AP World History: Modern - AMSCO Prologue
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
patriarchy
domination of men

Agricultural Revolution
As the climate warmed after an ice age, humans began to plant crops and raise animals for food

Mesopotamia
Land between two rivers; world's first civiliation
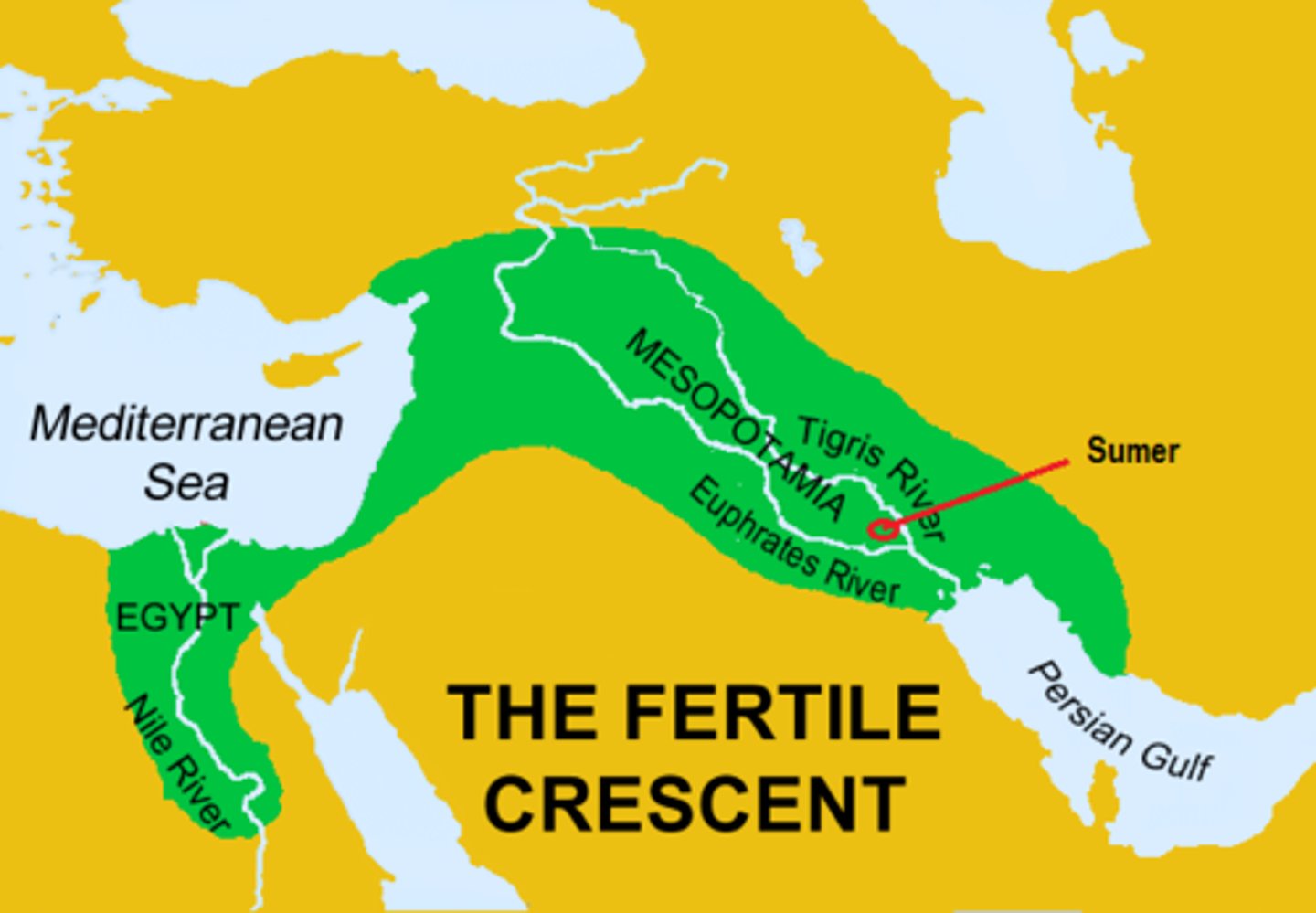
Ziggurats
temples built by Sumerians to honor the gods and goddesses they worshipped

city-state
independent state consisting of a city and its surrounding territory
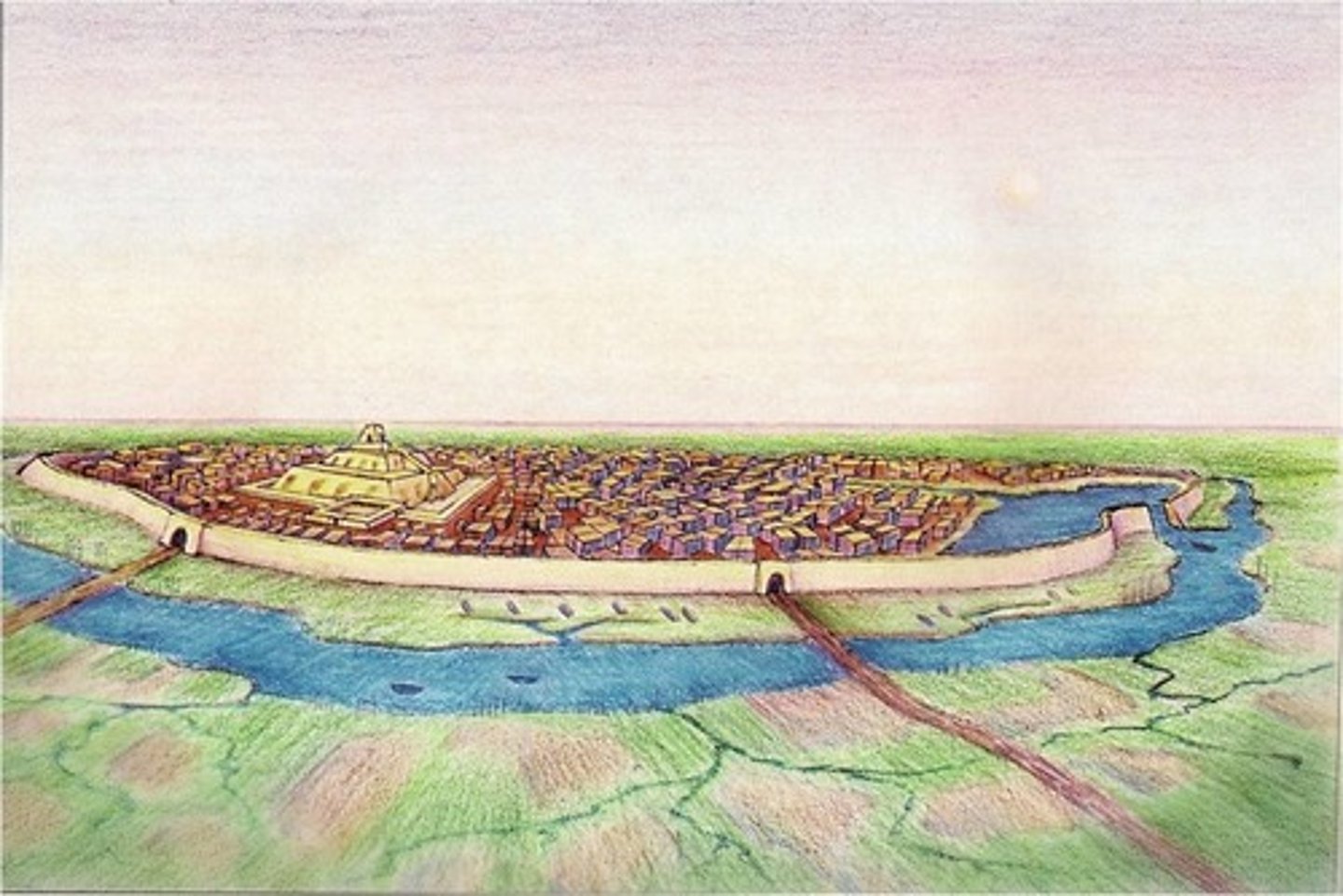
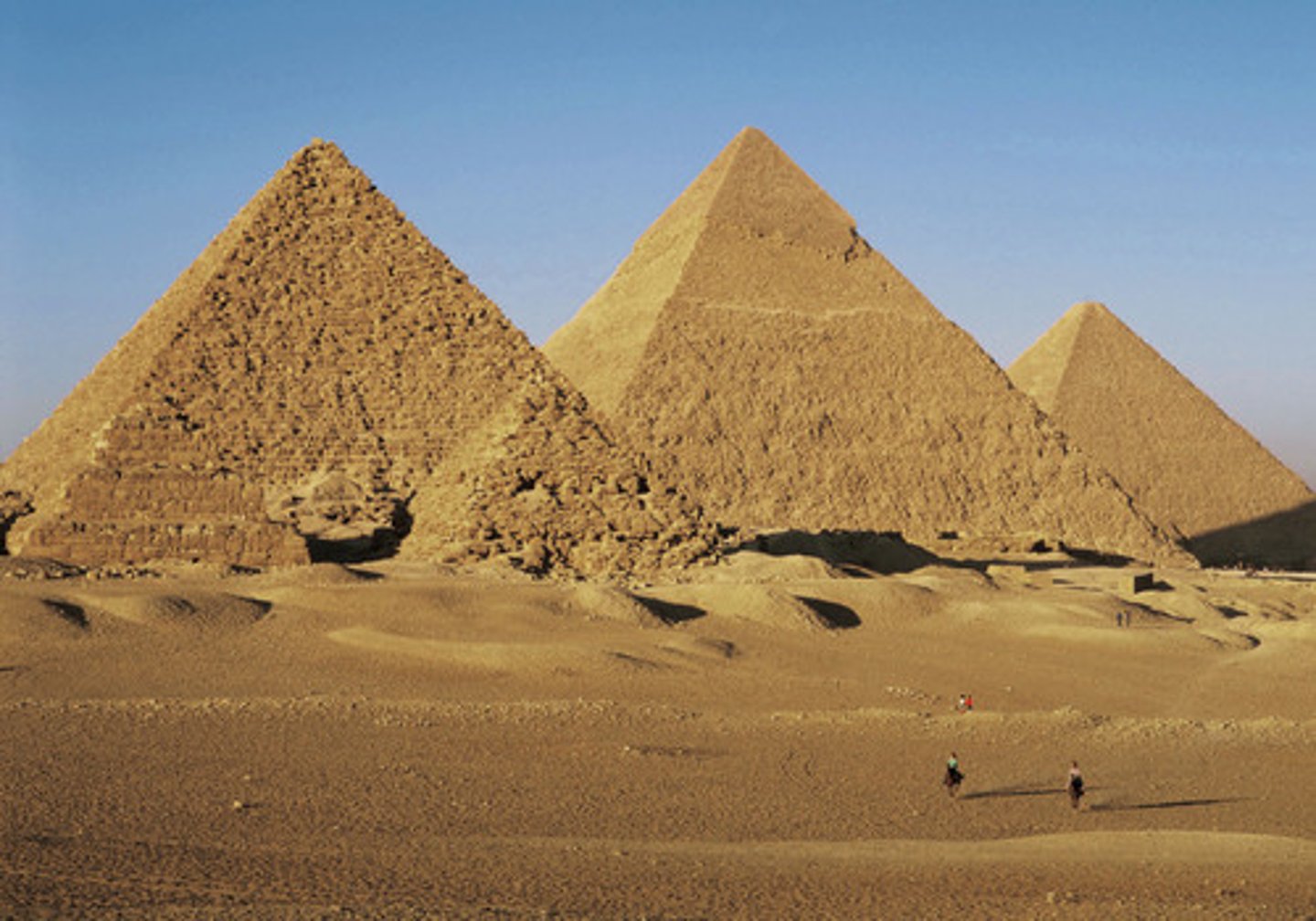
Egypt
Civilization in the Nile River Valley
Centralized under a pharaoh
Built pyramids to show power
Gave women a few more rights

