Lectures 10-18
1/299
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
300 Terms
What are clinical signs of abdominal pain?
Decreased appetite
Abnormal posture (stretching, arched back)
Kicking at the abdomen
Repeatedly lying down and getting up
Restlessness
Lethargy
What clinical signs of abdominal pain are more common in SA?
Tender/tense on abdominal palpation
Reluctant to move, stilted gait
Whine
Excessive salivation
Play / prayer pose
What clinical signs are more common in ruminants?
Grinding teeth (bruxism)
Grunt/groan
Abdominal distension
What clinical signs of abdo pain are more common in horses?
Colic
Pawing
Sweating
Quivering upper lip
Flank watching
Kicking at abdomen
What GI mechanisms cause abdominal pain?
Distention / stretch of intestinal wall
Mesenteric tension
Inflammation
Ischemia
Spasm
Deep mucosal ulceration
What are some non-obstructive causes of colic?
Spasmodic / gas colic
Proximal enteritis
IBD
Colitis
Sand (can be obstructive)
Peritonitis
Gastric ulcers
What are some simple obstructive causes of colic?
Stomach impaction - rare
Small intestinal impaction - ileum
Ascarid impaction - foals
Eosinophilic enteritis - mural bands
Large colon impaction - common
Large colon displacement - R/L dorsal
Enteroliths - alfalfa diet
Cecal impaction
Small colon impaction
What are some strangulating causes of colic?
Strangulating lipoma of small intestine
Small intestinal volvulus
Mesenteric rent
Epiploic foramen entrapment
Gastrosplenic entrapment
Intussusception
Large colon torsion
Strangulating lipoma of small colon
What is the diagnostic approach to abdominal pain?
Obtain a complete Hx
Perform a thorough PE
Eq: Rectal exam & NG tube
Assess severity
Cardio status, GI condition, recurrent signs of pain
Observe response to pain meds (fasted)
More advanced Dx PRN
Diagnosis → does p need surgery?
What are history questions or ask for abdo pain?
You already know this so here’s a picture lol

How do you perform a PE for abdo pain?
General appearance
Grade pain level if present
BCS & weight
General PE
TPR
Hydration/perfusion
GI auscultation / percussion
Eq: digital pulses
SA: abdo palpation
What diagnostics can you run for abdominal pain?
Blood gas
CBC/Chem
Imaging
Abdominal fluid analysis
Rectal palpation
NG tube for LA
What is the treatment for abdominal pain?
Remove feed
Control pain
Supportive care
Identify and treat primary dx
Surgery PRN
What are indications for surgery in patients with abdominal pain?
Diagnosis of strangulating lesion
Intestinal obstruction that does not respond to medical therapy
High level of pain / persistent pain
What is abdominal distention?
Enlargement of the abdomen due to various causes including:
Pregnancy
Obesity
Accumulation of fluid or gas
Accumulation of ingesta
Organomegaly
Mass
What is the definition of constipation?
Infrequent or difficult evacuation of hard, dry feces
What are causes of constipation?
Dietary - low fiber, indigestible material
Dehydration - decreased intake or increased loss
Obstruction - mechanical or functional
What are treatments for constipation?
Fluid therapy
Laxatives, cathartics
Address primary problem
What is colic?
A broad term referring to abdominal pain in horses, characterized by pawing, abdominal distention, sweating, etc.
Define tenesmus
Ineffective and repeated straining at defecation (or urination) resulting from disease of the large intestine or lower urinary tract
Define dyschezia
Difficult and/or painful evacuation of feces due to disease of the anus and perianal tissue
What are causes of tenesmus?
Inflammatory condition of lower GI
Hepatic failure (ruminants and horses)
Rectal Dx
Reproductive
Urinary - urolithiasis
What can tenesmus result in?
