Biomechanics: Key Concepts and Calculations
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What is biomechanics?
The study of the mechanics of living organisms.
What are the three main branches of mechanics relevant to biomechanics?
Statics, dynamics, and kinematics.
What is the difference between scalar and vector quantities?
Scalars are described by magnitude only (e.g., distance, speed), while vectors are described by both magnitude and direction (e.g., displacement, velocity).
What is the formula for Pythagoras' Theorem?
c² = a² + b², used to determine the length of a side when no angular information exists.
What are the assumptions made about projectile motion?
Vertical and horizontal components are considered independently, acceleration is constant, gravity is the only force acting vertically, and there is no acceleration horizontally.
What is the acceleration due to gravity in vertical motion?
± 9.81 m/s².
What is the relationship between time taken to reach peak height and time taken to come back down in projectile motion?
They are equal.
What is the formula to calculate the angle of a projectile given horizontal and vertical velocities?
θ = tan⁻¹(opposite/adjacent), where opposite is the vertical velocity and adjacent is the horizontal velocity.
What is the initial velocity (u) in the context of uniform acceleration?
The velocity of the object at the start of the time period.
What is the final velocity (v) in the context of uniform acceleration?
The velocity of the object at the end of the time period.
What does 's' represent in the equations of uniform acceleration?
The displacement of the object.
What is the equation relating final velocity, initial velocity, acceleration, and time?
v = u + at.
What is the equation relating final velocity, initial velocity, acceleration, and displacement?
v² = u² + 2as.
What is the equation for displacement in terms of initial velocity, time, and acceleration?
s = ut + ½ at².
How do you determine the scaling factor from a measurement?
By converting the measured distance into real units, e.g., if 0.5 m is represented as 8 mm, then 1 mm equals 0.0625 m.
In the scaling example, how far did the ball travel if it moved 13 mm on screen?
0.81 m in real life.
What is the value of acceleration horizontally in projectile motion?
0
What is the maximum height reached by a trampolinist who is in the air for 2.4 seconds?
To find this, consider only the down phase and use the equation s = ut + ½ at² with u = 0 and a = 9.81 m/s².
What is the scaling factor if 70 mm on screen corresponds to 1 m in reality?
1 mm on screen equals 0.0143 m in reality.
What is the angle of a projectile with horizontal velocity of 8 m/s and vertical velocity of 6.5 m/s?
θ = tan⁻¹(6.5/8) = 39.1°.
What should be considered when analyzing vertical problems in projectile motion?
Consider the up phase and the down phase separately.
What is the formula for calculating displacement (s) under uniform acceleration?
s = ut + ½ at², where u is the initial velocity, a is acceleration, and t is time.
What is the acceleration due to gravity when considering the upward phase of motion?
a = -9.81 m/s².
What does Newton's First Law of Motion state?
Every body continues in a state of rest, or uniform motion in a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by external forces.
What does Newton's Second Law of Motion state?
The acceleration of a body is proportional to the force causing it, and the change takes place in the direction the force acts.
What does Newton's Third Law of Motion state?
For every force exerted by one body on another, there is an equal and opposite force exerted by the second body on the first.
What is the principle of conservation of momentum?
Momentum before collision equals momentum after collision.
How do you calculate the total momentum before a collision?
Total momentum = Momentum of Player 1 + Momentum of Player 2.