Indus
The civilization from the Indus River Valley which we know little about due to not being able to decipher their language
Hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms. The Vedas were brought down by the Aryans.

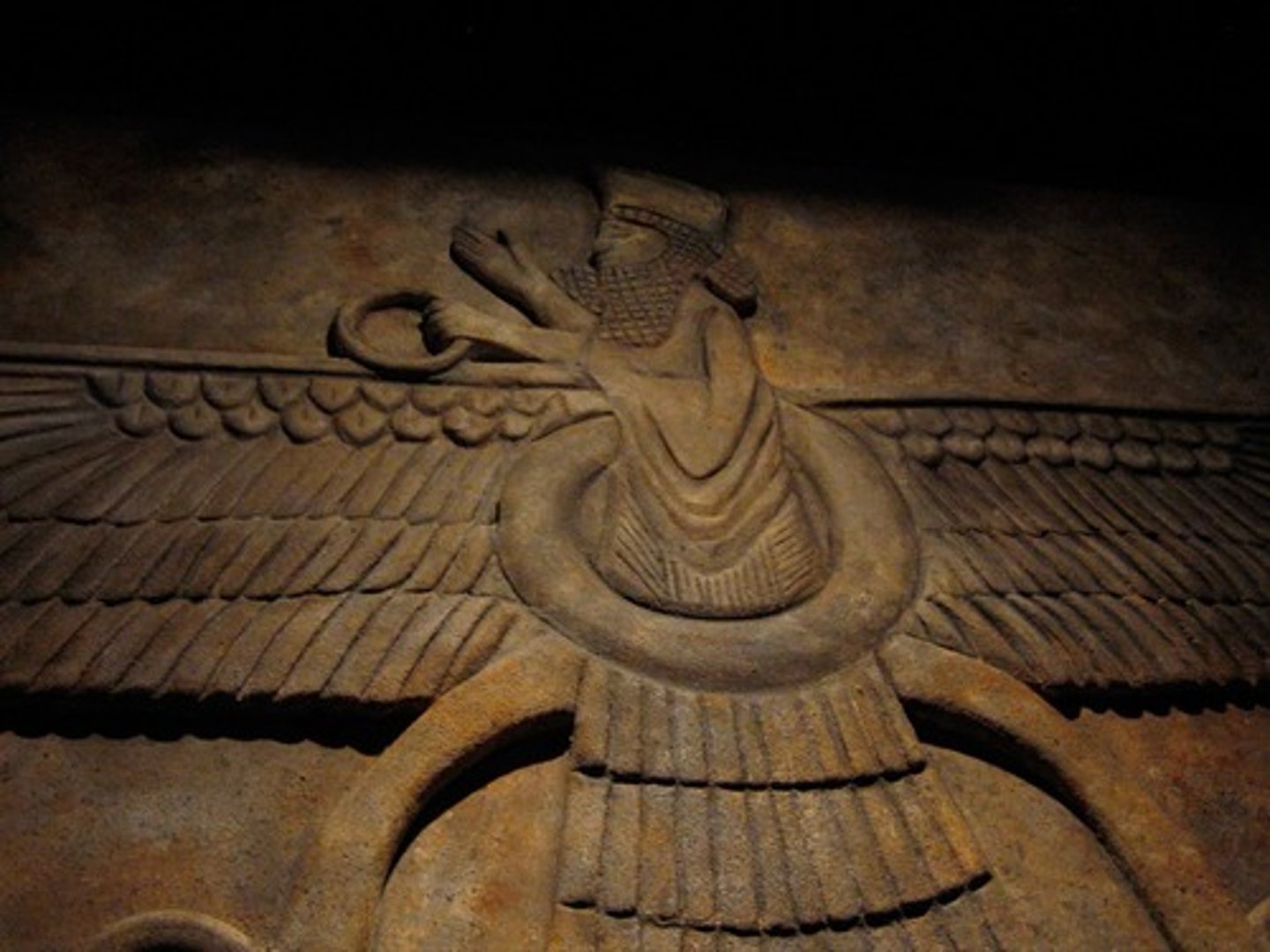
Zoroastrianism
One of the first monotheistic religions developed around Persia. Focused on free will and the battle of good vs evil.

Judaism
Monotheistic religion developed in Israel based on the teachings of Abraham.

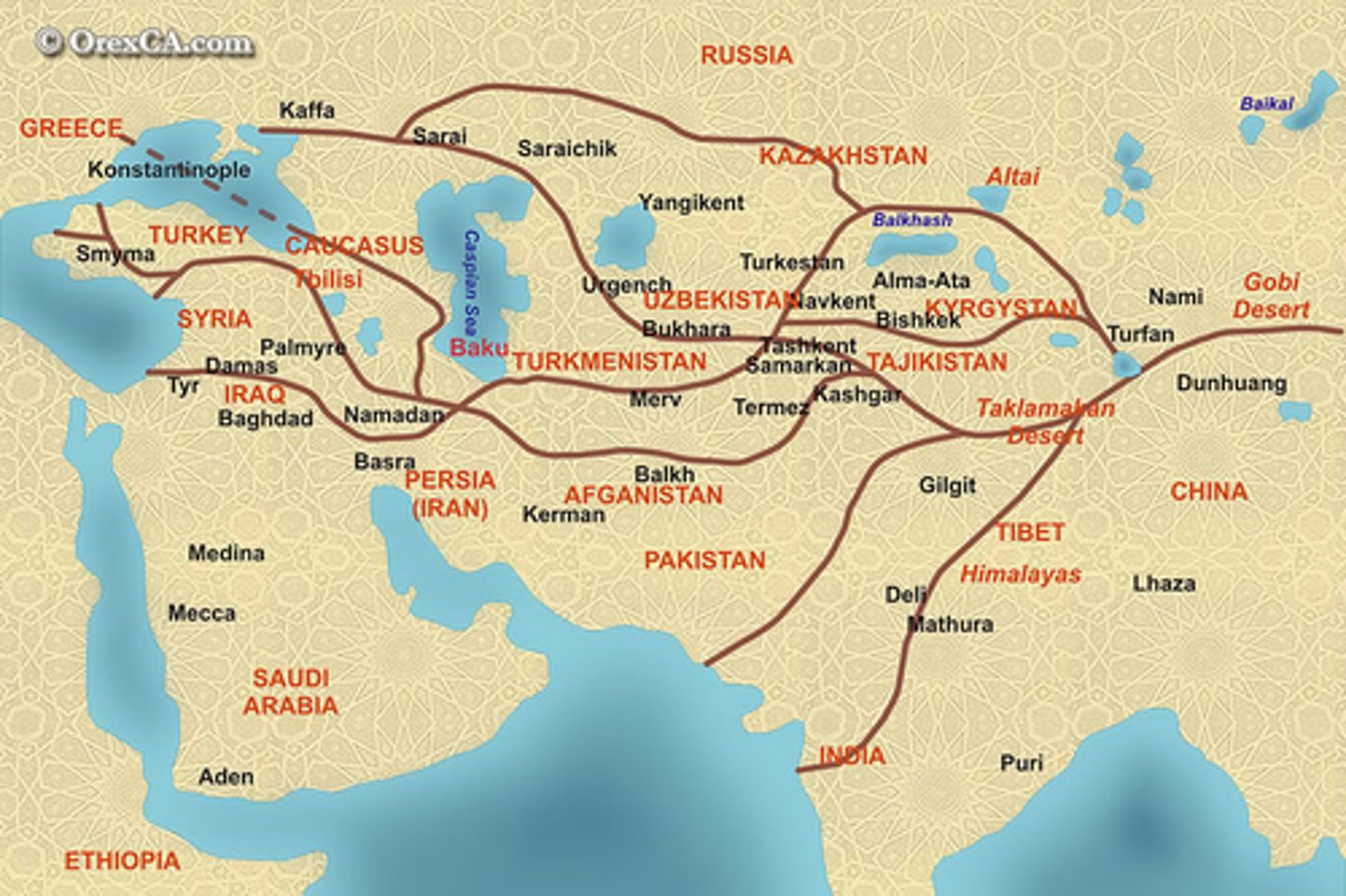
Silk Road
Caravan routes connecting China and the Middle East across Central Asia and Iran.
Buddhism
a religion based on the teachings of the Buddha that developed in India in the 500s BC from Siddhartha Gautama

