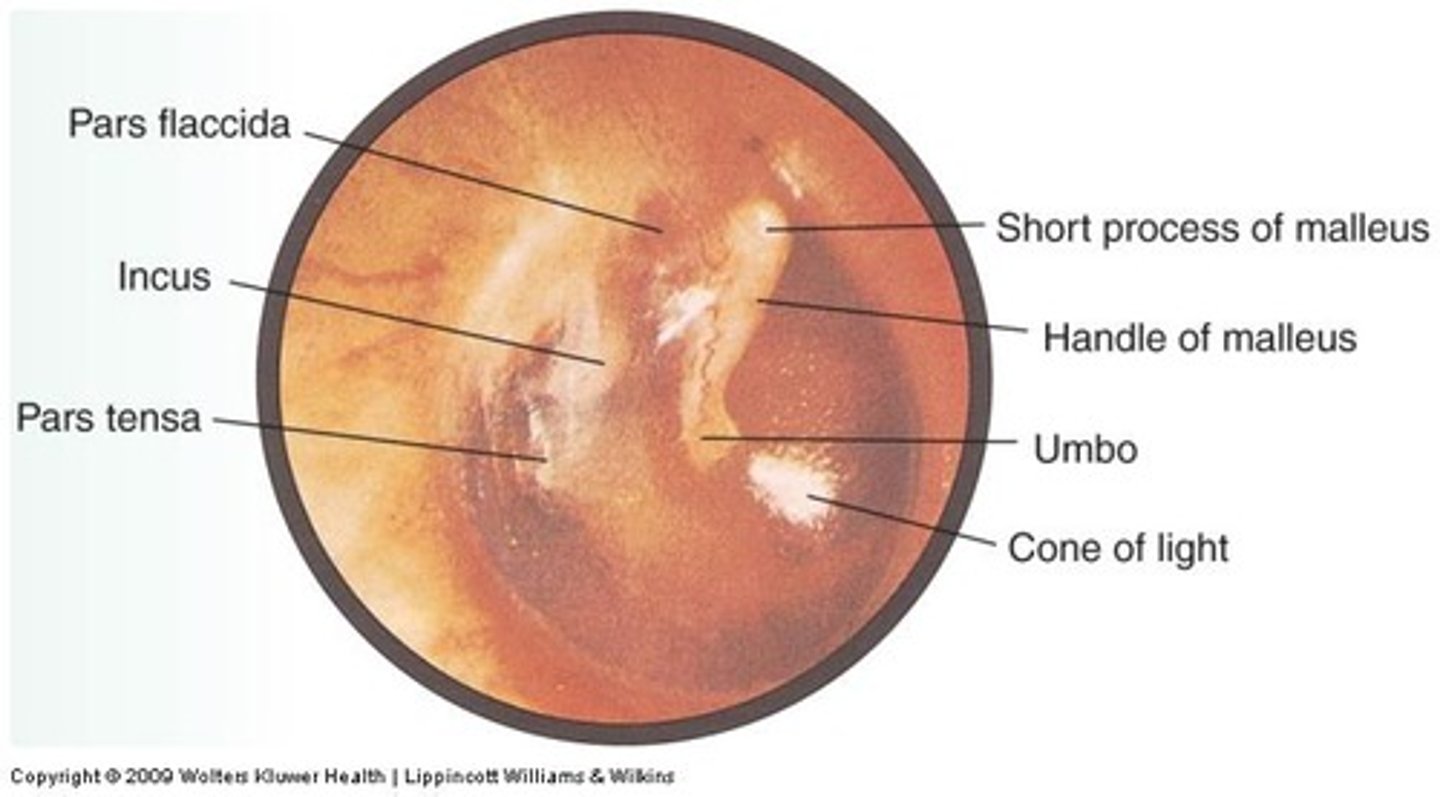
Describe the appearance of the tympanic membrane
-circular
-semi-transparent
-pearly grey in color
-coned inward
What is the tip of the cone called?
the manubrium (handle of the malleus)
What are the four features of the tympanic membrane?
umbo, pars flaccida, pars tensa, "cone of light"
Umbo
the center point of the cone
What attaches to the umbo of the tympanic membrane?