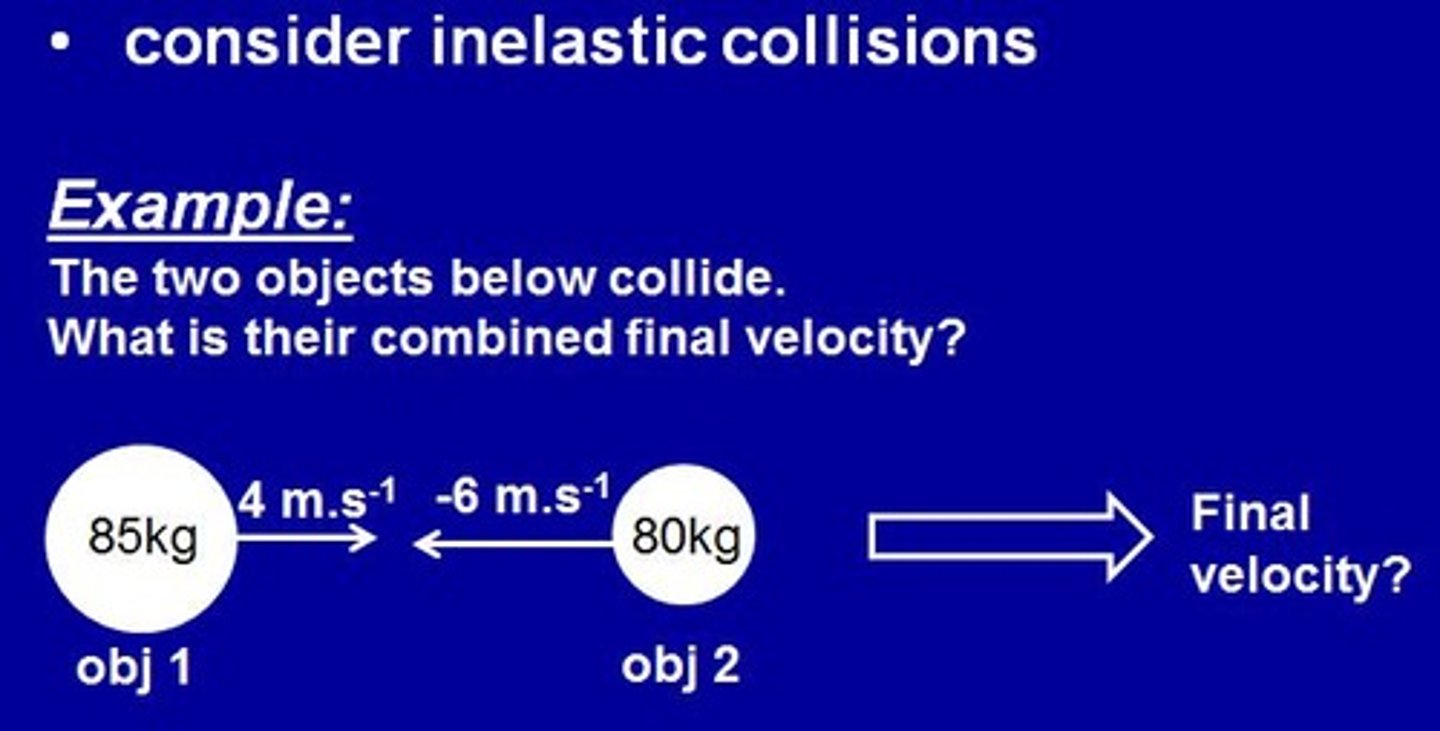
What is the final velocity of two colliding players with masses of 106 kg and 82 kg, and initial velocities of 4.1 m/s and -5.8 m/s?
Final velocity = -0.22 m/s.
How is impulse calculated?
Impulse = Force x time.
What is the impulse of a golf ball hit with a force of 6000 N for 0.03 seconds?
Impulse = 6000 N x 0.03 s = 180 N.s.
What is the formula for calculating pressure?
Pressure = Force / Area.
How do you determine the area of a rectangle measuring 5.1 cm by 2.4 cm in meters?
Area = 0.051 m x 0.024 m = 0.001224 m².
What is the pressure acting on an area of 0.001224 m² with a force of 360 N?
Pressure = 360 N / 0.001224 m² = 294117.65 Pa or 294.12 kPa.
What is the formula for work done?
Work = Force x distance.
How do you calculate the work done by gravity when lifting a 40 kg barbell 0.5 m?
Work done = -392.4 N x 0.5 m = -196.2 J.
What is the formula for kinetic energy?
Kinetic Energy = 1/2 mv², where m is mass and v is velocity.
What is the kinetic energy of a runner with a mass of 68 kg traveling at 8.3 m/s?
Kinetic Energy = 1/2 x 68 kg x (8.3 m/s)².
What is the formula for potential energy?
Potential Energy = mgh, where m is mass, g is acceleration due to gravity, and h is height.
What is the formula for strain energy?
Strain Energy = 1/2 kx², where k is the spring constant and x is the displacement.
