Brain Fissures, Areas, etc
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
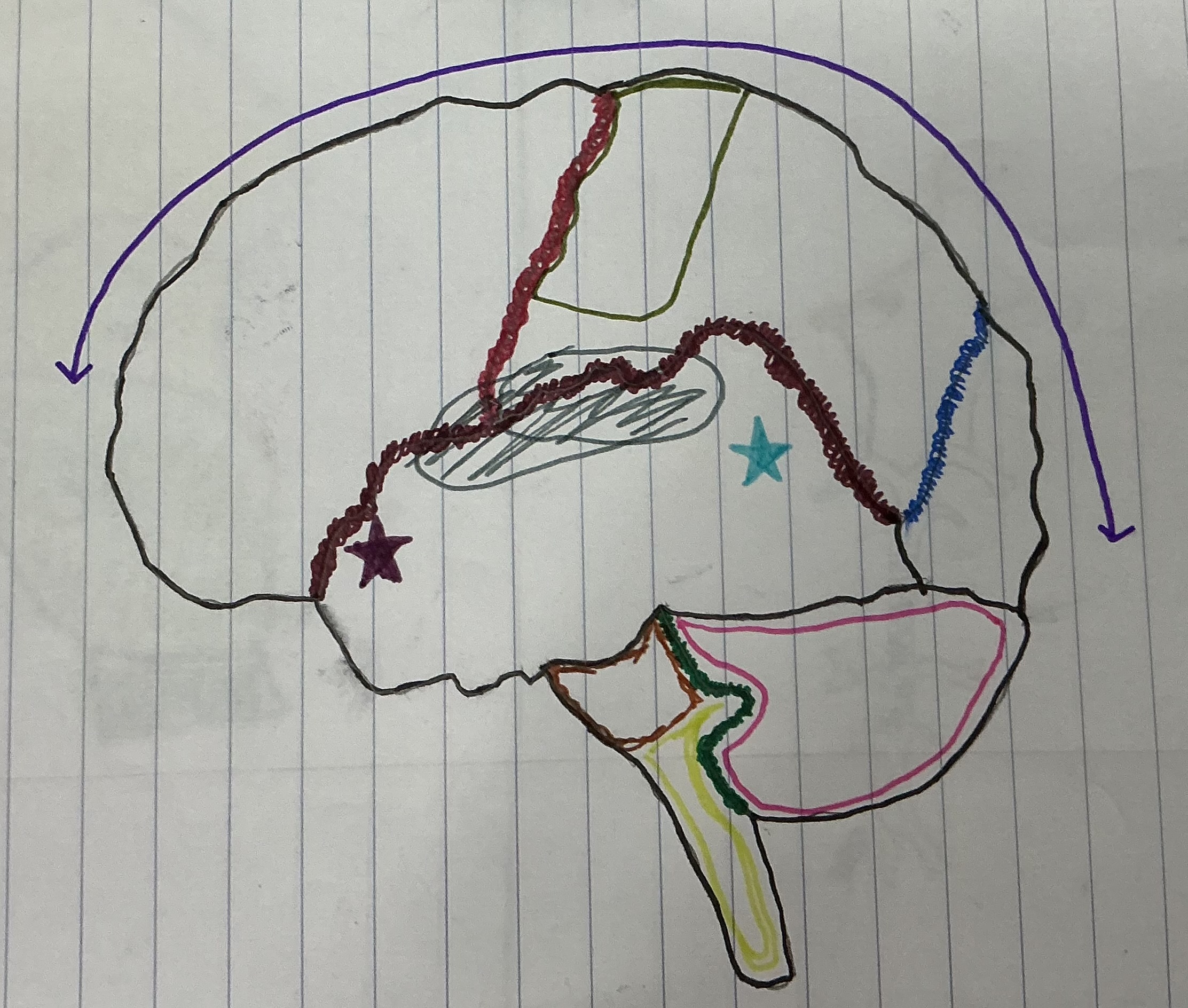
What color is the Central Sulcus
Red
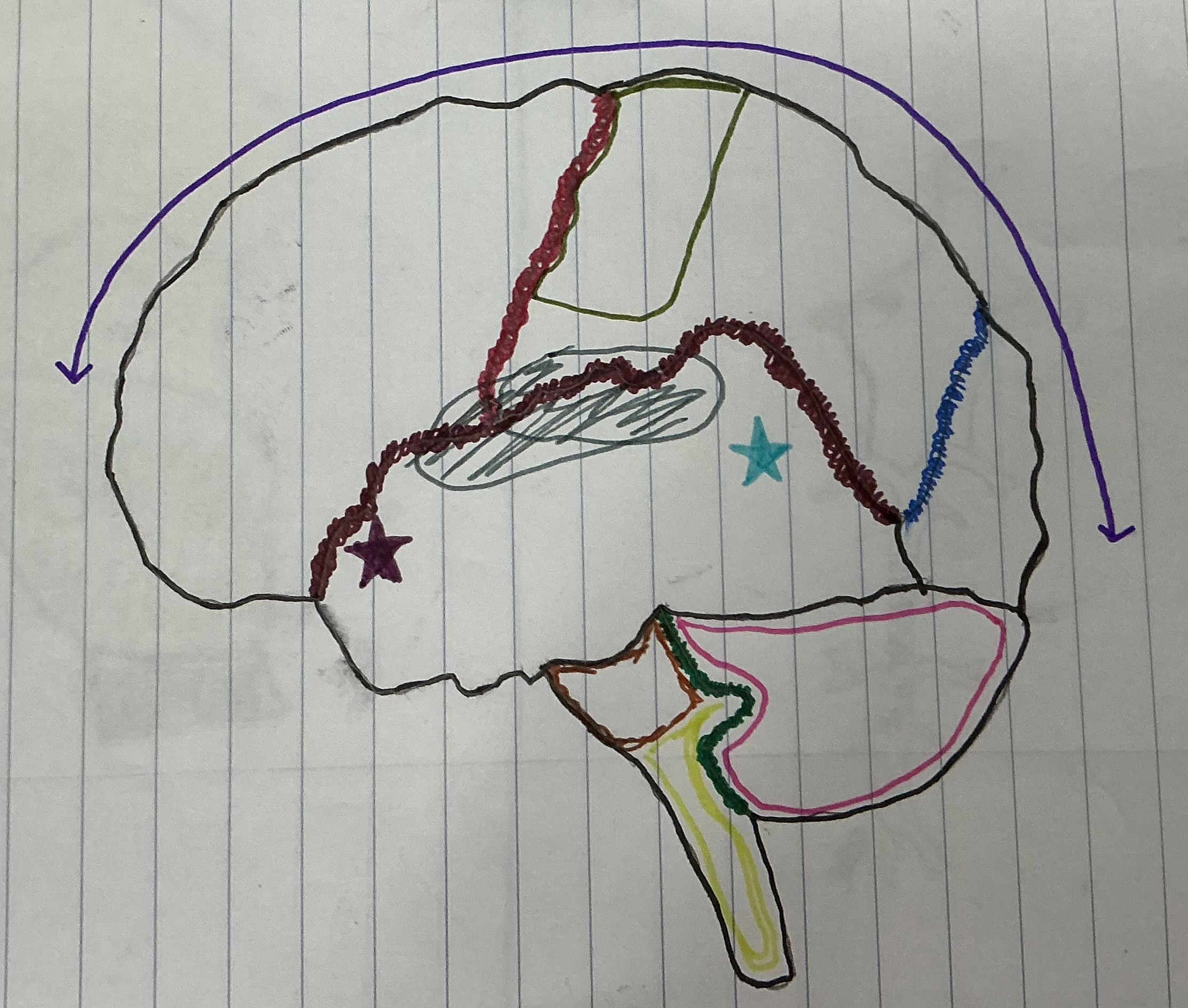
What color is the Lateral Sulcus
Dark Red
