pathology II EXAM 1
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
204 Terms
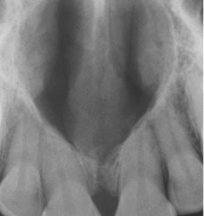
fibrous dysplasia
bone condition characterized by replacement of normal bone by fibrous connective tissue intermixed with abnormal bone
mccune albright syndrome
polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, cafe au lait spots and endocrinopathies indicate?
polyostotic
fibrous dysplasia that affects multiple bones
fibrous dysplasia
lesion with GROUND GLASS appearance diagnosis?
low recurrence rate
All of the following are true for fibrous dysplasia EXCEPT:
single or multiple
occurs in teenagers and young adults
low recurrence rate
expansile lesion
polystotic
type of FIBROUS DYSPLASIA that occurs in children
neurofibromatosis 1
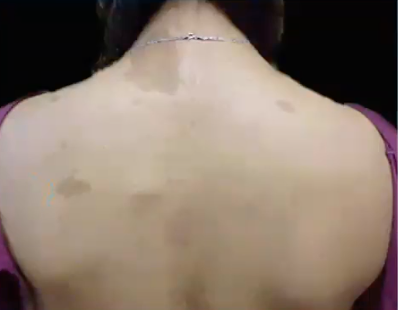
SMALLER cafe au lait spots that CROSS MIDLINE
mccune albright syndrome
LARGER cafe au lait spots that DO NOT cross midline
cenento osseous dysplasia (COD)
most common fibro-osseous lesion
periapical cemento osseous dysplasia (COD)
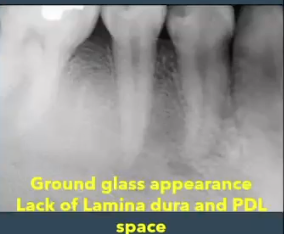
history: middle-aged African American woman, teeth are vital and asymptomatic, LOSS of LAMINA DURA

focal COD (cemento osseous dysplasia)
history: middle-aged Africa-American woman, tooth is vital and asymptomatic
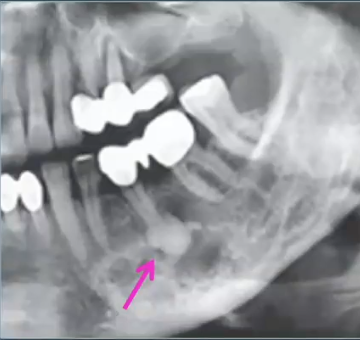
hypercementosis
diagnosis?
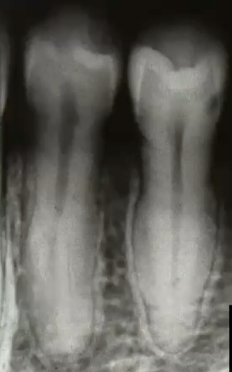
florid COD (cemento osseous dysplasia)
typically found in middle-aged African American women, vital teeth and asymptomatic radiographic findings.
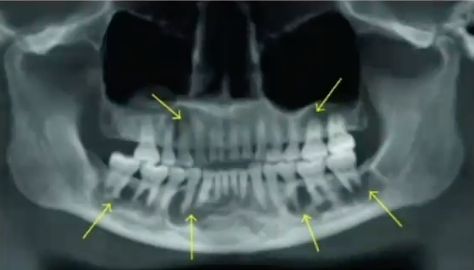
follow up
trreatment of COD (cemento osseous dysplasia)
cementoblastoma
benign neoplasm of cementum, VITAL teeth but PAINFUL
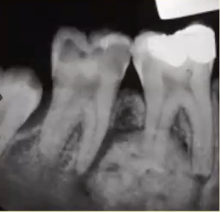
COD (cemento osseous dysplasia)
location is ALWAYS at apex of tooth
osteogenesis imperfecta
genetic disorder of fragile bones due to defective type 1 collagen synthesis, leading to frequent fractures.
osteogenesis imperfecta
presents with low bone density (OSTEOPENIA) and BLUE SCLERA
osteogenesis imperfecta
blue/grey teeth with OBLITERATED PULP CHAMBER (shell teeth)
increase in bone density (bone density decreases in OI)
which of the follwing is FALSE for osteogenesis imperfecta:
AD most common inheritance
affects bone, teeth, and sclera
increase in bone density
affects type 1 collagen
Osteopetrosis/Albers-schonberg/marble bone
decreased osteoclatic activity leading to INCREASED BONE DENSITY
decreased bone density
All of the following are features of Alber-schonberg disease (osteopetrosis) EXCEPT:
multiple fracture
decreased bone density
blindness
deafness
Cleidocranial dysplasia
AD disorder associated with prolonged rention of teeth and SUPERNUMERARY TEETH
cleidocranial dysplasia
diagnosis
hypodontia
which of the following is FALSE regarrding cleidocranial dysplasia:
AD inheritance
affects clavicles and skull
hypodontia
prolonged teeth retention
cherubism
PAINLESS BILATERAL posterior mandible ENLARGEMENT in children