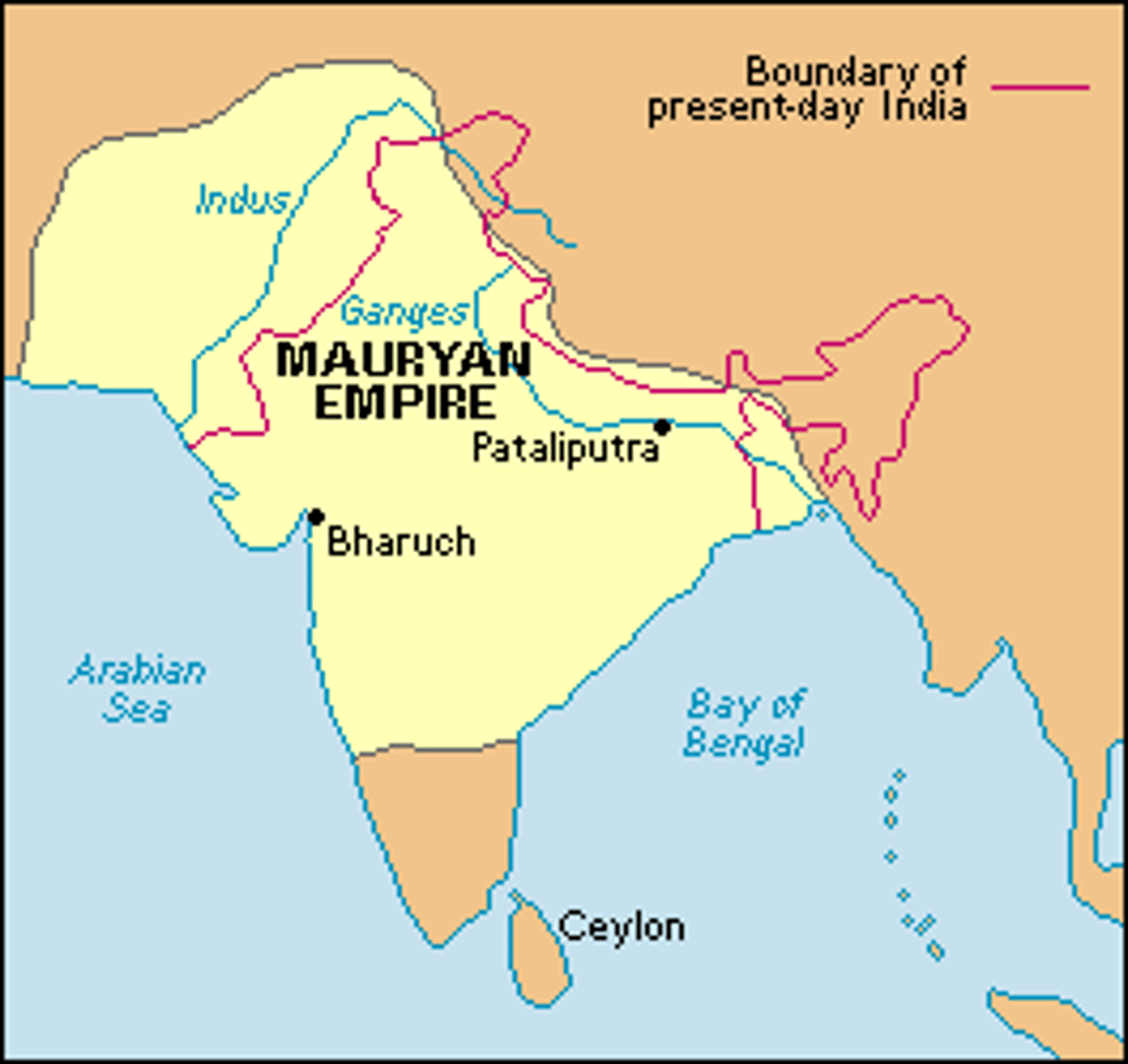
Mauryan Empire
This was the first centralized empire of India who was lead by Ashoka at its height. He converted to Buddhism which spread it throughout India.
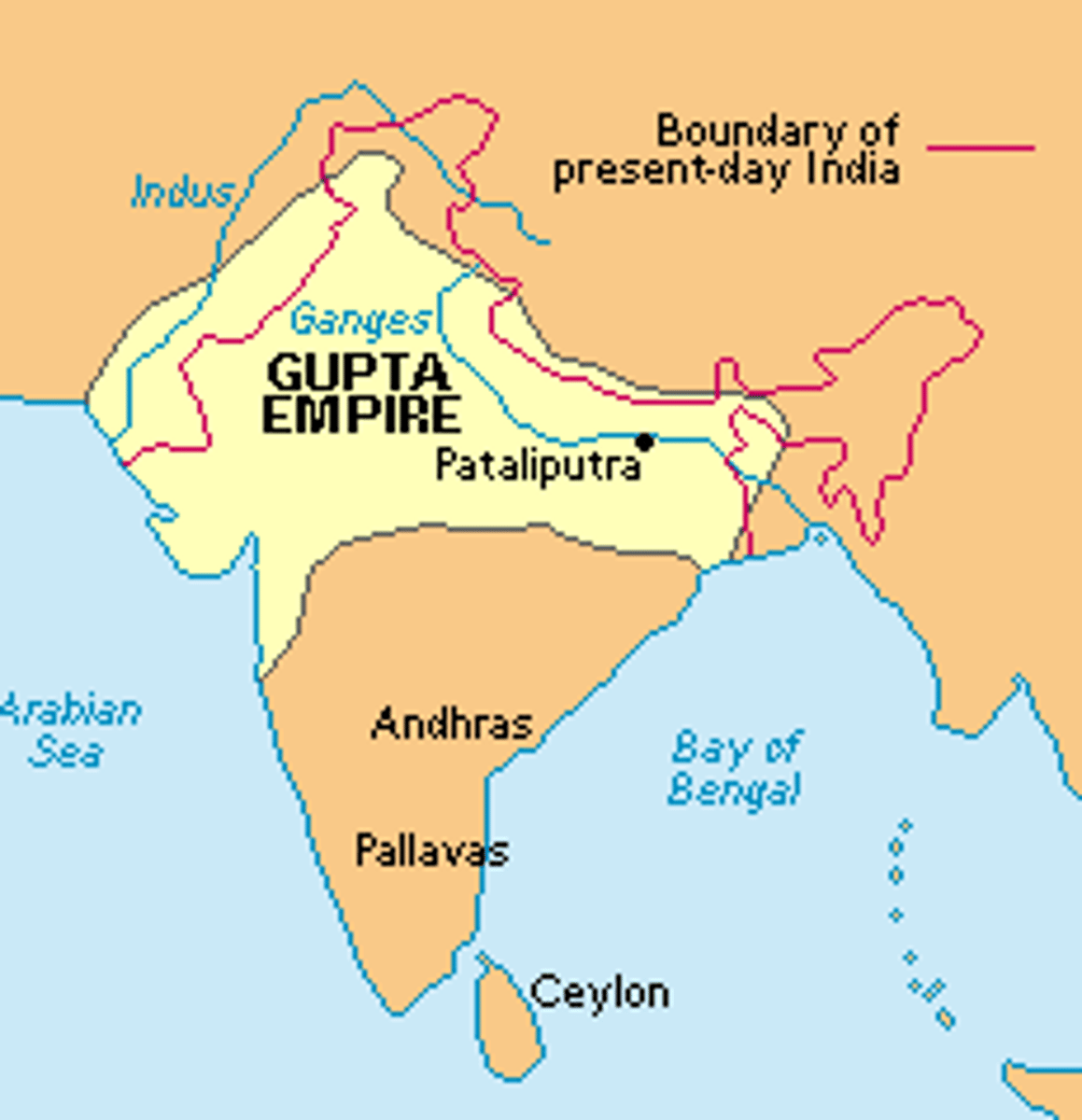
Gupta Empire
Golden Age of India; ruled through central government but allowed village power; restored Hinduism
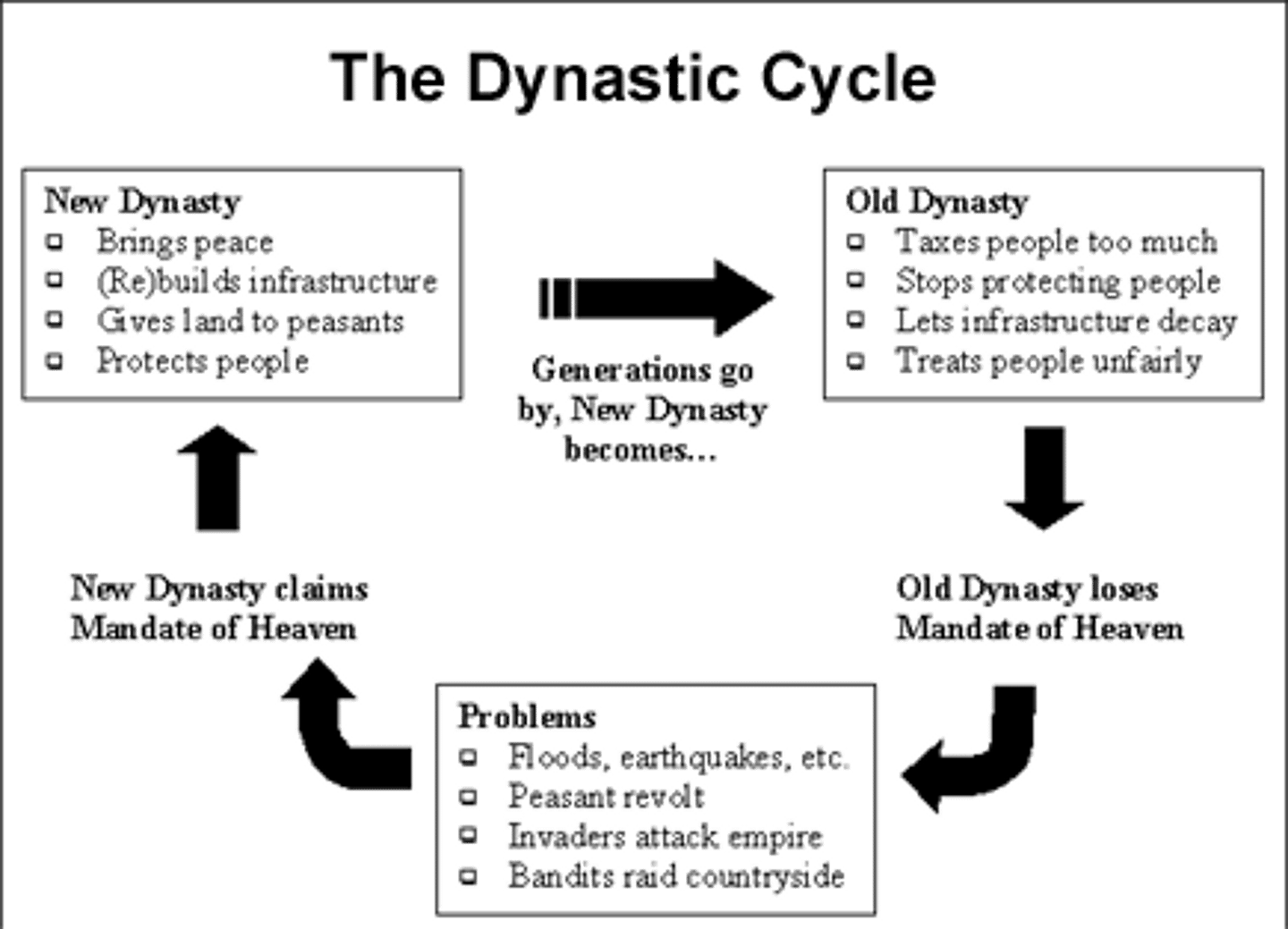
Mandate of Heaven
the belief that the Chinese king's right to rule came from the gods
Confucius
Founder of Confucianism who lived in the Warring States Period (focused on how people could live in harmony with each other)