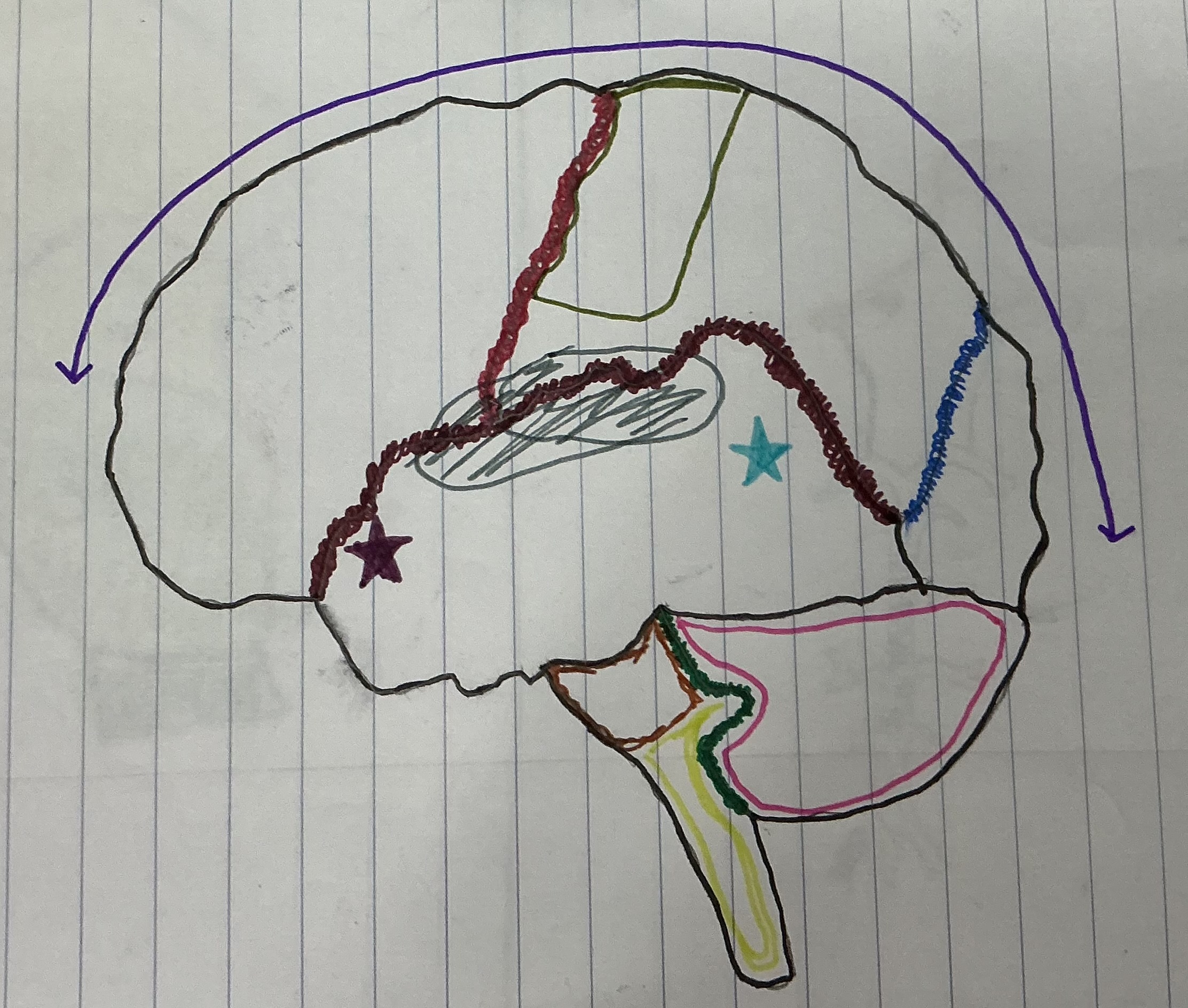
What color is the Longitudinal Fissure
Purple
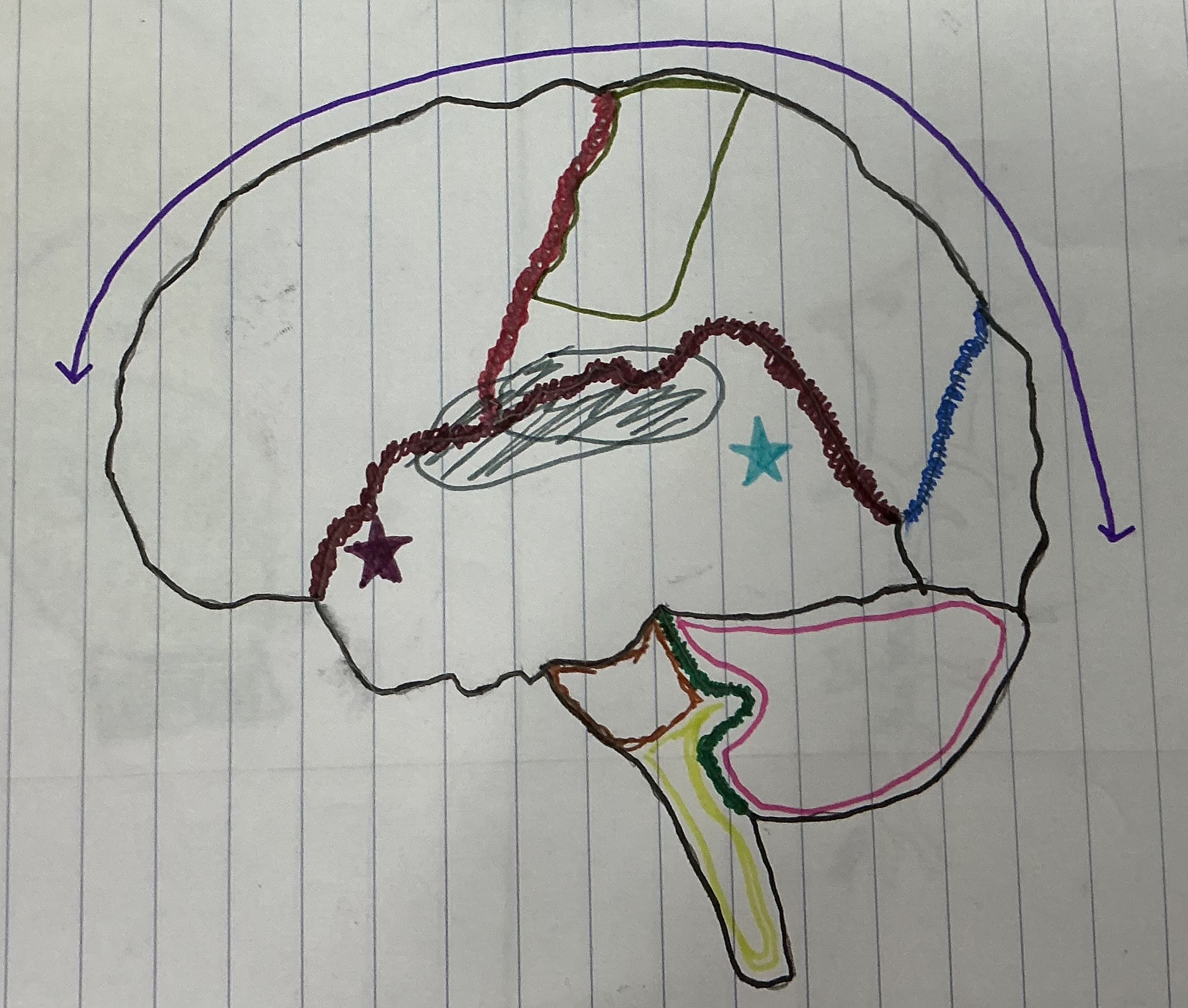
What color is the parieto-occipital fissure?
Dark Blue
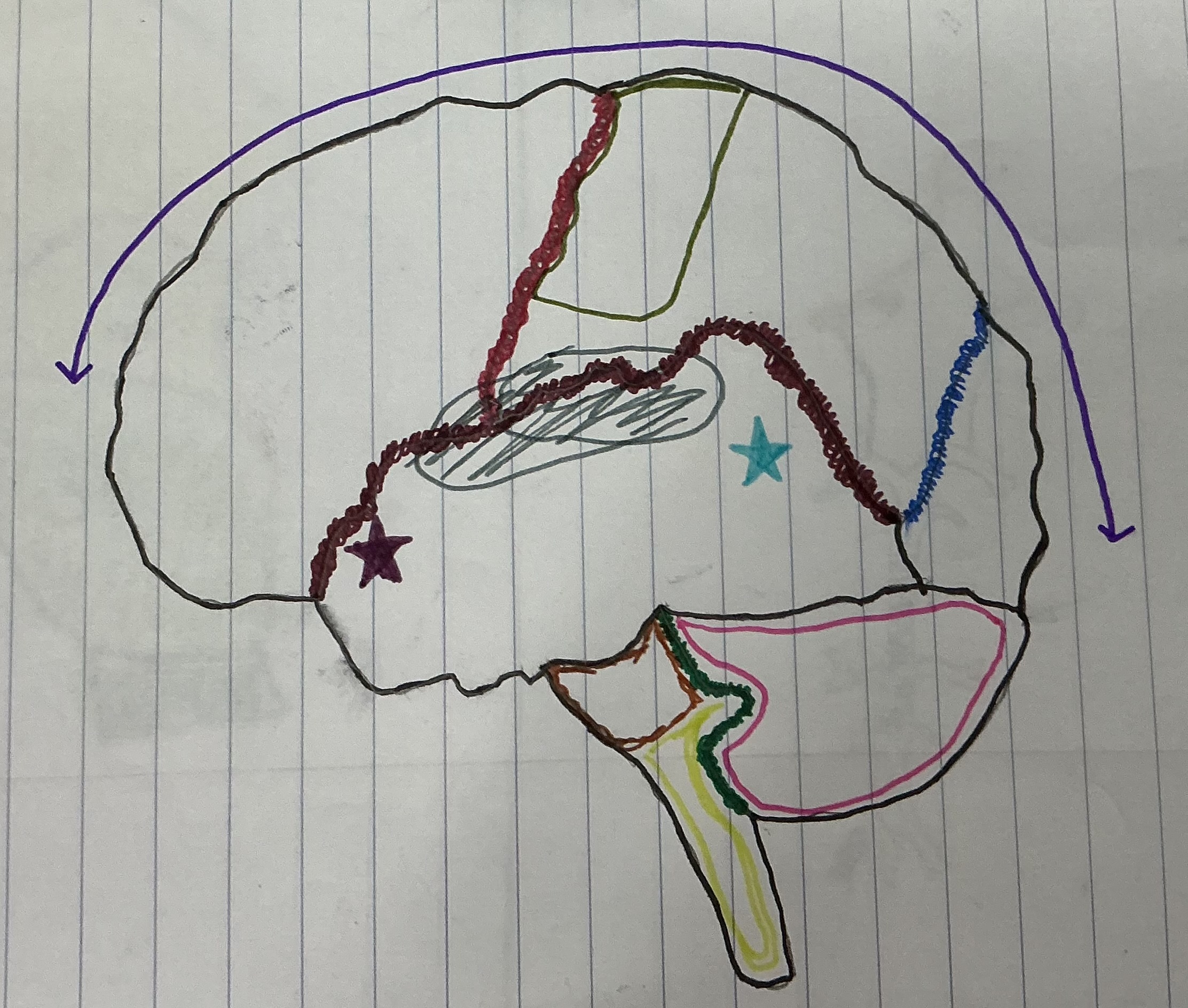
What color is the transverse fissure