the tip of the manubrium of the malleus
Pars Flaccida
-superior quadrant of the TM
-2 tissue layers: skin and mucus membrane
-not under tension
Pars Tensa
-3 tissue layers: skin, connective, mucus membrane
-under tension (from inward pull of the tensor tympani muscle)
-primarily responsible for sound transmission from outer to middle ear
What makes up the superior surface of the middle ear?
tegman tympani
Tegman Tympani
thin, very hard bone
-separates tympanic cavity from the brain
-roof of tympanic cavity and the floor of the cranium
What is the superior surface of the tegman tympani covered by?
dura matter (outer-most layer of meninges)
What is the inferior surface of the tegman tympani covered by?
mucosa
Where is the epitympanic recess (attic) located?
near the tympanic membrane, above the malleus
-within the tympanic cavity
-on the superior surface
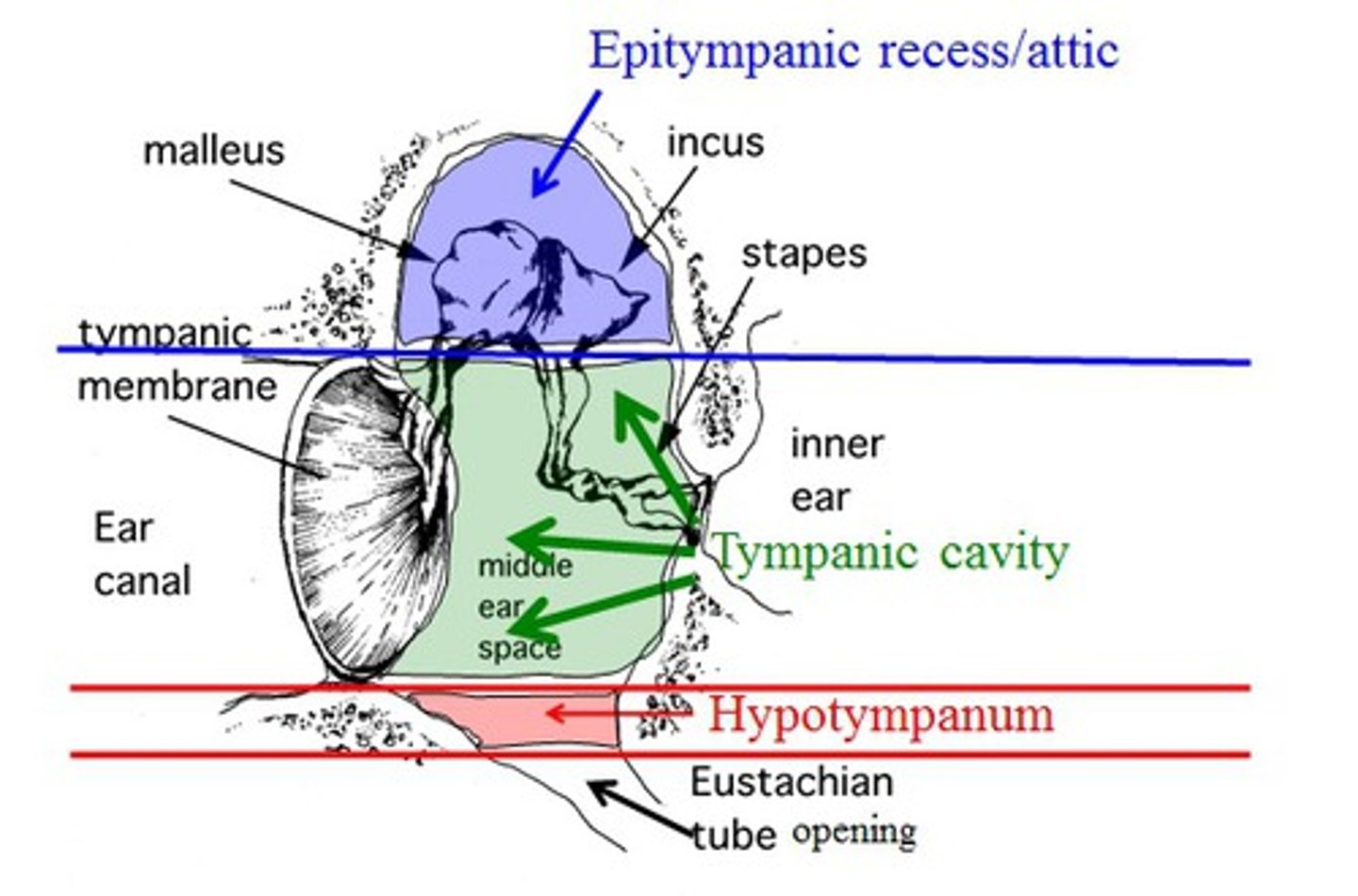
What does the epitympanic recess accomodate?