Rectal collapse
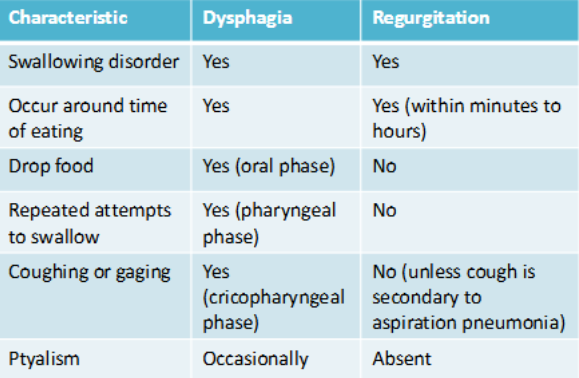
Define dysphagia
Difficulty or painful swallowing due to oral or pharyngeal disease
Define regurgitation
Passive retrograde expulsion of food or fluid from the oral/pharyngeal cavity or esophagus, not involving abdominal muscles.
Define vomiting
Forceful ejection of food or fluid through the mouth, from the stomach or proximal duodenum, involving abdominal muscle contraction
What does swallowing require?
Normal tongue and pharyngeal muscle motility
Normal innervation of tongue, pharynx, larynx, cricopharyngeal m., and upper esophagus
Need to sense bolus
How is swallowing initiated?
By voluntary passage of bolus into retropharynx. Once food is in pharynx, an involuntary pharyngeal phase is triggered
Swallowing is a complex reflex action requiring coordination of what 4 things?
Anatomic structures
Cranial nerves VII, IX, X, XII
Brain stem
Swallowing center in brain (medulla)
What are the 3 phases of swallowing?
Oropharyngeal
Esophageal
Gastroesophageal
What is the oropharyngeal phase?
The first phase of swallowing, comprising the oral (voluntary), pharyngeal (involuntary), and cricopharyngeal subphases
What occurs in the pharyngeal subphase of swallowing?
Contractions move bolus from tongue to cricopharyngeal passage
Soft palate is pulled upwards
Vocal cords approximated, epiglottis closes
Larynx is pulled cranially and ventrally
Begins opening of UES
What happens in the esophageal phase of swallowing?
Primary and secondary peristaltic waves move bolus
Define dysphagia
Difficult or painful swallowing; trouble when picking up food and forming a bolus
What are causes of dysphagia?
Pain during prehending or swallowing process
Mechanical obstruction of the oral cavity or pharynx
Neuromuscular dysfunction
Pharyngeal and cricopharyngeal dysphagia often accompany __________ ________ disorders
esophageal motility
What is an important zoonotic differential to keep in mind for dysphagia?
Rabies!
What are clinical signs of dysphagia?
Can have decrease or absent appetite
“Strange behavior” → turkey poking or gobbling
Dropping food while eating
Tilted head back
Chewing on one side
What are some common causes of dysphagia?
Congenital defects
Dental, periodontal Dx
Trauma
Inflammatory Dx
FB
Neoplasm
Disease - botulism, masticatory myositis, rabies, tick paralysis, etc.
What immune mediated Dx in cats can cause oral dysphagia? What do those cats commonly have that causes this?
Feline Lymphoplasmacytic Stomatitis;
Commonly have FIV ± calici virus
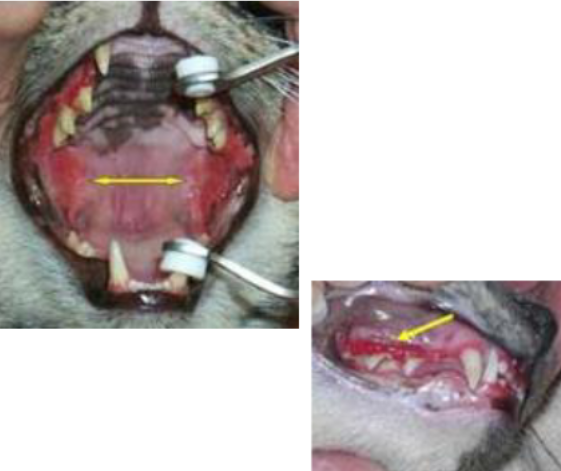
What is Feline Lymphoplasmacytic Stomatitis?