Green
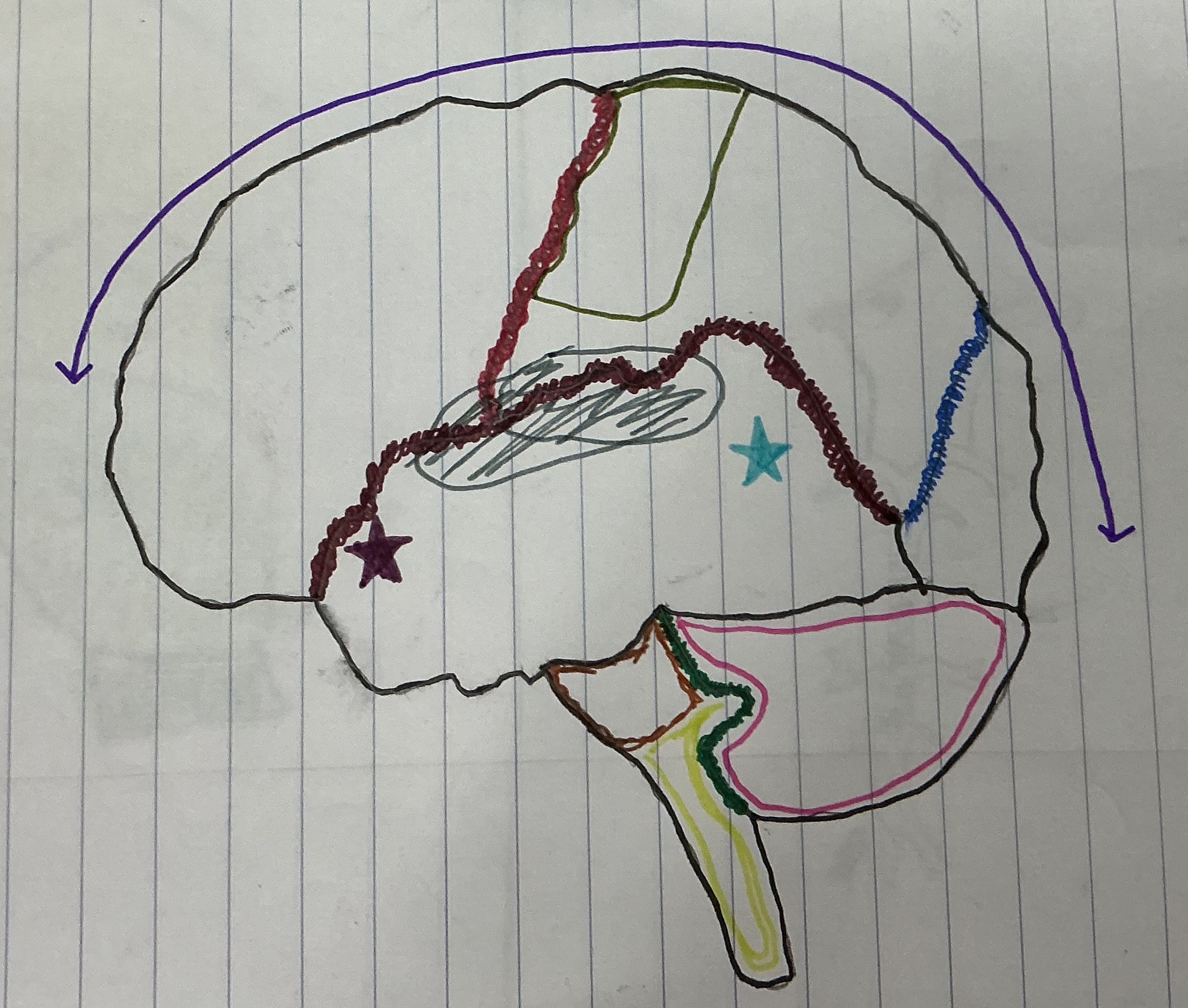
What color is the area that holds the sensory and motor strip
Dark green
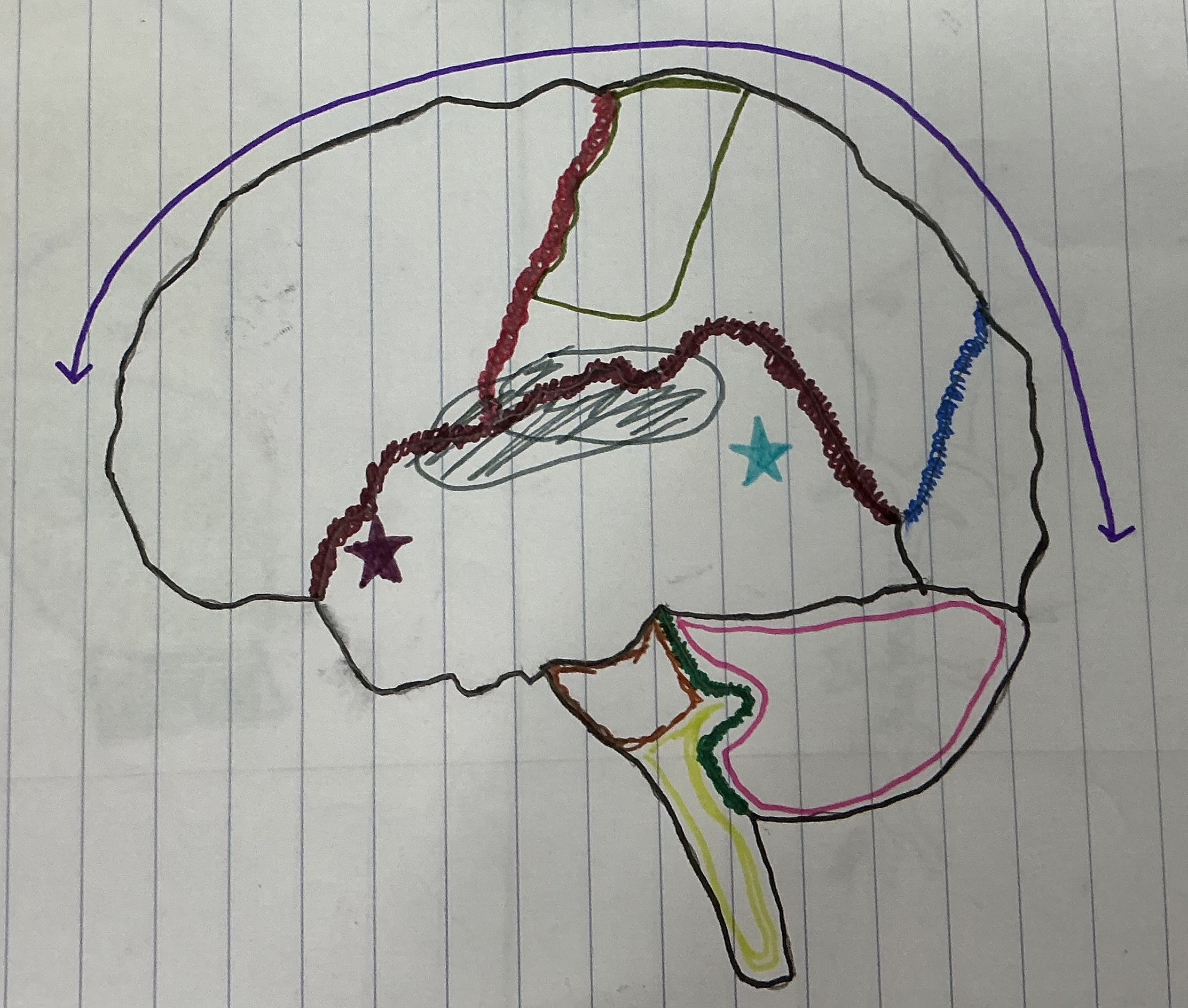
What color is Broca’s area?
Dark purple
What color is Wernicke’s Area?
