IB Biology: Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen.
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules, basic carbohydrate units.
Pentose Sugars
Monosaccharides with five carbon atoms.
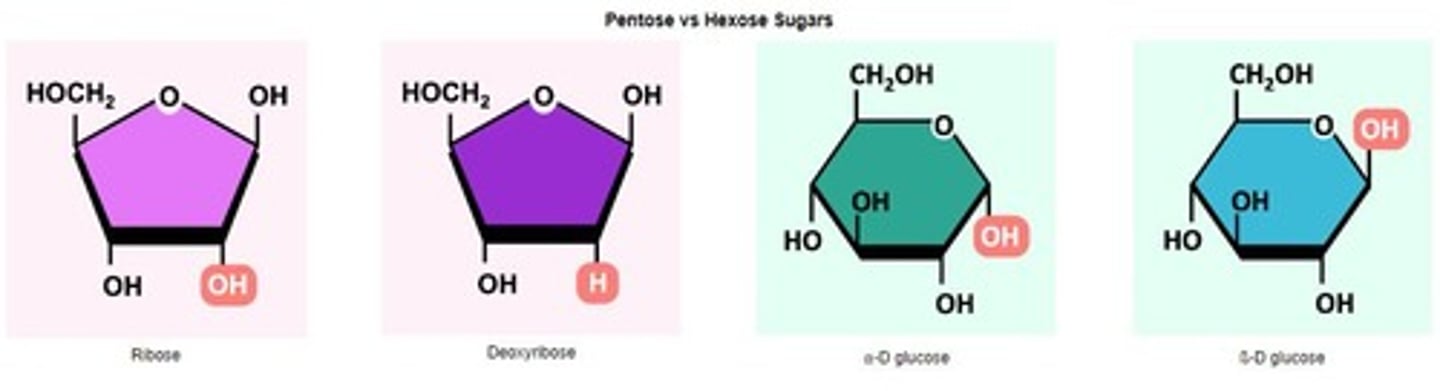
Hexose Sugars
Monosaccharides with six carbon atoms.
Ribose
Pentose sugar in RNA nucleotides.
Deoxyribose
Modified ribose lacking one oxygen atom.
Glucose
Primary energy source for cellular respiration.
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula but different structures.
⍺-D Glucose
Isomer of glucose with specific hydroxyl orientation.
ß-D Glucose
Isomer of glucose with different hydroxyl orientation.
Energy Source
Primary function of monosaccharides in cells.
Cellular Respiration
Process of breaking down glucose for ATP.
Hydrophilic
Substance that dissolves easily in water.
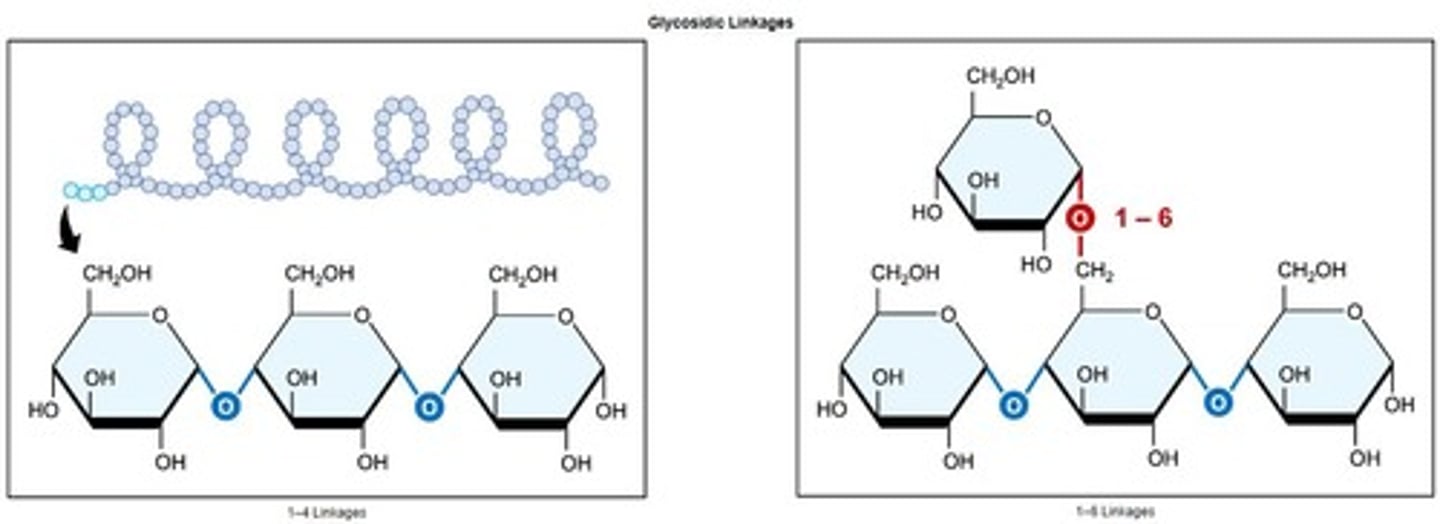
Glycosidic Linkage
Bond formed between monosaccharides in carbohydrates.