Severe lymphocytic / plasmocytic inflammation of gingival, periodontal structures, and pharynx
What is the treatment for Feline lymphoplasmacytic Stomatitis?
Partial or full-mouth tooth extraction
Medical management: antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory or analgesic medications
What is a Ranula?
A sublingual mucocele caused by rupture of sublingual salivary duct that causes accumulation of saliva and mucus at the base of the frenulum
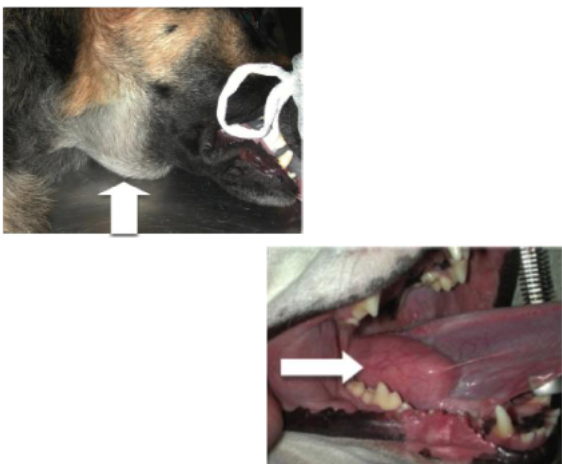
How does a ranula cause dysphagia?
Accumulation of saliva causes inflammatory and fibrous tissue which prevents normal tongue function
What is the treatment for a ranula?
Excising a portion of sublingual mucosa overlying the mucocele and suturing the rim of the oral mucosa to connective tissue ± removal of the mandibular and sublingual salivary glands
Define pharyngeal dysphagia
Trouble with the tongue bringing bolus back to the pharynx. Swallowing starts but is not completed
What is the diagnostic for pharyngeal and cricopharyngeal dysphagia?
Often distinguished with fluoroscopy
Define cricopharyngeal dysphagia
No relaxation of cricopharyngeal muscles. Problems with muscle that forms much of the UES
What are the 2 most common causes of pharyngeal and cricopharyngeal dysphagia?
Congenital abnormalities and neurological diseases (see picture for others)

When examining a patient with dysphagia, you need to watch them eat. How will a patient with oral dysphagia eat?
Difficulty BEFORE swallowing. Animal may tilt or throw head back while eating and drop food
When examining a patient with dysphagia, you need to watch them eat. How will a patient with pharyngeal dysphagia eat?
Chew normally. Repeated attempts to swallow, often with flexing and extending of neck
When examining a patient with dysphagia, you need to watch them eat. How will a patient with cricopharyngeal dysphagia eat?
Start to swallow then cough or gag. Bolus enters cricopharyngeus but it does not relax, bolus hits larynx and initiates cough
What diagnostics are performed for the dysphagic patient?
Complete PE
Neuro exam
Survey rads
CBC, Chem, UA
Contrast fluoroscopy motion study / endoscopy
How do you treat a dysphagic patient?
Identify and eliminate underlying disorder
Feeding tubes may be necessary at times
Treat secondary complications
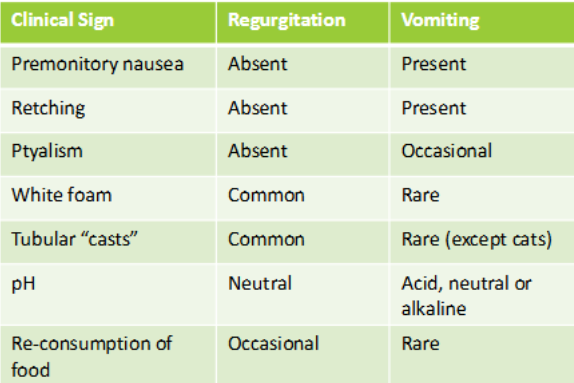
Define regurgitation. What does it produce?