Daoism
Focused on how people could live in harmony with nature (emphasized internal reflection)

Qin Dynasty
Short Dynasty that used legalism to unify China after the Warring States Period

Han Dynasty
Lead China to a golden age where trade prospered and many inventions arose (magnetic compass, paper, rudder)

Civil Service Exam
An examination created by the Hans where students had to analyze Confucian teachings to serve in the government bureaucracy

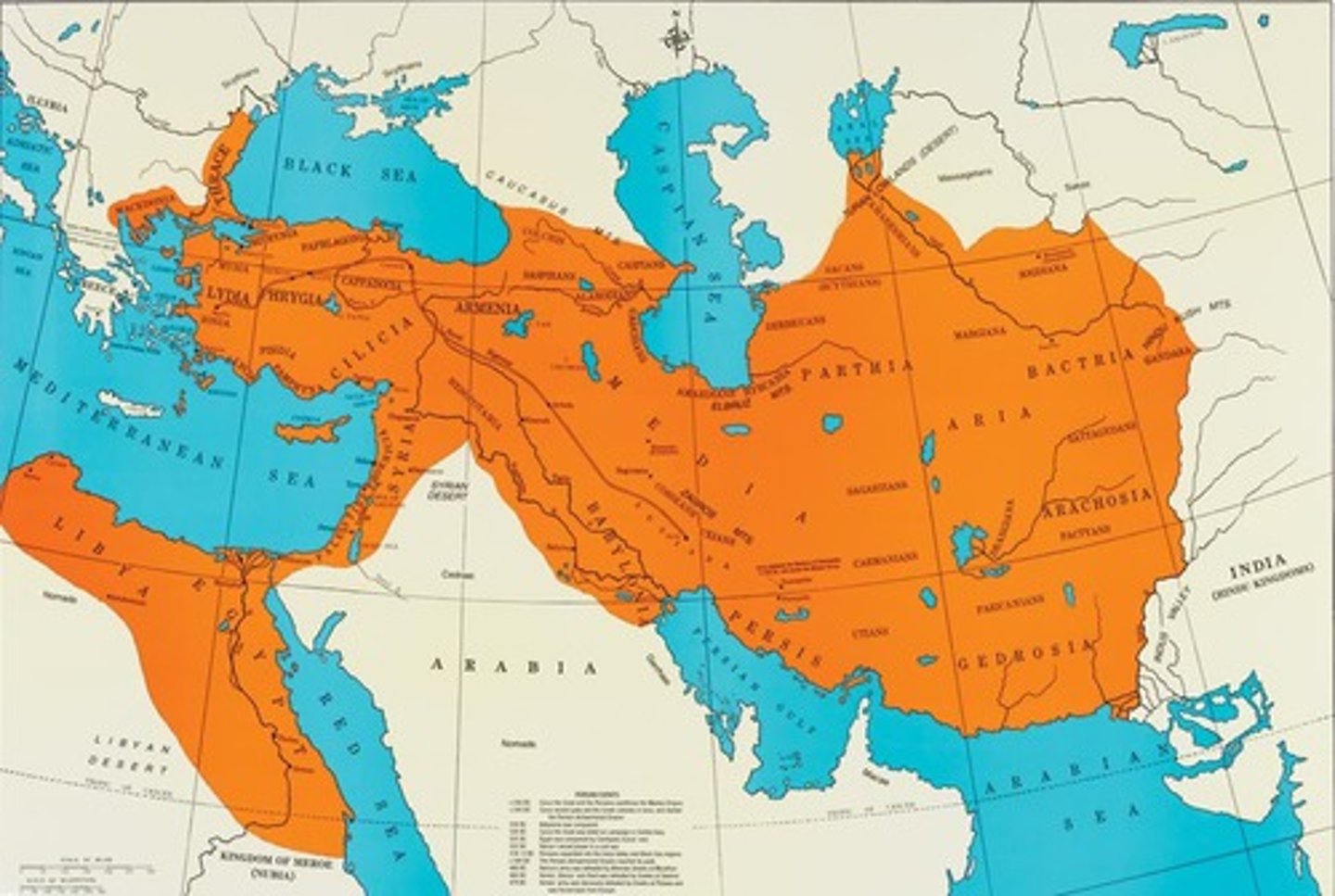
Persian Empire
A major empire that expanded from the Aegean Sea to India that supported trade, a strong bureaucracy, and religious toleration
Alexandrias
A series of cities founded by Alexander the Great

Hellenistic
Greek-like

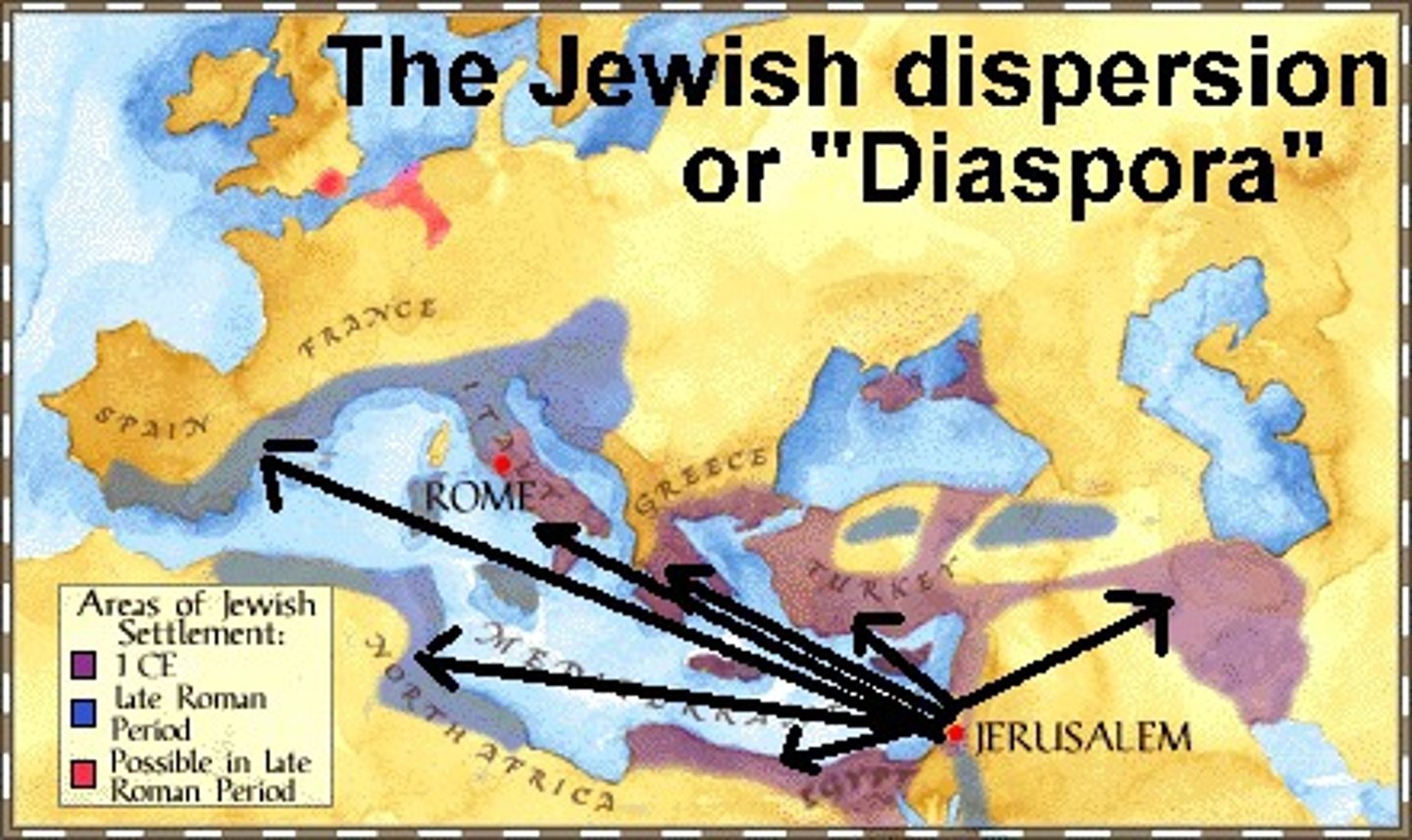
Diaspora
A dispersion of people from their homeland (Jews)
Christianity
Religion worshipping Jesus that grew popular amongst poor people and became the official religion of Rome under Emperor Constantine