cherubism (mixed dentition with multilocular radiolucencies)
diagnosis?
supernumerary teeth
which feature is NOT a feature of CHERUBISM:
billateral enlarged mandible
painless
supernumerary teeth
occurs in children
paget disease of bone/ osteitis deformans
metabolic disease characterized by abnormal resorption and deposition causing INCREASE in SKULL SIZE (dentures no longer fit)
paget disease
generalized increased in bone most commonly in maxilla
paget disease
COTTON WOOL appearance, loss of lamina dura, and hypercementosis
paget disease
high serum alkaline phosphatase levels with NORMAL calcium and phosphorus levels
osteosarcoma
concern with paget disease
multilocular
All of the following are radiographic features of paget disease EXCEPT:
loss of lamina dura
cotton wool appearance
hypercementosis
multilocular
condensing osteitis is a type of osteomyelitis

odontogenic keratocyst
which of the foolowing clinic features is not part of mccune albright syndrome?
osteitis deformans (Pagets)
generalized hypercementosis is associated with:
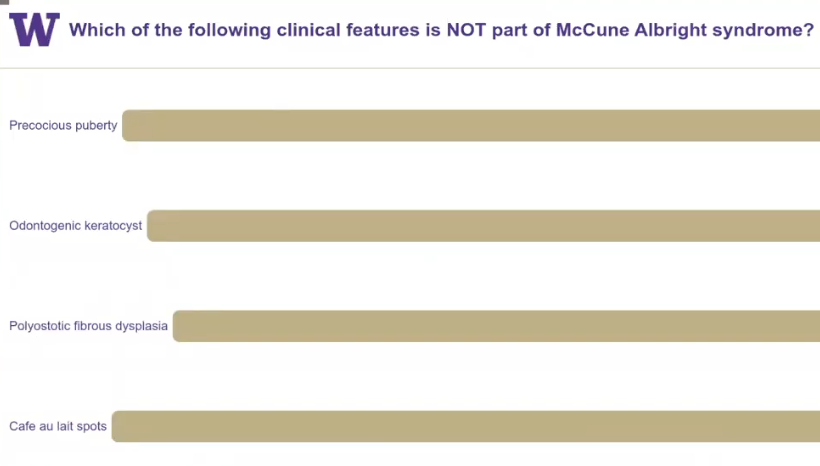
periapical cyst
periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
diagnosis?
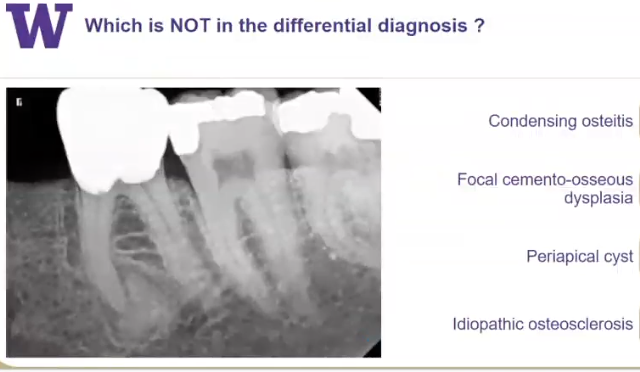
ground glass
what is the description of this radiographic feature?
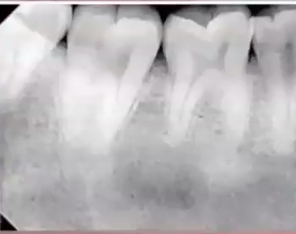
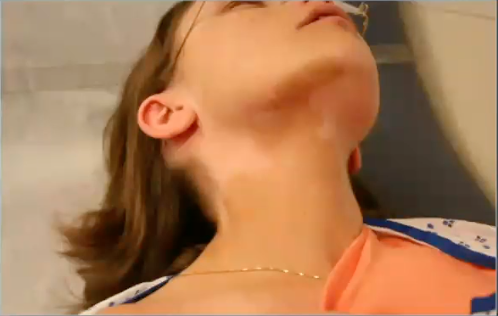
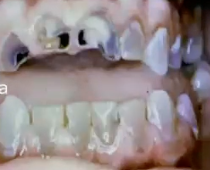
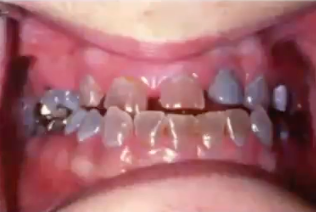
osteogenesis imperfecta
what condition is associated with this clinical image?
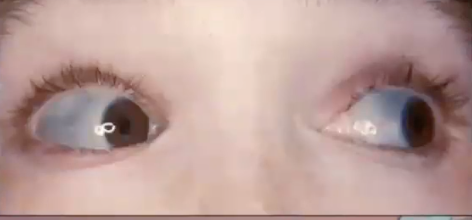
paget disease
diagnosis?

