Kinship System, Political Organization
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Consanguineal or Affinal
Scientists explore kin relations that can be through:
Consanguinity or Consanguineal Relation
- Measures BIOLOGICAL or blood ties
Affinity or Affinal Relation
- Forged through rituals (e.g: Marriage)
Kinship System
- A network of people who are related by marriage, blood, or adoption
- A system of meaning and power relations to determine relationships, rights, responsibilities, and expectations
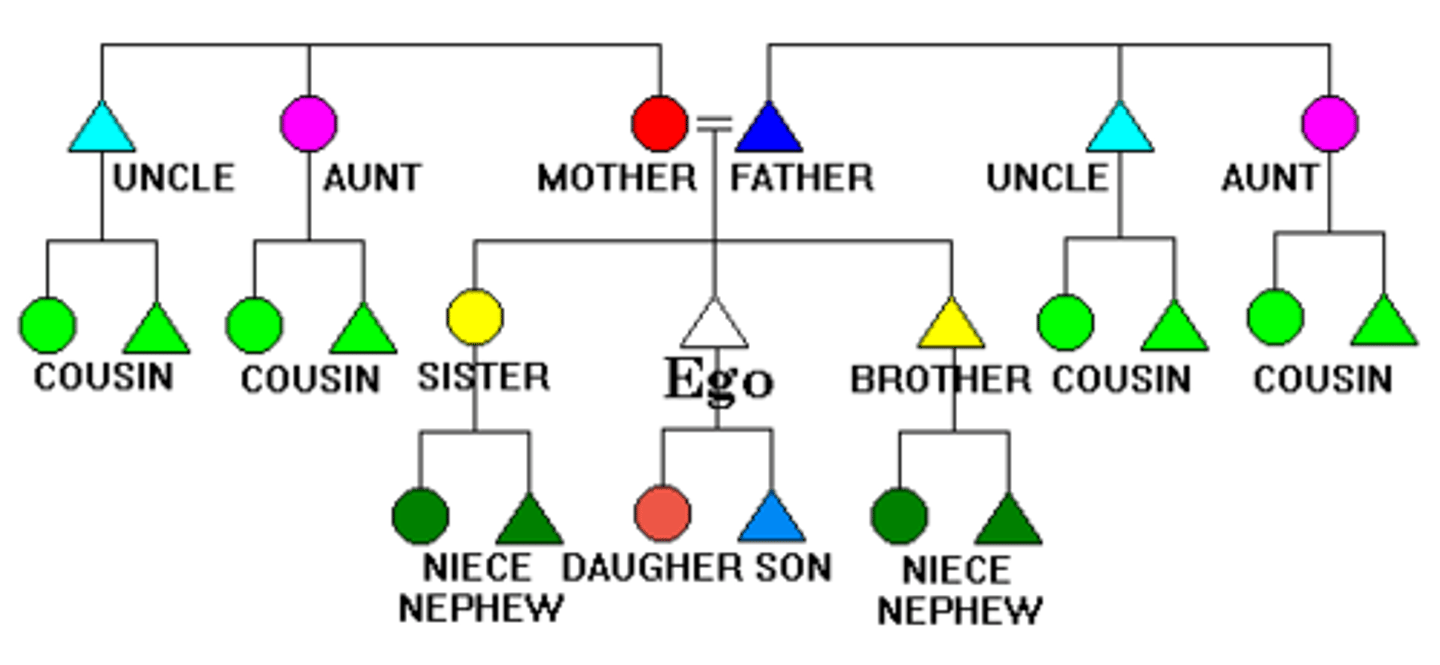
Ego
- Point of REFERENCE(focus) to anyone part of the kin
Kinship
- In societies around the world, it provides means to bind successive generations
Vertical Function of Kinship
- To pass properties, political office, and traditions within and to subsequent generations
- Inheritance perspective of kinship
Horizontal Function of Kinship
- Refers to the ties of people across a single generation through marriage
- Can be for expansion of the political and economic wealth of kin
Descent Groups
- A permanent social unit whose members claim common ancestry; fundamental to tribal society.