Roman Empire
an empire established by Augustus and divided into the Western Roman Empire and the Byzantine Empire
Entrepot
coastal trading center

Byzantine Empire
Eastern half of the Roman Empire that survived the fall of the Western half
Teotihuacan
first major metropolis in Mesoamerica that featured streets laid out on a grid and temples dedicated to gods

Mayans
Most influential Mesoamerican classical civilization. They had a complex written language and are famous for their complex calendars. They also understood the concept of 0.
Islam
Religion created by a merchant names Muhammad that focuses on the Qur'an and the Five Pillars

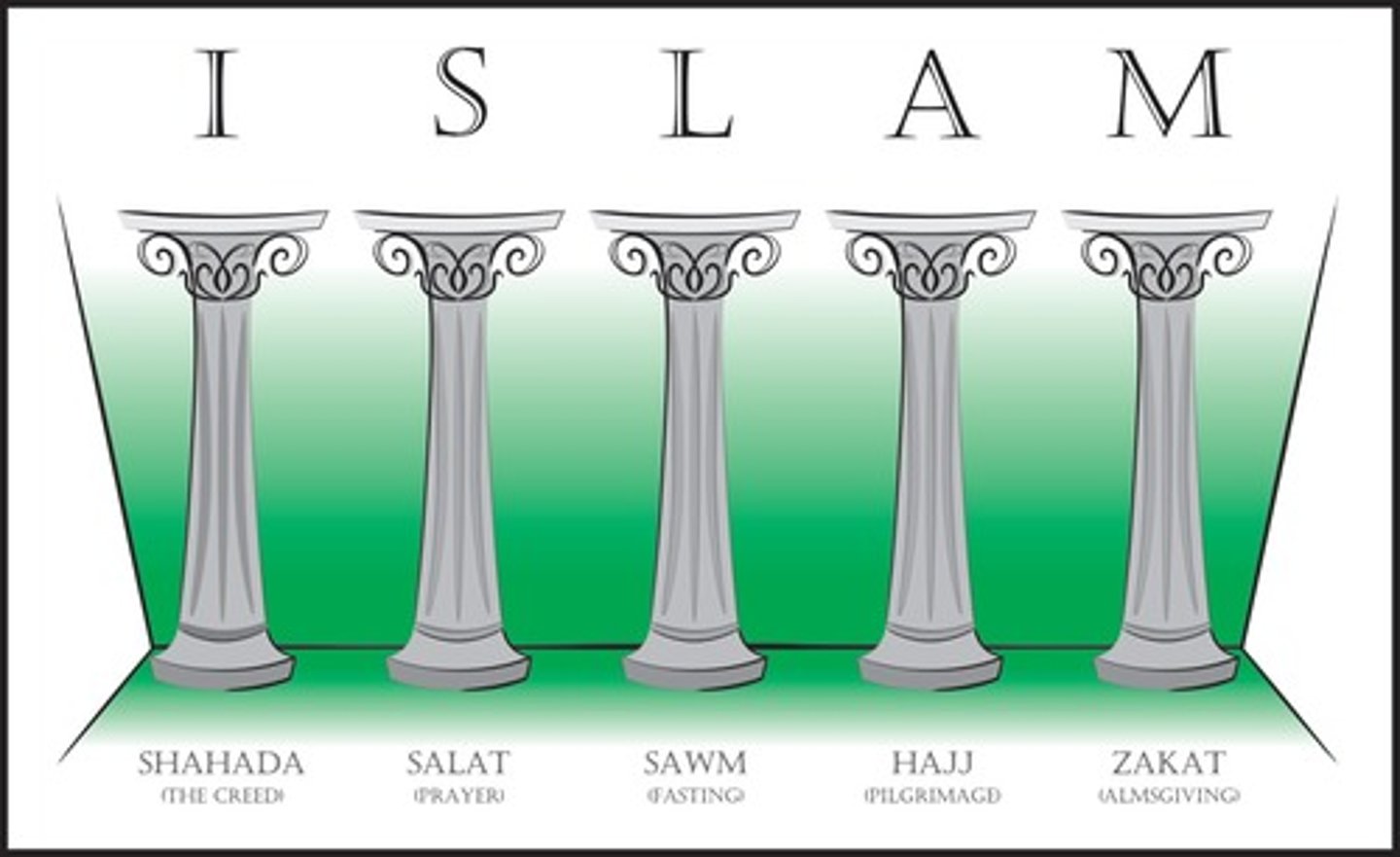
Five Pillars of Islam
Declaration of faith, prayer, alms, fasting, and pilgrimage
Sunni Muslims
believed successor of Muhammad could be an elected caliph

Shi'a Muslims
Believe that the leader of the Islamic faith should be a direct descendant of the prophet Muhammad (mostly in Iran, Iraq today)

Dar al-Islam
"House of Islam" that united Spain, North Africa, the Middle East, and parts of India
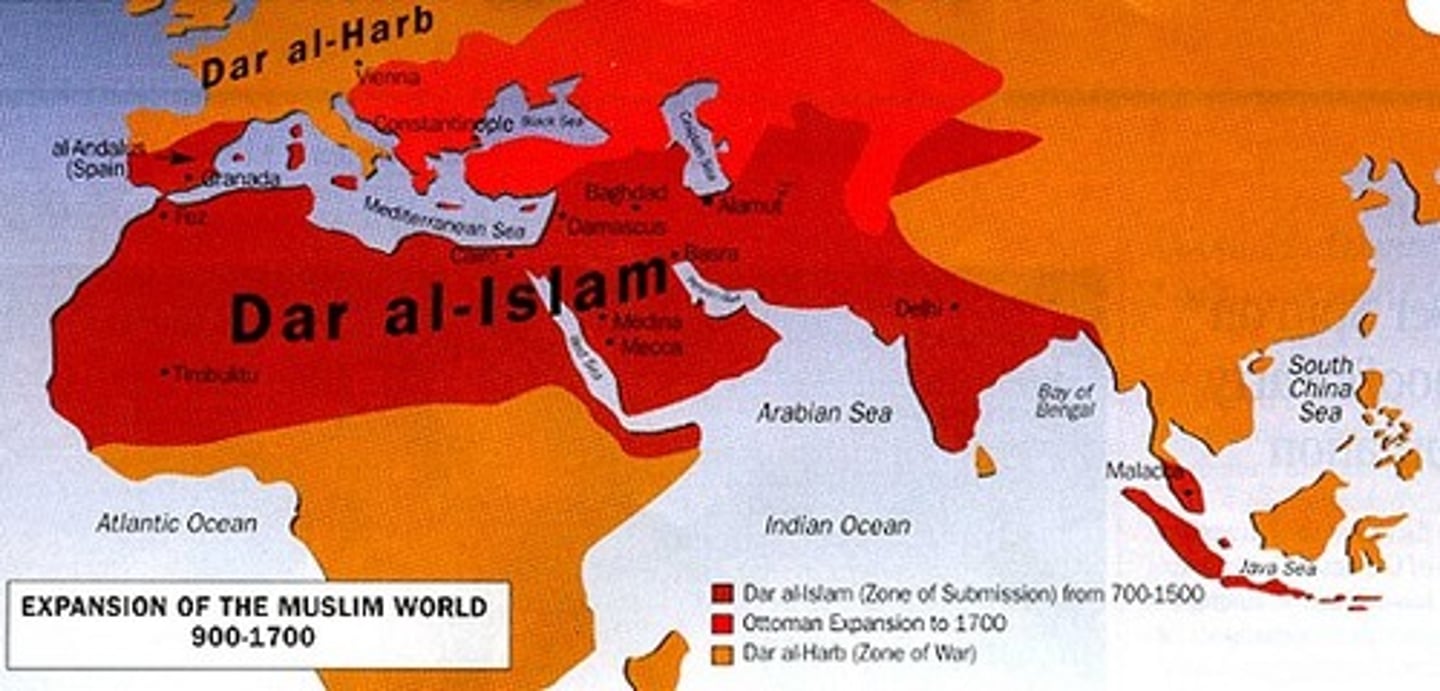
Abbassid Caliphate
This is the third and most important of the islamic caliphates. They helped trade expand and founded many scientific advancements. They were later overtaken by the Mongols.

