Storms 4: Hail, Mamatus clouds, Atmospheric Rivers
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
mammatus clouds
form below anvil (underside)
What effects do winds have?
1) cause damage directly
2) blows in more warm humid air (ex. storm fuel!)
moisture advection
blow in warm humid air to feed storm
positive feedback
longer-lasting storms
Force equation
F= m x a
force mass x acceleration
newtons second law
if you push on an object harder (bigger force), it will accelerate faster in the direction you push it
Acceleration
the change in velocity during time
(V new - V old)/ time
SPEED & DIRECTION
ex. car increases speed 50 to 90 km in 15 seconds, it accelerates.
if car maintain 50km/h, acceleration = 0
Air parcel
hypothetical blob of air about size of a city block
Forecast Equation for the Wind
wind (horizontal or vertical)
V new = V old + [(f/m) x delta t]
tells us how wind will increase or decrease or change direction depending on forces that act on the air parcel
What does buoyancy force cause in storms?
vertical movement
causes up & downdrafts
What does Pressure-gradient force (PGF) in storms?
horizontal or vertical movement
hortizontal winds
Warm air rises, cold air sinks cause what phenomena in storms?
updrafts and downdrafts
why?? temperature affects density affects buoyancy
Buoyancy of air parcel depends on
Parcel temp vs Temp of surrounding air
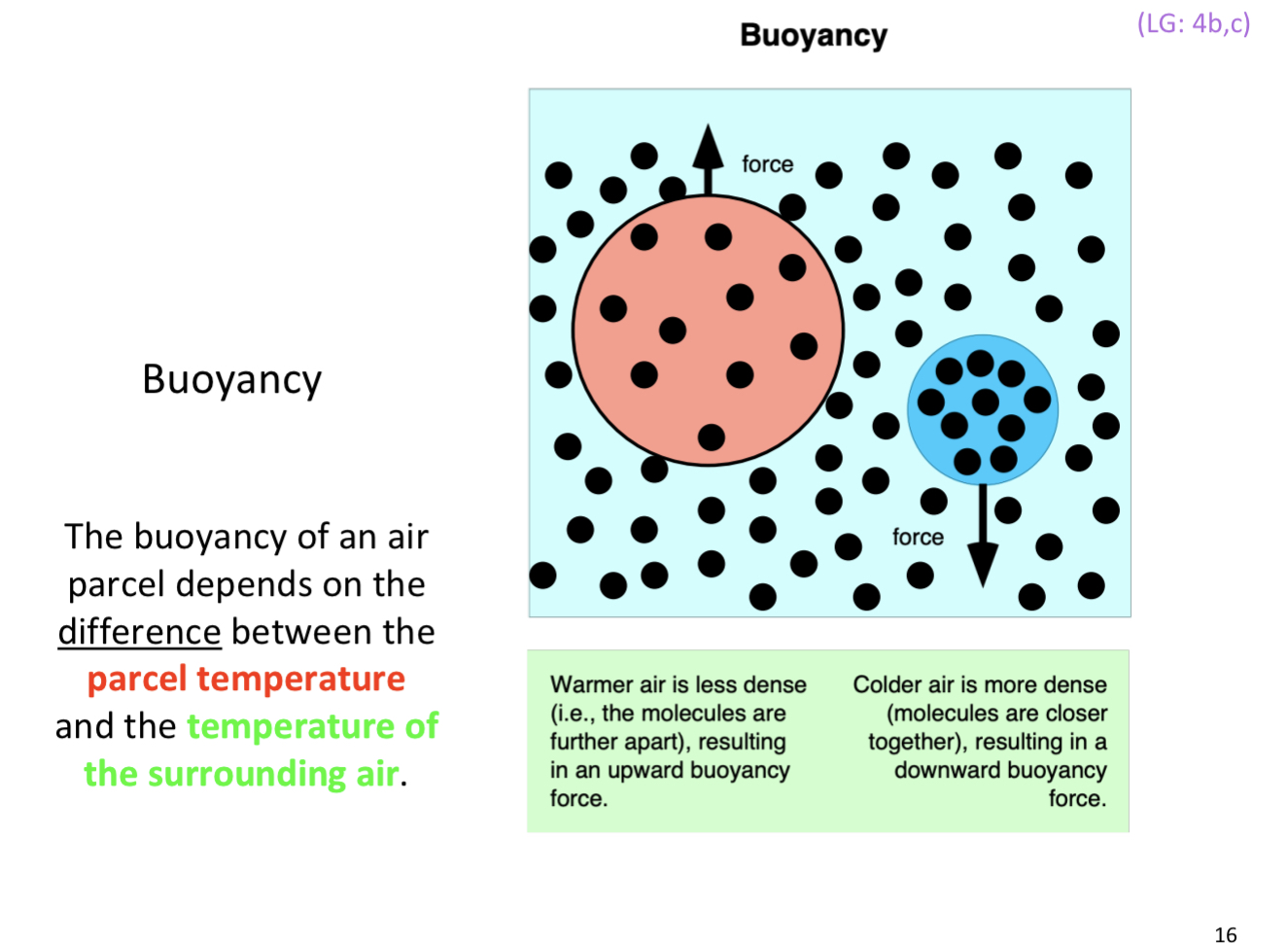
Buoyancy drives Thunderstorms
condensation in thunderstorms release latent heat
latent heat warms thunderstorm (latent—>sensible heat) , making it buoyant, causes air to rise
Drives violent updraft of thunderstorm
Pressure equation
P = F / A
Pressure = force/area
Temperature alters Pressure to drive horizontal winds!!
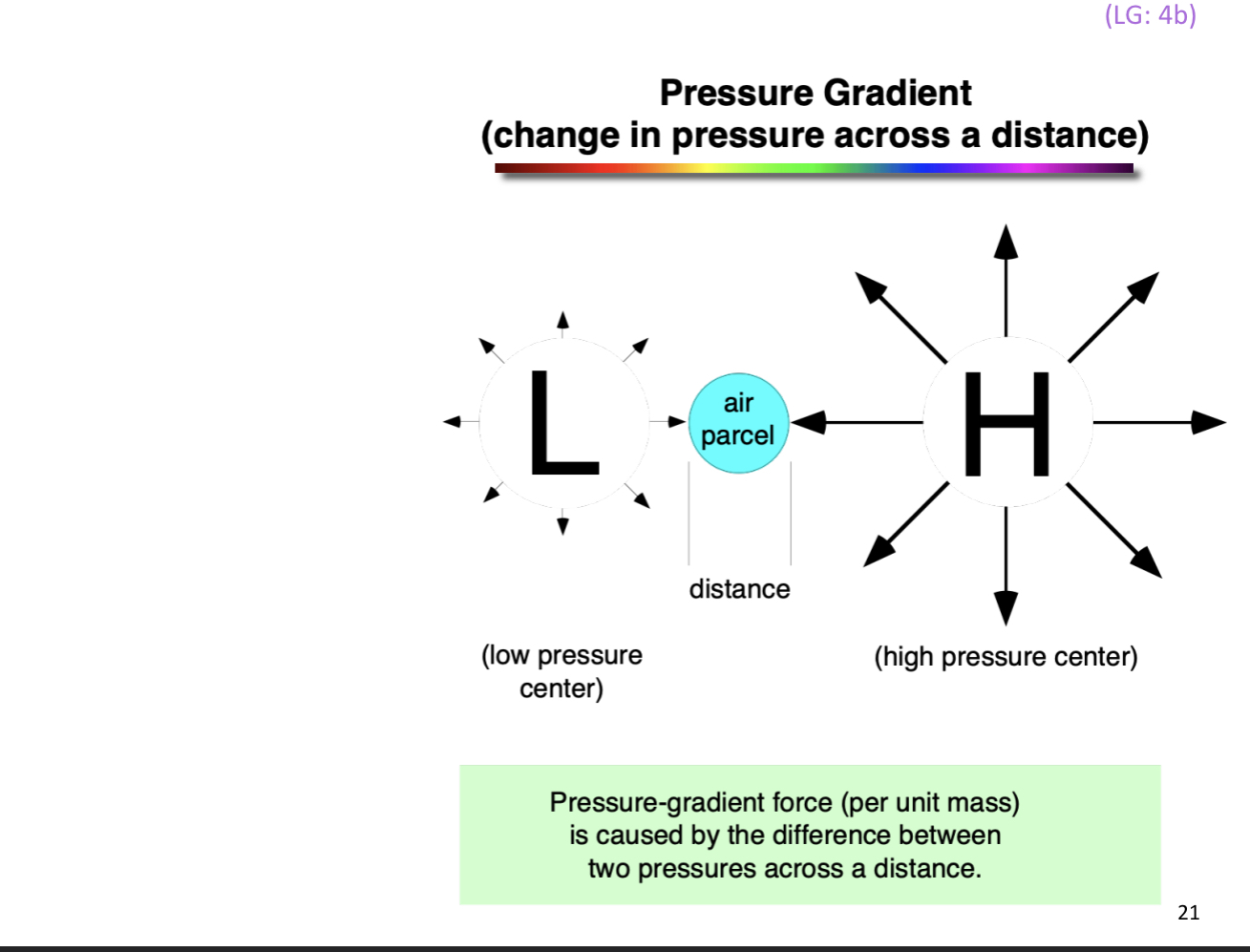
Pressure differences important because,,
pressure difference across a distance is called PRESSURE GRADIENT
these pressure gradients form in hurricanes