the large head of the malleus
What is the inferior surface of the middle ear?
floor of tympanic cavity
What two features does the inferior surface spearate?
the tympanic cavity from the jugular fossa
What passes through the jugular fossa?
internal jugular vein with the jugular bulb directly beneath the tympanum
Fossa
ditch or trench
What does the anterior surface separate?
the tympanic cavity from the carotid canal
What does the carotid canal house?
internal carotid artery
What opening is in the anterior wall of the middle ear?
the opening of the eustachian tube
-pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube
What emerges from the anterior wall?
the tendon of the tensor tympani emerges from the anterior surface and attaches to the malleus
What are the three features of the posterior surface of the middle ear?
-pyramidal eminence
-aditus to antrum of mastoid
-branch of the facical nerve (VIIth)
Where is the pyramidal eminence located?
the posterior surface
What does the pyramidal eminence house?
the stapedius muscle
What window is on the posterior wall of the middle ear?
the aditus to antrum of the mastoid
-the entrance to the cavity of the mastoid
Aditus
entrance to a cavity or channel
Antrum
cavity
What passes from the posterior wall to the anterior wall, just behind the ear drum (TM)?
the branch of the facial nerve (VIIth) called the chorda tympani
Chorda Tympani
sensory nerve for the anterior part of the tongue
What are the four features of the medial surface?
oval window, round window, canal for VIIth nerve (facial nerve), promontory
Where is the oval window located?
medial surface of the middle ear
Oval Window
-non-permeable membrane
-leads to the inner ear
-covered by the footplate of the stapes
Where is the round window located?
on the medial wall of the middle ear
-below the oval window
Round Window
-lower portion
-covered by a non-permeable membrane
-leads to inner ear
Non-permeable
fluid cannot get through
Where is the canal for the VIIth nerve (facial nerve) located?
on the superior portion of the medial surface of the middle ear
Where is the promontory located?
on the medial surface of the middle ear
-between the oval window and round window
Promontory
bony accomodation for the base (first turn) of the cochlea
Ossicular Chain
provides mechanical linkage between the TM and the oval window
-the malleus is attached to the TM
-the stapes footplate covers the oval window
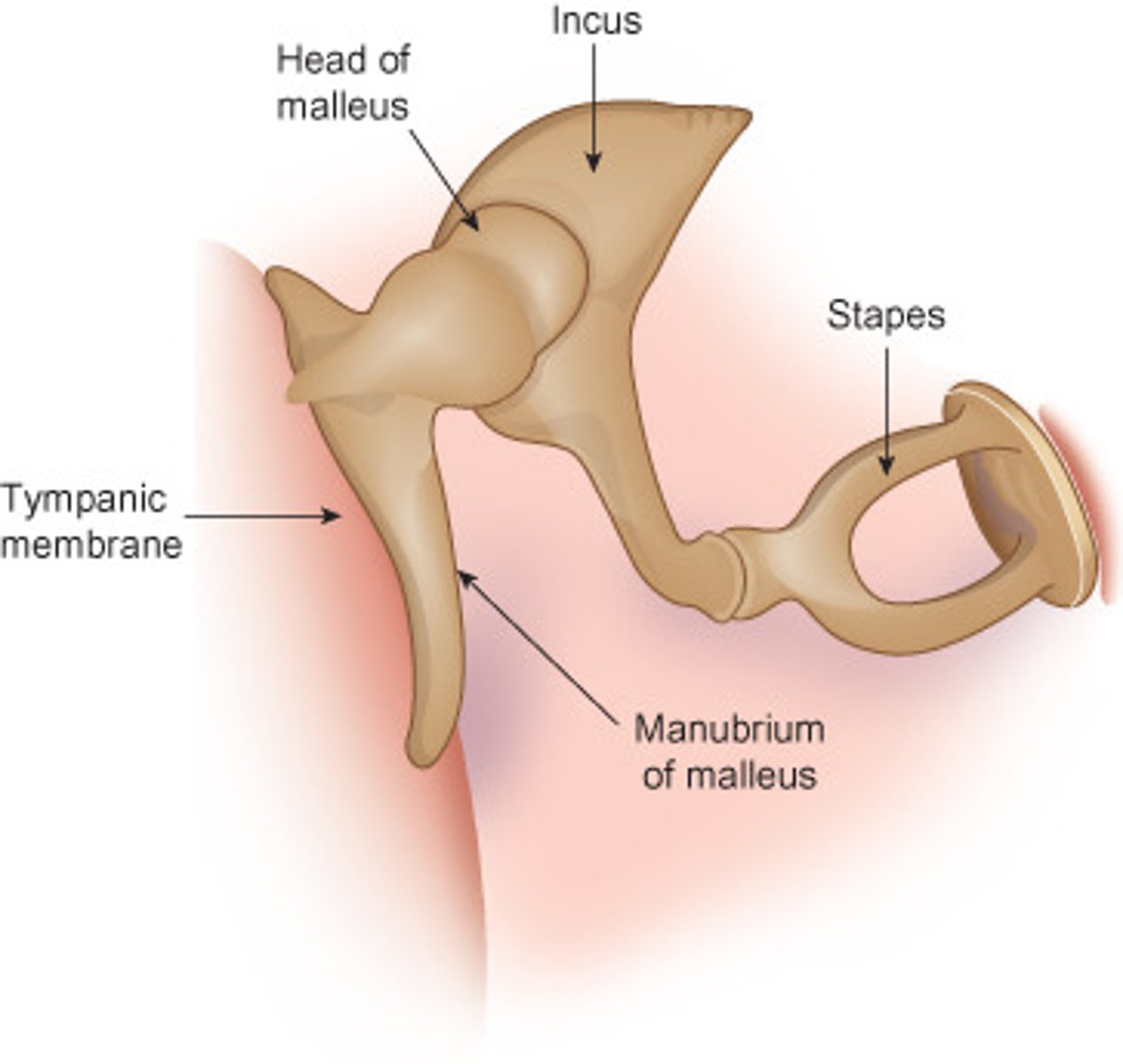
What are ossicles?
the mechanical link between the outer and inner ear
What are the three interconnected bones of the ossicular chain?