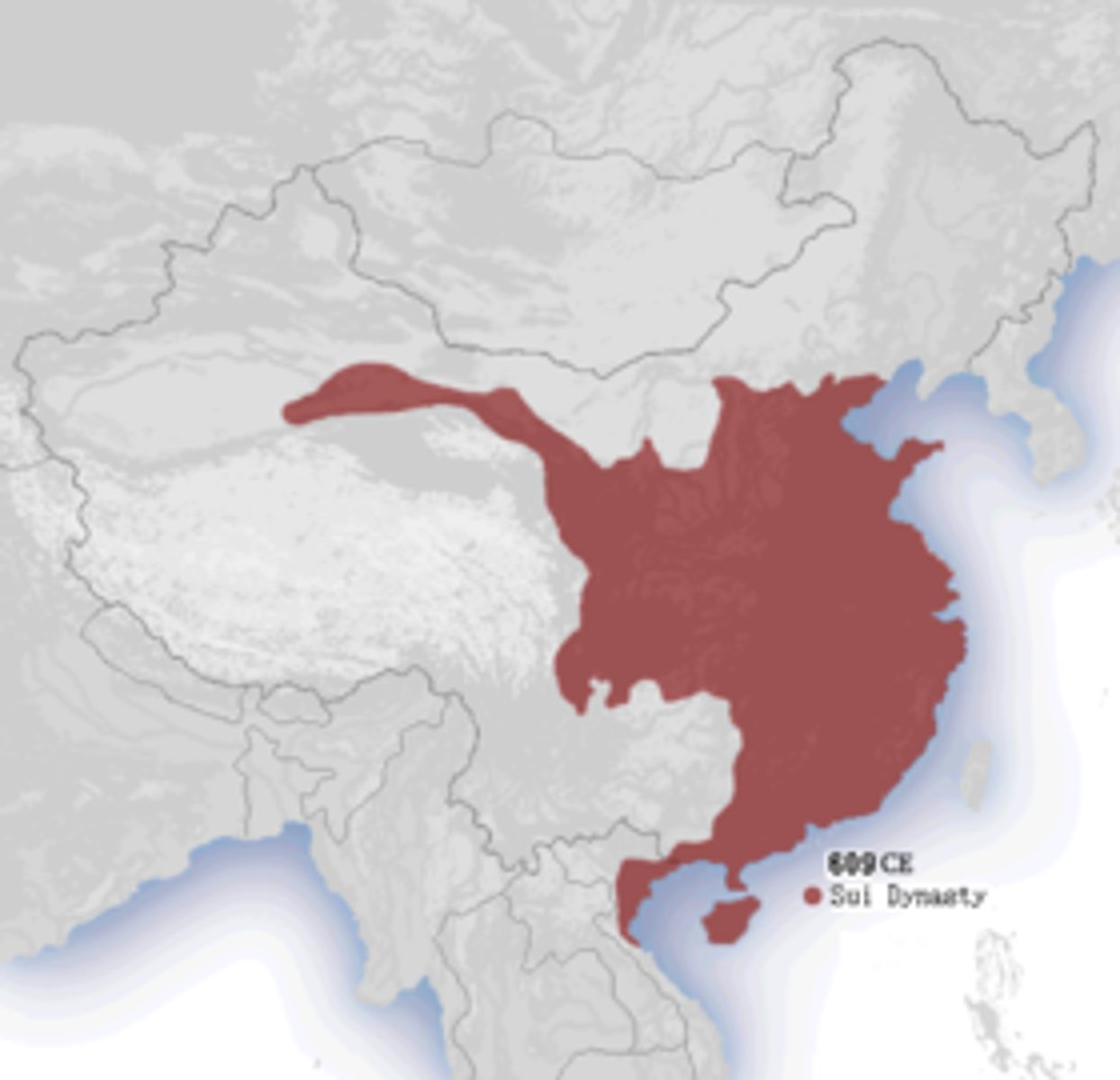
Sui Dynasty
Short dynasty that brought back the centralized government and founded the Grand Canal
Tang Dynasty
Chinese dynasty that learned to grow Champa Rice and expanded the imperial bureaucracy. They made gunpowder and developed forms of paper money.

Shinto
traditional Japanese religion based on the veneration of ancestors and nature spirits

Roman Catholic Church
Church established in western Europe during the Roman Empire and the Middle Ages with its head being the bishop of Rome or pope.

Orthodox Church
Eastern church which was created in 1053 after the schism from the western Roman church; its head is the patriarch of Constantinople. (also called the Byzantine Church)

Shogun
A general who ruled Japan in the emperor's name.

Daimyos
powerful warlord that controlled big estates; the best person from this class would become the shogun

