Intergumentary System
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
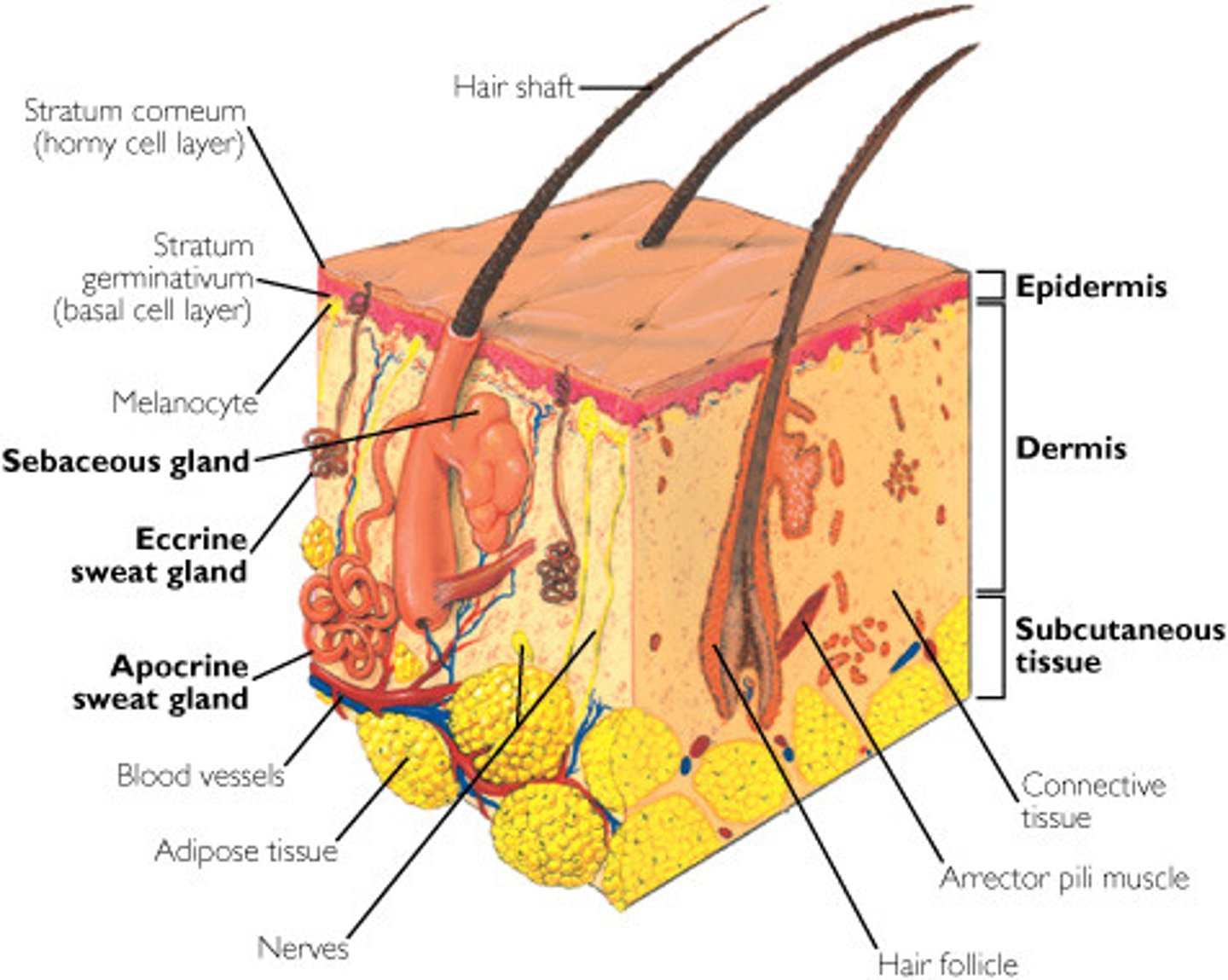
The integumentary system consist of
skin, hair, nails, sudoriferous sweat glands, sebaceous (oil) glands
main functions of the skin
1. first and foremost a barrier
2. protection
3. body regulation
4. cutaneous sensations
5. metabolic functions
6. blood reservoir
7. excretion of wastes
How skin protects
1. secretes many chemicals: sweat (antimicrobial proteins) and sebum
2. Acid Mantle: low pH of skin = less bacterial multiplication
3. MELANIN: chemical barrier against UV radiation damage.
How skin regulates body temperature
Hot: Sweating, and vasodilation
Cold: Shivering, vasoconstriction, brown adipose fat
What is insensible perspiration?
does not produce visible wetness, 500ml a day
- under normal resting body temperature
What is sensible perspiration?
- body temperature rises
- dilation of dermal vessels increase sweat gland activity (profuce 12L)
- noticeable sweat
how skin function as a cutaneous sensation
Exteroreceptors respond to stimuli outside body:
1. temperature
2. touch
3. and pain
What vitamin does the skin produce and its function?
Vitamin D
- needed for calcium absorption
how skin function as a blood reservoir?
Hods up to 5% of the body's total blood volume
- vessels can be constricted to shunt blood to other organs (exercising muscle)
how skin helps with excretion of wastes?
- Secretes limited amounts of nitrogenous wastes:
1. ammonia
2. Urea
3. Uric Acid
- Can cause slat and water loss
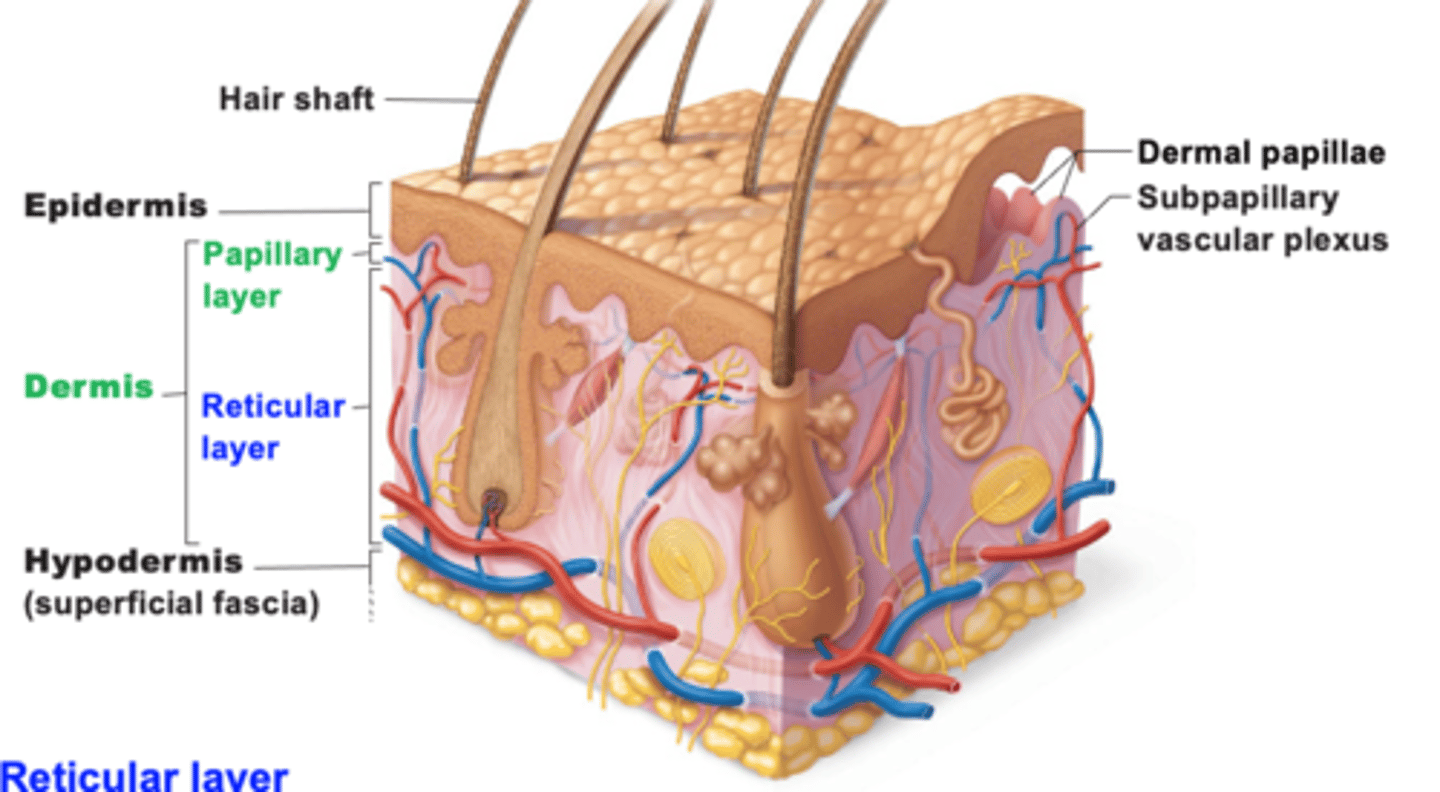
two distinct regions of the skin
1. Epidermis: superficial region
- epithelial and avascular
2. Dermis: underlies epidermis
- fibrous connective tissue and vascular
What is the hypodermis?
- subcutaneous layer deep to skin
- not part of skin but shares some functions
- mostly adipose tissue that absorbs shock and insulates
- anchors skin to underlying structures: mostly muscles
The epidermis is composed of
- mostly keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
- thin outer layer
- In 4/5 distinct cell layers
Keratinized vs non-keratinized
Keratinized- cells that have no nuclei & form a tough, resistant layer on the surface of the skin. (found on the palms & soles)
Nonkeratinized- cells that have nuclei & act as a cushion against mechanical stress & wear. (Softer & more flexible) (WET areas)
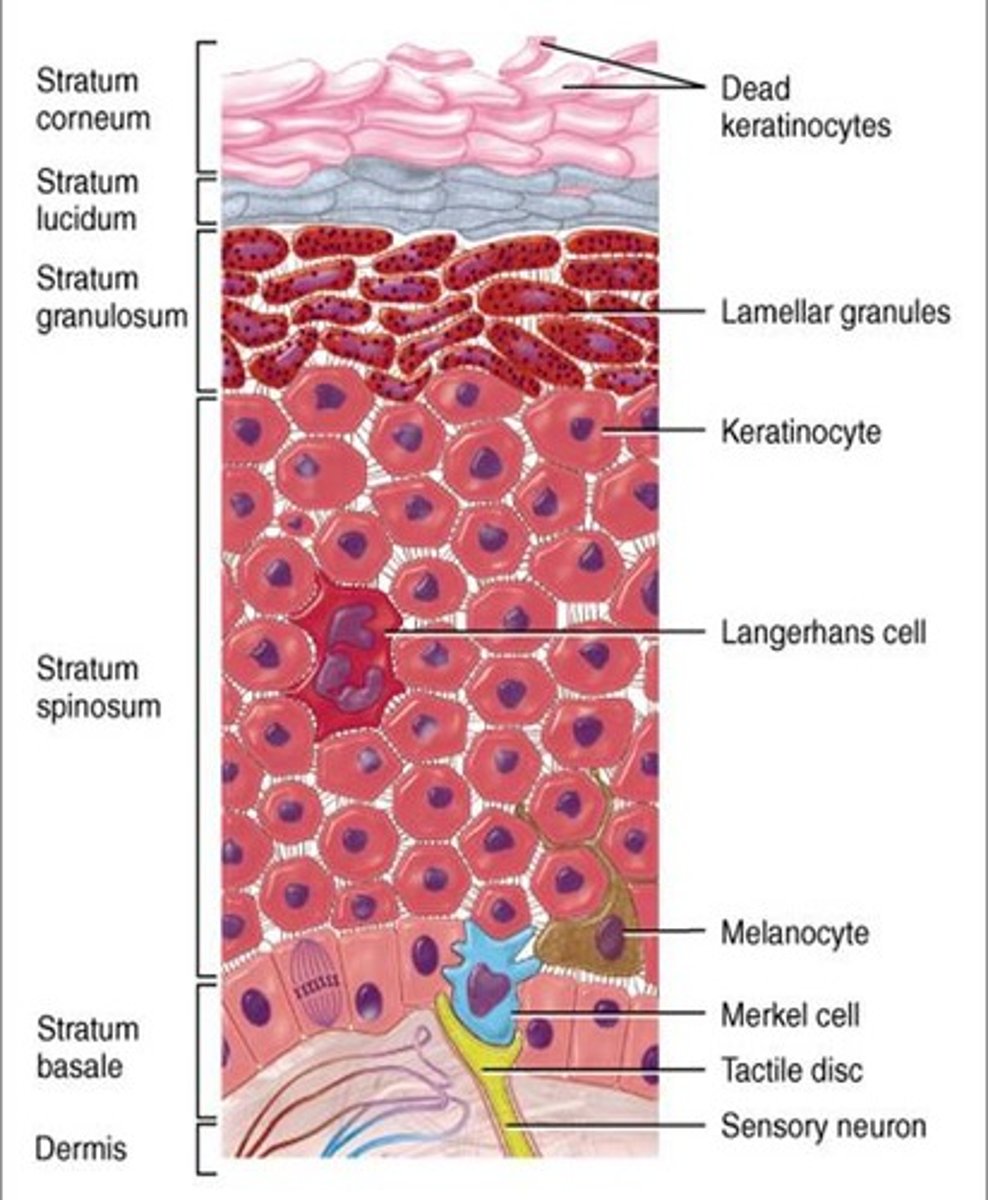
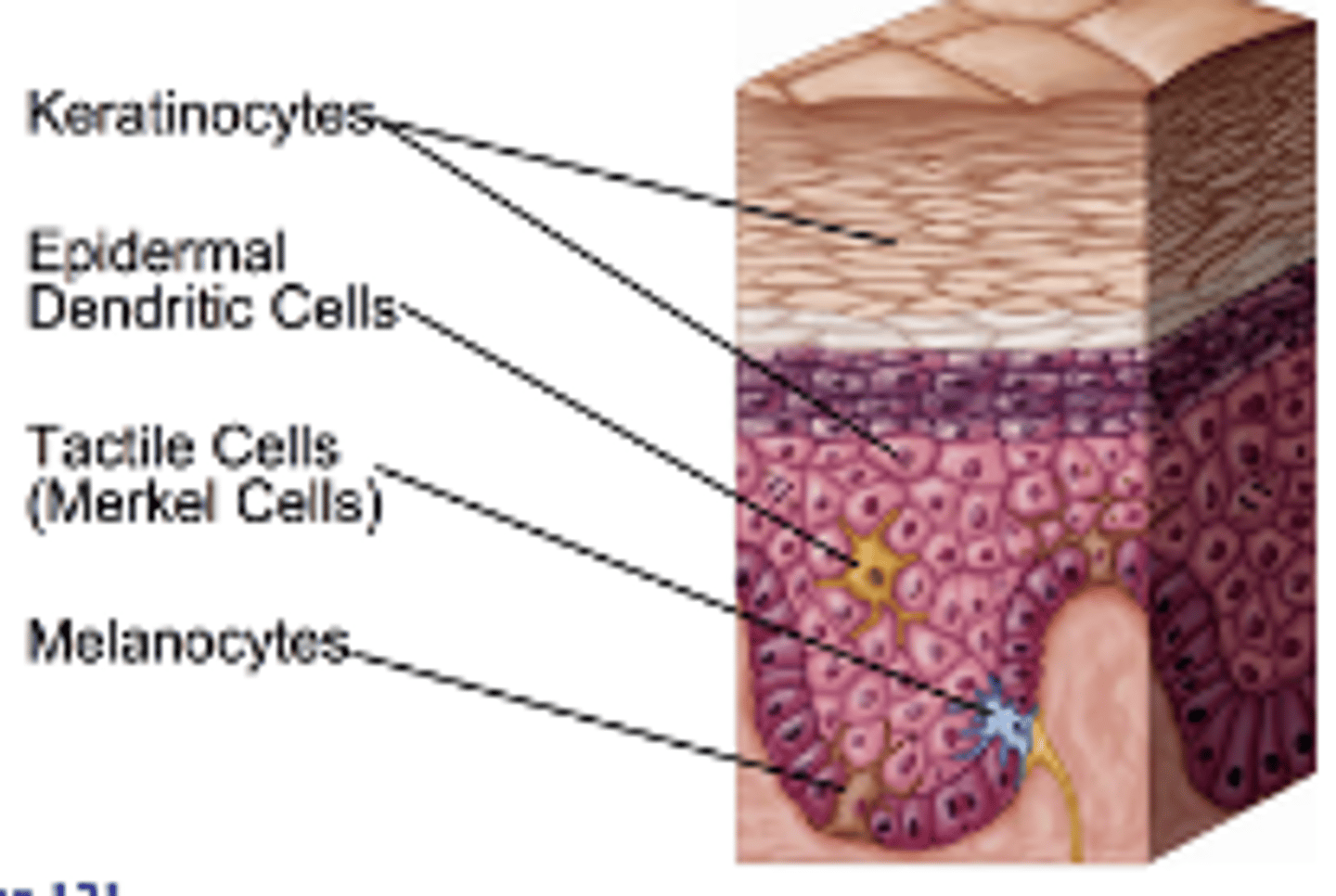
What are the 4 cells of the epidermis?