Where in a hurricane are there lots of thunderstorms?
in the core! condensation in the core makes the core even warmer
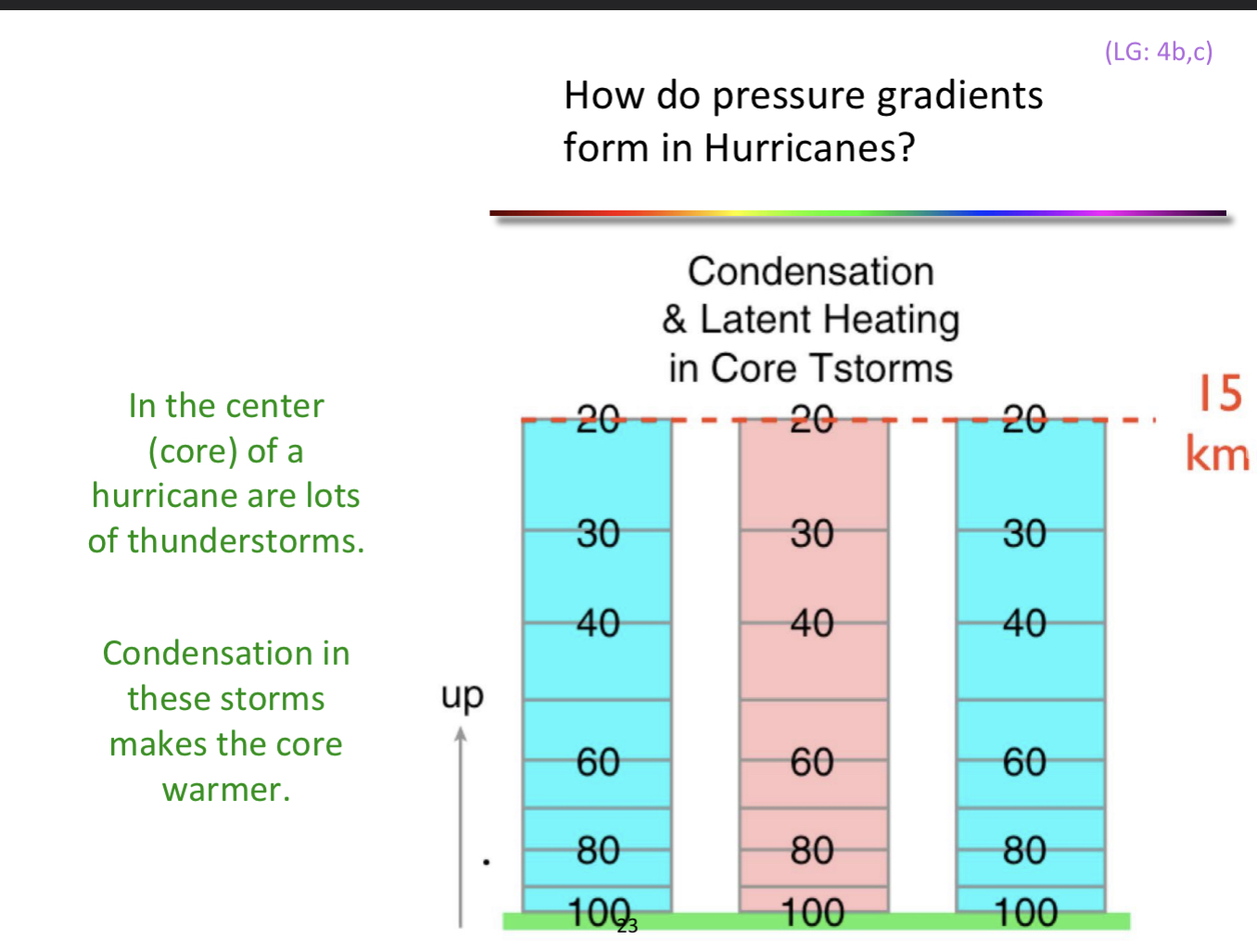
What happens as warm air expands in core?
warm air less dense than cool air—> takes up more space
pressure at top of core is > surrounding pressure
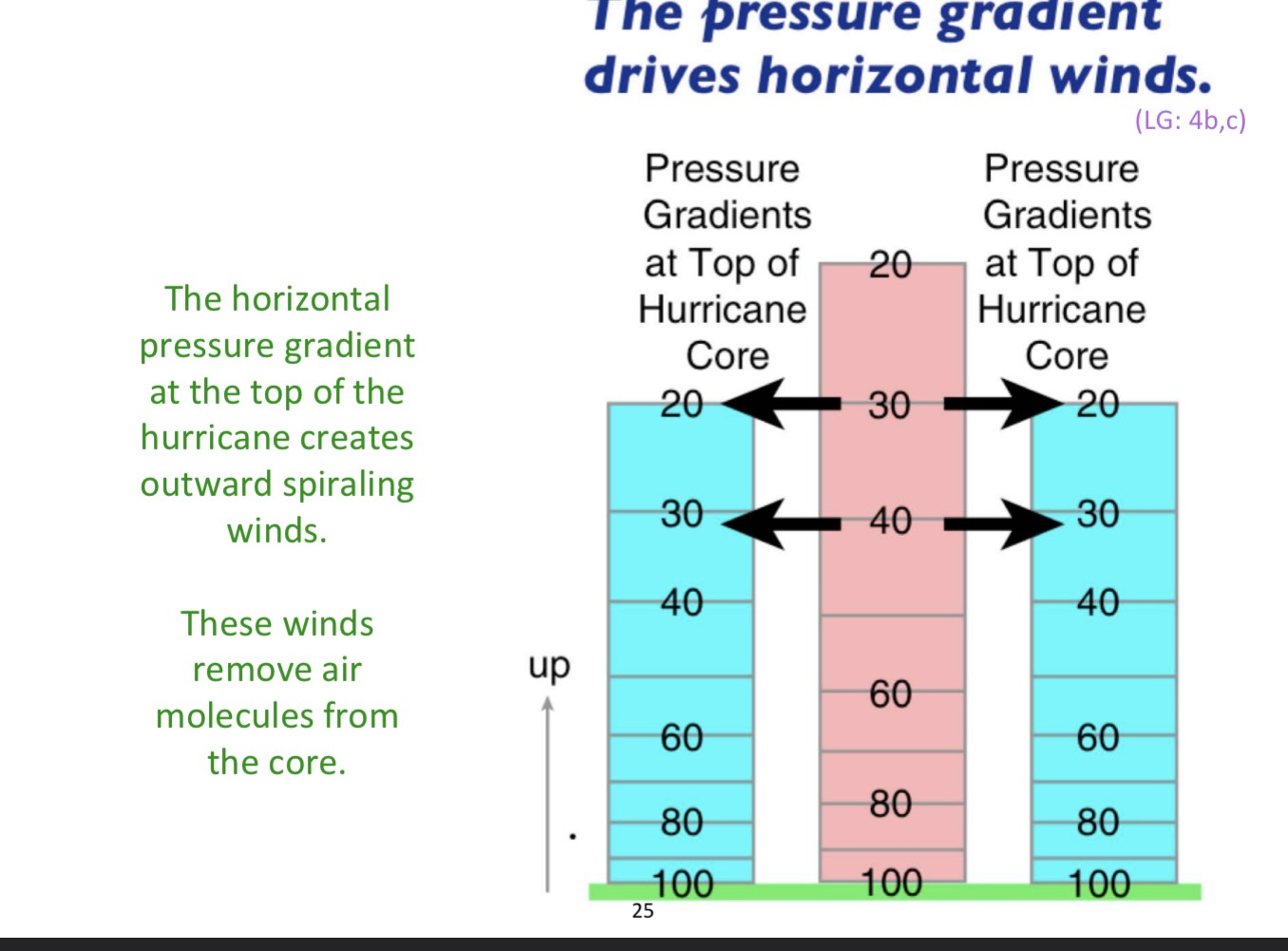
Pressure gradient drives..
drives horizontal winds
creatures outward spiralling winds
winds remove molecules from the core
How does the storm—> spiral inflow into bottom of hurricane?
low pressure at bottom of core creates pressure gradient that sucks in air
the inflow advects in more fuel