malleus, incus, stapes
What are the four features of the malleus?
head, neck, manubrium, anterior process
-malleus = hammer head
-manubrium = handle
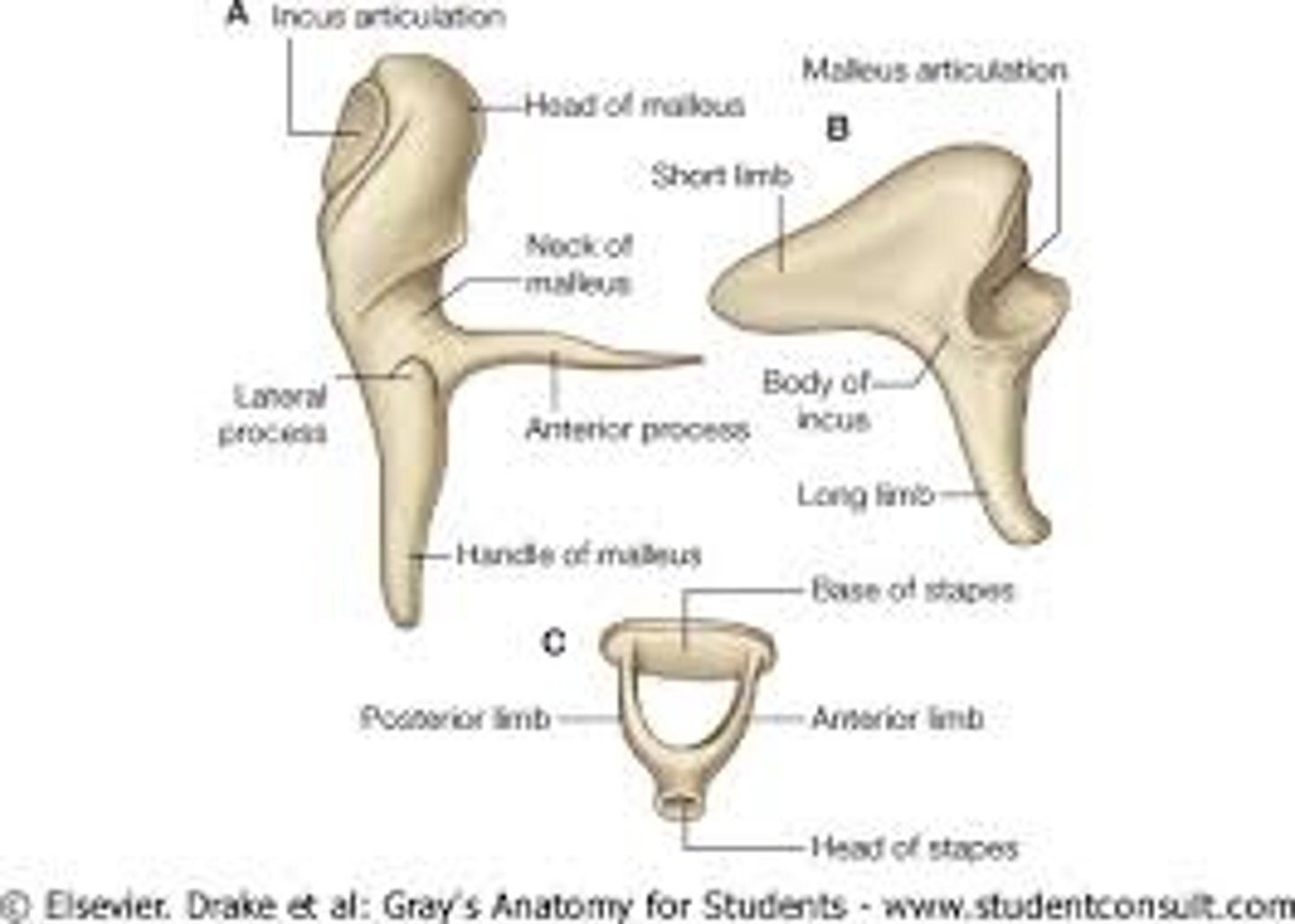
What are the parts of the incus?
articulating facet, body, short process, long process, lenticular process
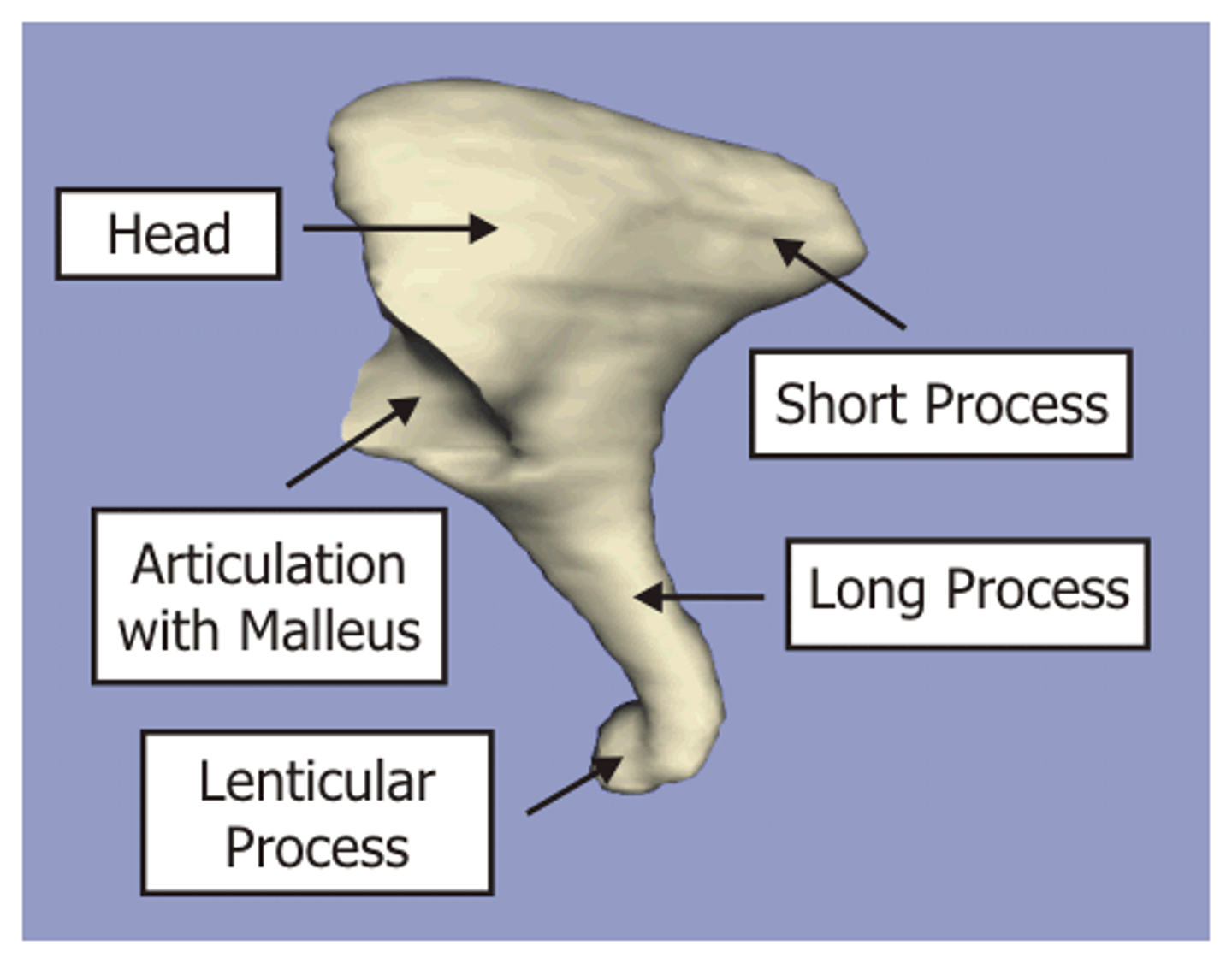
Where is the articulating facet located?
under the head of the malleus
Lenticular
similar in shape to the lentil bean (convex)
What are the four parts of the stapes?
head, neck, crura (anterior crus and posterior crus), footplate
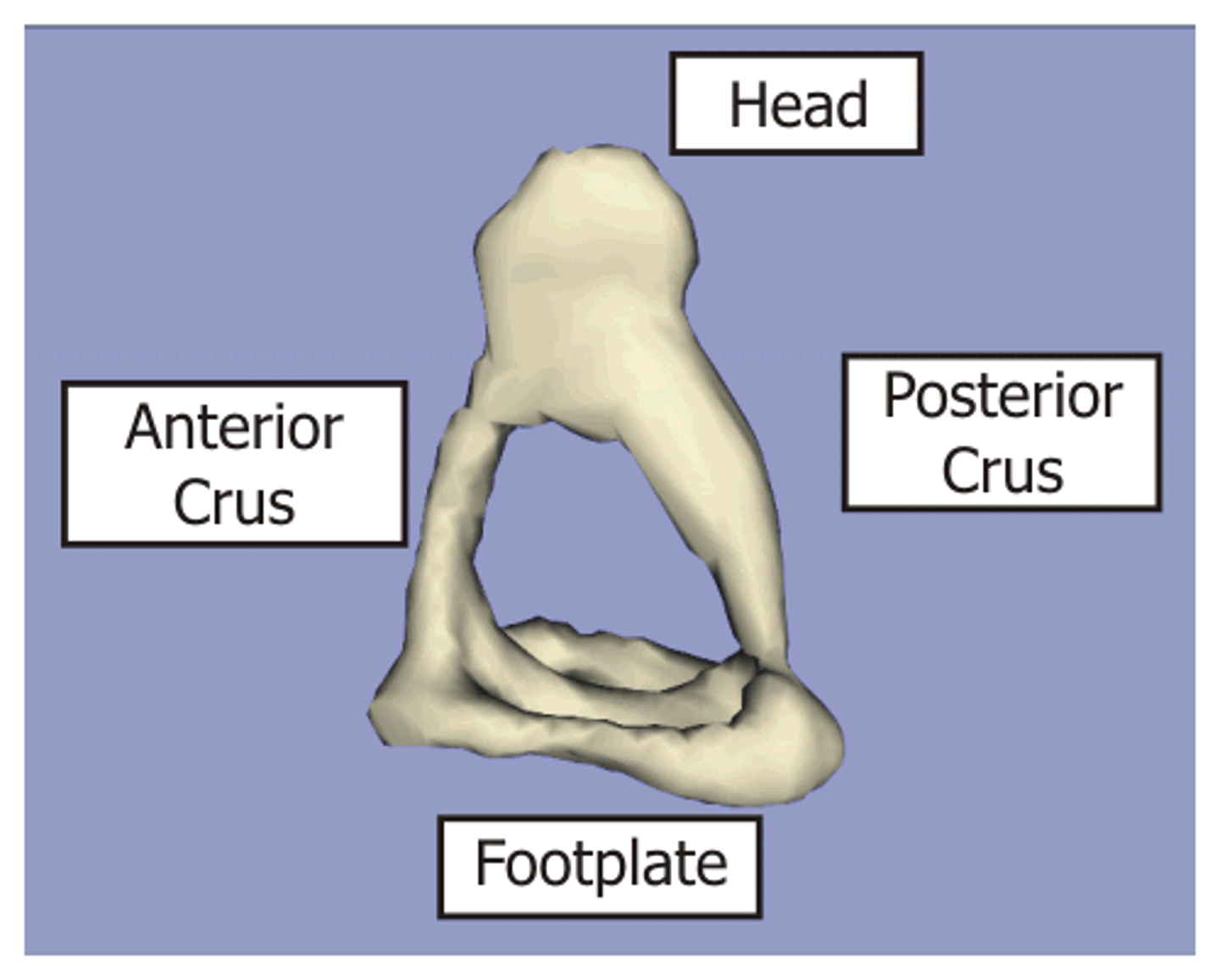
What path does the tendon of the tensor tympani follow?
from the medial or anterior wall of the tympanic cavity
What does the tensor tympani attach to?
the manubrium of the malleus (Vth cranial nerve)
What does the tendon of the tensor tympani do?
-pulls malleus anteriorly and medially
-regulates the tension on the tympanic membrane
Is the tendon of the tensor tympani involved in the human acoustic reflex?
it is not involved in the human acoutic reflex, unless the stimulating sound is suffuciently intense and unexpected to produce a startle response
Can non-auditory stimuli cause contraction of the tendon of the tensor tympani?
yes
(ex. puff of air to the eye)