1. keratinocytes
2. melanocytes
3. Denditric cells (Langerhans)
4. Tactile (Merkel) cells
Function of keratocytes cells
- production of fibrous KERATIN = give skin protective properties
- MAJOR cells of epidermis
- Tightly connected by desmosomes
- Millions slough off every day
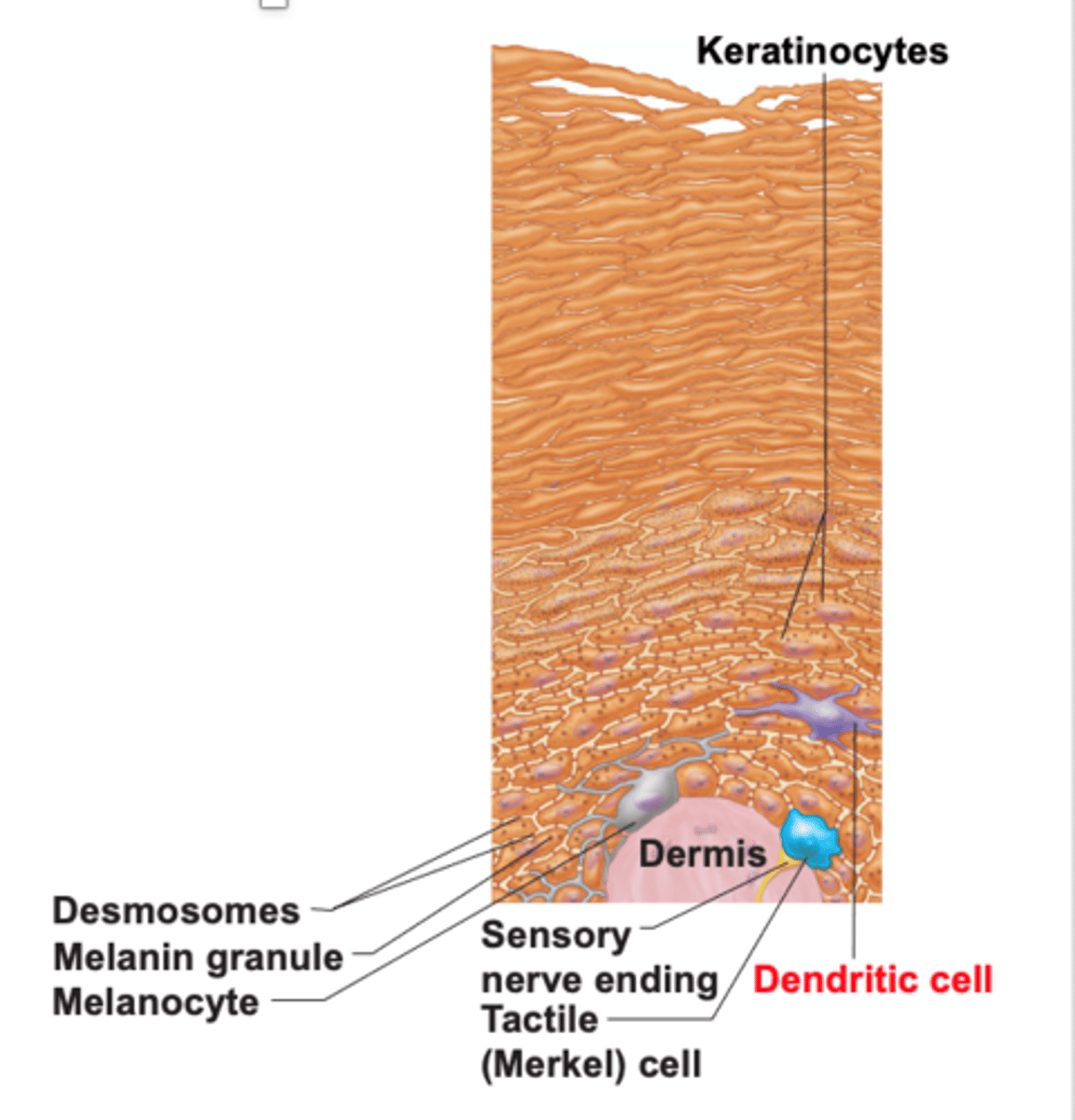
function of melanocytes
- melanin protects skin from sun damage
- spider-shaped cells, found deepest epidermis

how melanocytes protects skin from the sun?
- pigment melanin is packed with MELANOSOMES
- Melanosomes are transferred to keratinocytes = they protect nucleus from UV damage
function of dendritic cells
- Star-shaped macrophages that patrol deep epidermis
- are KEY activators of immune system
function of tactile cells
- sensory receptors that sense touch
skin color according can indicate what diseases
1. cyanosis: blue; low oxygenation of hemoglobin
2. pallor; anemia, low blood pressure, fear, anger
3. Erythema: redness; feber, hypertension, inflammation, allergy
4. Jaundice: yellow, liver disorders
5. Bruises(black and blue marks); clotted blood beneath skin
6. Brown/black necklace or bruise: hyperpigemented dark areas in axillae and around neck = insulin resistance and elevated blood glucose levels
skin color that might indicate anemia
pallor
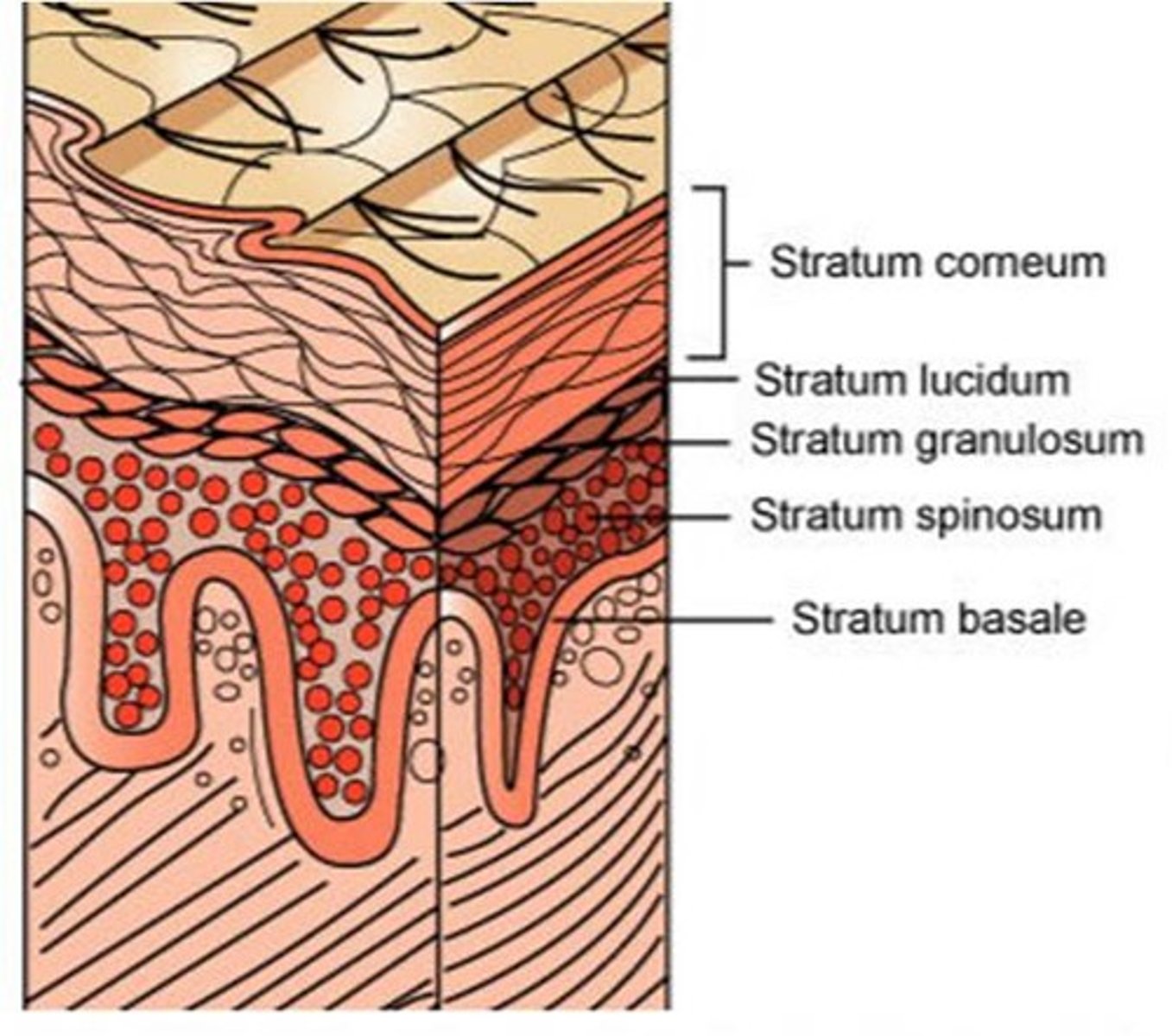
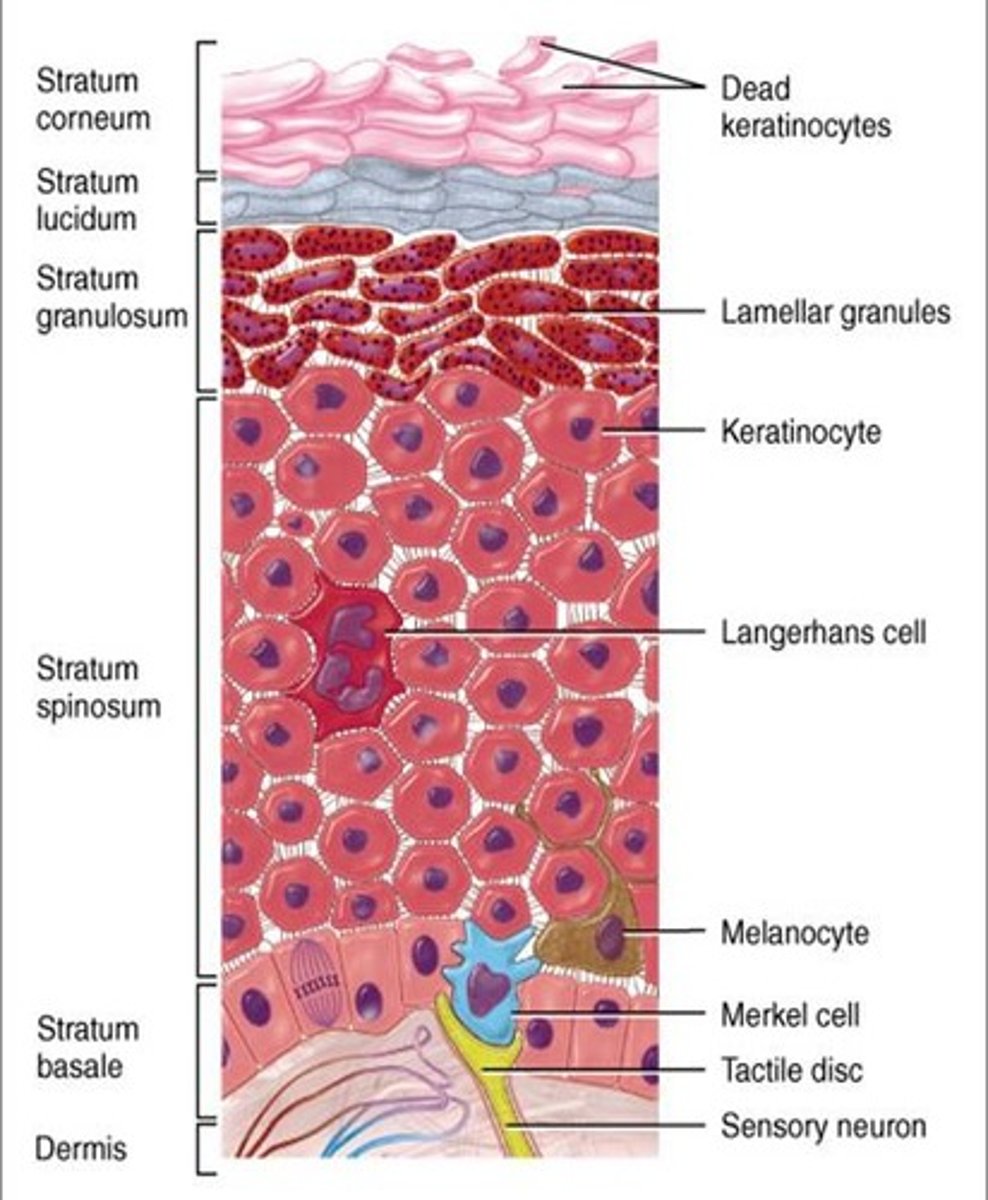
Layers of the epidermis
1. Stratum basale
2. Startum spinosum
3. Startum granulosum
4. Stratum lucidum )only on thick skin)
5. Stratum corneum
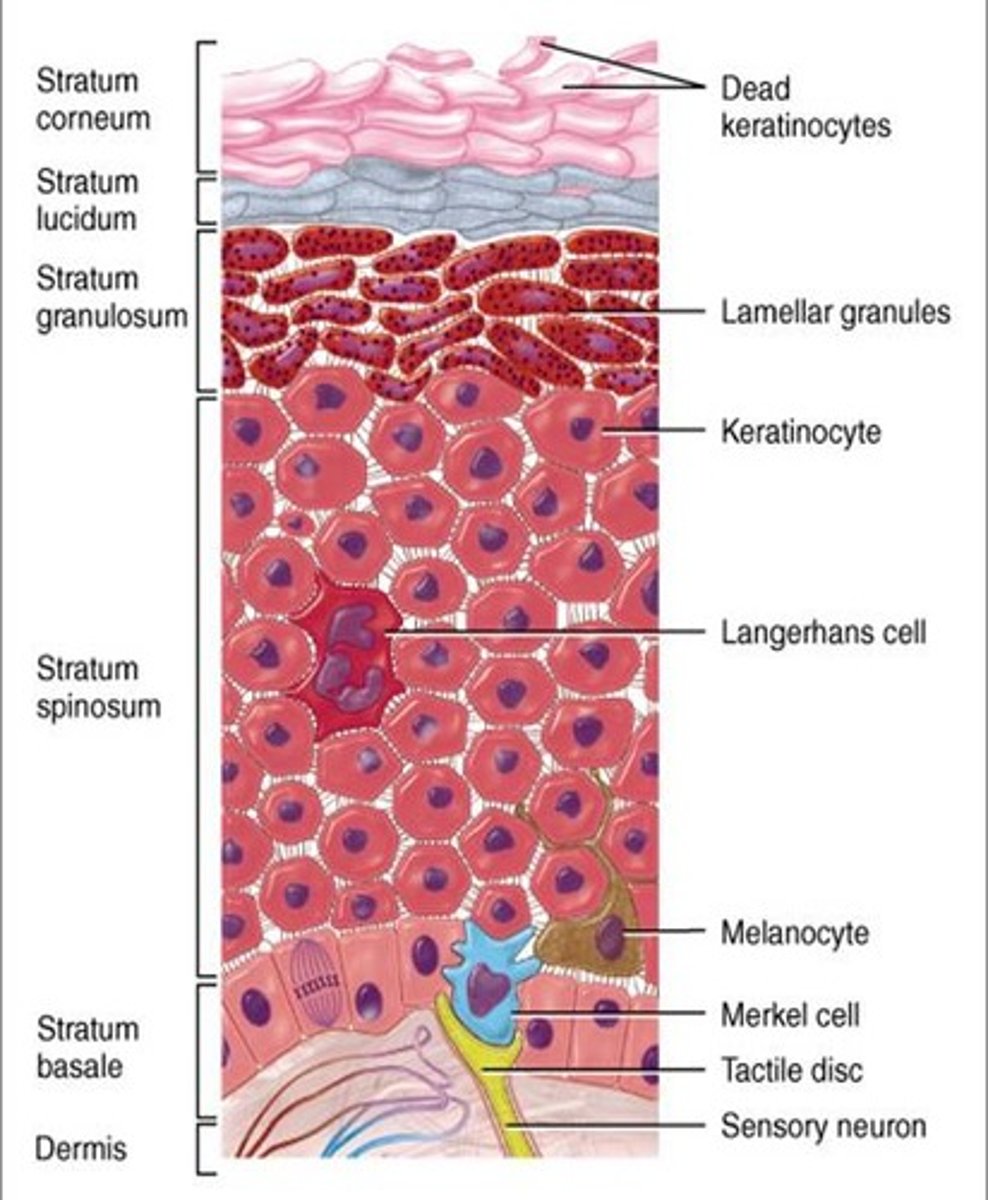
Thick vs thin skin (epidermis layers)
Thick skin: Contains FIVE layer; found ion high-abrasion areas(hands/feet)
Thin skin: contains ONLY 4 strata
- does NOT contain Stratum lucidum
stratum basale
BASAL LAYER
- deepest of ALL epidermal layers
- firmly attached to DERMIS
- single row of stem cells; actively divide (mitosis)
- when it dies = moves toward the surface