Summary of pressure gradients driving horizontal winds
horizontal changes in temp—>
horizontal changes in pressure increase with height—>
pressure gradient increase at higher altitudes
drives faster winds @ higher altitude
-drives violent winds in hurricanes
-drives atmospheric rivers
Hurricane anatomy
occluded front
cold front
warm front
know location of high and low pressure
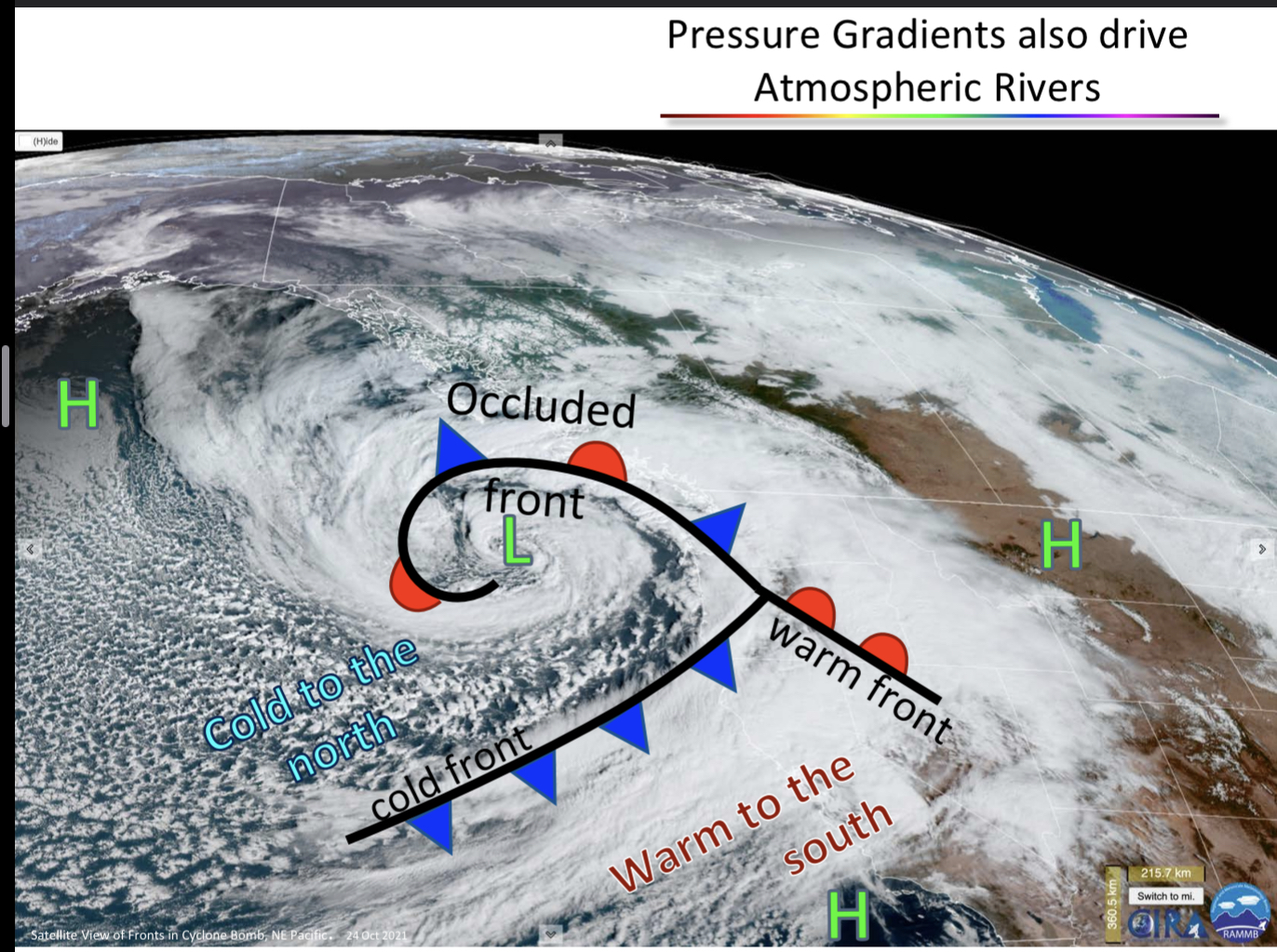
atmospheric rivers
giant flowing streams of water vapor
weaker ones bring rainfall, extreme ones can cause flooding and mudslides
caused by pressure gradients
Air molecules (continuity concept)
air molecules spread evenly
don’t leave gaps