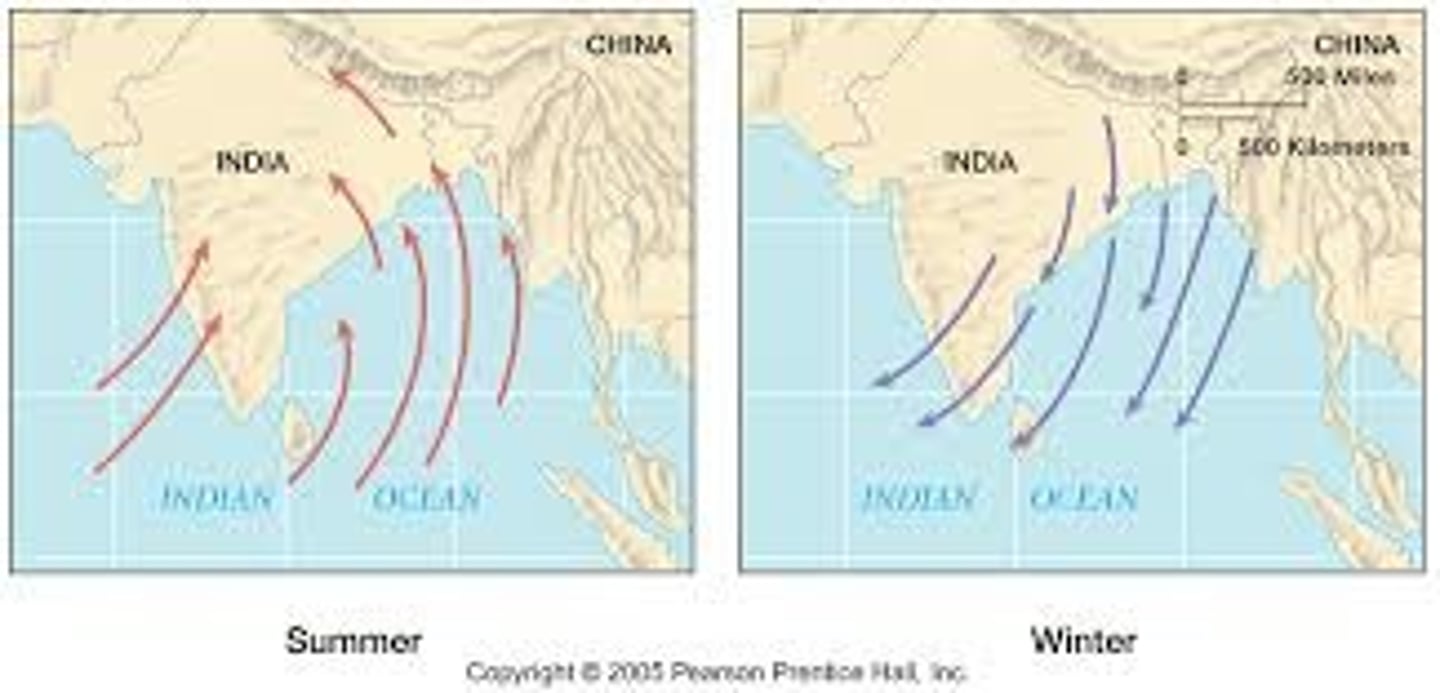
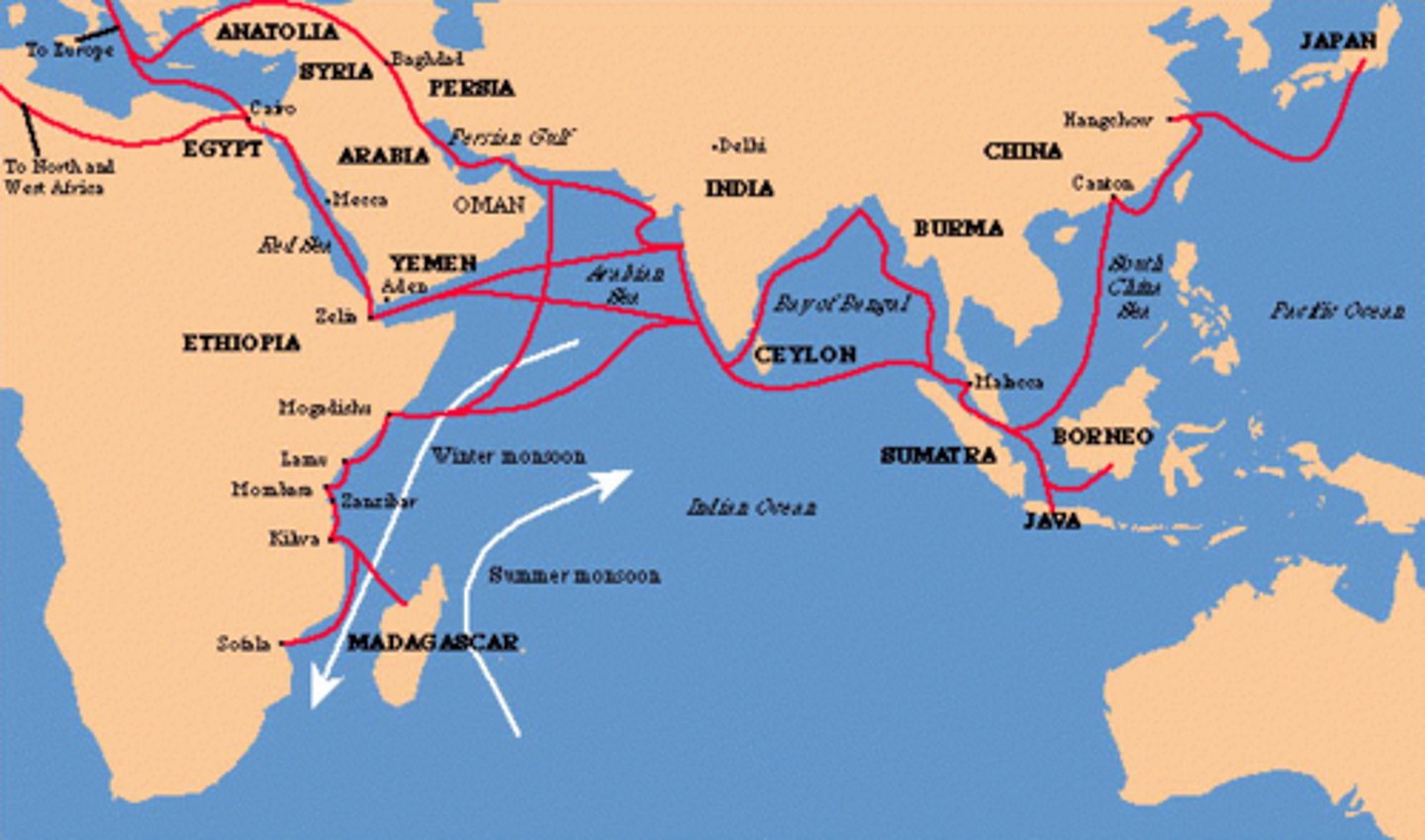
monsoon winds
These carried ships on the Indian Ocean between India and Africa
Mississippian
A Native Indian culture that flourished in the modern day midwest. They resided in the Mississippi river valley. Mound builders.
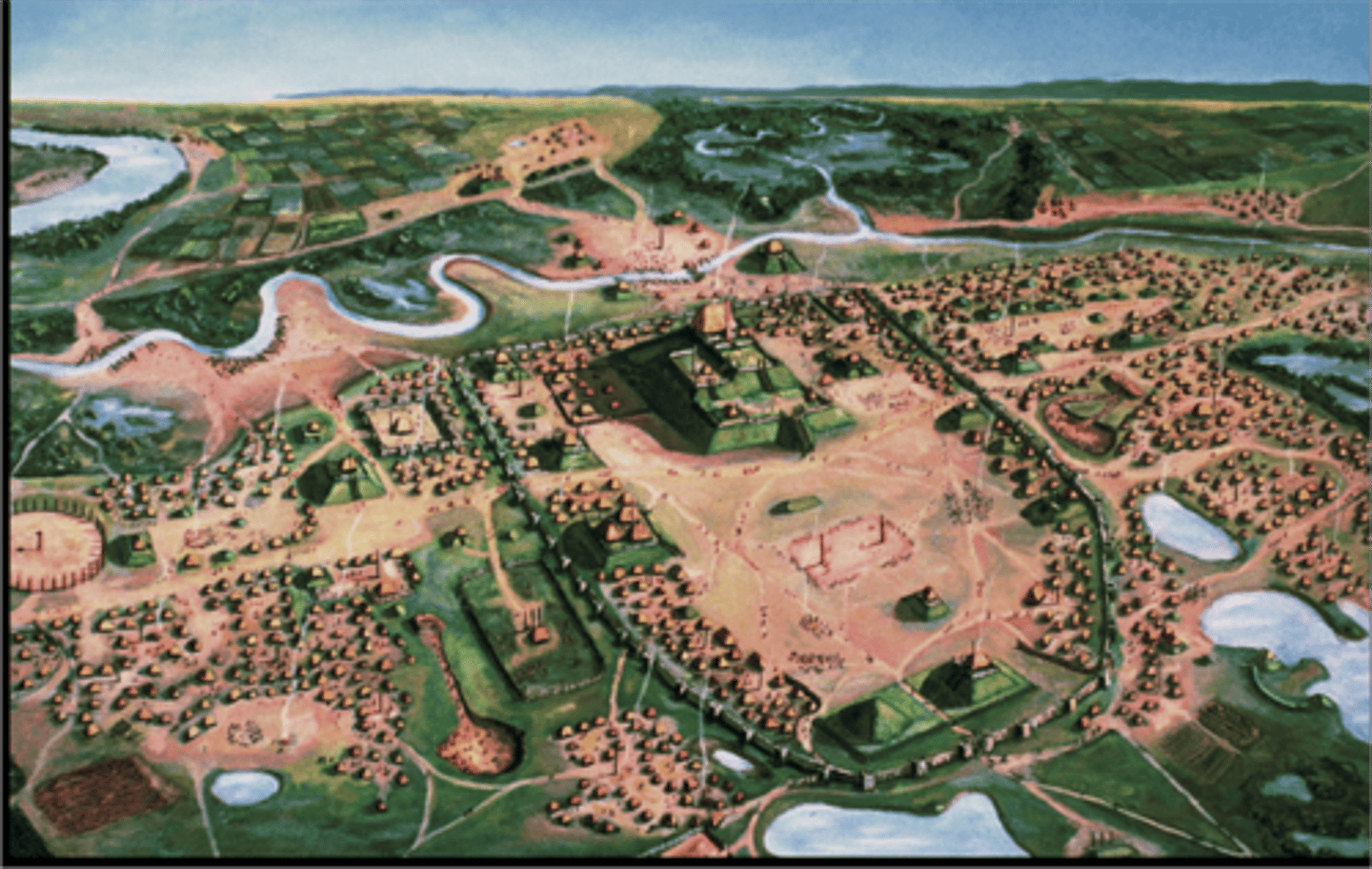
Toltecs
Powerful postclassic empire in central Mexico (900-1168 C.E.). It influenced much of Mesoamerica. Aztecs claimed ties to this earlier civilization.
Indian Ocean Trade Route
A sea route of trade that connected India, China, the Middle East, and Eastern Africa.
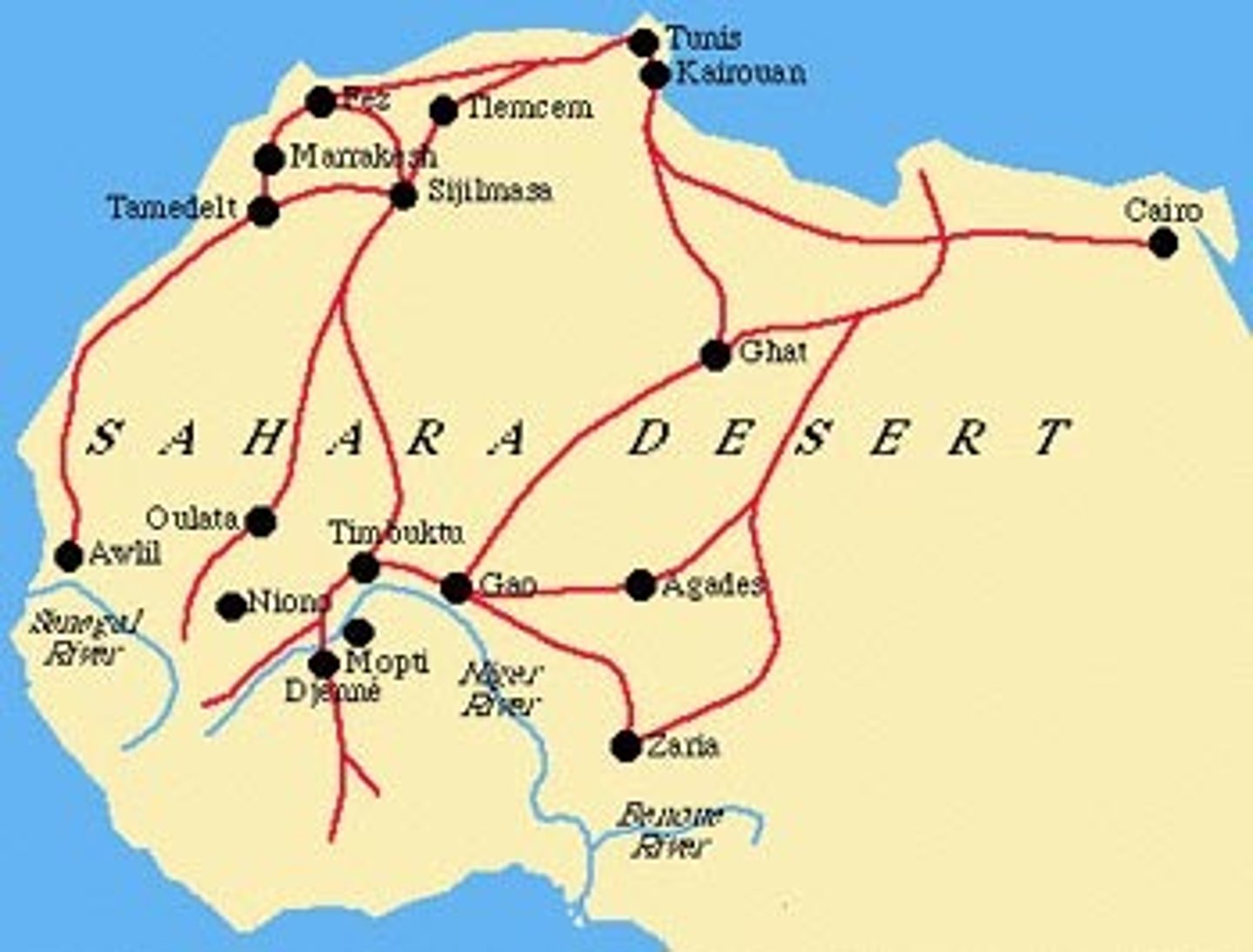
Trans-Saharan Trade
route across the Sahara desert. Major trade route that traded for gold and salt, created caravan routes, economic benefit for controlling dessert, camels played a huge role in the trading
Ancient Greece
A civilization that lasted from the 8th/6th century BCE to 600 AD. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine Era. Because of conquests by Alexander the Great of Macedonia, Hellenistic civilization flourished from Central Asia to the western end of the Mediterranean Sea. Classical Greek culture, especially philosophy, had a powerful influence on the Roman Empire, which carried a version of it to many parts of the Mediterranean Basin and Europe, for which Classical Greek is generally considered to be the seminal culture which provided the foundation of modern Western culture.