Passive expulsion of gastric or esophageal contents resulting from local mechanical events within esophagus.
Produces undigested food, tubular shape, and frothy saliva.
What helps determine if regurgitation is proximal or distal? Explain each.
Timing helps determine location of problem:
Proximal = immediately after eating
Distal = up to several hours after eating
What are the clinical signs of regurgitation?
Appetite increased
Weight loss or poor growth
What causes regurgitation?
Megaesophagus
Esophagitis
Mechanical obstructions
Endocrine disorders
Neuropathies
Immune mediated
What type of vascular anomalies cause regurgitation?
Persistent right aortic arch is most common
Can be subclavian artery
What are common findings in patients with regurgitation from vascular anomalies?
Fibrous band encircling esophagus
Dilation of esophagus before the heart
What is the treatment for vascular anomalies causing regurgitation?
Surgery to remove fibrous band (may cause long term esophageal problems)
Vomiting is a ________ of _______ disease
hallmark;
gastric
Vomiting is a _______ NOT a _________
clinical sign;
disease
Where does vomiting occur from if it’s centrally mediated?
Vomit center in medulla oblongata - motor activity
CTZ on floor of 4th ventricle - BBB less effective here
*Discharge of CTZ stimulates vomit center.
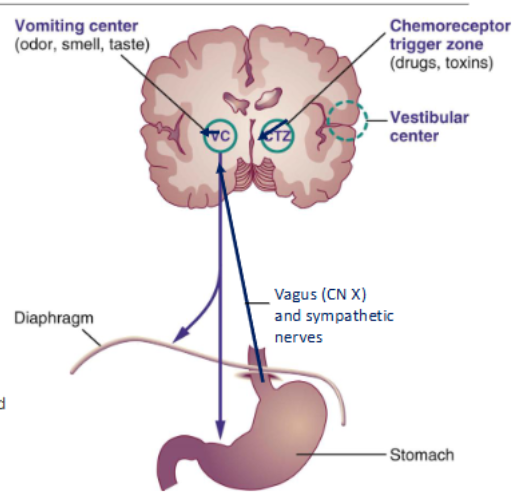
What activates receptors in the vomiting reflex?
Inflammation, irritation, distension, or hypersensitivity
What stimulates the vomiting reflex?
Directly: certain blood borne drugs, toxins
Indirectly: Afferent nerves or the CTZ
Abdominal viscera: impulses along afferent nerve fibers in vagus & sympathetic nerves
What are the phases of vomiting?
Nausea
Retching (contraction of abdo mm.)
Vomiting (+ pressure in thorax)
What is acute vomiting and who is it more common in?
Less than 7 days
May be more severe vomiting
Consider dietary indiscretion, gastritis, obstruction of GI tract, viral diseases
More common in younger dogs/cats
What is chronic vomiting and who is it more common in?
More than once a day for more than 5 days or twice a week for more than 2 weeks
More common in middle-aged to older animals because response takes time to develop
What are some complications of vomiting?
Fluid loss or dehydration
Electrolyte imbalance
Hypokalemia
Hypochloremia
Hyponatremia
Acid-base changes
Should NOT affect glucose
Graph for differentiating Dysphagia vs. Regurgitation
Graph for differentiating Regurgitation vs. Vomiting
Animals must maintain what in order to maintain proper function of their cells?
An aqueous environment
Aqueous and electrolyte components can be lost through what excretions?
Ocular, nasal, oral, urine, feces, sweat, and milk
What are evaporative losses?
The loss of water and electrolytes through the skin and respiratory tract, primarily due to sweating and breathing. This process is crucial for thermoregulation in animals
What 2 compartments do non-excretable body fluids exist in?
Intracellular and extracellular compartments
ECF can be subdivided into what?
Intravascular (IV-ECF) and extravascular/interstitial (EV-ECF)
What is the 3rd pool in which water exists in the body?
The transcellular fluid compartment
What charged particles are regulated in the ECF and the ICF?
