ANSCI 201--Dairy
1/143
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
What is the main constituent of milk (87.0%)?
Water
What is the leading solid constituent of milk (5.0%)?
Lactose
What % of milk does fat constitute?
3.8%
What % of milk do caseins constitute?
2.8%
What % of milk do albumins/globulins constitute?
0.7%
What % of milk do proteins (caseins + albumins/globulins) constitute?
3.5%
What % of milk do ash/minerals constitute?
0.7%
What % of milk do solids non-fat (SNF) constitute?
9.2%
What gives milk its flavor?
Fat
What % of calories does fat contribute to milk?
48%
How does fat exist in milk?
As a temporary emulsion with globules suspended in liquid
How heavy are fat globules?
Lightweight
What shape are fat globules?
Spherical
What is the fat globule membrane composed of? What is its charge?
Phospholipids
Slight negative charge
Which chemical component makes up the greatest % of milk lipids?
A. Triglycerides
B. Phospholipids
C. Sterols
D. Vitamins
Triglycerides
Which fat-soluble vitamins are present in milk lipids?
A, D, E, and K
What does vitamin A help with?
Vision
What does vitamin D help with? ☼
Calcium absorption
What does vitamin E help with?
Immunity
What does vitamin K help with?
Blood clotting
What is a triglyceride made of?
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Why are phospholipids good emusifying agents?
Half is soluble in water, half is soluble in fat
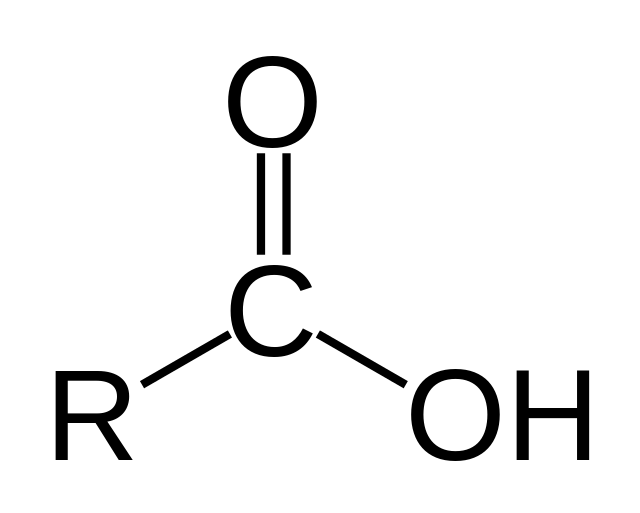
What does this structure represent?
A fatty acid
Are saturated fatty acids solids or liquids?
Solids
Do saturated fatty acids contain double bonds between carbon atoms?
No
Are unsaturated fatty acids solids or liquids?
Liquids
Do unsaturated fatty acids contain double bonds between carbon atoms?
Yes
What % of fatty acids in milk fat are saturated?
hint: they’re evil
66%
What % of fatty acids in milk fat are unsaturated?