osteopetrosis
diagnosis?
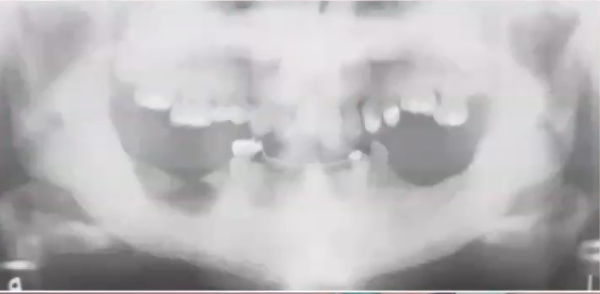
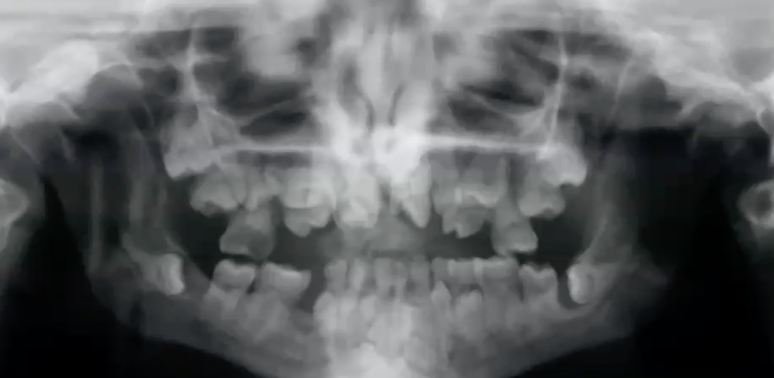
mccune albright syndrome
diagnosis?
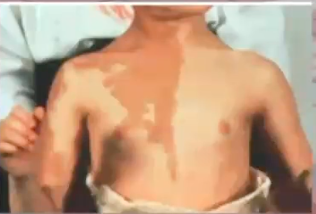
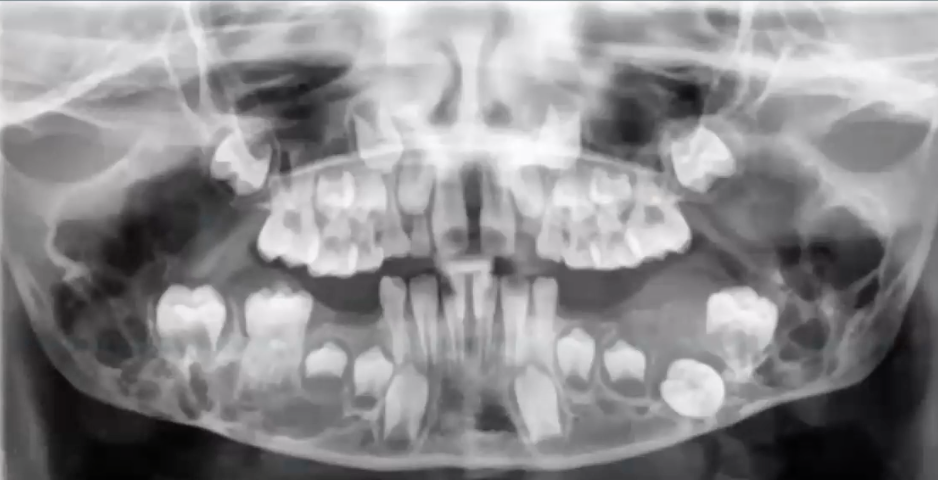
osteogenesis imperfecta
what is the condition?
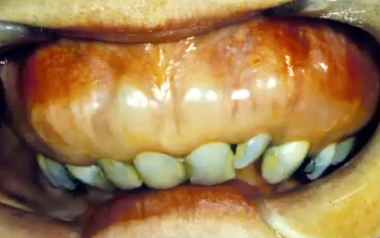
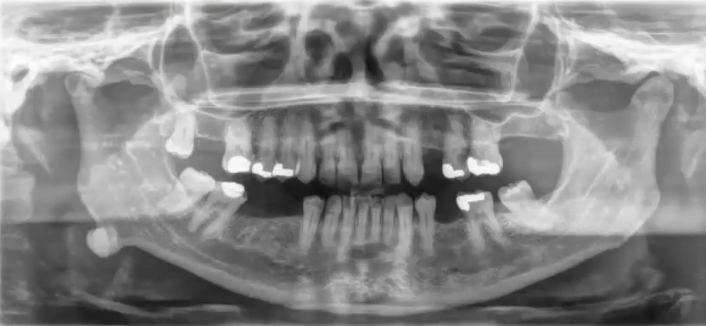
hypercementosis
diagnosis?

osteoma