don’t get bunched together
Continuity causes circulations
1) buoyant parcel rises (hole where it used to be—> partial vaccum (lower pressure than surrounding air)
2) surrounding air molecules get sucked in to fill hole (maintain continuity)
3) above the rising parcel, molecules compressed ( higher pressure) expands laterally
initial VERTICAL MOTION due to buoyancy (generates)
HORIZONTAL MOTION in surrounding air
—> CIRCULATION
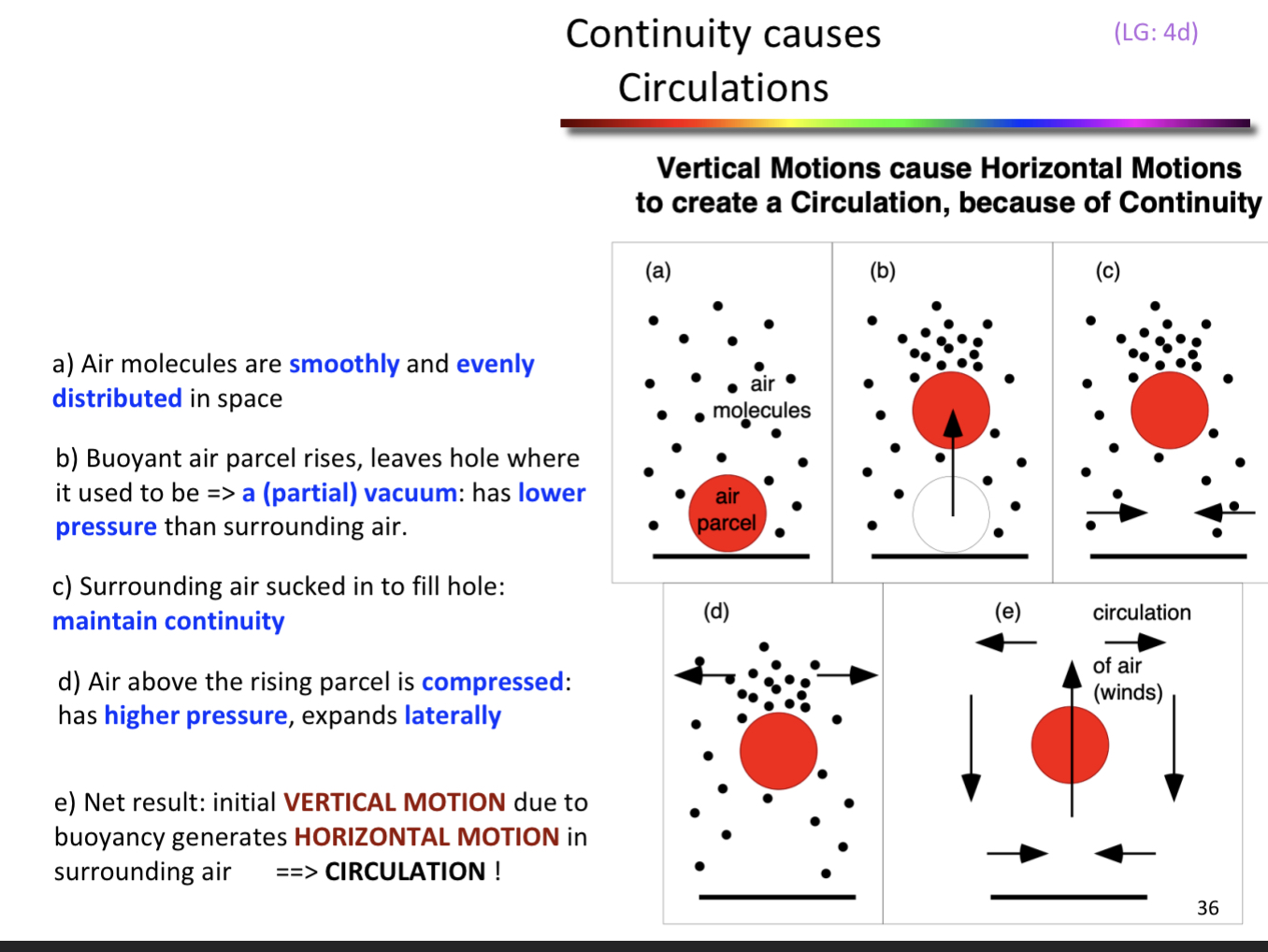
vertical horizontal motions linked by effect of ..
continuity
Hail Safety
1) wear safety glasses
2)if possible, turn away from storm and drive away
3) stay under a roof, inside a car, under farm tractor. to protect from falling hail
Rain Hazards
Hazards:
downpours cause flash floods, reduced visibility while driving
Safety:
move to high ground, dont drive though water of unknown depth
Hail Hazards
Occurence
can come from any large thunderstorm- most common with supercell Low precipitation
Hazards
injury, death, dent metal cars, break windows, flatten crops, kill livestock
Safety
get indoors
park under a roof
close eyes to keep shards out
What is true about the eye of a hurricane?
1) It occupies more space because its warmer (particles more spread out)
2) High Pressure @ the top
3) Low Pressure @ the bottom