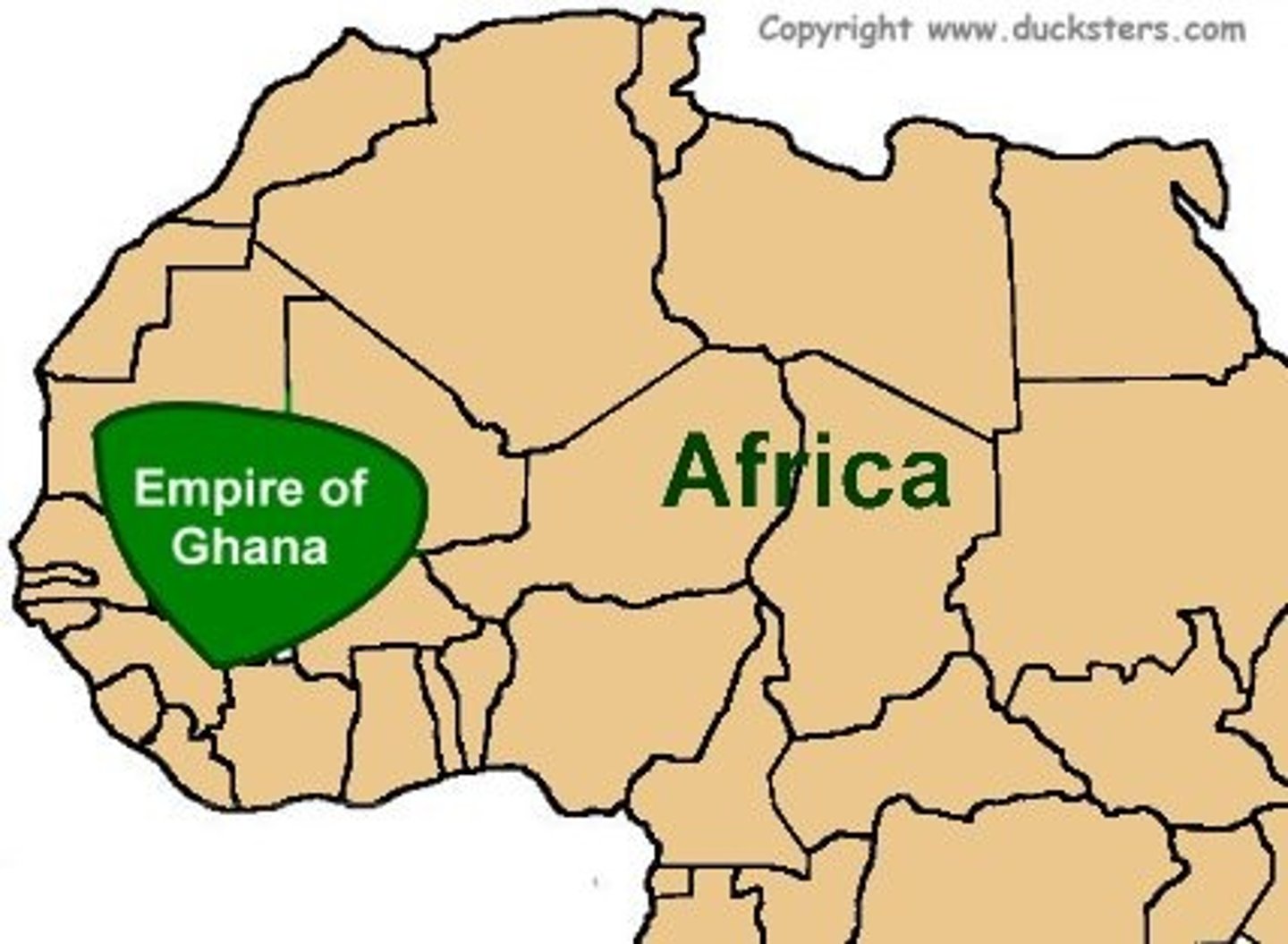
Ghana
First known kingdom in sub-Saharan West Africa between the sixth and thirteenth centuries C.E. Also the modern West African country once known as the Gold Coast. gold and salt trade.
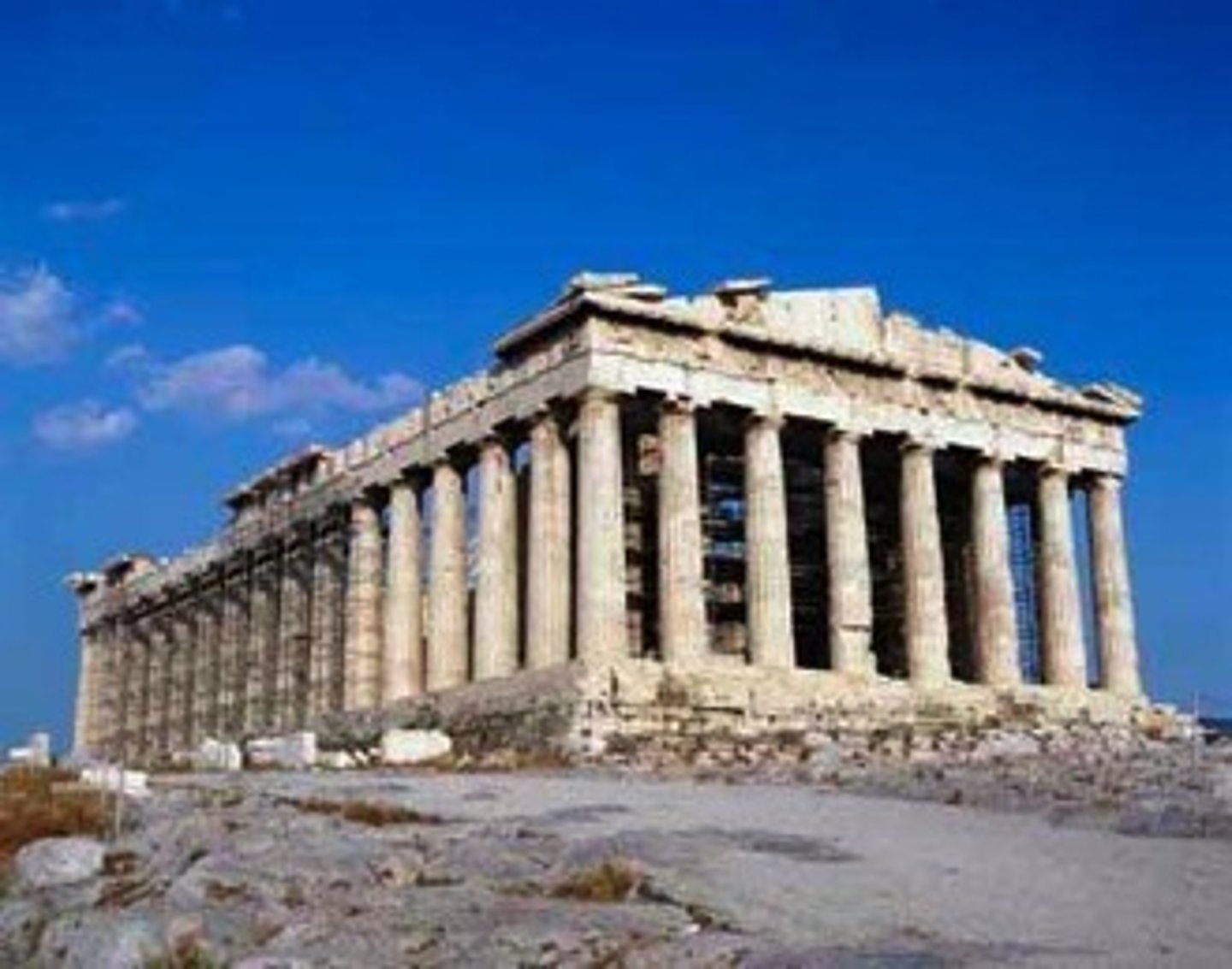
Great Zimbabwe
A powerful state in the African interior that apparently emerged from the growing trade in gold to the East African coast; flourished between 1250 and 1350 C.E. Known for stone buildings and walls.

Paelolithic Age
the earliest period of human history, Old Stone Age, time of discovery of stone tools, humans were hunters, gatherers, nomadic and used simple tools, people had no permanent home and moved from place to place

Neolithic Age
"New Stone Age"; About 10,000 years ago marked by advances in the production of stone tools. Shift from hunting and gathering to agriculture

civilization/complex society
a type of society characterized by most of the following: dense population, agricultural economy, cities, complex social hierarchy, job specialization, centralized state, monumental building, a writing system, and a dominant belief system

cultural diffusion
The spread of ideas, customs, and technologies from one people to another; often by trade
