L8A Variables, Loops & Arrays
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Variables
Values that can be changed over time.
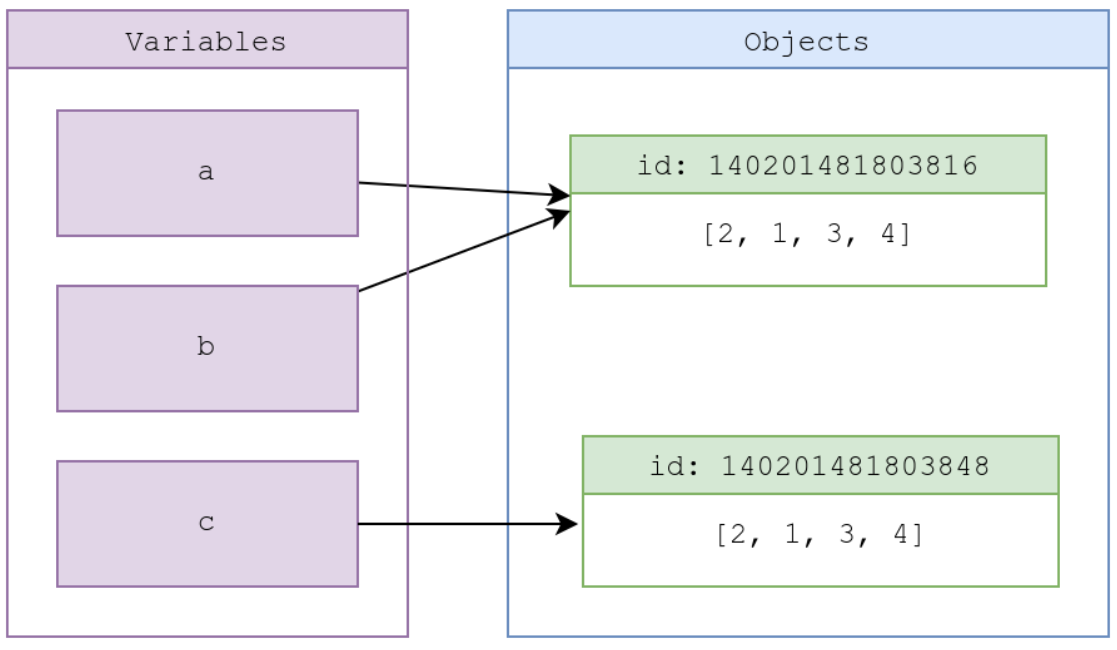
Think about a pointer system, where the variable points to the allocated memory where the value is stored
Assignment Statements
Expression is evaluated first before being assigned to the variable
Conversely, its a variable pointing to a value
Assignment: Pros & Cons
Allows us to create object with state that can differ over time
Harder to debug/verify correctness and the subsitution model fails
Assignment vs Declaration
Assigning a new value to a declared name
Declaring a new name in a frame, in source names must be declared with a value assigned to it
Why subsitution model breaks down?
The subsitution model fails to account for the changes that happens during the assignment of variables.
In the example, the assignment on line 3 is not reflected in the subsitution model.

Mutable Data
Data that can be changed after being declared.
Arrays (Python Lists)
Data structure that stores a sequence of data elements accessible via index, starting 0. Read and write at Log(1) while in length of array.
Factorial with Loops Example

Break VS Continue
Break stops the whole loop
Continue skips the remaining iteration of the loop and moves on to the next iteration
Destructive Function
Function that changes a pair in anyway