- 10-25% composed or MELANOCYTES
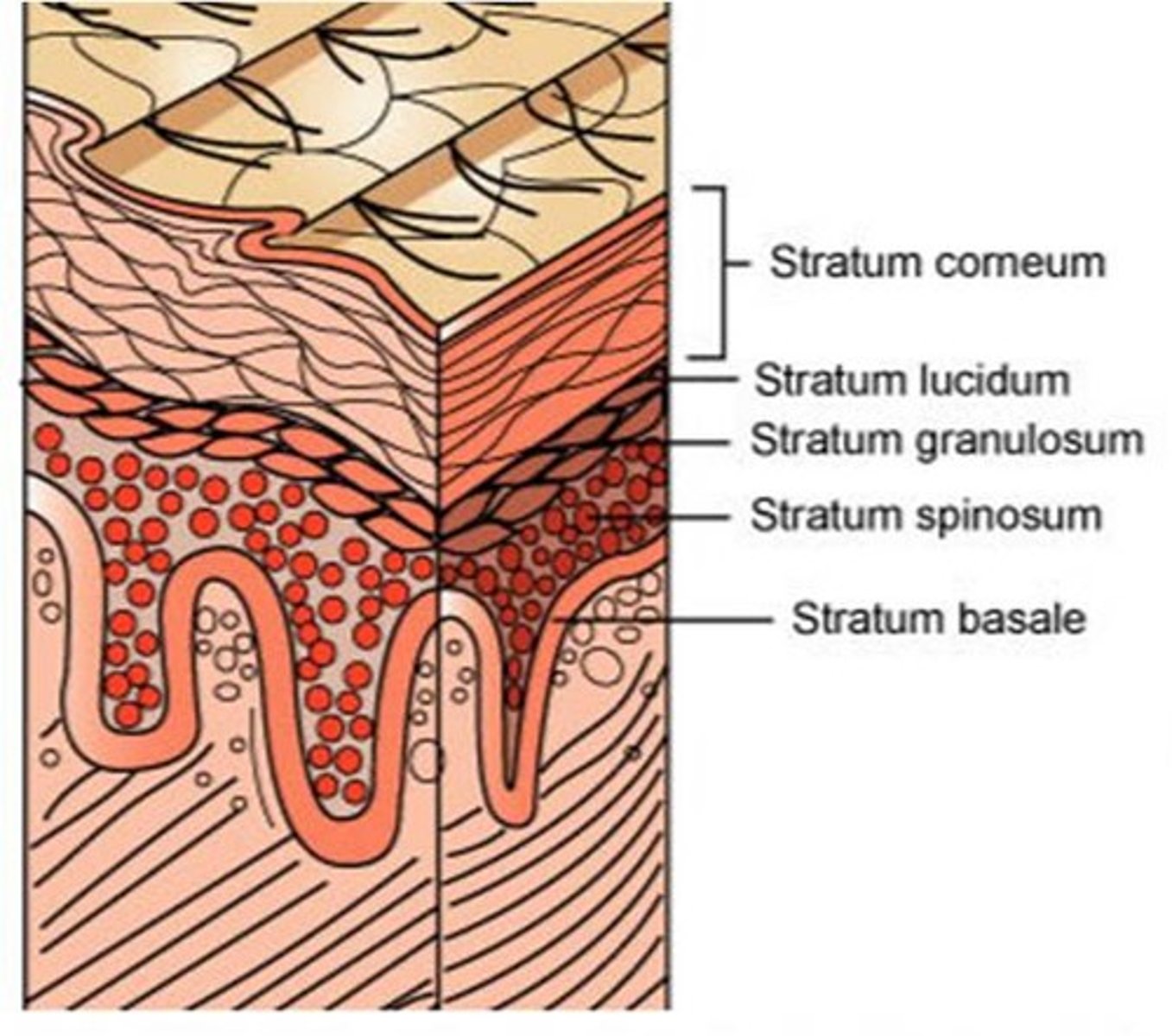
stratum basale is also known as... and why?
- Stratum germinativum because active mitosis
Stratum Spinosum (Prickly Layer)
- Several cell layers thick,
- cells contain a weblike system of intermediate prekeratin filaments attached to desmosomes.
-Keratinocytes appear SPIKEY = prickle cells
- among keratinocytes, abundant melanosomes and dendritic cells
stratum granulosum (granular layer)
1. Four to six cells thick, but cells are flattened, so layer is thin
2. Cell appearance changes
- Cells flatten, nuclei and organelles disintegrate
- Cells above this layer die
Too far from dermal capillaries to survive
in what layer does keratinization begins and lamellar granules accumulate? Function?
Stratum granulosum
- Keratinization begins; Cells accumulate keratohyaline granules that help form keratin fibers in upper layers
-Cells accumulate lamellar granules, a water-resistant glycolipid that slows water loss
Startum Lucidum (Clear Layer)
- ONLY in THICK skin (palms, feet)
- thin, translucent band of two/three rowas of clear, flat DEAD keratinocytes
- Superficial to the stratum granulosum
Stratum corneum (horny layer)
20-30 rows of flat, anucleated, keratinized dead cells
Accounts for three-quarters of epidermal thickness
Function of dead cells in stratum corneum
Though dead, cells still function to:
1. Protect deeper cells from the environment
2. Prevent water loss
3. Protect from abrasion and penetration
4. Act as a barrier against biological, chemical, and physical assaults
how can cells changes, what process do they go under?
Apoptosis: controlled cell death
how many cells humans can shed every min?
50,000
melanocytes function and location
in stratum basale,
- produce melanin
- transfer melanin granules to actively growing keratinocytes
what happens when melanocytes produce NO melanin?