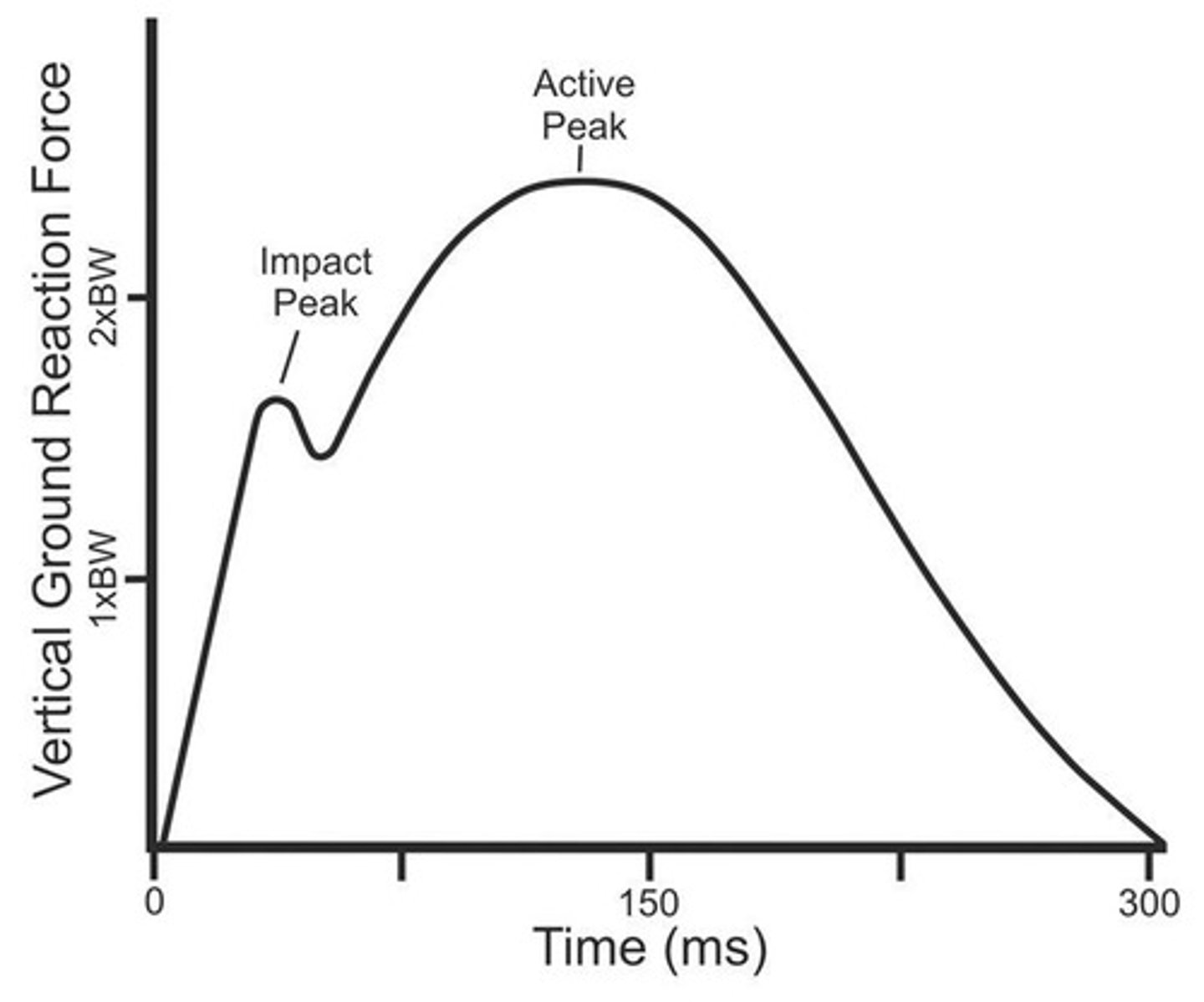
What are typical force time histories during running?
Vertical (Fz) and Anterior-Posterior (FY).
What is the significance of considering both the up and down phases in motion analysis?
It ensures accurate calculations of velocity and displacement, as initial velocity (u) changes.
What is the formula for kinetic energy (KE)?
KE = 1/2 mv²
How much kinetic energy does a mass of 68 kg moving at 8.32 m/s have?
2342.3 J
What is the formula for calculating friction force (F)?