Disaccharide
Two monosaccharides linked together.
Polysaccharides
Carbohydrate polymers made of many monosaccharides.
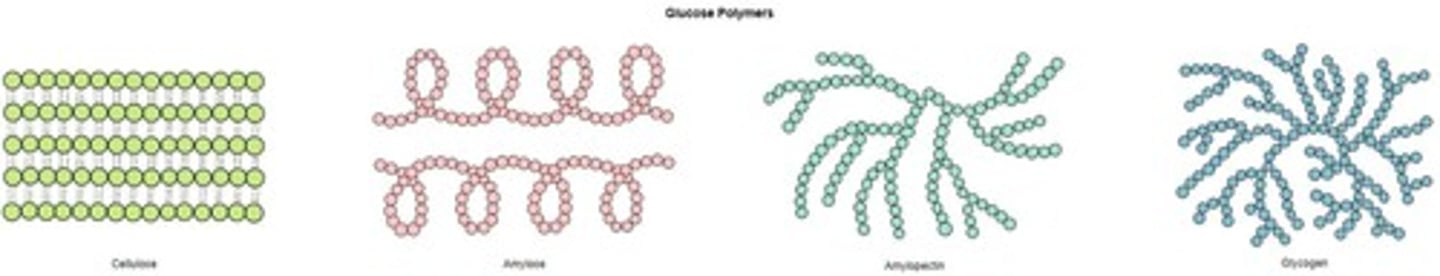
Cellulose
Polysaccharide made of ß-glucose subunits.
Starch
Polysaccharide of ⍺-glucose, energy storage in plants.
Glycogen
Highly branched polysaccharide for energy storage in animals.
Amylose
Unbranched form of starch with helical structure.
Amylopectin
Branched form of starch with both linkages.
Energy Storage Polymers
Polysaccharides used for storing energy.
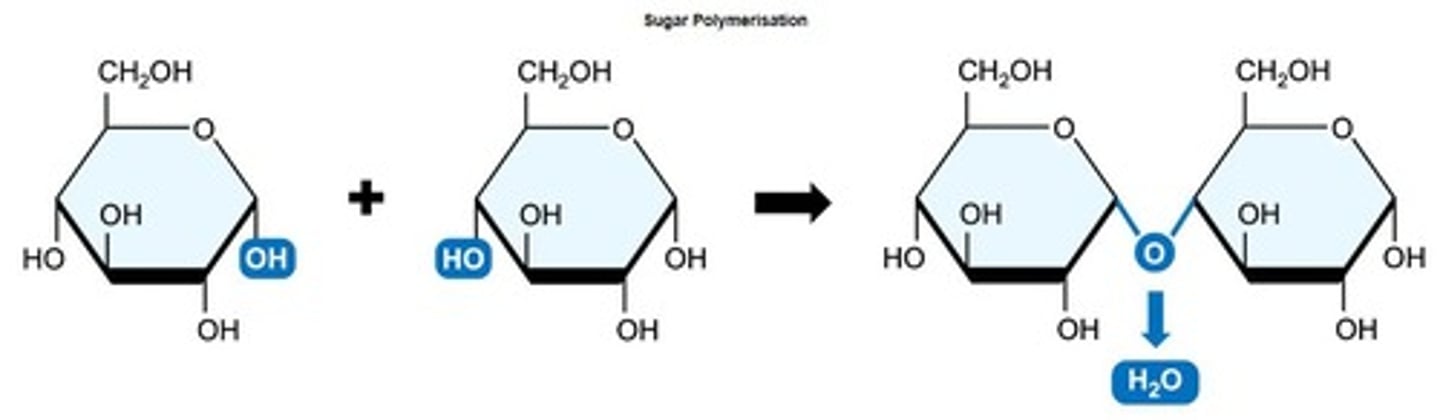
Condensation Reaction
Process linking monomers, releasing water as by-product.