Albinism
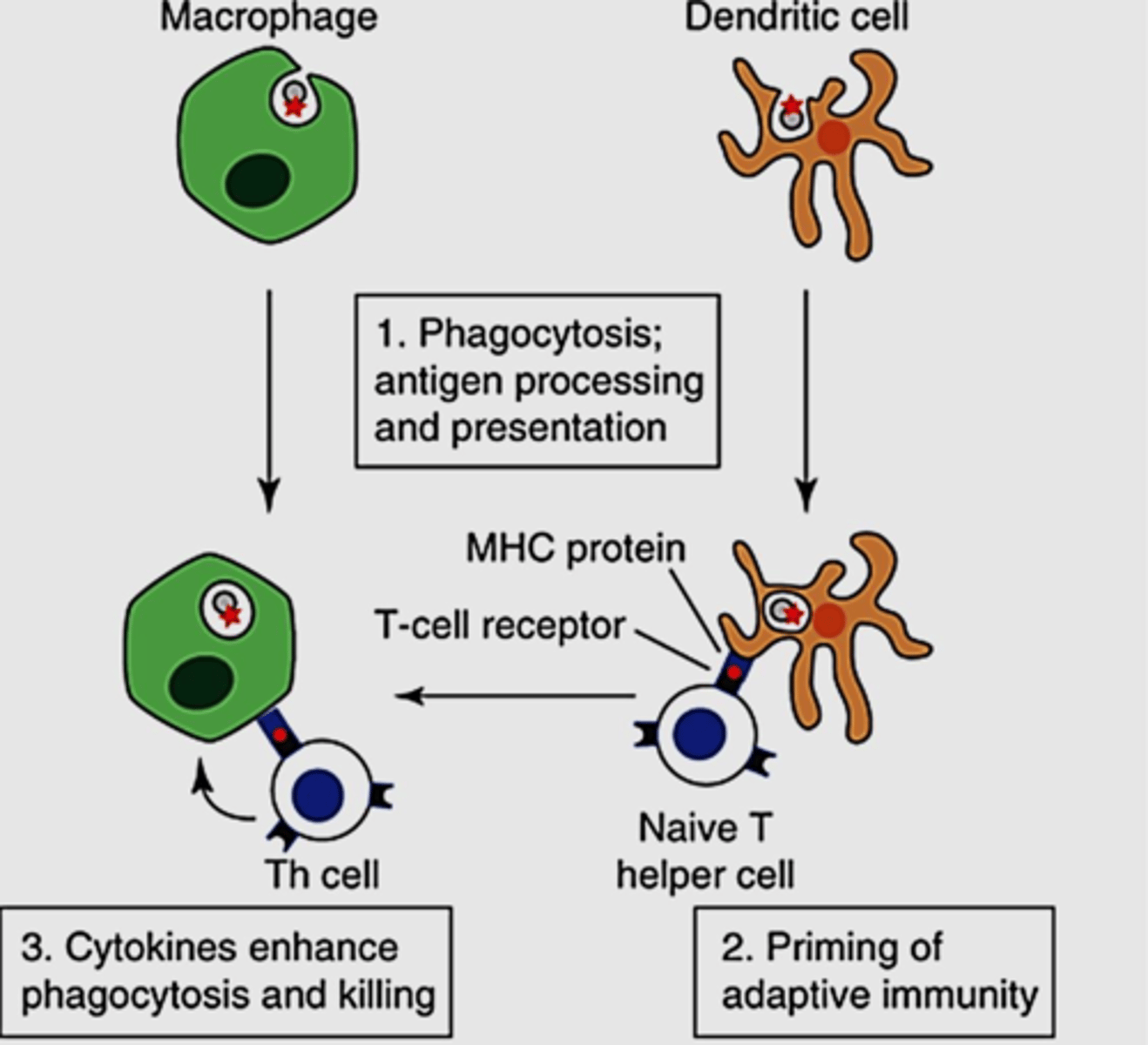
Function of dendritic cell and location
- Also called Langerhans cells
- Originate in bone marrow
- Migrate to epidermis as part of body's defense against disease
How dendritic cells work
Capture invaders (bacteria, viruses) and present them to our immune cells to activate an immune response
Keratinocytes (function and location)
- Found in epidermis
- 85-95% of the cells in the epidermis
- form 4-5 distinct cell layers of keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
- Produce KERATIN protein to toughen skin
- Produce GLYCOLIPIDS to waterproof the skin
Thin vs Thick Skin (Epidermis)
thin: has only 4 layers: includes most areas of the body
Thick: has ALL 5 layers
- found on soles, palms and fingertips
Layers of the epidermis (superficial to deep)
Come (Stratum corneum)
Let's (Stratum lucidum)
Get (Stratum granulosum)
Some (Stratum spinosum)
Beer (Stratum basale)
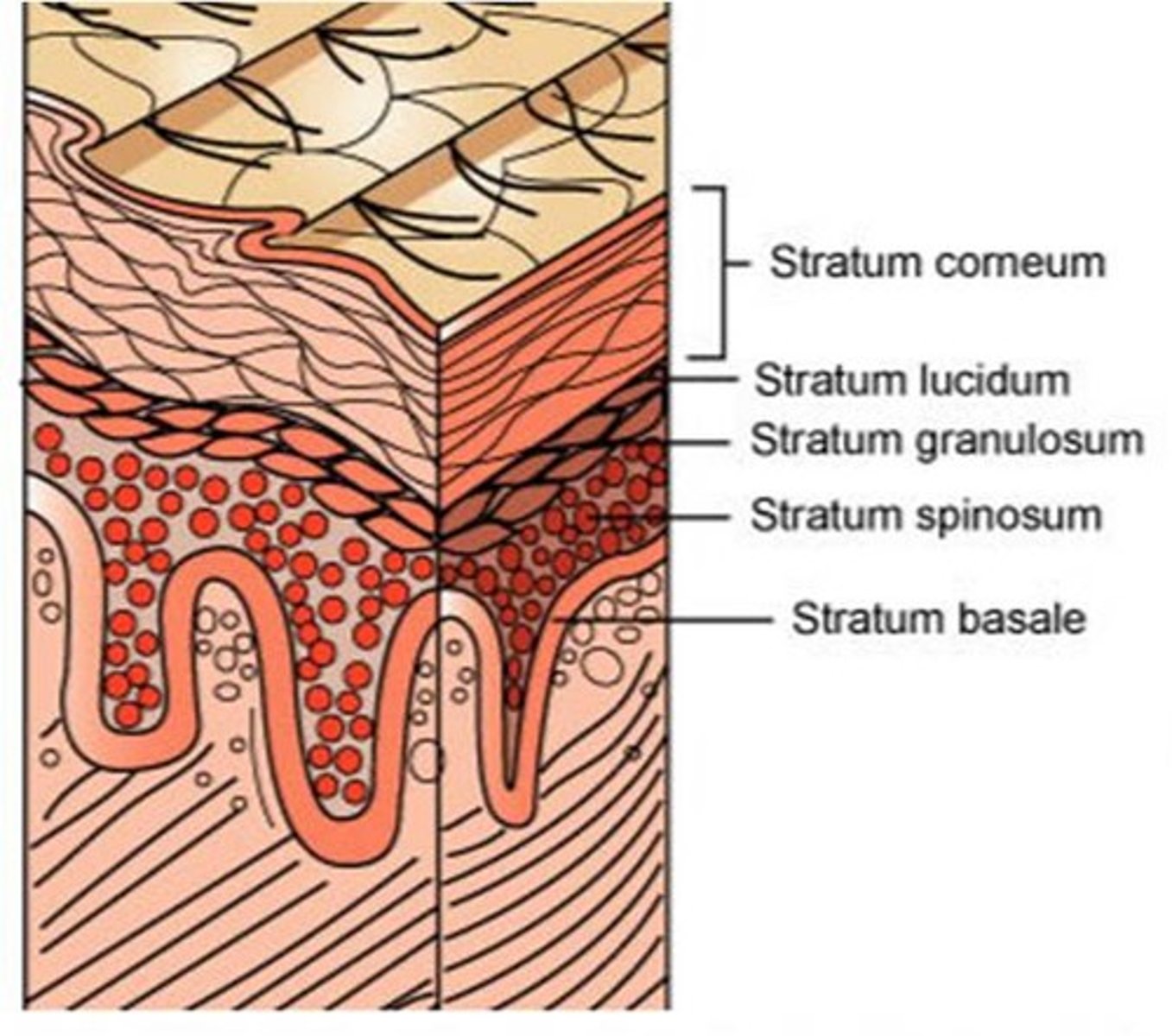
where are keratinocytes dead and why?
In the stratum Lucidum and corneum because they are too far from the blood vessels in the dermis
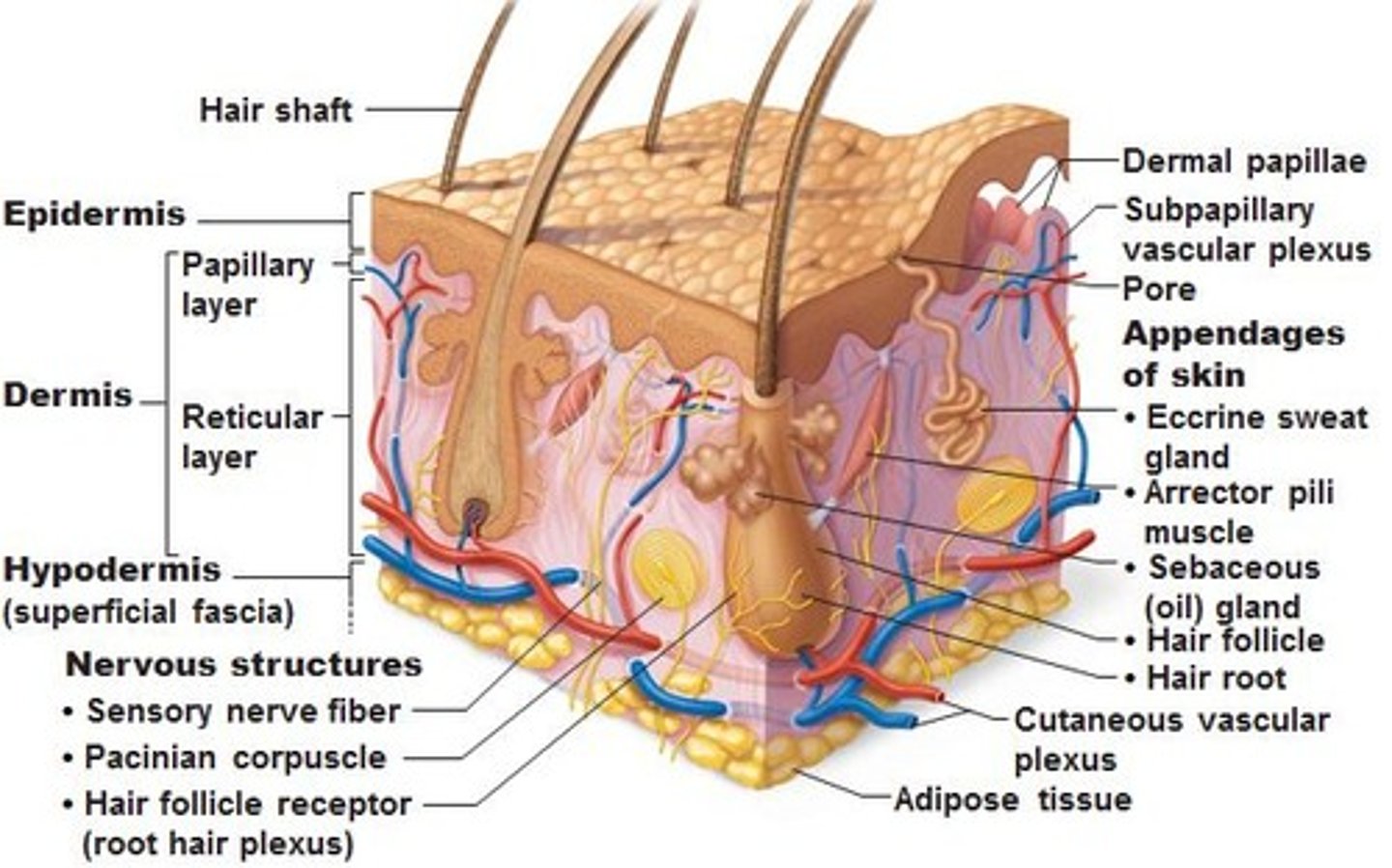
Characteristics of the dermis
1. Strong, flexible connective tissue
2. Cells include fibroblasts, macrophages, and occasionally mast cells and white blood cells
3. Fibers in matrix bind body together
4. contains nerves, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
5. contains epidermal hair follicles, oil glands, and sweat
how many layers are in the dermis
2 layers
- papillary
- Reticular
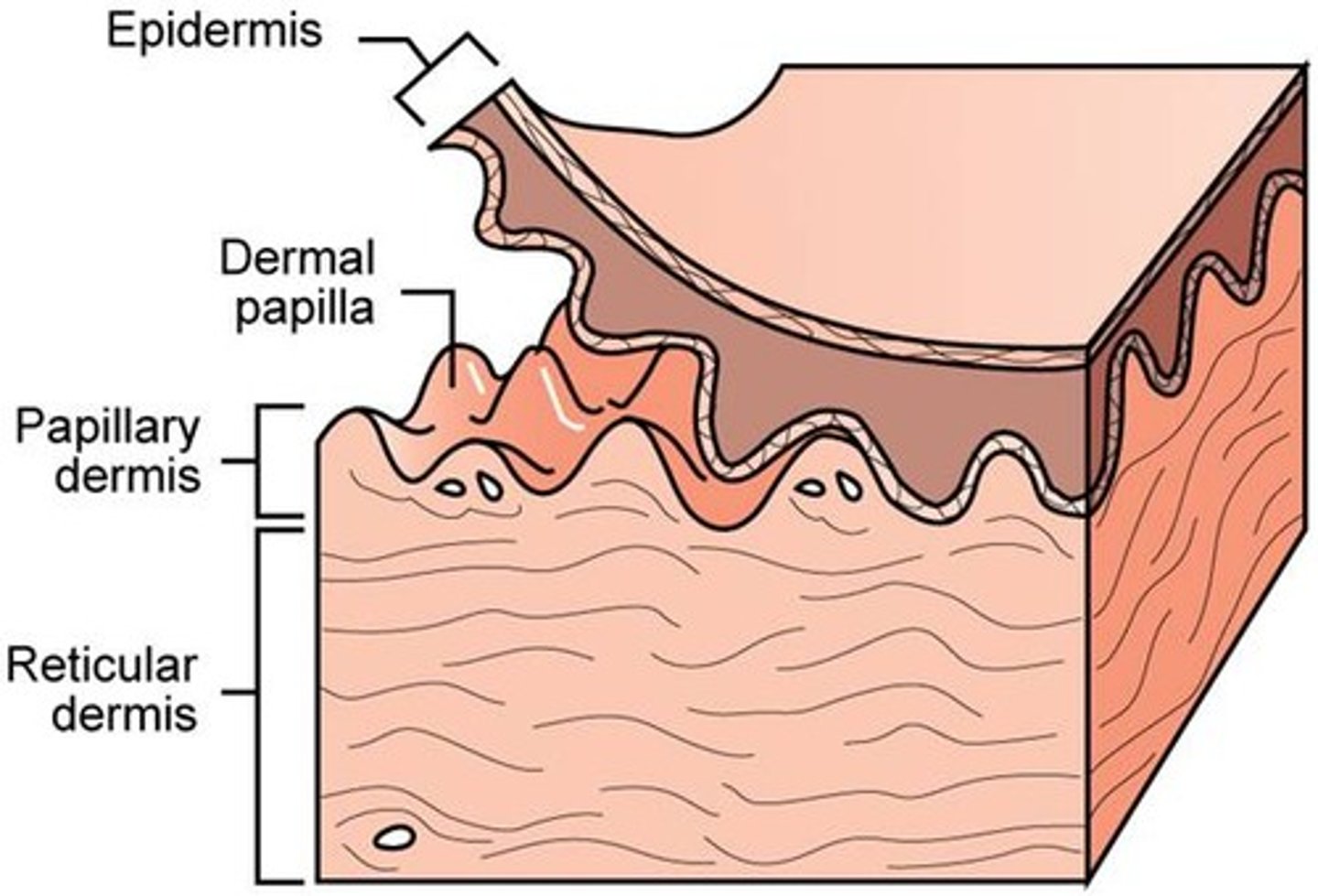
What is the papillary layer? Location and function
- Thin outer layer