What path does the tendon of the stapedius muscle follow?
from the posterior wall (pyramidal eminence), or from the medial wall to the neck of the stapes (VIIth cranial nerve/facial nerve)
What does the tendon of the stapedius mucle do?
in response to specific auditory stimuli, the stapedius muscle pulls the stapes away in a posterior direction
Is the tendon of the stapedius muscle part of the human acoustic reflex?
yes
What is the measure of response by the tendon of the stapedius muscle called?
acoustic reflex threshold
What generally happens in response to high level sounds?
the opposing pull of these two muscles acts to tighten the ossicular chain and reduce the intensity of low frequency sounds travelling to the inner ear
Where is the eustachian tube located?
starts on the anterior wall of the tympanic cavity
-terminates into the nasopharynx in the back of the throat (posterior to nose and superior to the soft palate)
What is the course of the eustachian tube in infants?
anteriorly and medially
What is the course of the eustachian tube in adults?
anteriorly, medially, inferiorly
What are the features of the eustachian tube?
-osseous: begins at anterior wall of tymoanic cavity
-cartilaginous membranous
-terminates at the torus tubarius in the nasopharynx
-lined with mucosa
-downward pointing cilia (little hairs)
What do cilia do?
help keep out debris (such as mucus)
What is the function of the eustachian tube?
-only source of air for the iddle ear
-normal middle function requires air pressure to be equal on both sides of the tympanic membrane
-removes mucus and bacteria from the middle ear into the nasopharynx
What is the only source of air for the middle ear?
eustachian tube
Where does the mucus and bacteria go when the eustachian tube removes it from the middle ear, and into the nasopharynx?
into the throat
What mechanism opens the eustachian tube?
the two muscles in the nasopharynx
What are the two muscles in the nasopharynx?
tensor veli palatini (TVP) - primary
lavator veli palatini (LVP) - secondary
Is the opening of the eustachian tube at the torus tubarius normally collapsed?
yes
How does the eustachian tube open?
during swallowing, yawning, sneezing or coughing, the muscles contract which pinches open the eustachian tube
Mastoid
part of the middle ear air pathway
-connection point
How does the mastoid have access to air cells?
via aditus, located in the posterior wall of the tympanic cavity
-air cells are lined with mucosa
Sternocleidomastoid Muscle
two-headed neck muscle
-connects the manubrium of the sternum, the clavicle, and the mastoid process of the temporal bone