Hydrolysis Reaction
Process breaking down polymers into monomers.
Glycosidic linkages
Covalent bonds linking sugar monomers in polysaccharides.
Starch
Polysaccharide composed of amylose and amylopectin.
Amylose
Linear starch form with 1' - 4' linkages.
Amylopectin
Branched starch form with 1' - 4' and 1' - 6' linkages.
Cellulose
Structural polysaccharide in plant cell walls.
Beta-glucose
Monomer unit of cellulose with alternating arrangement.
Hydrogen bonds
Attractive forces stabilizing cellulose bundles.
Glycoproteins
Proteins with carbohydrate attachments for cell recognition.

Glycosylation
Process of adding carbohydrates to proteins.
Blood group A
Contains type A glycoproteins on red blood cells.
Blood group B
Contains type B glycoproteins on red blood cells.
Blood group AB
Possesses both type A and B glycoproteins.
Blood group O
Lacks A and B glycoproteins on red blood cells.
Hydrophobic properties
Characteristics of lipids that repel water.
Fatty acids
Hydrocarbon chains forming the basis of lipids.
Amphipathic molecules
Molecules with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions.
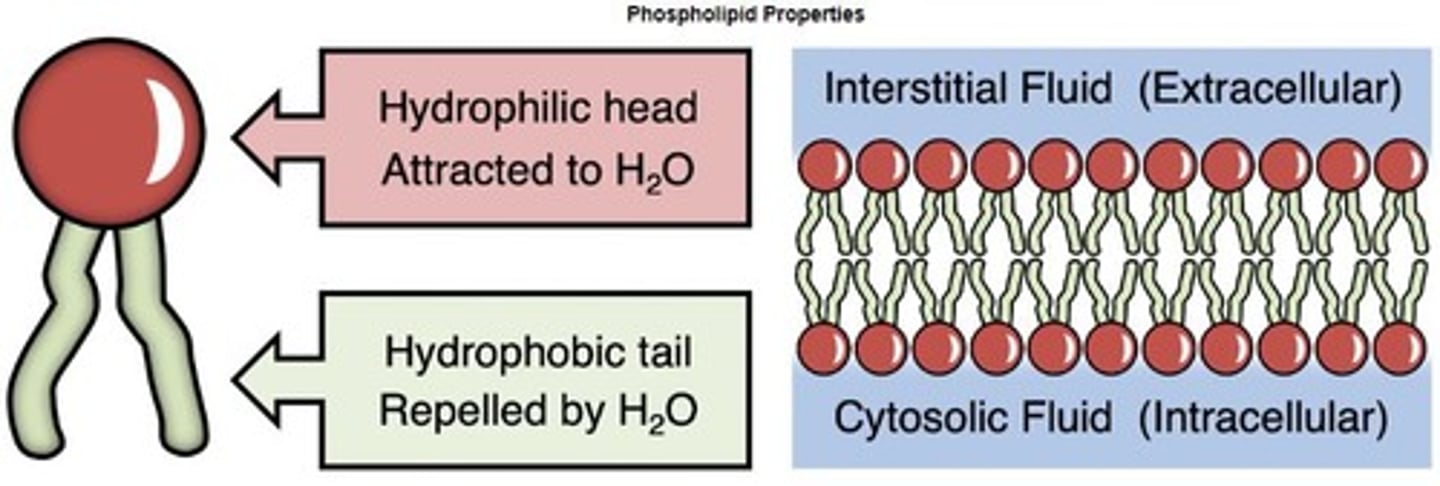
Phospholipids
Lipids forming cell membranes with hydrophilic heads.