- Areolar connective tissue with collagen and elastic fibers and blood vessels
- attaches to the stratum basale of the epidermis
dermal papillae
Found in the upper layers of the dermis, they create your fingerprint pattern
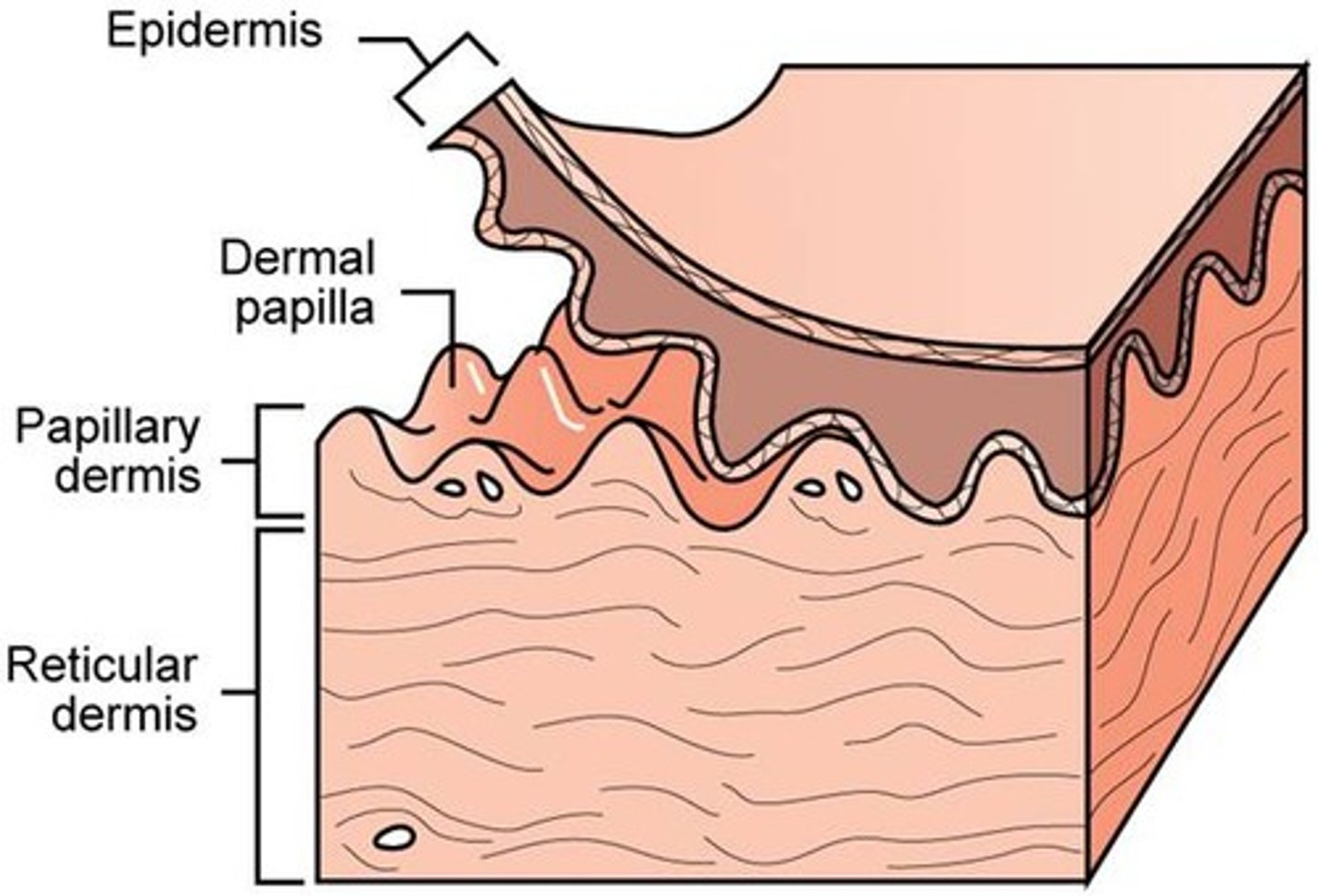
what nourishes the avascular epidermis
capillaries in the dermal papillae
reticular layer of dermis
- dense, irregular connective tissue
- surrounds blood vessels, hair follicles, nerves, and glands
interwoven collagen fiber bundles
Dense Irregular CT (function/ location)
dermis of skin
Function: withstands tension exerted in many directions: provides structural strength
Location: fibrous capsules of organs and of joints, submucosa of digestive system
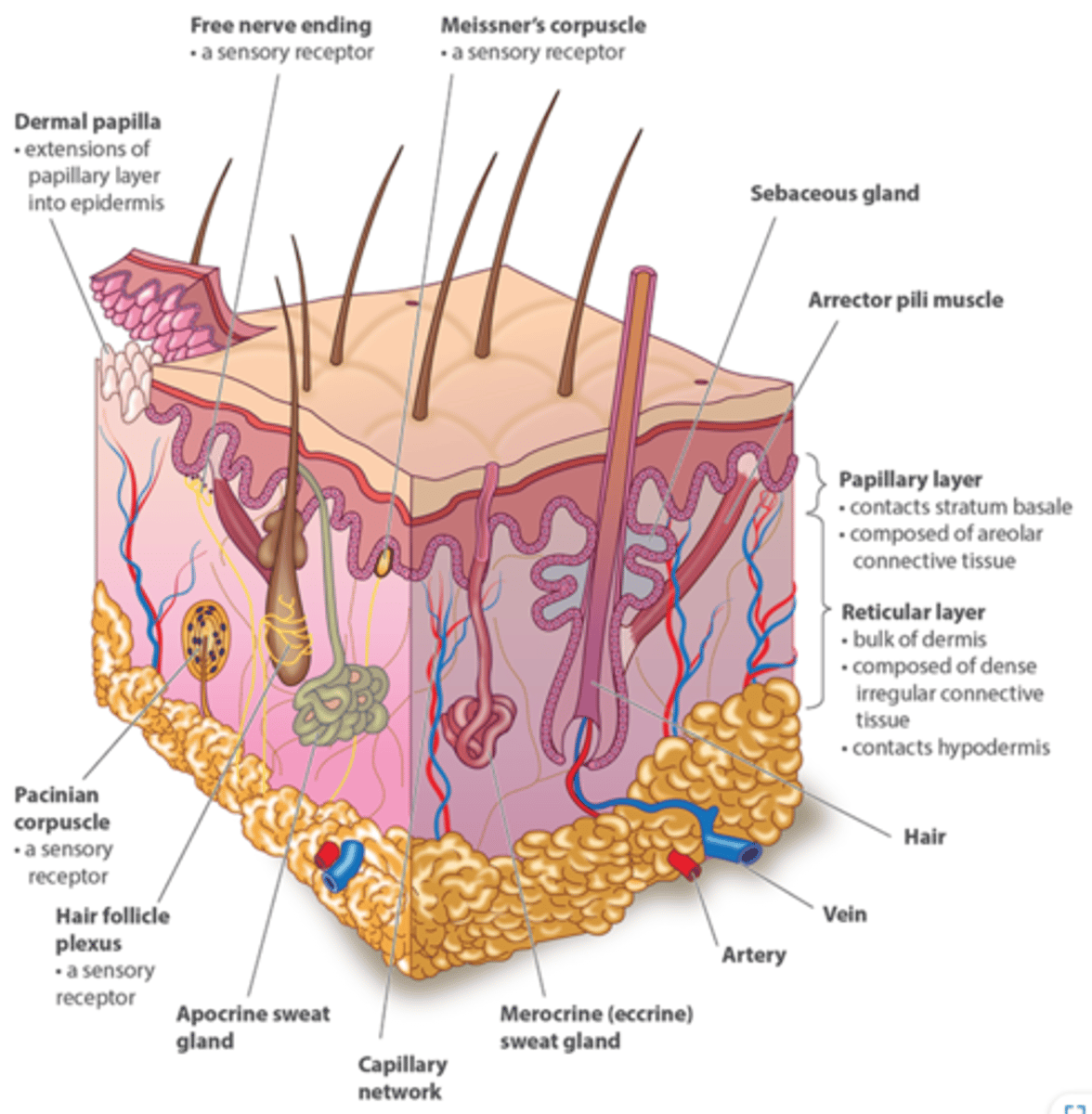
reticular layer of dermis includes
- nervous structures
- eccrine sweat gland
- arrector pili
- sebaceous gland
- hair follicle
examples of nervous structures in reticular layer of dermis
- sensory nerve fiber
- pacinian corpuscle
- hair follicle receptor
what are sensory nerve fibers?
afferent sensory fibers that send sensory info to the brain like touch, taste, smell and sight
(reticular layer of dermis)
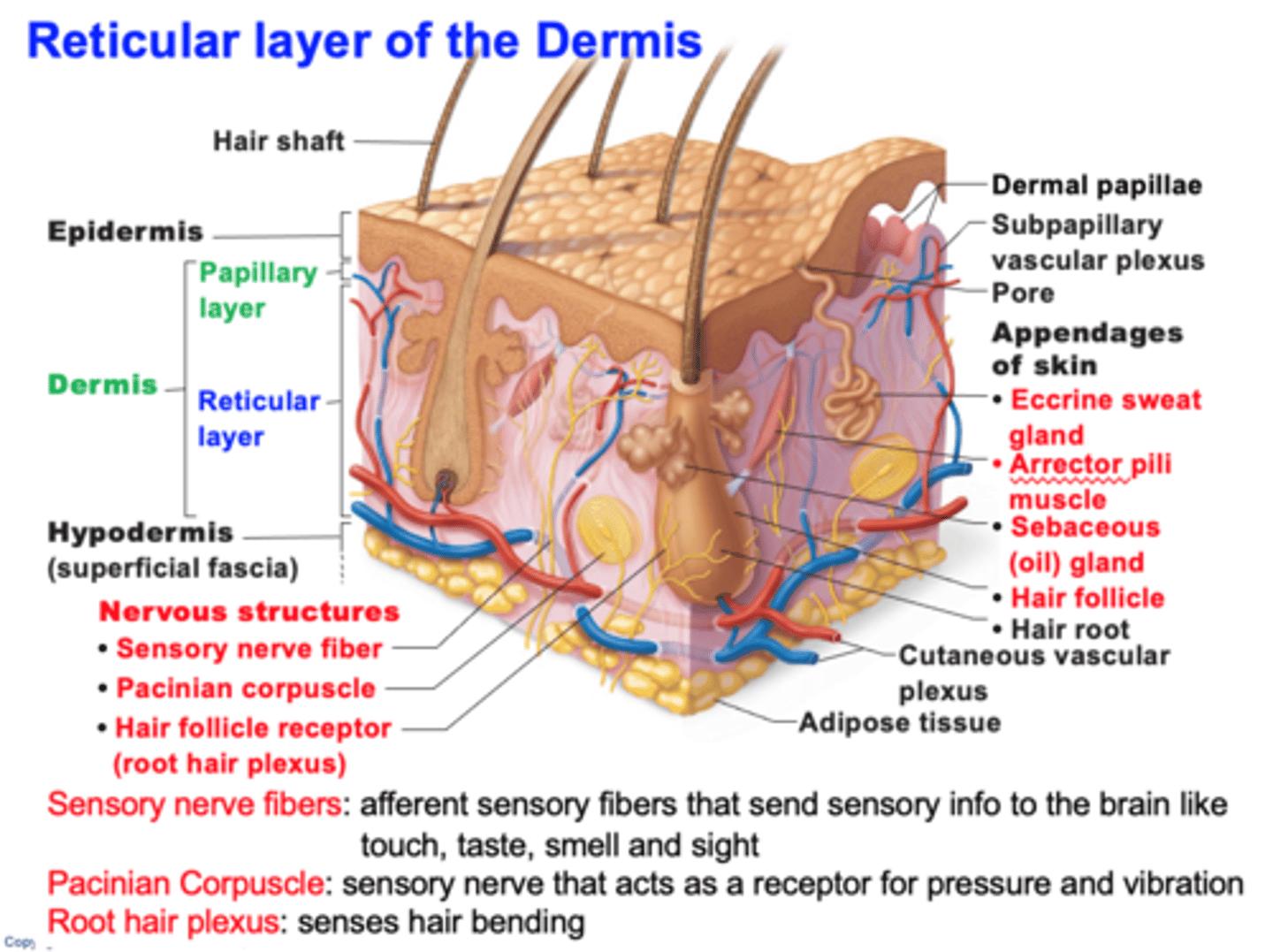
What is a pacinian corpuscle?
They are nerve endings in the skin, responsible for sensitivity to deep pressure touch and high frequency vibration.
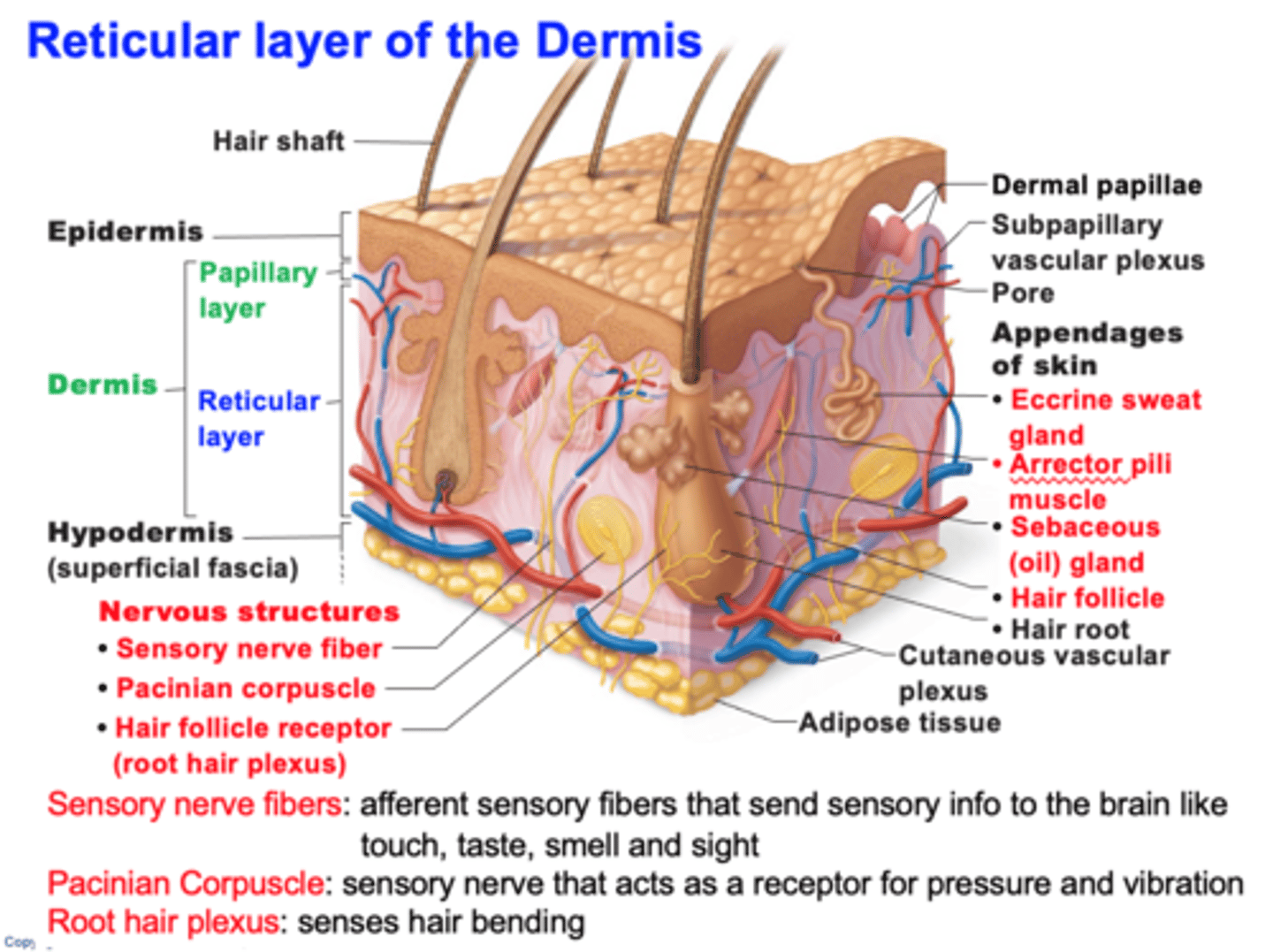
characteristics of reticular layer
- makes up 80% of dermal thickness
- consist of coarse, dense fibrous CT
- Collagen fibers provides stretch-recoil properties
- Cutaneous plexus
- extracellular matrix contains pockets of adipose tissue
what is the cutaneous plexus?