ECF: Sodium, chloride, and albumin
ICF: Potassium and phosphate
Depleting the ________ pool of fluid may have a negative impact on the cardiovascular function and tissue perfusion WITHOUT actual dehydration
intravascular
Circle one: With severe enough changes in the ECF / ICF, electrolyte changes will also occur in the ECF / ICF
ECF; ICF
What mathematical equation has been a good estimator of ECF in adult and neonate LA? (Remember these are overestimates)
Adults: 0.3 x BW
Neonates: 0.5 x BW
What mathematical equation has been a good estimator of ECF in adult and neonate SA? (Remember these are overestimates)
Adults: 0.4 x BW
Neonates: 0.6 x BW
Most fluid plans can be divided into ____________ and ____________
Replacement and maintenance
Why are replacement fluids used?
To correct deficits, present in initial evaluation
Why are maintenance fluids used?
To keep the animal within certain homeostatic parameters for a longer period of time
When we determine a rationale for administration of fluids, we create a fluid therapy plan consisting of what 4 things?
Type of fluid
Rate of administration
Route of administration
Schedule and type of monitoring
What are Crystalloids?
Salts that are commonly used in fluid therapy to replace water and correct electrolyte and acid-base disturbances (e.g., Norm-R, LRS, Normal Saline)
What are Colloids?
Plasma, protein, or synthetic substances used in fluid therapy to replace lost protein, supply deficient immunoglobulin, or increase IV-ECF oncotic pressure
Blood or blood replacers have the same benefit as _______ and increase the oxygen carrying capacity of blood
Colloids
Lipid, glucose, and amino acids in fluids used to what?
Provide energy
What is the general rule for a shock dose?
Up to a blood volume may be given over 20 minutes. Shock doses may be repeated if there is insufficient response, especially when a partial dose is given
How is dehydration assess for the non-shocky patient?
Usually based on % body weight lost but pre-dehydration weight not always available or reliable. Clinically, use data: BUN and Creat, PCV, TP, Lactate
Dehydration table

For replacement, the calculated percentage of body weight is usually given over ________
2-4 hrs
What does Goal-directed fluid therapy look for?
Changes in specific parameters such as central venous pressure, urine output, or blood lactate to judge sufficiency of fluid replacement
The amount of maintenance fluids administered should roughly equate what?
The amount used or lost over the same period of time
Chart for maintenance fluids
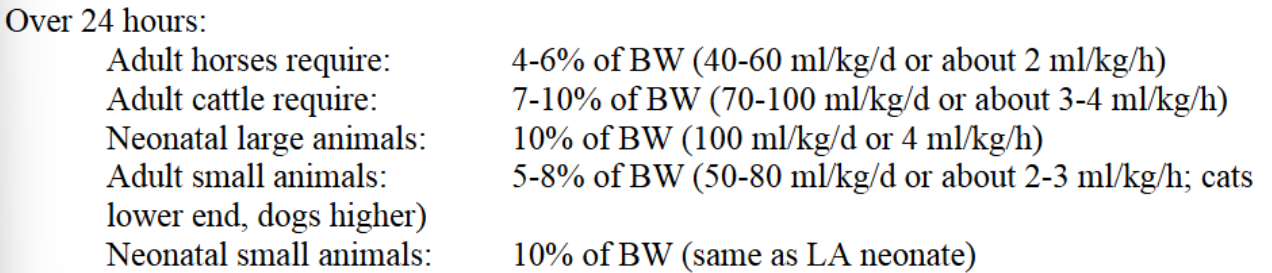
What are the 5 routes of fluids administeration?
Oral
Subcutaneous
Intravenous
Intraosseous
Intraperitoneal
What parameters should be monitored to prevent overhydration, overtreatment, and justify sufficiency of current plan?
Body weight
Physical determinants: HR, NN, skin turgor, eye luster
Central Venous Pressure
PCV/TP
Urine volume
Evidence of pulmonary, cerebral, or peripheral edema