Triglycerides
Lipids formed from glycerol and three fatty acids.
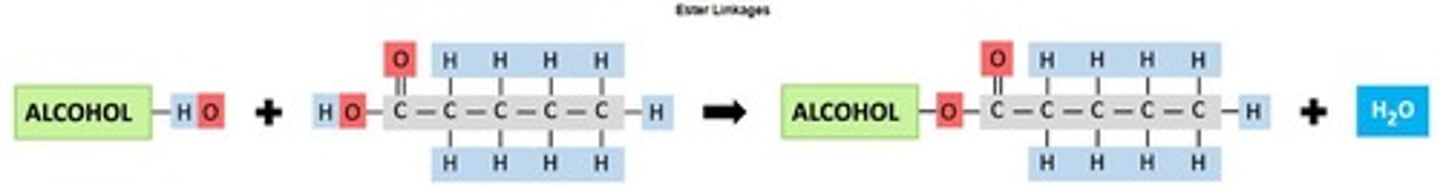
Condensation reactions
Chemical reactions forming esters by removing water.
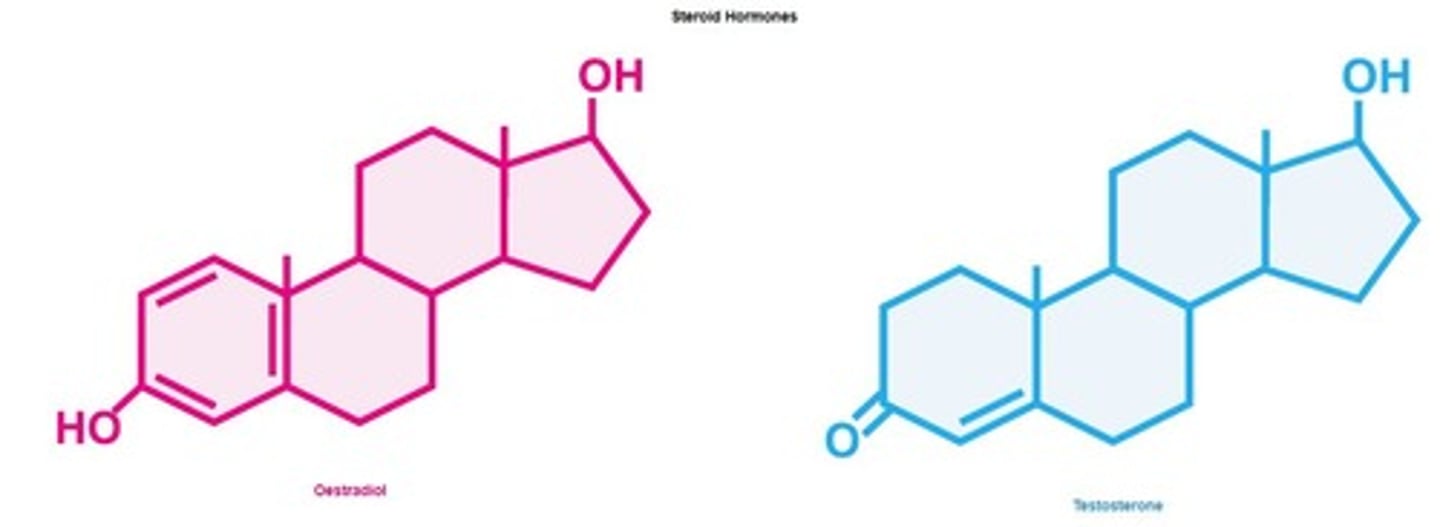
Steroid hormones
Lipids acting as signaling molecules in the body.
Lipoproteins
Protein-coated fat packages for transport in blood.
Cholesterol
Steroid lipid with a polar hydroxyl group.
Ester Linkage
Bond formed between fatty acids and alcohols.