network of blood vessels between reticular layer and hypodermis
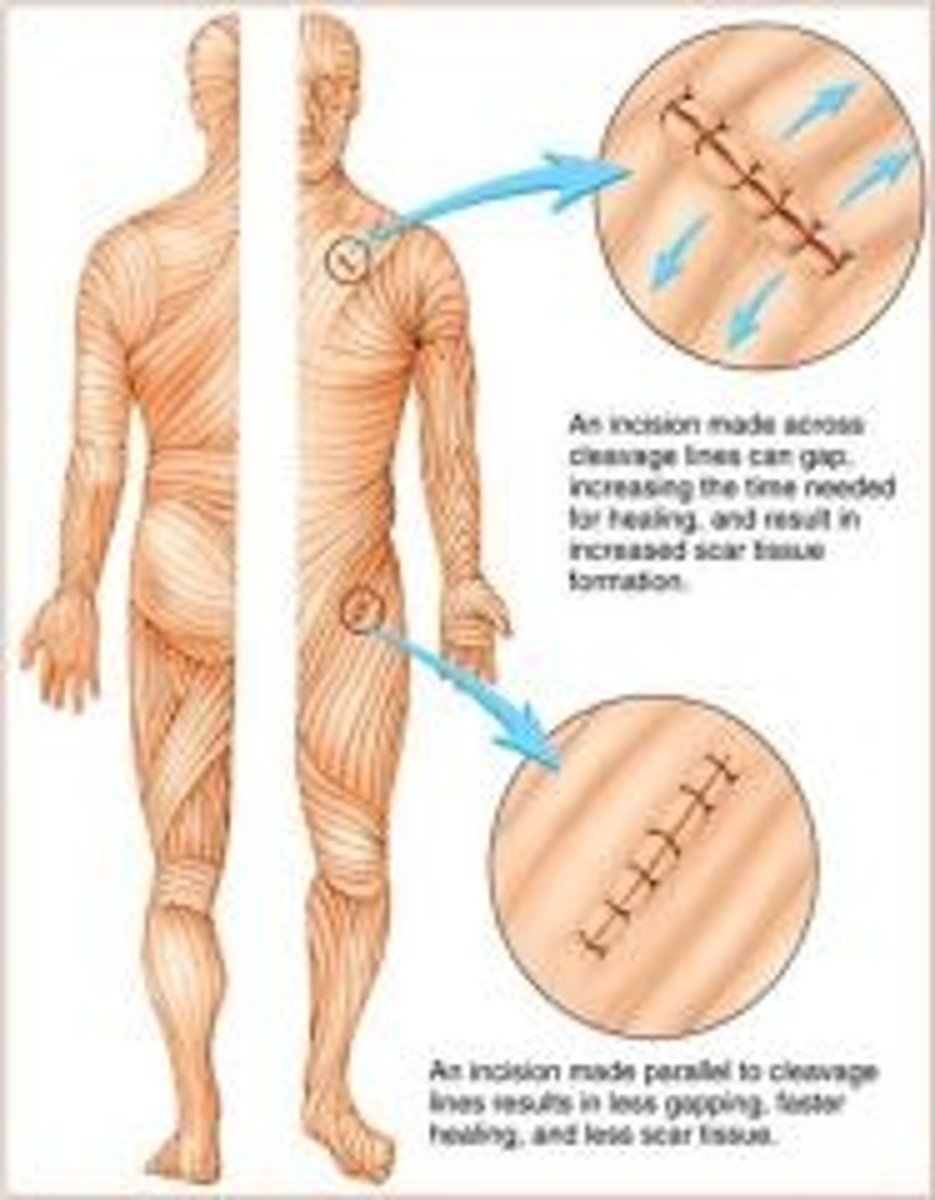
What are cleavage (tension) lines?
in reticular layer are caused by many collagen fibers running parallel to skin surface
- Externally invisible
- Important to surgeons because incisions parallel to cleavage lines heal more readily
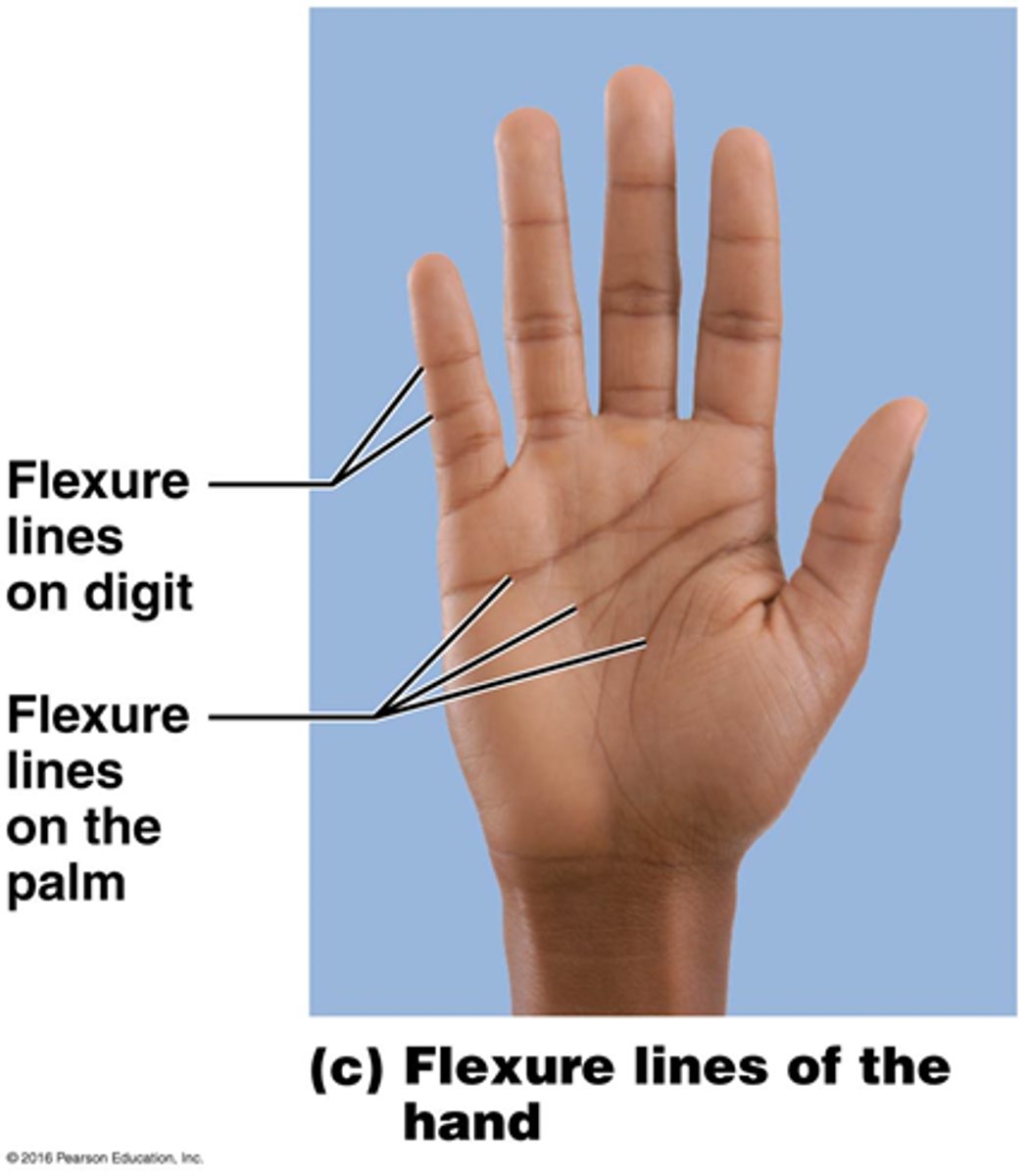
What are flexure lines?
dermal folds that occur at or near joints, where the dermis is tightly secured to deeper structures
- skin's inability to slide easily for joint movement causes deep crease
- visible on hands, wrists, fingers, soles, toes
What are stretch marks?
- Extreme stretching of the skin can cause dermal tears, leaving silvery white scars called STRIAE
what can cause blisters?
acute, short-term traumas to skin
- fluid-filled pockets that separate epidermal and dermal layers
what is the hypodermis?
- Subcutaneous tissue
A layer of adipose (fat) tissue that stores energy and cushions other organs
- areolar CT
- NOT A SKIN LAYER
-let skin slide over muscle
how is the anatomy of the hair
- consists of dead keratinized cells
- none located on palms, soles, lips, nipples and portion of external genitalia
what is the function of the hair?
- warn of insects on skin
- hair on head guards against physical trauma
- protect from heat loss
- shields skin from sunlight
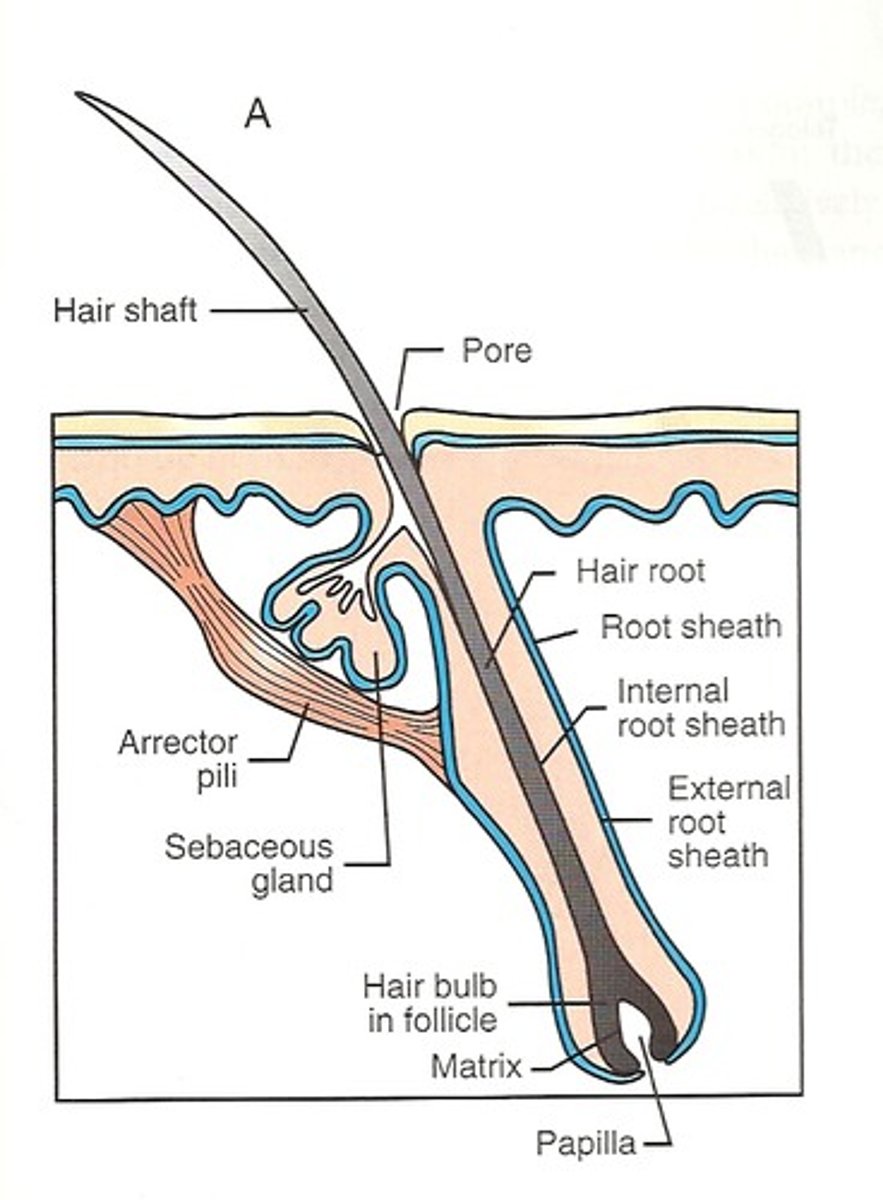
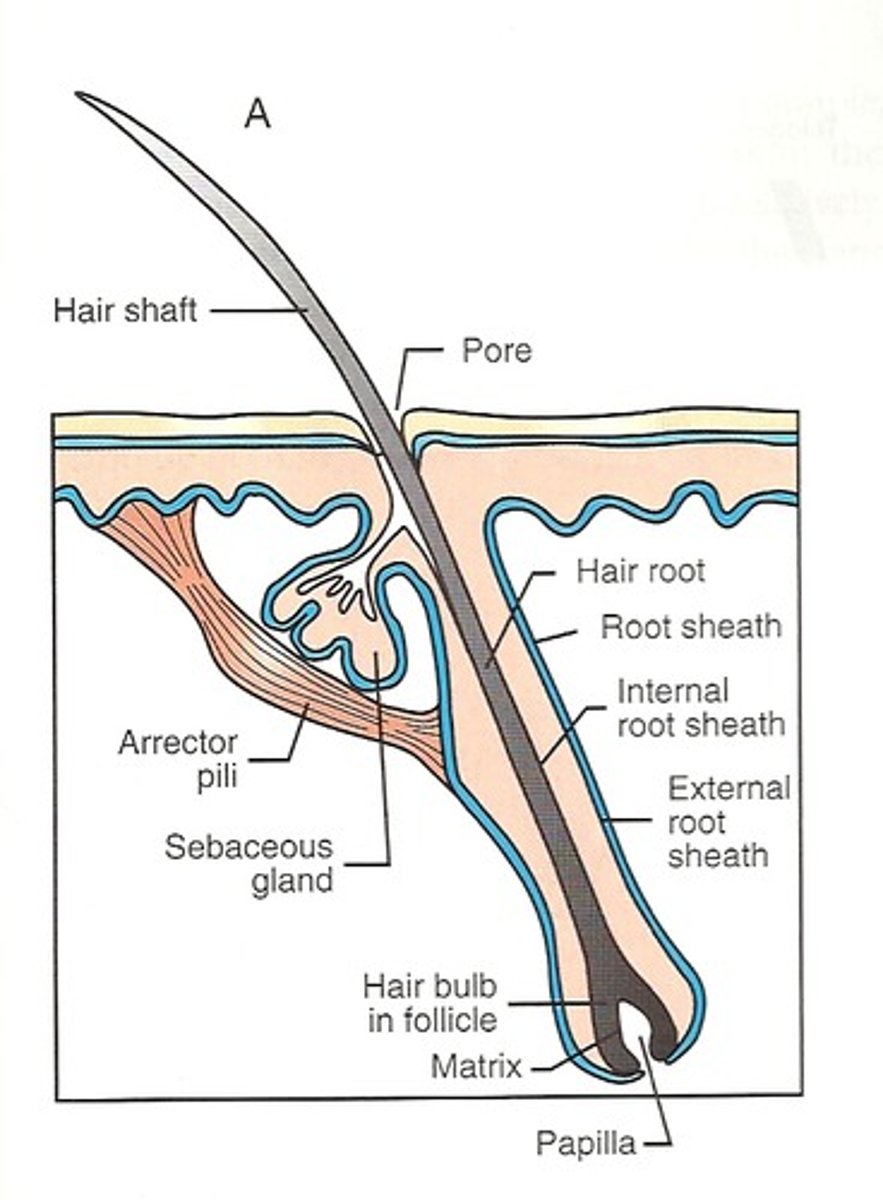
Anatomy of a single hair
- Hairs also called pili = flexible strands of dead, keratinized cells
- produce by hair follicles
- contains HARD KERATIN (NOT like keratin found in skin)
regions of the hair
1. Shaft: area that extends above scalp, where keratinization is complete
