Unit 3
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
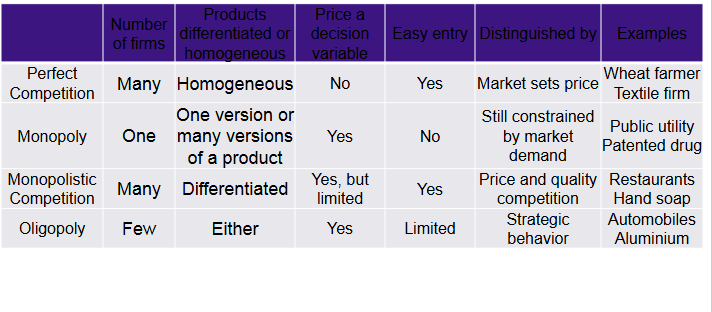
what is oligopoly
when few dominant firms
products can be homogeneous or different
what are forces that affect competition in oligopoly
suppliers
buyers
substitutes
potential entrants
what does it mean when a market is perfectly contestable
there are no barriers to entry, if Oligopoly is this, it is like a perfectly competitive market
what is a cartel (basically monopoly)
a group that sets the price and quantity of a product in the market
like drug cartel
what is game theory
the idea that your outcome depends on other people’s actions
what is strategy
a complete and contingent plan
You know what you will do in every situation
what is dominant strategy
when you take the same action no matter what the opposition does
what is bridge-crossing dilemma
when you don’t have a complete strategy
what is demand schedule
a table with the prices and quantities demanded
what is cournot model
basically duopoly
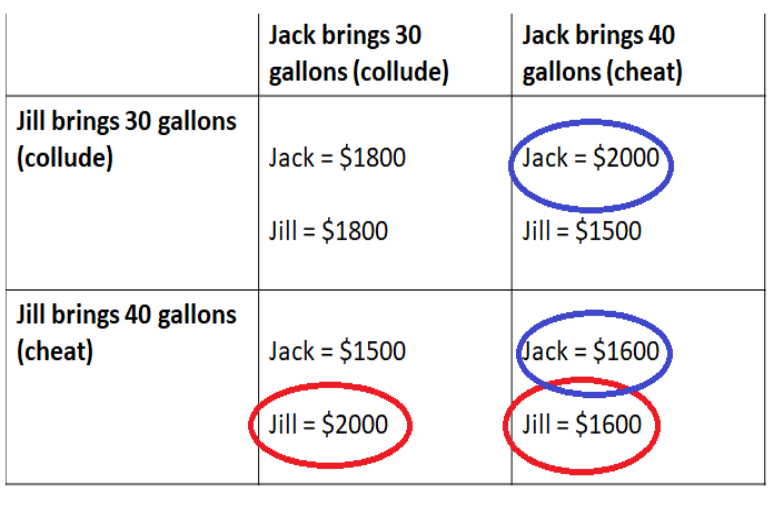
when deciding to collude (work together) or cheat (one firm sells more quantity of a product):
if one firm cheats
that firm earns more money
if both firms cheat
the firms earn the same amount, but less than if they colluded
what is nash equilibrium
when both firms in a duopoly play their best response/dominant strategy (best quantity to always max out their possible profit)
BASICALLY A BOX WHERE THERE ARE 2 CIRCLES
how can oligopoly behave?
like monopoly - cartel (control price and quantity)
oligopoly - normal
like perfectly competition - perfectly contestable (no barriers to entry)
what is best response
when you choose the action that gives you the highest payoff (can be different for each of the other player’s possible actions)
what are the antitrust stuff
mergers
what is merger
when one firm wants to buy another
the department of justice (DOJ) or federal trade commission (FTC) evaluates mergers
what are arguments in favor and against mergers
favor
efficiency
economies of scale or scope (scale is produce more good bc cheaper price, scope is costs go down if produce more than 1 type of product)
against
less competition
more power to charge a price higher than MC (P>MC)
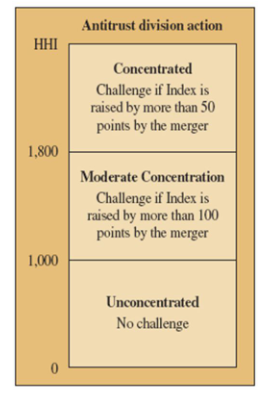
what is Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI)
index of market concentration
found by adding the square of % shares of firms in the market
results of HHI
if HHI > 1000
challenge merger if HHI goes up by 100 or more after merger
if HHI > 1800
challenge merger if it goes up by 50 or more after merger
what is in monopolistic competition
different products (“brand name”)
many firms
no barriers to entry
what is horizontal differentiation
personal opinions on different types of products
what is vertical differentiation
facts that makes some products better than others
are there profits in the long-run for monopolistic competition?
no
when do monopolistic competition firms produce in the long run
when PRICE > MC, thus they are inefficient
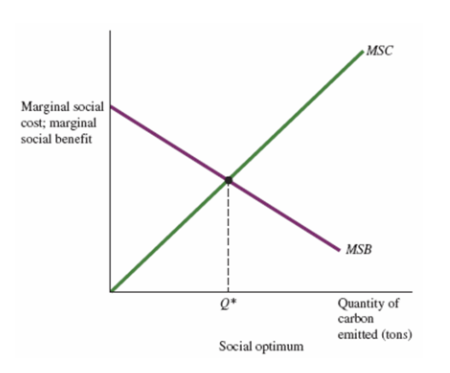
what is marginal social cost (MSC)
the cost of society caused by the production of an additional unit of a good or service
MSC = MC + MEC (marginal external cost)
what does social optimum graph look like
basically demand and supply curves
how to fix externalities
private bargaining and negotiation (coase theorem)
government regulations
taxes (for negative externalities) and subsidies ($ support for positive externalities)
sale or auction of rights to impose externalities (like creating a market for the problem, cap and trade)
what is coase theorem and what are 3 conditions for it
it is idea that sometimes the government doesn’t need to be involved to solve problems (mainly PROPERTY LAWS)
conditions
property rights
few people involved
clear communication (low transaction costs)
how to do cap and trade (reduce externalities)
the gov’t sets a limit for a good
the firm in the industry for the good that has the LOWEST cost should reduce its quantity
that firm can then sell their permits to the other firm in the industry, price depends on MC
how to find market demand for private vs public goods
private - add horizontally
public - add vertically
how to tell negative externalities based on a graph
the MSC (marginal social cost) line is to the LEFT of MC curve
how to tax to fix negative externalities
tax the market so that MC + tax = MSC
what is cap and trade example
MC are the numbers in the boxes
firm B would save 6 dollars if firm A sells the rest of its permits (6,3,1)

what should total willingness to pay equal
MC
what is tiebout hypothesis
public goods are affected by consumer preferences, which are based on housing prices
what is expected value
each payoff weighted by the probability of something occurring (basically weighted average)
what is risk-averse
when someone prefers an option that is certain rather than an uncertain one
what is risk-neutral
when a person likes options that have expected value of 0
what does risk-averse, neutral, and loving look like on graph
averse - decreasing slope (exponential decrease)
neutral - constant positive slope (linear increase)
loving - increasing slope (exponential increase)
what is averse selection
when there is asymmetric information and one high-quality product is taken out of a market bc the seller cannot prove its high quality
what is a moral hazard
when people in a contract change their behavior in response to that contact (like when seatbelts were made, ppl drove faster)
what is progressive tax
a tax that makes income distribution more equal (usually rich ppl pay)
what is regressive tax
a tax that makes income distribution less equal (usually poor ppl pay)
what is expected utility
the sum of all utilities, which weighs the probability of events occuring.