34%
Does milk have a high % of short-chain acids or long-chain acids compared to other animal products?
Short-chain
Why does cream rise to the top?
Fat has a lower specific gravity than milk
What kind of solution does lactose form?
True molecular solution
Milk proteins are very high quality and are only second to protein from which food?
Eggs
Lactose is a dissacharide and is made of which two monosaccharides?
Glucose and galactose
Lactose is _________ soluble and _________ sweet than sucrose.
Less
What % of calories in whole milk does protein account for?
22%
What % of solids non-fat in whole milk does protein account for?
38%
What kind of solution does protein in milk exist in?
Colloidal dispersion
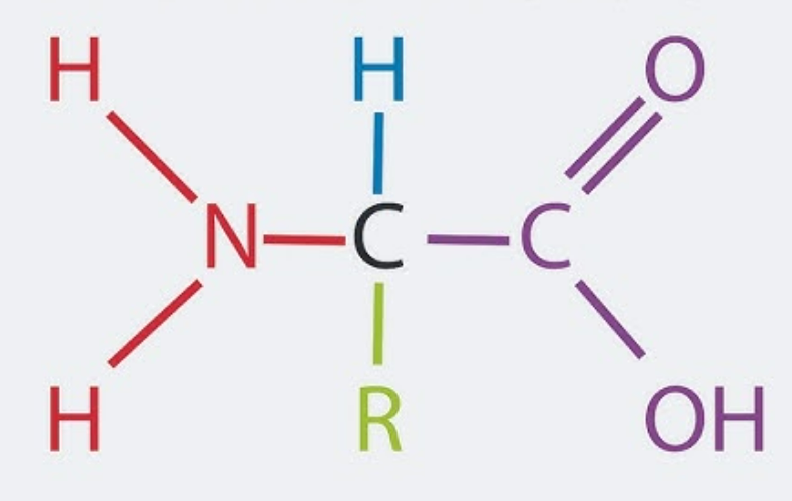
What is this?
Amino acid
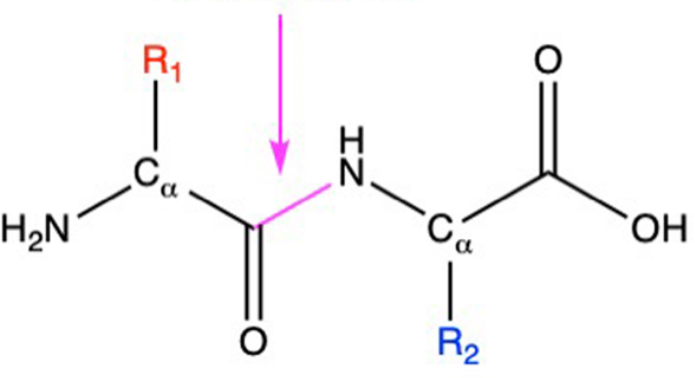
What kind of bond is this?
Peptide
What are the two types of milk proteins?
Caseins and whey proteins
What are the two whey proteins?
Lactalbumin and lactoglobulin
Surplus of which amino acid in milk helps offset deficiencies found in cereal proteins?
Lysine
Which milk protein accounts for 82% of total milk protein?
Caseins
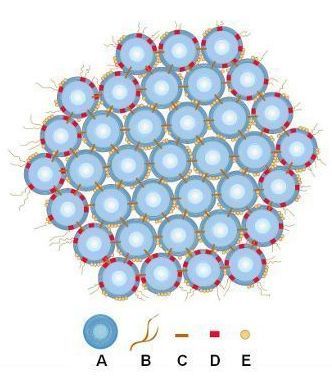
Caseins are contained as what structure?
Micelles
Which milk protein accounts for 18% of total milk protein?
Whey proteins
Whey proteins contain which important substance that provides immunity?
Immunoglobulins
The enzymes rennin and pepsin result in which type of curd (hard/soft)?
Hard
Acids result in which type of curd (hard/soft)?
Soft
What makes sweet whey sweet?
Lactose
Rennin and pepsin bind with which ions?
Calcium
Rennin converts casein to what structure?
Calcium paracaseinate
Which pH results in the formation of a soft curd?
4.67
Do soft curds contain more or less minerals than hard curd?
Less
An equal number of _________ combine during acidic curd formation.
Positive and negative charges