2. area within scalp, where keratinization is still ongoing
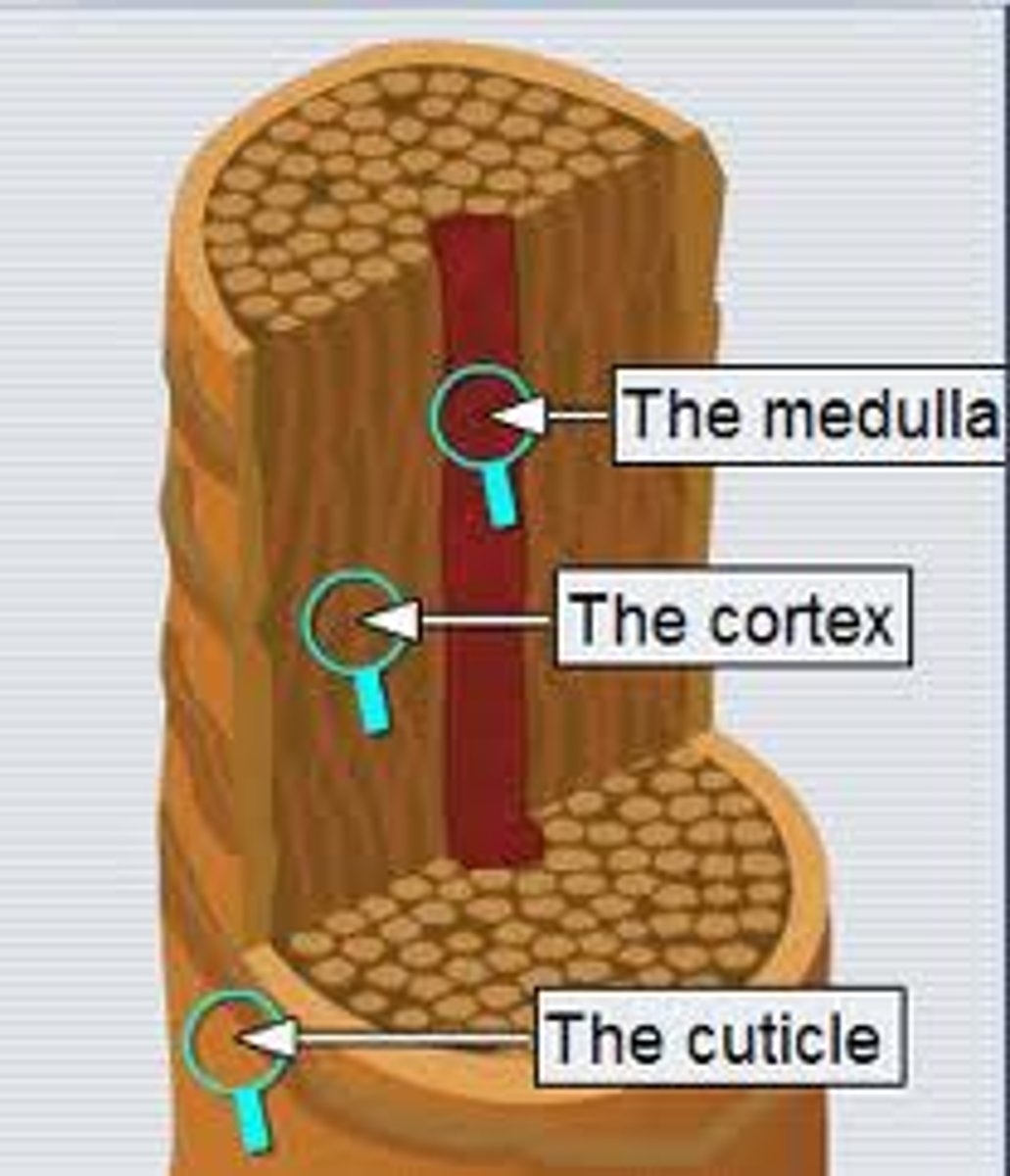
regions of hair shaft
medulla: central core of large cells and air
Cortex: several layers of flattened cells surrounding medulla
cuticle: outer layer consisting of overlapping layers of single cells
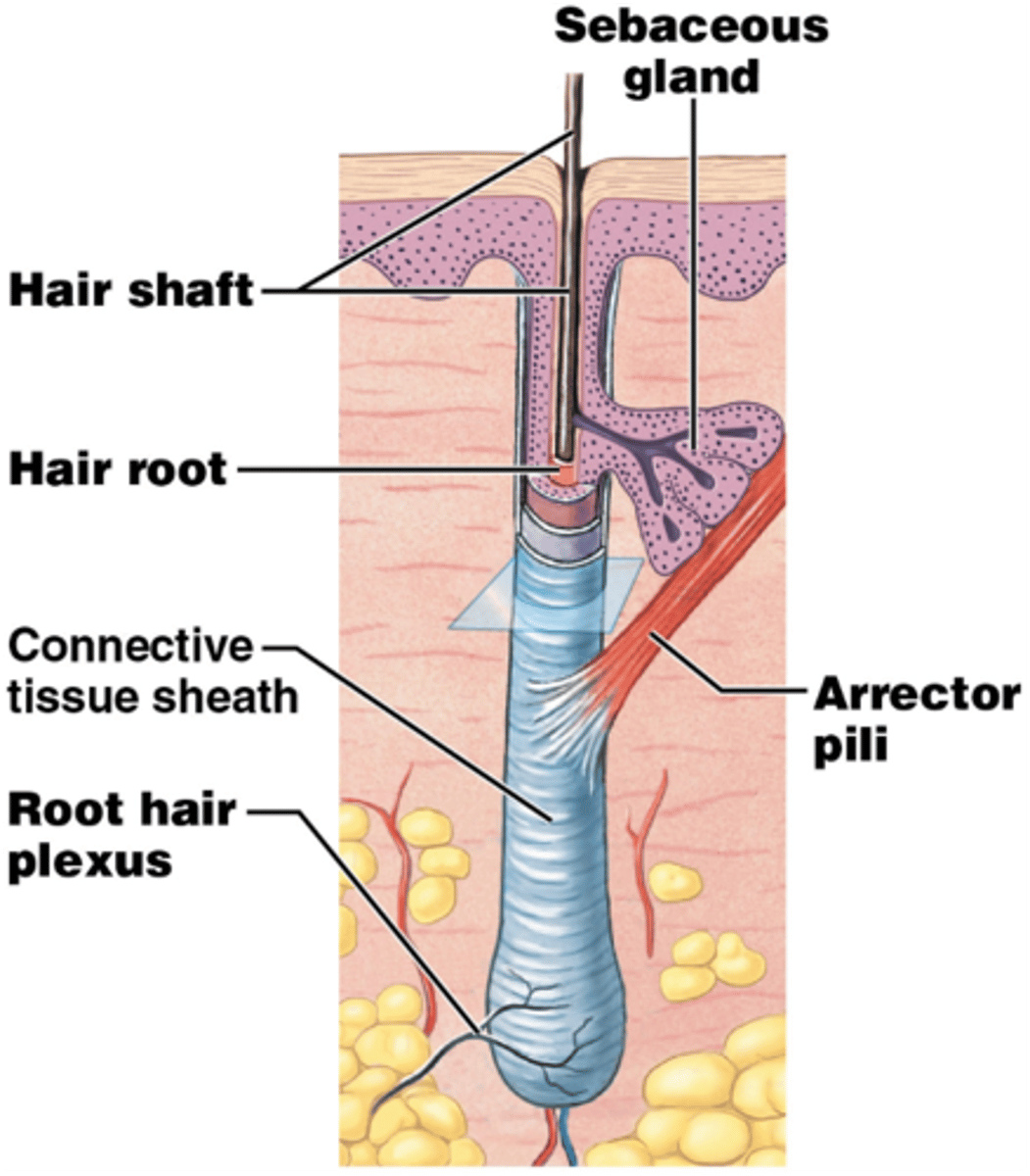
structure of hair follicle
-extends from epidermal surface to dermis
-Connective tissue root sheath
-Hair receptors entwine each follicle
-Piloerector muscle
*goose bumps
what are hair pigments made of
melanocytes in hair follicles
- combination of different melanins = all the hair colors
Red hair has additional ___ pigment.
Pheomelanin
gary/white hair happens when...
melanin production decreases and air bubbles replace melanin in shaft
What is the hair bulb?
expanded area at deep end of follicle
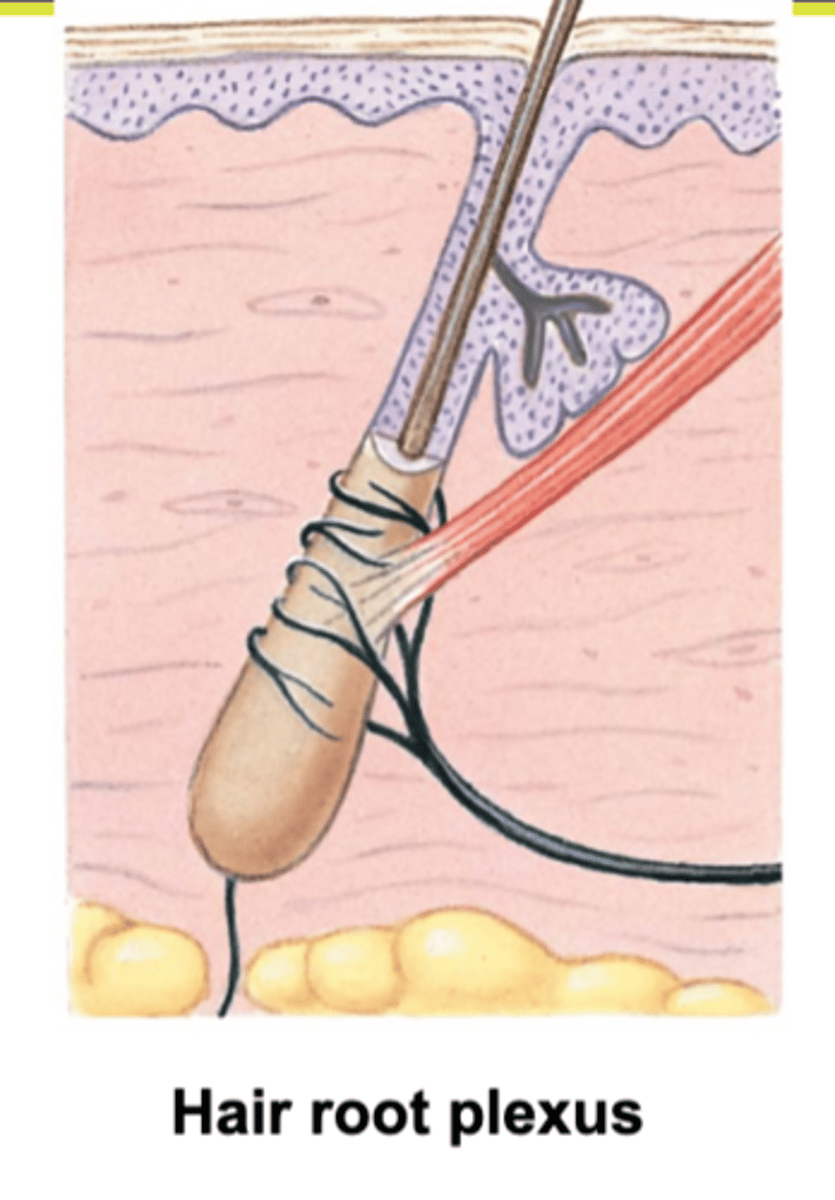
hair folicle receptor
Nerve receptors that detect hair movement, wraps around each hair bulb
hair matrix
actively dividing area of the hair bulb that produces the hair
- new cells, pushes old ones upward
function of arrector pili
small band of SMOOTH muscle attached to each HAIR follicle
- GOOSE pimple phenomenon
- autonomic nervous system control
- caused by cold, fear, tickling, or excitement
-ALARMS an approaching predator in nonhumans
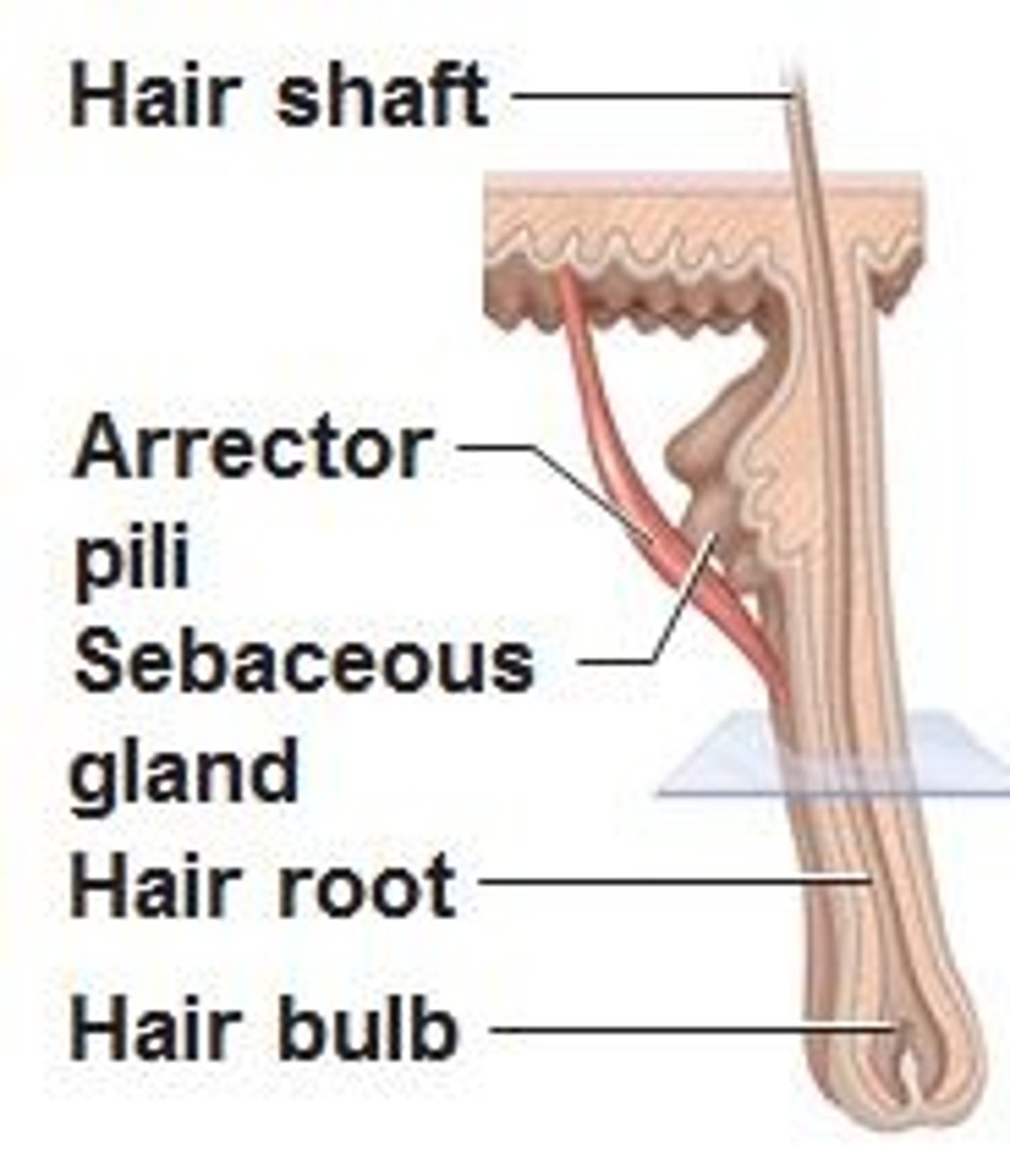
arrector pili is what type of muscle
smooth muscle
Types of Hair
• Vellus hair
-Pale, fine body hair of children and adult females
• Terminal hair
-Coarse, long hair of eyebrows, scalp
-At puberty
-Appear in axillary and pubic regions of both sexes
-Face and neck of males
What affects hair growth?