Light blue
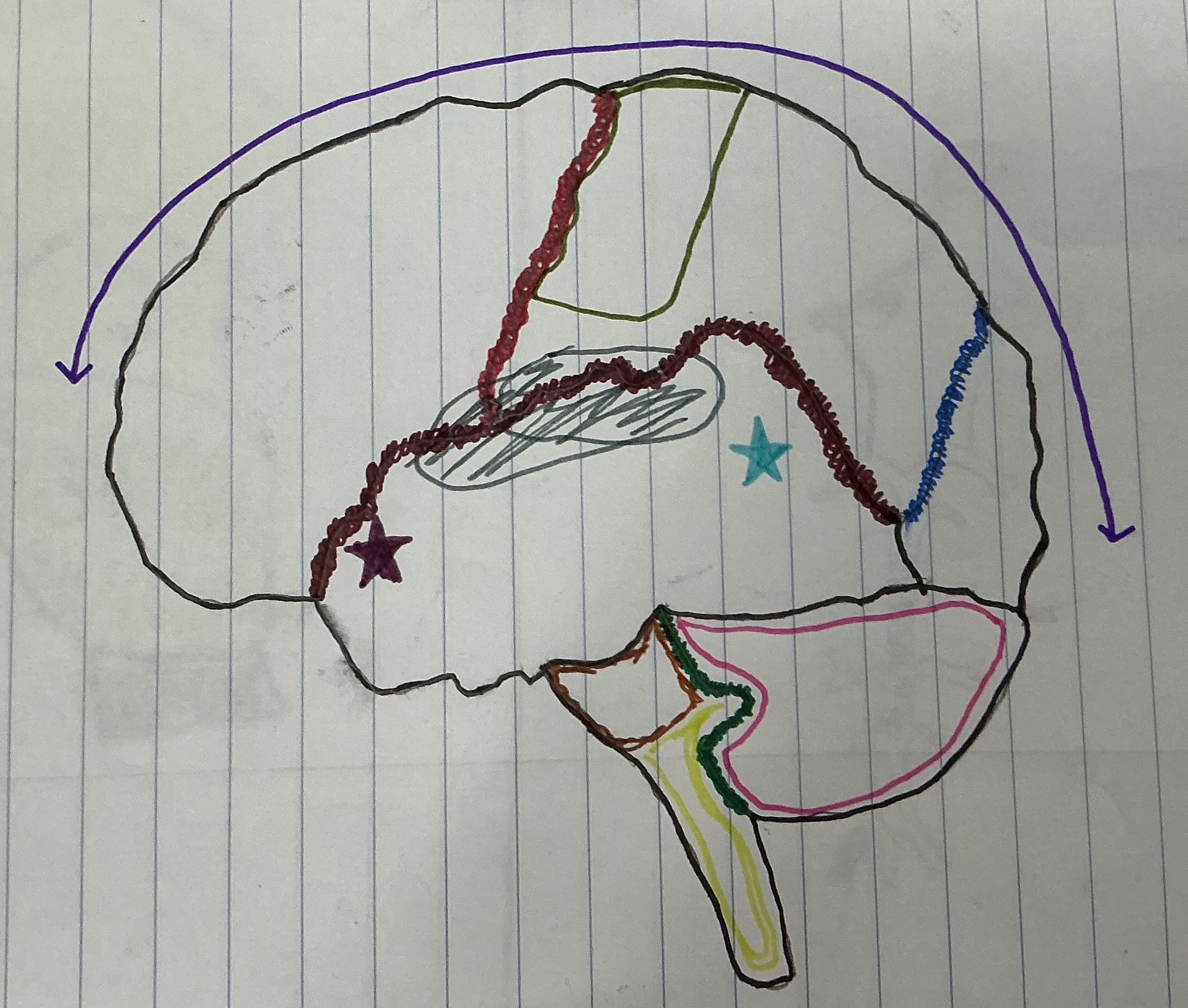
What color is the brain stem?
Light green
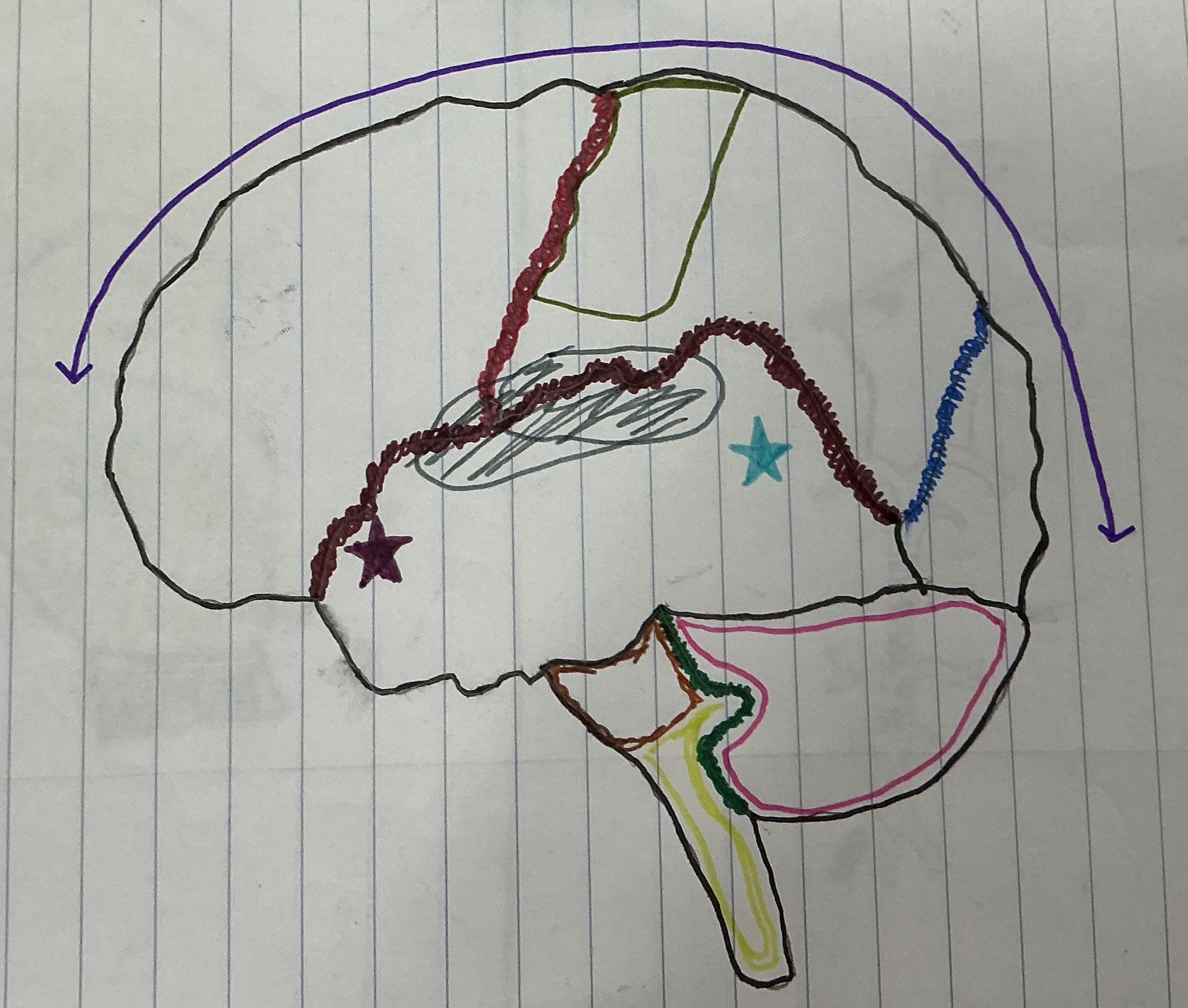
What color is the cerebellum?
Hot pink
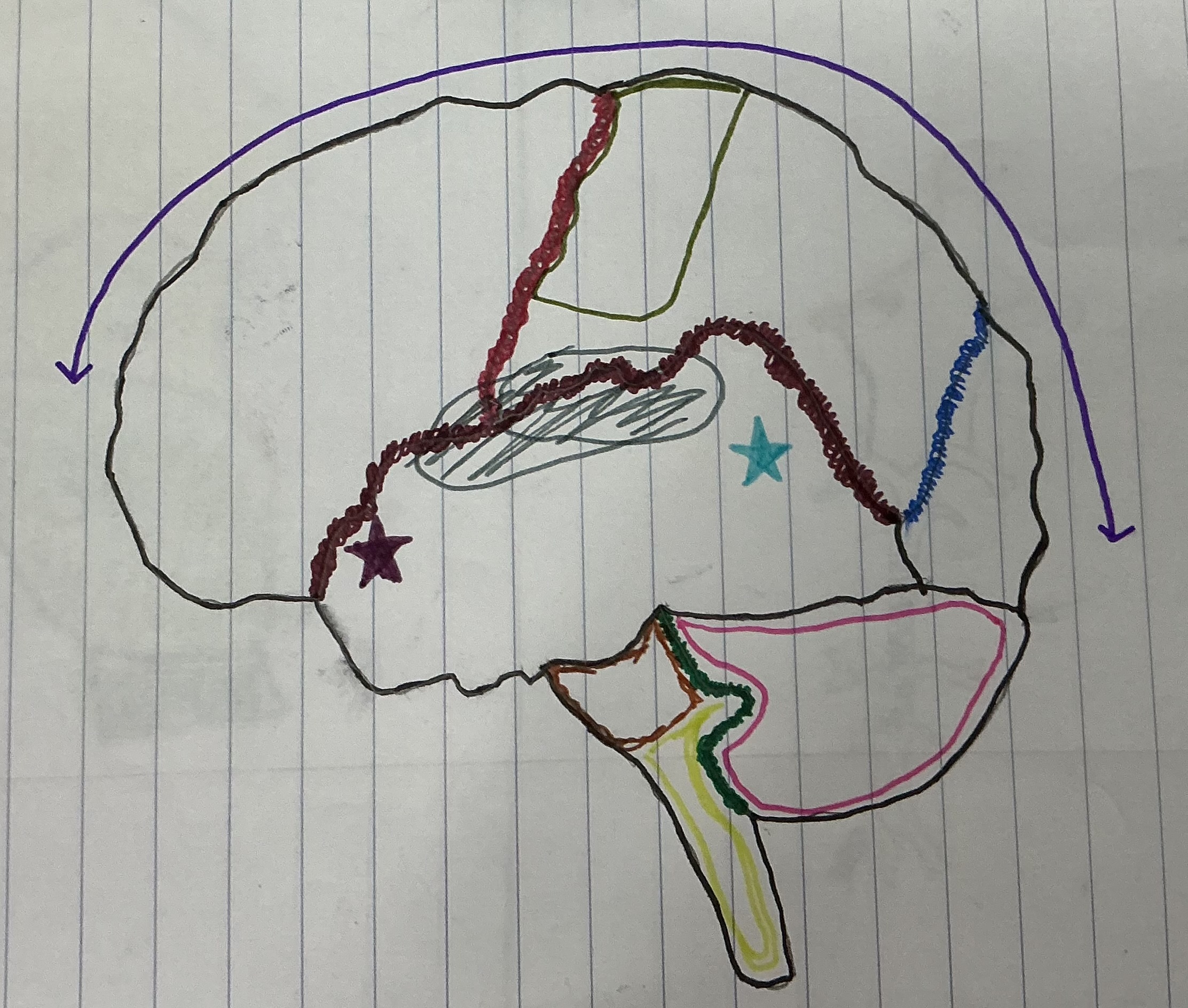
What color is the Pons
Brown
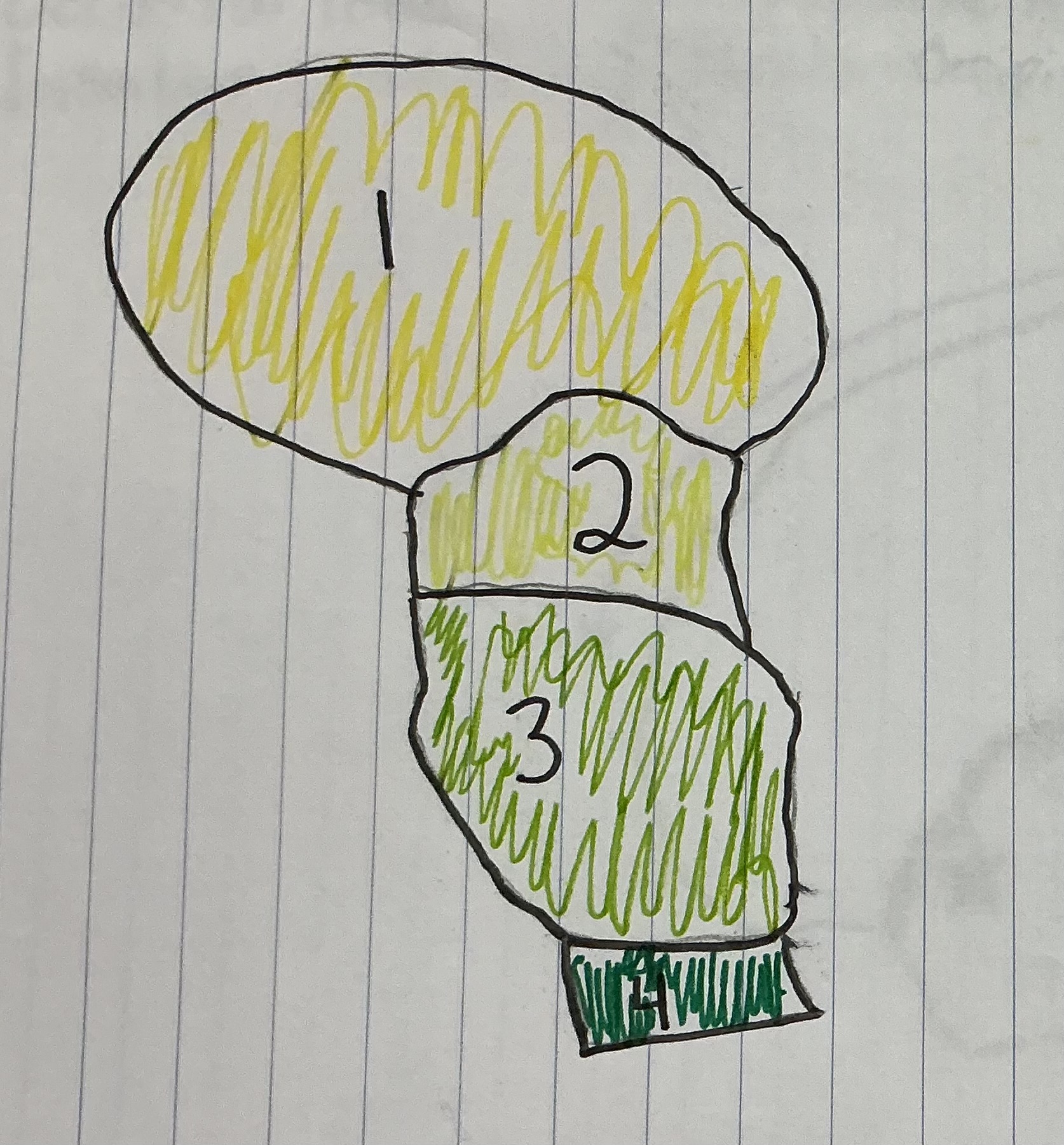

What number represents the Thalamus
1
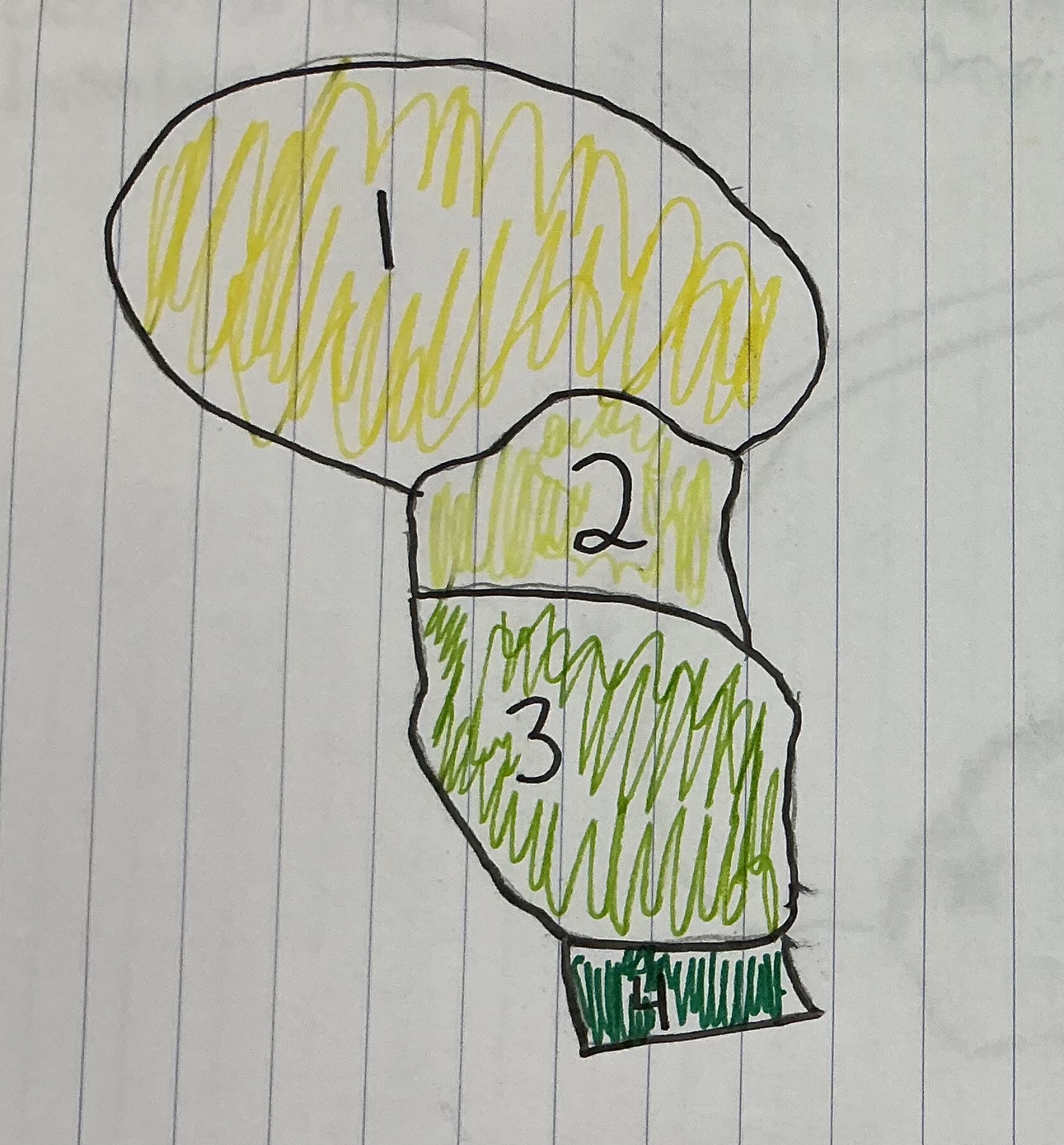

What number represents the midbrain
2
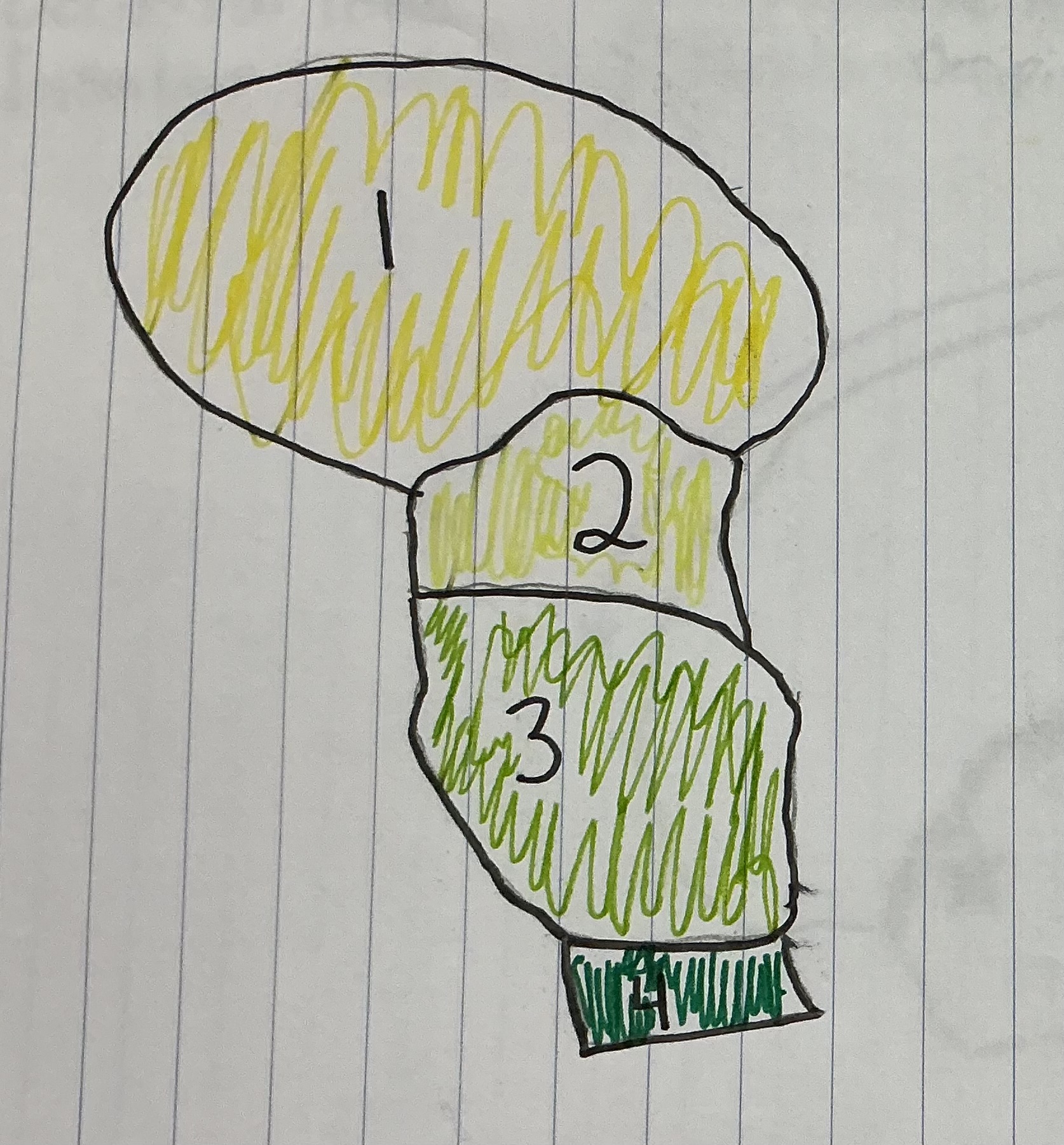

What number represents the Pons
3
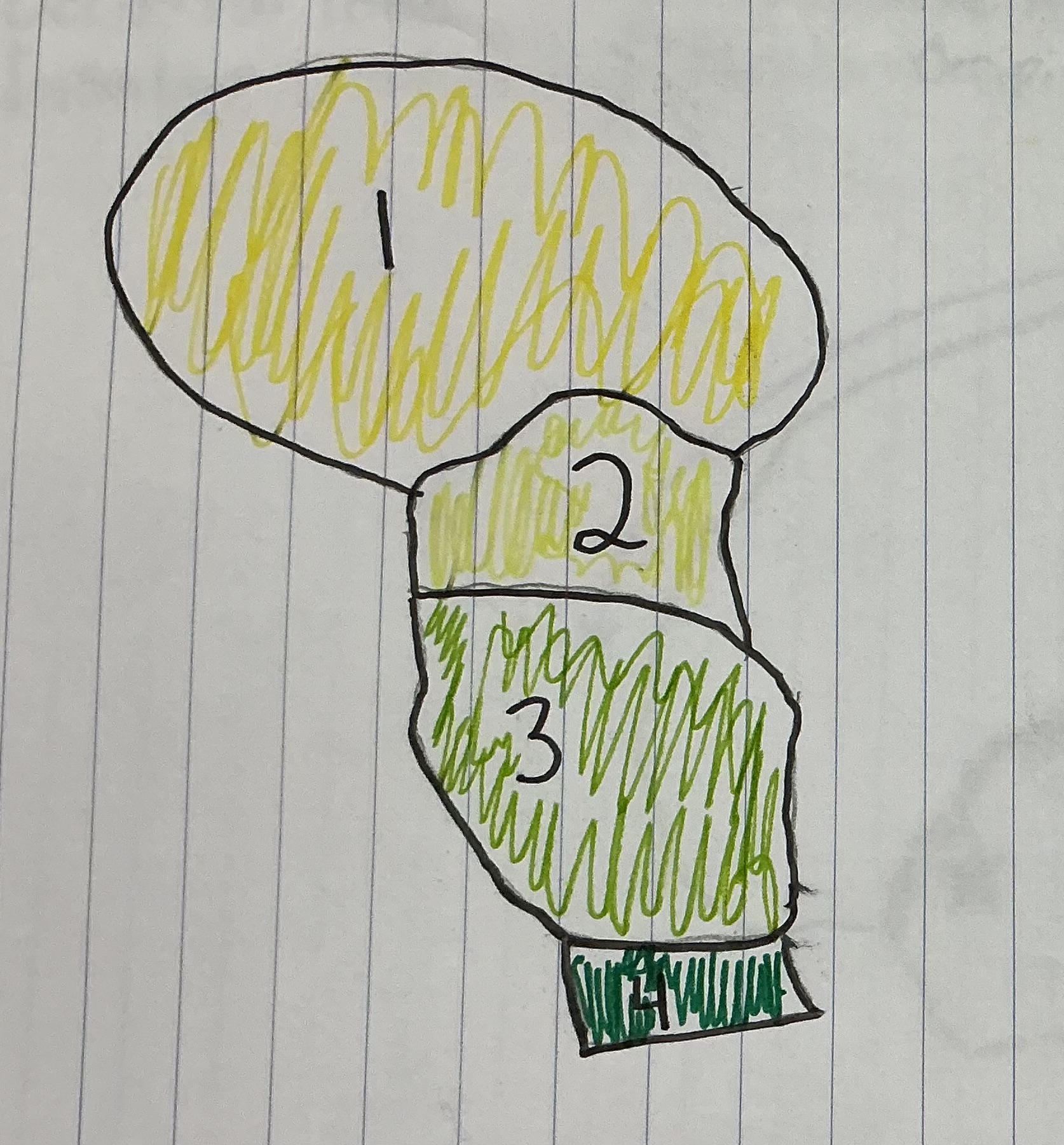

What number represents the Medulla
4
What does grey matter do in the brain?
Process information, muscle control, sensory perception
What does the white matter do?
Composed of Myelin Axons. Used as communication pathways in the brain.
What are functions of the Frontal lobe
Motor/Planning, executive function, attention
What are the functions of the parietal lobe?
Processes sensory (touch, smell, pain), Spatial awareness
What are the functions of the Temporal Lobe
Auditory processing, language comprehension, emotional responses
What are the functions of the Occipital lobe?
Vision
What are the functions of the Cerebellum?
Coordination, balance
What are the functions of the brain stem?
Basic consciousness, sleep, heart rate, blood pressure
What are all four lobes of the brain together called?
Cerebrum
Where are upper motor neurons located?
Brain and spinal cord
Where are lower motor neurons located?
Everywhere but the brain and spinal cord
What is the somatic nervous system
Voluntary efforts such as skeletal muscle
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Involuntary efforts, such as your heart beating or your lungs breathing automatically.
What direction does sensory information go towards
Afferent pathway
What direction does motor information go towards
Efferent pathway
What types of synapses occur in the anterior gray of the spinal column?
Motor
What type of synapses occur in the poster gray of the spinal column?
Sensory
Do motor functions run ipsilateral or contralateral from brain to body?