benign bone tumor in MANDIBULAR BODY, associated with gardners syndrome
gardner syndrome
what. syndrome is associated with multiple osteoma
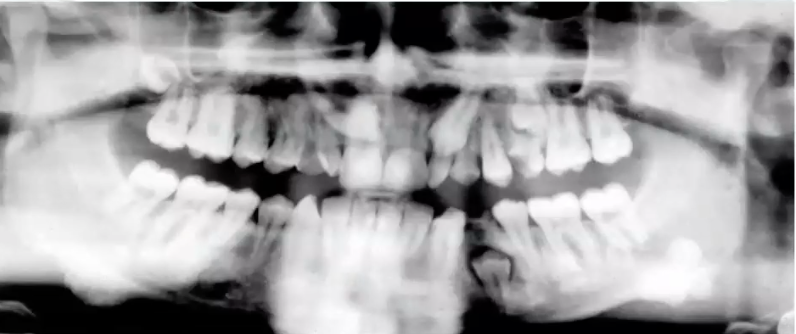
osteoma
well circumscribed radiopaque lesion in angle of mandible, diagnosis?
colorectal cancer
major risk with GARDNER SYNDROME
gardner syndrome (multiple osteoma)
what is the diagnsis?
small, slow-growing, and found in skull
Which of the following is CORRECT for osteoma