-Nutrition and hormones affect hair growth
• Follicles cycle between active and regressive phases
• Average 2.25 mm growth per week
• Lose 90 scalp hairs daily
3 Hair Growth phases
1. Anagen: active phase, new hair growth production
2. catagen: transition phase, marks the END of the active phase
4. Telogen Phase: resting period for the follicle
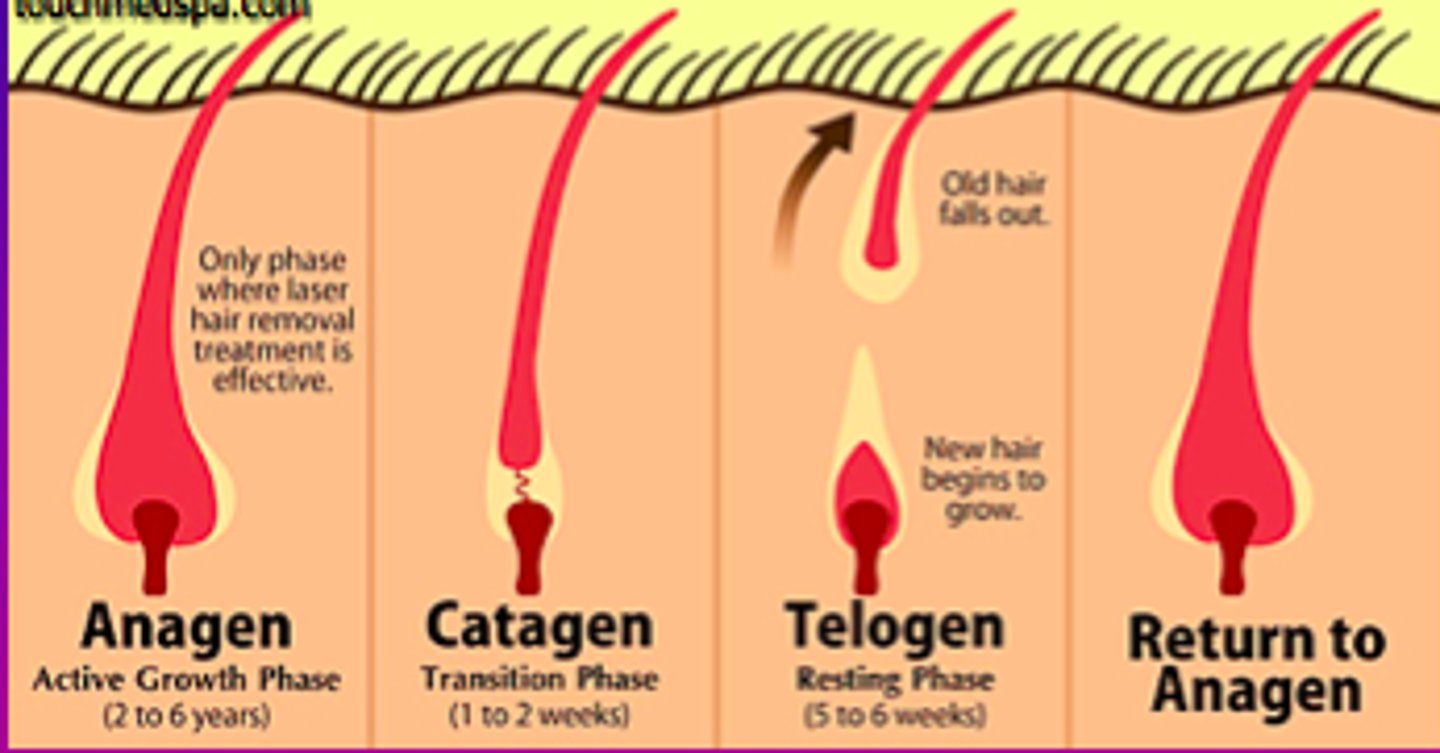
What is alopecia?
hair thinning in bot sexes after age of 40
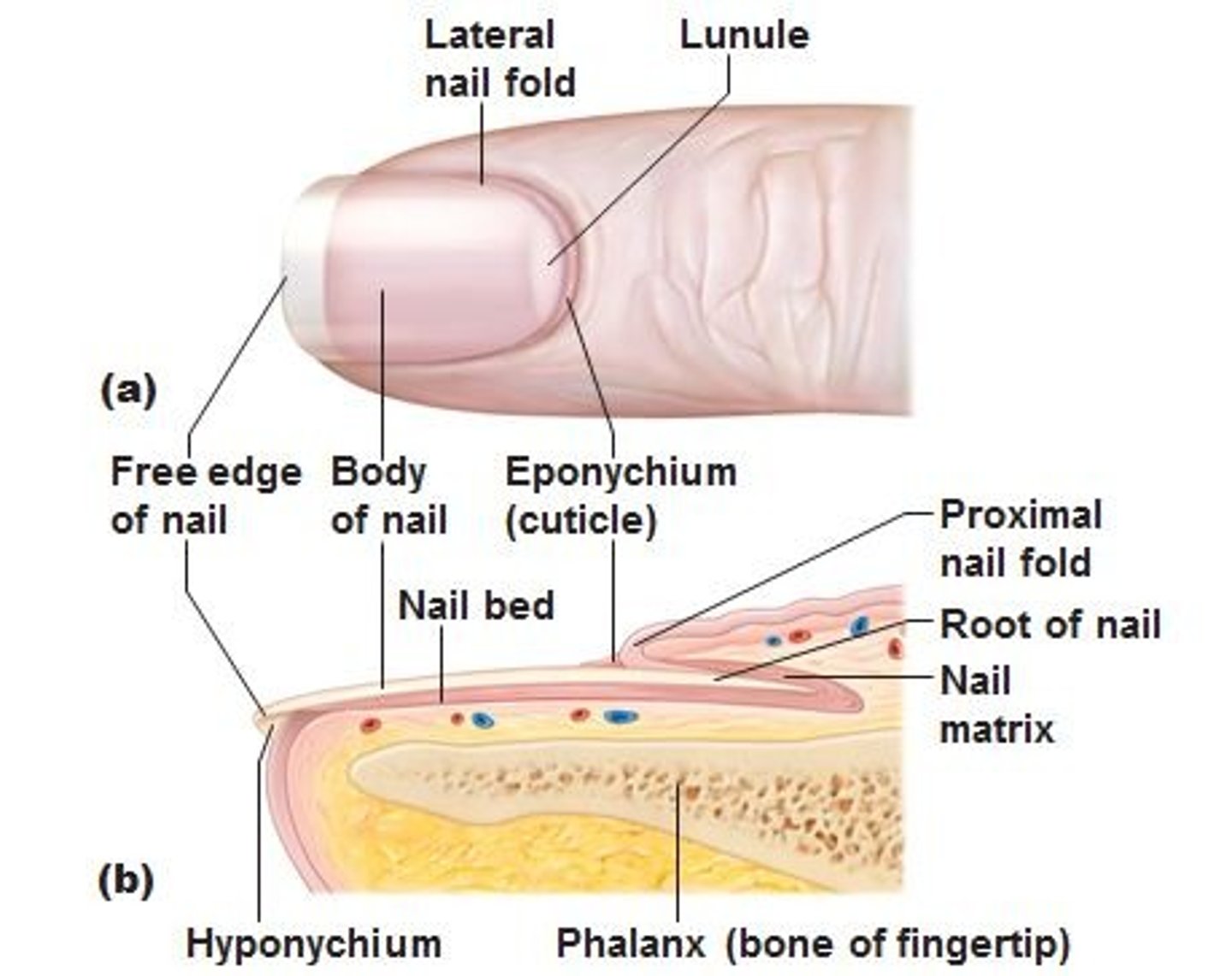
Anatomy of nail
- Scale-like modifications of epidermis that contain HARD KERATIN
- protective cover for distal, dorsal surfacew of fingers and toes.
Nails consist of
free edge, nail plate, and root
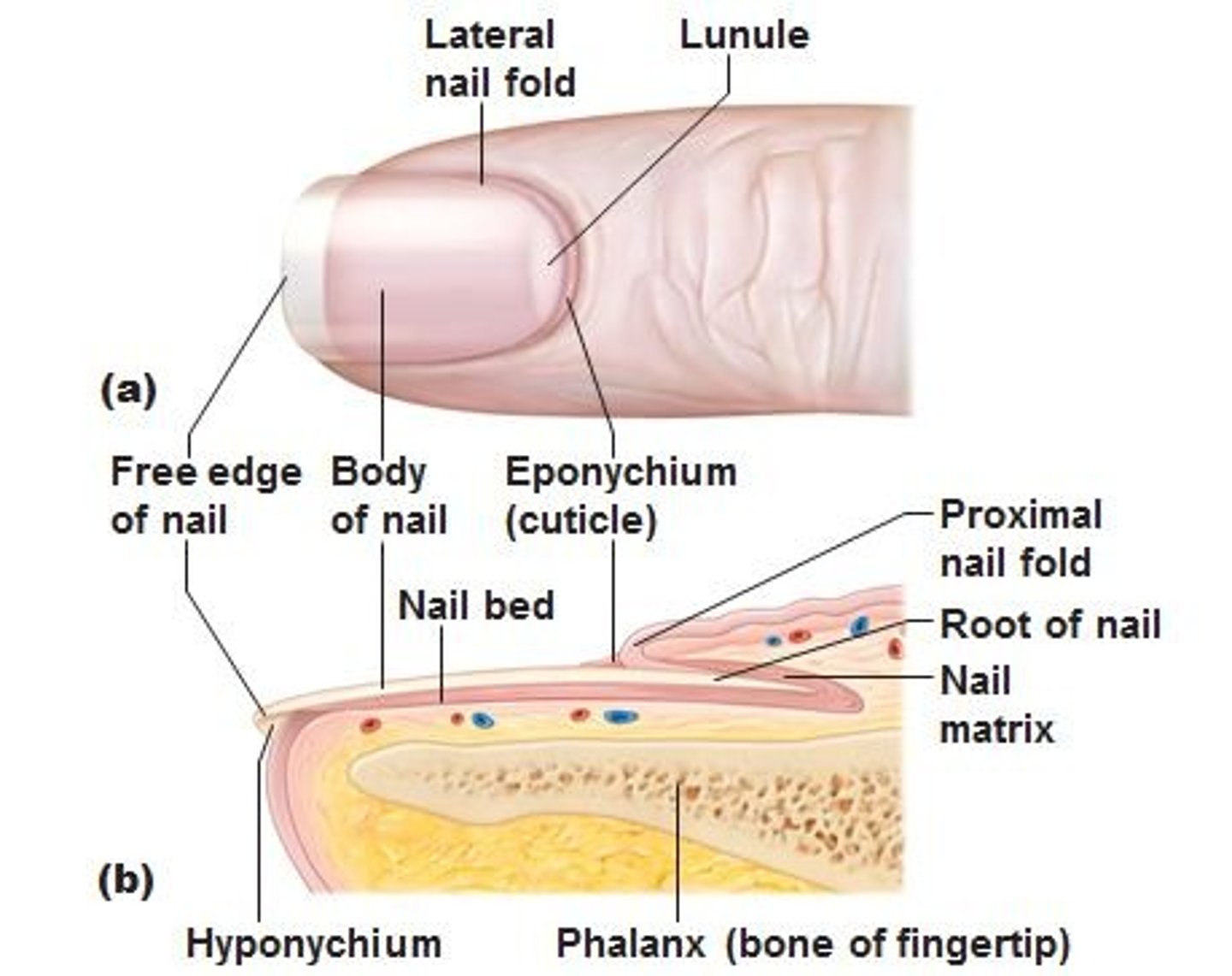
What is the nail bed?
epidermis underneath keratinized nail plate
nail matrix is
actively growing part of the nail