Contralateral
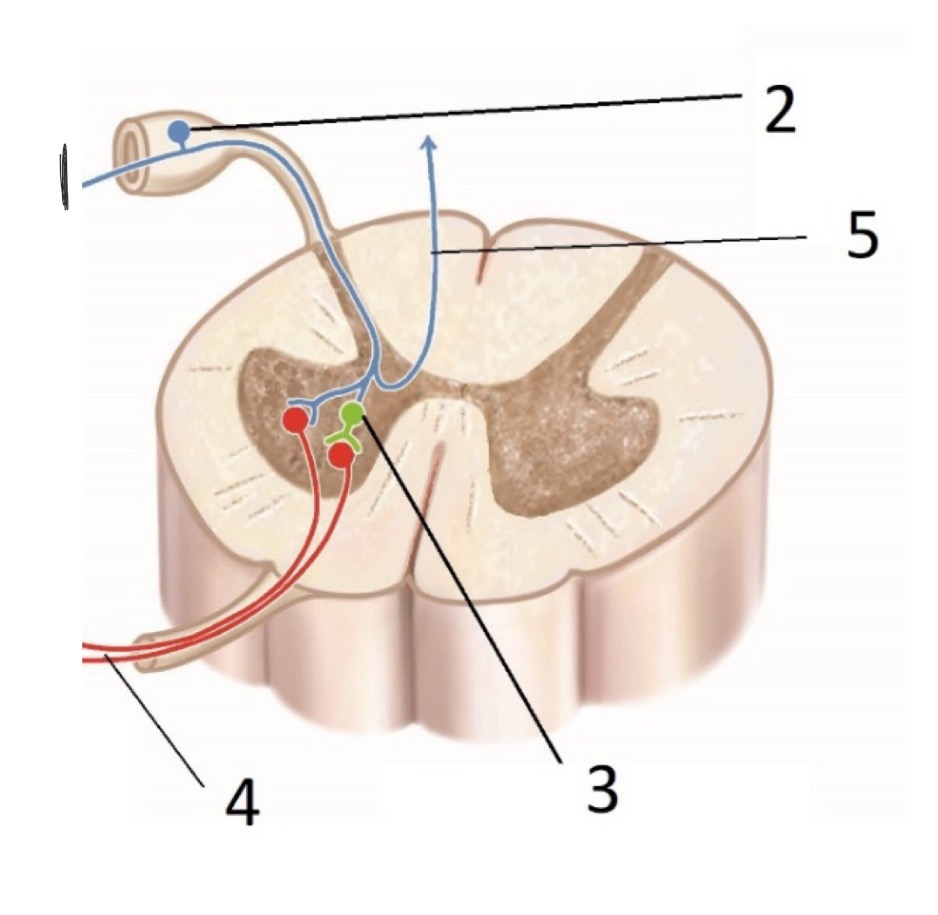
What is #1 (Sensory receptor)
PAN - Peripheral Afferent Neuron
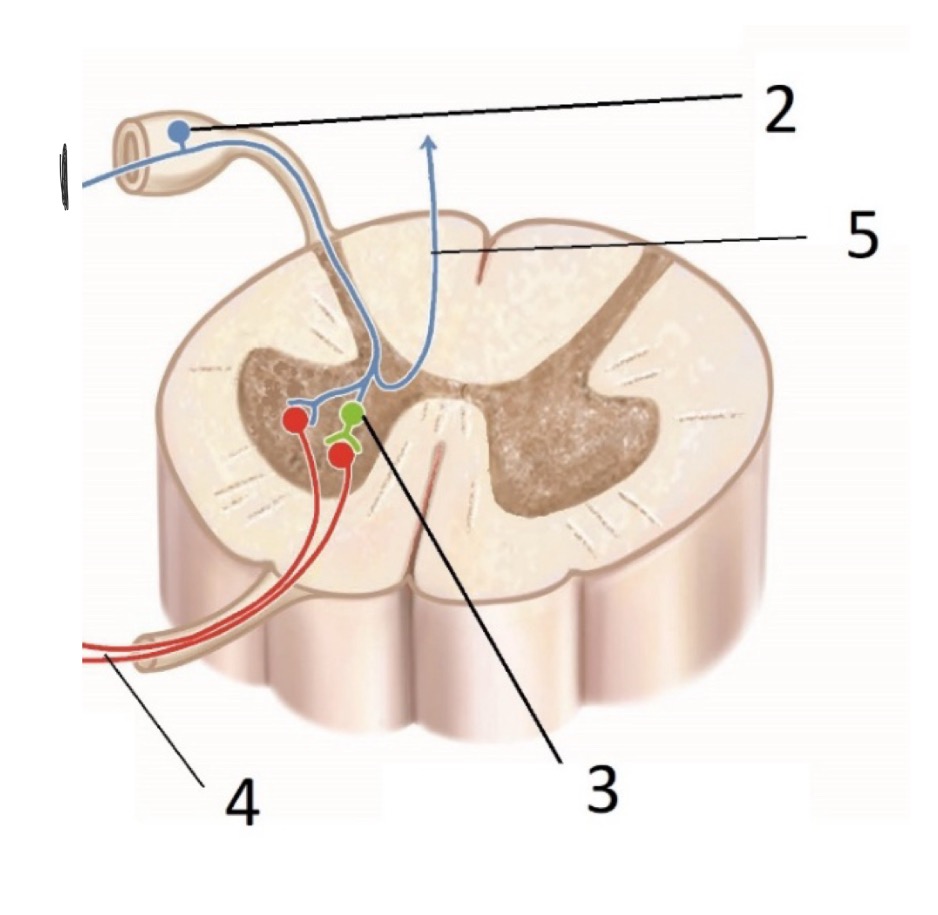
What is #2 (Sensory receptor)
Dorsal root Ganglion
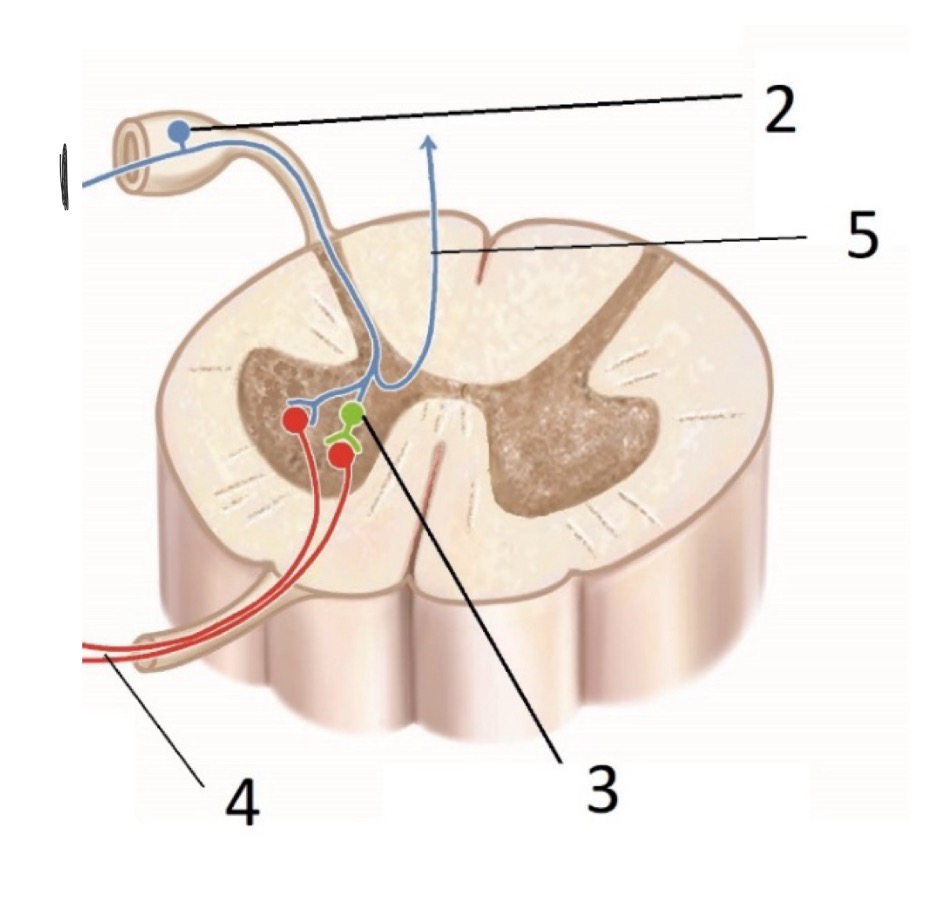
What is #3? (Sensory receptors)
Interneuron
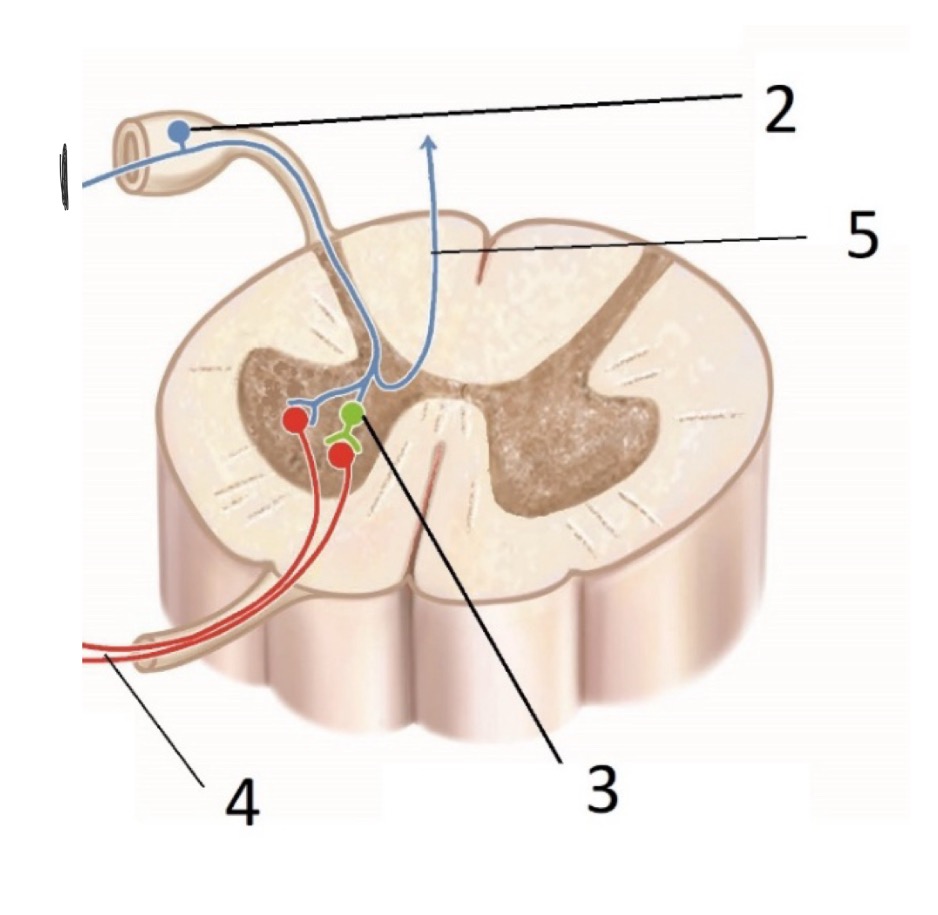
What is #4? (Sensory receptors)
LMN - Lower Motor Neuron
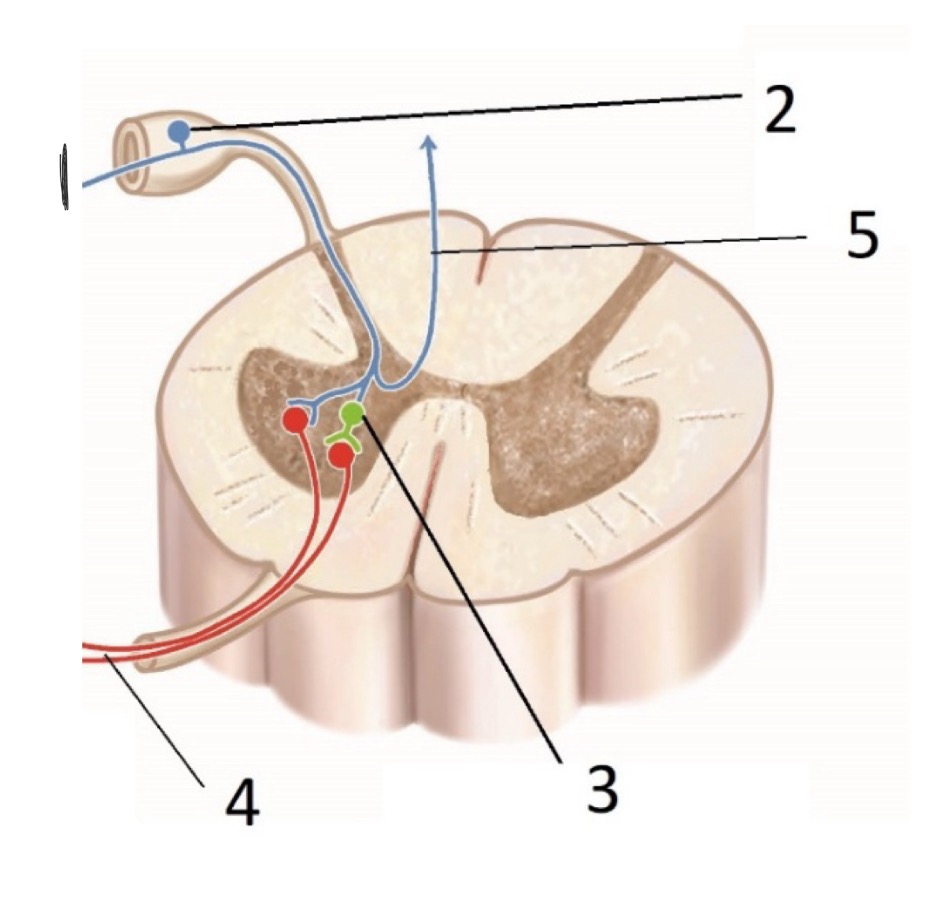
What is #5? (Sensory Receptors)
CAN - Central Afferent Neurons
What is the first meningeal layer?
Dura Matter
What is the structure of the Dura Matter?
Leathery and tough
What is the second meningeal layer?
Arachnoid Layer
What is the structure of the Arachnoid layer?
Webbed, honeycomb like
What is the third meningeal layer?
Pia Matter
What is the structure of the Pia Matter?
Thin milky fluid veil that coats the cerebral cortex
You’re doing great my friend
Yeah I am!!!

What ventricle is #1
Lateral Ventricle / Body ??