cafe au lait spots
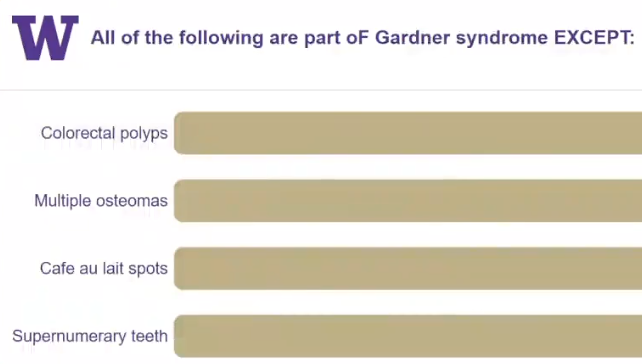
All of the following are features of Gardner syndrome EXCEPT:
osteoblastoma
benign bone tumor larger than 2-4 cm, causes nocturnal PAIN not relieved by aspirin
relieved by aspirin
Which of the following statements about OSTEOBLASTOMA is FALSE
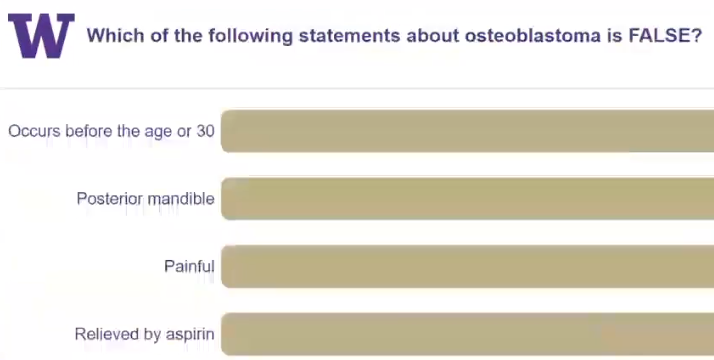
cementoblastoma
benign odontogenic neoplasm of cementoblasts
cementoblastoma
diagnosis? radiopaque lesion with radiolucent border in molar area, can be symptomatic
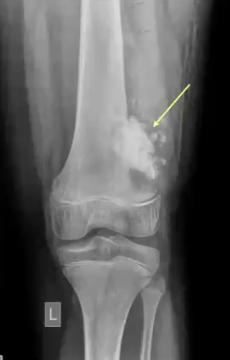
radiolucent mass
which of the following is INCORRECT for cementoblastoma

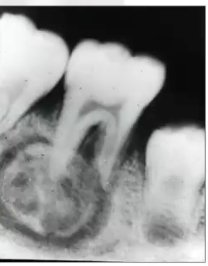
osteosarcoma
MALIGNANT bone neoplasm, most commonly found in distal femur and proximal tibia
osteosarcoma
ill defined MOTH EATEN appearance, and widening of PDL space
osteosarcoma
presents with SUNBURST appearance
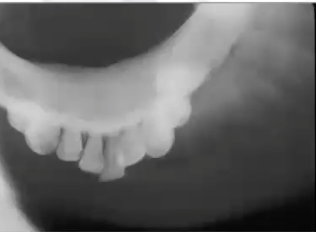
osteosarcoma
diagnosis?
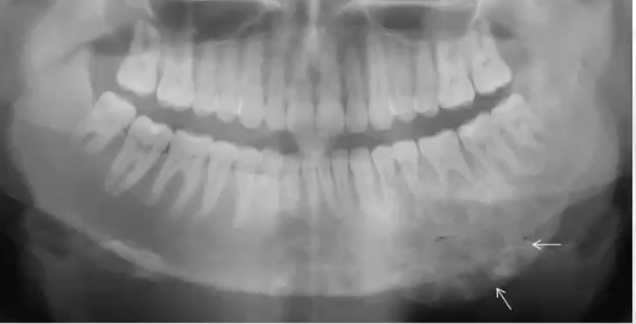
radiolucent halo rim
which of the following feature is NOT typically associated with osteosarcoma
chondrosarcoma
malignant bone tumor of cartilage
surgery (resistant to chemo and radiation)
ONLY treatment for chondrosarcoma
Ewing sarcoma
highly lethal primary malignant tumor of bone
ewing sarcoma
irregular defined borders, and can present with onion skin or sunray appearance
post radiaiton bone sarcoma
sarcoma in bone that has been previosly subjected to radiation therapy
breast
most common origin of metastasis in jaws
more common location is gingiva
which of the following statements about METASTATIC DISEASE to the head and neck is FALSE