Descent
- Denotes the relationship that bonds the child to the mother or father
- It constitutes the transmission of their status
- Produces a line of connection from ego to anyone part of descent historically
1. Unilineal
2. Non-unilineal
Two types of Rules of Descent
Unilineal Descent
- Refers to the tracing of ancestry through only one parent, either the mother's or father's line, NOT the combination of the two
- Foraging, small-scale farming, nomadic herding socieities
Matrilineal and Patrilineal Descent
(2) Variations of Unilineal Descent
Matrilineal Descent
- Refers to the ego's ancestry through the female line
- Ego's female ancestors are related to him or her
Patrilineal Descent
- Tracing descent through the male line
- Both males and females, belong to their father's kin
- Only males can pass on their family identity to their children
Cognatic or Non-unilineal Descent
- Allows rules construction based on social groups
- BONDS are traced either from the side of either mother or father
1. Double Descent or (Bilineal)
2. Ambilineal Descent
3. Parallel Descent
4. Bilateral Descent
(4) Variations of Non-Unilineal Descent
Double Descent or Bilineal
(Ex: Yäko of Nigeria)
- Rare
- Males and Females are traced both matrilineally and patrilineally
-Inheritance and obligations descend only to one side (i.e: males have/do that, females have/do this)
Parallel Descent
Bilineal Descent:
- The obligations on marriage and funerals are also passed matrilineally
Ambilineal Descent
- Allows parents to choose to affiliate with either the father's or mother's descent group
- Which side of the kin to affiliate their children
- Advantageous in protecting properties and economic purposes
Bilateral Descent
- An ego is EQUALLY related to both mother's and father's side of the kin
- An ego creates links to everyone part of the kin, even those are not part of the blood line
- Common in foraging societies
Marriage
- Characteristic of human relations and social groupings that exists in all cultures
- BUILDS kinship ties
- Involves emotional and physical intimacy
- Sexual reproduction, companionships, legal rights, and inheritance
1. Monogamy
2. Polygyny
3. Polyandry
Three forms of Marriage
Monogamy
- Marriage between man and woman that is a widely accepted norm worldwide
Polygyny
- Marriage that permits man to marry more than one woman
Polygandry
- It permits a woman to marry more than one man
Endogamy and Exogamy
Two primary patterns in terms of affinal ties:
Endogamy
Marriage within a group -- (social, ethnic, or in a caste system)
Exogamy
Social norm of marrying outside a social group
Child-rearing
Primary responsibility of parents when enculturation begins
1. Patrilocal
2. Matrilocal
3. Bilocal (Ambilocal)
4. Neolocal
5. Avunculocal
Types of Residence Rules
Patrilocal
- Refers to the pattern in which married couples live with or near the husbands' parents
Matrilocal
- Refers to the pattern in which married couples live with or near the wives' parents
Bilocal or (Ambilocal)
- Refers to the pattern in which the bride and groom pick which family to live near or with
Neolocal
- Refers to the pattern in which newly married couples set up their own households
Avunculocal
- Married couple goes to live with the groom's mother's brother (or their uncle)
Hemophilia
- A hereditary disease where blood does not coagulate to stop bleeding
- Slows down the blood clotting process
Childhood Familiarity Hypothesis
- Siblings raised together in the family are not erotically involved or sexually attracted to one another because of a biological tendency
- They develop sexual aversion and avoid incest
Fictive Kinship
(Ex: Compadrazgo or co-parenthood)
- Describes a form of kinship neither on consanguineal nor affinal ties
- It recognizes kinship oblications beyond biological
Political Organizations
- Defined as groups responsible for political and social cohesiveness, economic growth, and safety from internal and external threats
Power, authority and legitimacy
Key concepts that provide order and stability in political organizations
Power
- The exercise of will or force in order to achieve the desired outcome
Authority
- Manifestation of power
- The ability to bring out results through one's status, reputation, and degree of respect received from its constituents
Legitimacy
- Refers to the right and acceptance of one's power and authority without the threat or exercise of force
1. Bands
2. Tribes
3. Chiefdoms
4. States
Kinds of Political Organizations
Band
- A small group of mostly nomadic people in pursuit of a particular goal
- to ensure their survival and subsistence through foraging and at times hunting
- Membership and leadership are informal
Band leader
- They do not hold formal power over the band but mostly coordinates the movement such as the hunting and foraging activities of the group
Tribes
- A political group composed of several bands, occupying a particular territory with each having a common language and way of living
- Egalitarian in nature
Tribal leader
- May vary from one tribe to another
- Most of the time, they are selected based on their numbers and strengths of his following
Chiefdoms
- Composed of allied tribes and villages under one chief which can reach up to thousands of members
- Ranked
Chief
- Considered to be an "office" or an "institution" rather than just someone who leads the economic activities of the group
- Permanent and carries more responsibilities in maintaining constituents
State(s)
- A political organization which, through the government, exercises sovereign rule over a population within a defined territory
- Stratified
Internal duties
- Evolved from merely ensuring public order and social stability to include delivering public services to its constituents
External duties
- Involves ensuring national security and engaging with other states by means of treaties, membership in international groups with other states, and joint military exercises, among others
Head(s)
- _____ of the political organization can go by different number and names depending on the type of government
President
- Head of State
- in charge of foreign affairs and national defense
Prime Minister
- He/She are is by the parliament as Head of Government in charge of directing internal government affairs
Elman Rogers Service
- According to a cultural anthropologist (1962)
- Societies undergo various stages of social evolution. These stages are composed of specific political organizations which fit the structural and economic needs of the people