Triglycerides
Three fatty acids linked to glycerol for energy storage.
Phospholipids
Glycerol linked to two fatty acids and phosphate.
Glycolipids
Carbohydrate linked to fatty acids and alcohol.
Simple Lipids
Esters of fatty acids and alcohols, e.g., triglycerides.
Waxes
Fatty acid linked to long-chain alcohol, waterproofing.
Compound Lipids
Esters of fatty acids with additional groups.
Derived Lipids
Produced from hydrolysis of simple or compound lipids.
Fatty Acids
Long hydrocarbon chains found in most lipids.
Saturated Fatty Acids
No double bonds, straight hydrocarbon chains.
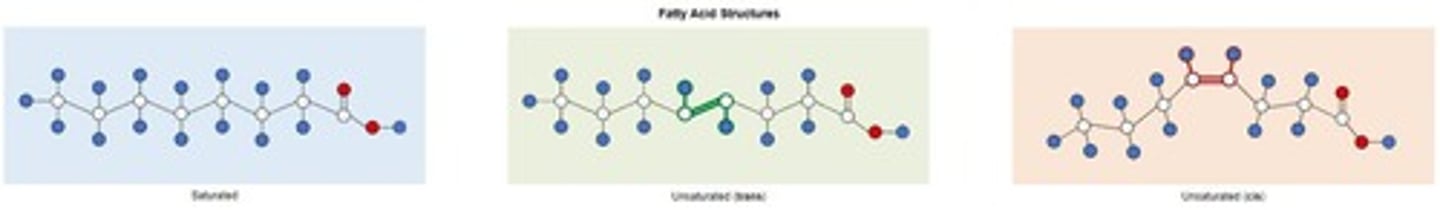
Monounsaturated Fatty Acids
One double bond in hydrocarbon chain.
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Multiple double bonds in hydrocarbon chain.
Cis Isomers
Hydrogens on the same side of double bond.
Trans Isomers
Hydrogens on opposite sides of double bond.
Fats
Saturated fatty acids, solid at room temperature.
Oils
Unsaturated fatty acids, liquid at room temperature.
Hydrocarbon Chain
Chain of carbon atoms in fatty acids.
Melting Point
Temperature at which a substance becomes liquid.
Intermolecular Forces
Attractive forces between molecules affecting states.
Energy Storage
Function of triglycerides in living organisms.
Cell Membranes
Phospholipids are key components of cell membranes.
Signalling Molecules
Derived lipids like steroids and prostaglandins.
Ruminant Animals
Produce trans fatty acids, e.g., cows and sheep.

Fatty Acids
Essential for liquid state at body temperature.
Saturated Fats
Solid fats produced by endotherms at higher temperatures.
Cis-Unsaturated Oils
Liquid oils produced by ectotherms in cold environments.
Poly-Unsaturated Fats
Essential fats like omega-3 and omega-6 from cold water fish.
Triglycerides
Energy storage molecules in adipose tissues.
Energy Storage
Triglycerides store twice as much energy as carbohydrates.
Thermal Insulation
Triglycerides provide insulation against cold exposure.
Phospholipids
Key structural components of cell membranes.
Amphipathic
Molecules with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Formed by phospholipids shielding hydrophobic tails.
Steroids
Lipids with four fused carbon rings, non-polar.
Steroid Hormones
Signalling molecules that diffuse across cell membranes.
Hydrophobic
Molecules that repel water and do not dissolve.

Carrier Proteins
Transport steroid hormones in the bloodstream.
Cholesterol
Precursor for steroid hormone synthesis.
Subcutaneous Fat
Insulating fat layer in cold-adapted mammals.
Obesity and Heat Stress
Obese individuals retain heat, increasing heat stress risk.
Glycerol
Component of phospholipid polar heads.
Fatty Acid Chains
Non-polar tails of phospholipids.
Hydrophilic Head
Water-loving part of phospholipids.
Hydrophobic Tails
Water-repelling part of phospholipids.
Aquatic Mammals
Have thick fat layers for thermal insulation.
Oestradiol
A type of estrogen, a sex steroid.
Testosterone
A male sex steroid hormone.