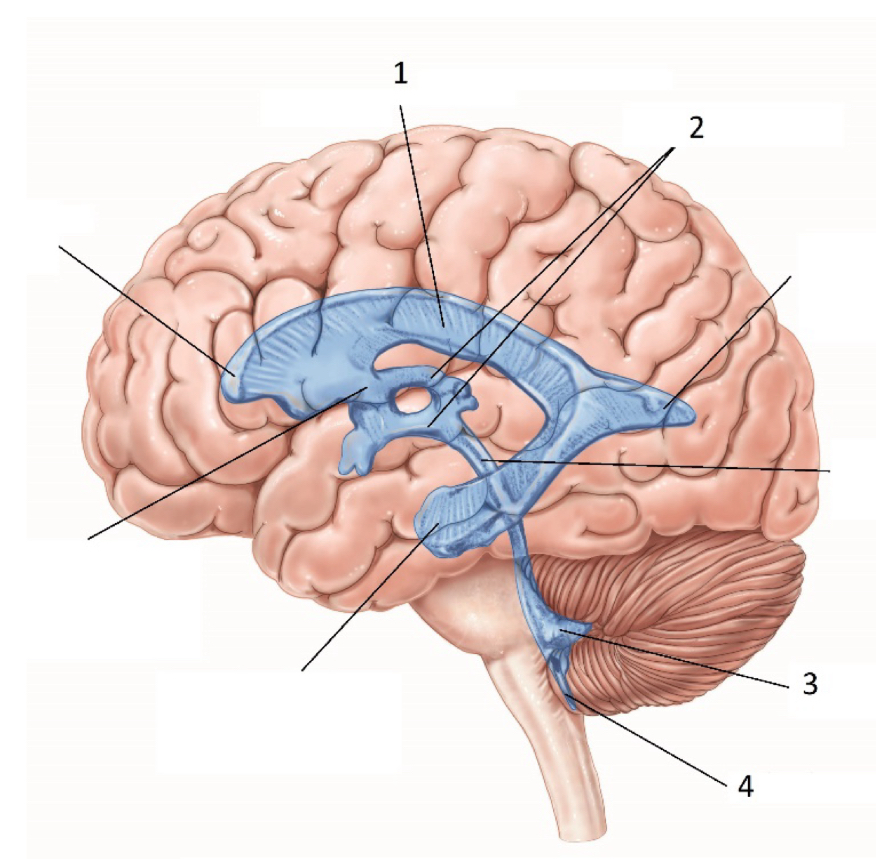
What ventricle is #2
3rd ventricle
What ventricle is #3
4th Ventricle
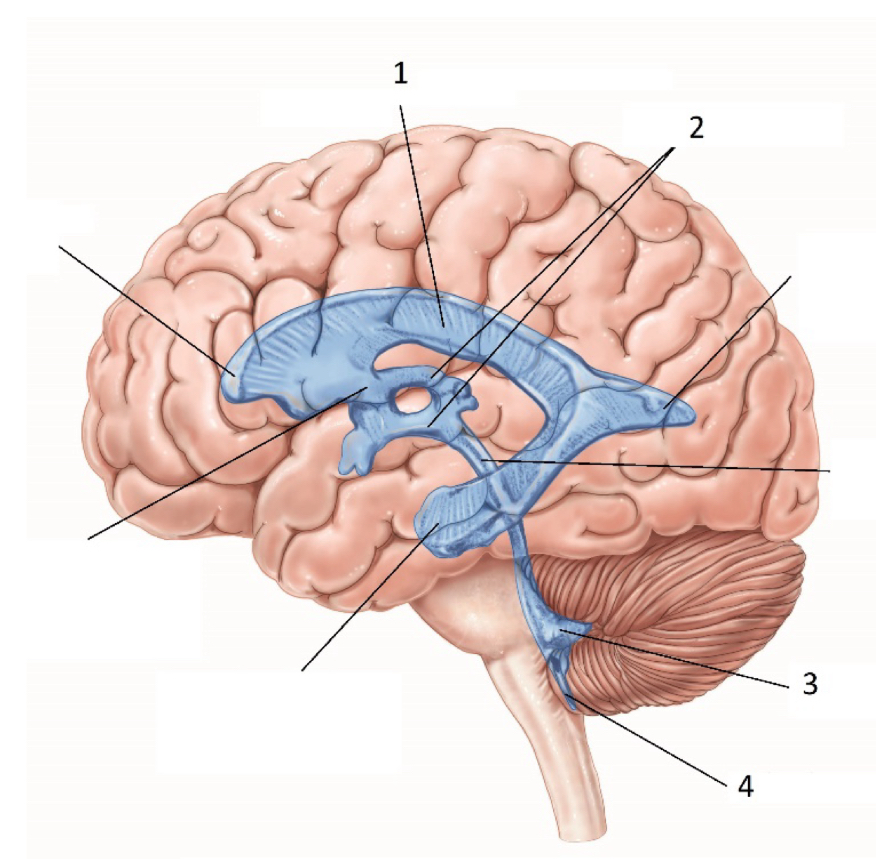
What structure is #4
Foramen of Magendie
What is CSF
Cerebral Spinal Fluid
What does Cerebral Spinal Fluid do?
Buoyancy, protection, nutrients, recycling waste
What are the four points of weakness?
Hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, blood brain barrier, basal ganglia
What are the three types of Basal Ganglia disorders?
Hypokinetic, Hyperkinetic, or a mixture
Symptoms of a hypokinetic disorder
Reduced movements
What is an example of a hypokinetic disorder?
Parkinson’s
What are the symptoms of a hyperkinetic disorder?
Excessive or Extraneous movements
What is an example of a hyperkinetic disorder?
Huntingtons
What blood supply affects speech?
MCA - Middle Cerebral Artery
What blood supply affects executive function?
ACA - Anterior cerebral Artery
What blood supply affects vision?
PCA - Posterior Cerebral Artery