What % of cheese is hard?
80

What are some examples of soft curd cheese?
Cottage cheese, cream cheese, and ricotta cheese
What is ash in relation to milk?
Minerals
What kind of solution does ash exist in?
True solution
What is the leading mineral present in ash?
Potassium (K)
Which minerals is ash a good source of?
K, Ca, S, P, Mg, Cl, Zn, Se
Which minerals is ash not a good source of?
Fe, Cu, Mn, Na

What role does ash play in human health?
Prevents osteoporosis through Ca and Vitamin D
What are the organic catalysts present in milk?
Vitamins
Which milk vitamins are fat soluble?
A, D, E, and K

Which milk vitamins are water soluble?
B and C

Yellow color in milk produced by Guernsey and Jersey cows is due to what pigment?
Carotene (precursor of vitamin A)
Which two vitamins are usually fortified during milk processing?
A and D
What is the major enzyme found in milk?
Lipase
Should leukocytes be present in high or low levels in milk?
Low
What minor constituent of milk are essentially the cow’s body cells?
Somatic cells

Do seals and polar bears have a high or low % fat in their milk to provide their young with energy?
High
What does a lactation curve look like?
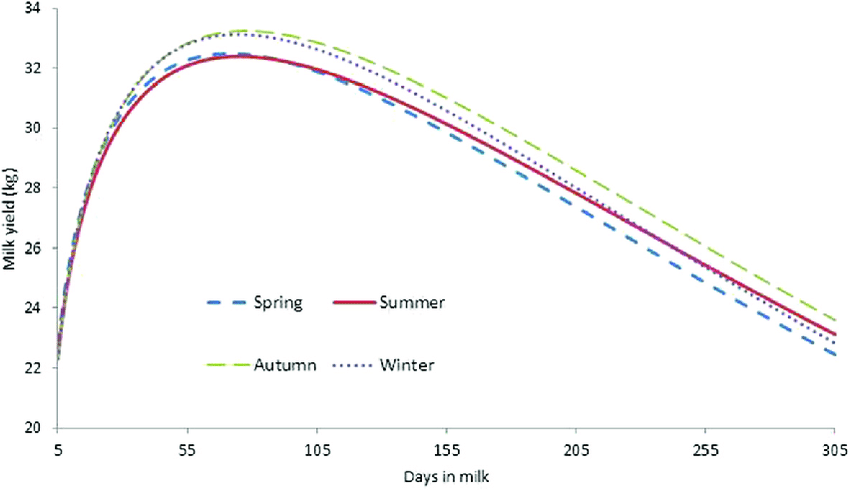
What is the first secretion from the mammary gland after birth called?
Colostrum
Colostrum contains a high % of which two proteins?
Albumin and globulin
As the stage of milking progresses, what happens to the % fat of milk?
Increases
What are some factors that can affect milk composition?
Nutrition
Disease
Genetics
Season of year
Age
What is the word for something that appeals to the senses?
Organoleptic
What is the most favorable milk flavor?
Bland and slightly sweet

What milk flavor does an absorbed defect produce?
Feedy, cowy, barny
What allows for milk to absorb flavor from the cow’s food?
High blood flow between the mammary gland and milk
What are some ways to prevent milk from absorbing flavor?
Don’t feed animals aromatic feeds near milking time
At home, keep milk away from aromatic items in fridge
What milk flavor does a bacterial defect produce?
Acidic, putrid, malty
What are the causes of a bacterial milk defect?
Improper cooling and poor sanitation
What is the flavor of a chemical milk defect?
Papery/cardboardy
What is the cause of chemical milk defects?
Oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids
What are the catalysts of chemical milk defects?
Copper, iron, and UV light
How can we prevent chemical milk defects?
Stainless steel equipment, proper packaging and storage
What is another term for chemical milk defects?
Oxidative rancidity
What is the flavor of hydrolytic rancidity milk?
Bitter and soapy
What is the cause of hydrolytic rancidity of milk?
Enzymatic hydrolysis of triglycerides by lipase
How can we prevent hydrolytic rancidity of milk?
Proper handling and storage, avoiding excess agitation and stirring, pasteurization
What is the process by which additional skim milk is added to milk to achieve the desired fat content?
Standardization
What will happen to you if you add water to milk?
Death

What is the process by which milk is heated to kill pathogenic bacteria?
Pasteurization
What is the process by which milk is heated at 145 degrees for 30 minutes?
LTLT (low temp long time) pasteurization
What is the process by which milk is heated at 161 degrees for 15 seconds?
HTST (high temp short time) pasteurization
What is the process by which milk is heated at 280 degrees for 2 seconds?
UHT (ultra high temp) pasteurization
What is is the process by which humans are heated at 280 degrees for 2 seconds?
Arson
What is the process that reduces the size of fat globules so that the milk fat doesn’t separate in the milk fluids?
Homogenization