focal osteoporotic bone marrow defect
area of hematopoitic marrow that produces radiolucency
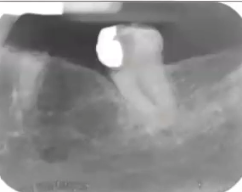
idiopathic osteosclerosis
well defined dense bone associated with VITAL tooth and is often asymptomatic
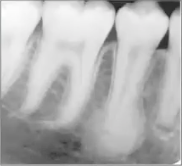
condensing osteitis
diagnosis?
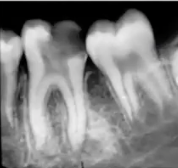
condensing osteitis
diagnosis?
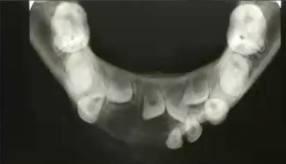
central giant cell granuloma
radiolucent, well defined, non corticated lesion in anterior jaw
central giant cell granuloma
occurs before 30 years old and crosses midline, diagnosis?
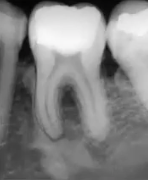
cementoblastoma
which of the following is NOT a multilocular lesion?

ewing sarcoma
Onion skin is associated with:
no expansion
which of the following is FALSE regarding ossifying firbroma

condensing osteitis
which of the following is NOT a NEOPLASM

focal osteroporotic bone marrow defect
all of the following are RADIOPAQUE lesions EXCEPT
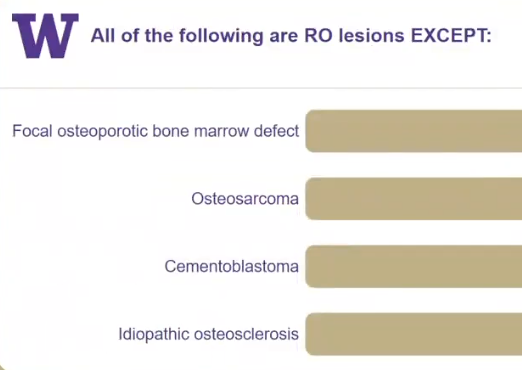
multilocular
which of the following is TRUE for focal osteoporotic bone marrow defect

cementoblastoma (first molar and radiolucent rim)
what is the diagnosis?
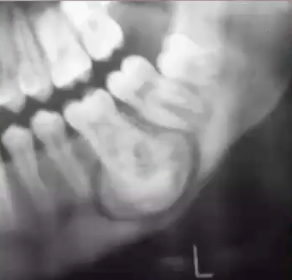
condensing osteitis
what is the diagnosis?
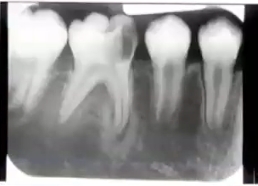
gardner syndrome
what is the condition associated with multiple radiopaque lesions at the angle of the mandible
idiopathic osteosclerosis
what is the diagnosis

multilocular
how would you describe this lesion
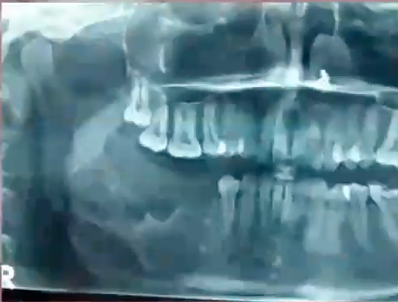
osteoporotic bone marrow defect
diagnosis?

periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia (COD)
diagnosis?
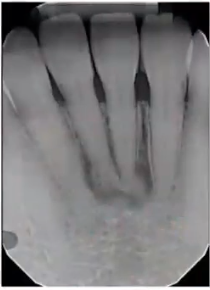
sunburst
how would you describe this lesion
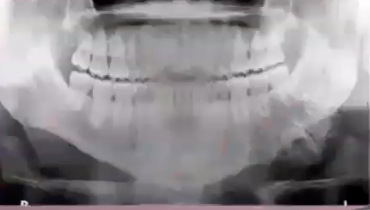
focal cemento-osseous dysplasia (COD)
what is the diagnosis?
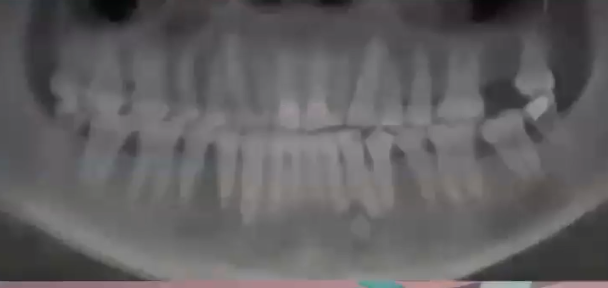
chondrosarcoma
diagnosis?
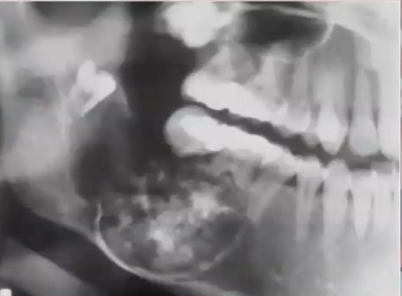
periapical (radicular) , residual, and buccal bifurcation
types of INFLAMMATORY CYSTS
stafne bone cyst/ lingual mandibular gland depression
developmental defect BELOW mandibular canal near angle of mandible, pseudocyst
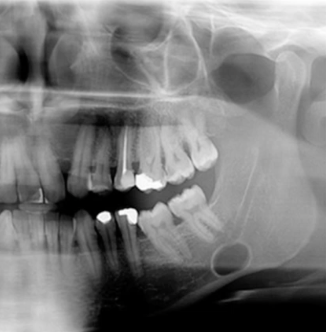
trraumatic bone cyst
scalloping radiolucency around VITAL teeth, EMPTY CAVITY
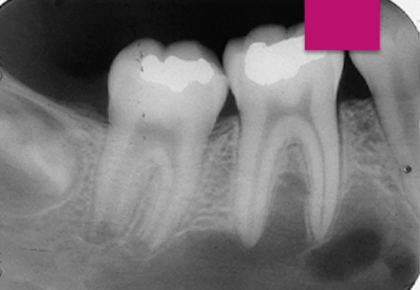
traumatic bone cyst
teeth are vital and asymptomatic, diagnosis?
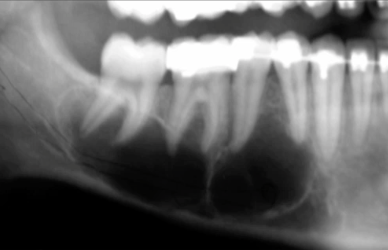
aneurysmal bone cyst
pseudocyst, blood filled spaces, characterized by rapid enlarging swelling in posterior mandile
traumatic bone cyst
which of the following exibits an EMPTY CAVITY
nasopalatine duct cyst
most common NONODONTOGENIC CYST of the oral cavity
nasopalatine duct cyst
diagnosis?