F = μR, where μ is the coefficient of friction and R is the normal reaction force.
If a tennis player of mass 72 kg has a maximum coefficient of friction of 0.45, what is the friction force?
F = 317.8 N, calculated using F = 0.45 x 706.32 N.
What is the normal reaction force (R) for a 72 kg tennis player?
R = 72 kg x 9.81 m/s² = 706.32 N.
How do you calculate the force applied to a ball with mass 0.16 kg and acceleration 412 m/s²?
Use the formula force = mass x acceleration, resulting in 65.9 N.
What is the horizontal distance of a long jumper with a horizontal velocity of 8.00 m/s in the air for 0.59 s?
s = 4.72 m, calculated using s = ut.
What is the formula to calculate the vertical velocity at takeoff for a volleyball player jumping at an angle?
Use sin(θ) = opposite/hypotenuse.
If a volleyball player jumps with a resultant velocity of 2.1 m/s at an angle of 81°, what is the vertical velocity at takeoff?
Vertical velocity = 2.07 m/s.
What is the formula for power produced when lifting an object?
Power = work done / time.
How much work is done by a weightlifter lifting a 120 kg bar 1.3 m with a force of 3800 N in 0.4 seconds?
Work done = 4940 J.

What is the power produced by a weightlifter lifting a bar in 0.4 seconds?
Power = 12350 W.
In a collision between two rugby players, how do you find the mass of Player B if Player A has a mass of 94 kg and they collide with combined velocity of 0 m/s?
Use conservation of momentum: mA vA + mB vB = 0.
What is the velocity of Player A in the rugby collision?
Player A has a velocity of 4.0 m/s.
What is the velocity of Player B in the rugby collision?
Player B has a velocity of -4.9 m/s.
What is the significance of the combined velocity being 0 m/s after the collision?
It indicates that the momentum before the collision is equal to the momentum after the collision.
How do you calculate the work done when lifting an object?
Work done = Force x Distance.

What is the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration?
Force = mass x acceleration.
What is the coefficient of friction for the tennis player sliding on clay?
0.45.
How long is the long jumper in the air?
0.59 seconds.
What is the resultant velocity of the volleyball player at takeoff?
2.1 m/s.
What is the formula for calculating momentum?
Momentum (p) = mass (m) x velocity (v)
Calculate the momentum of Player A with a mass of 94 kg and a velocity of 4.0 m.s-1.
Momentum of Player A (pA) = 94 kg x 4.0 m.s-1 = 376 kg.m.s-1
What is the expression for the momentum of Player B if their mass is mB and velocity is -4.9 m.s-1?
Momentum of Player B (pB) = -4.9 mB
What is the total momentum when Player A's momentum is 376 kg.m.s-1 and Player B's momentum is -4.9mB?
Total momentum = 376 - 4.9mB
What is the condition for total momentum when it equals zero?
Total momentum = 0 implies 376 - 4.9mB = 0.
How do you solve for mass B (mB) when the total momentum is zero?
Set 376 = 4.9mB, which gives mB = 76.7 kg.
What is the impulse experienced by an athlete with a mass of 79 kg who applies a net impulse of 135 N.s?
Impulse = change in momentum = 135 N.s.
How do you calculate the vertical take-off velocity (vf) of an athlete using impulse?
Using the equation Impulse = m(vf - vi), where vi = 0, we find vf = 135 / 79 = 1.71 m.s-1.
What is the acceleration of a 220 g ball hit with a force of 140 N?
Using F = mass x acceleration, convert mass to kg (0.22 kg) and solve: acceleration = 140 N / 0.22 kg = 636.4 m.s-2.
Calculate the change in momentum for a ball of mass 0.5 kg rolling at -2.1 m.s-1 and hitting a velocity of 29.4 m.s-1.
Change in momentum = momentum after - momentum before = (0.5 x 29.4) - (0.5 x -2.1) = 14.7 + 1.05 = 15.75 kg.m.s-1.
What is the total flight time for an athlete who jumps with a vertical velocity of 3.8 m.s-1 and lands at the same height?
Using the formula v = u + at, the time to reach the peak is t = 0.387 s, so total flight time = 0.387 s x 2 = 0.77 s.
What is the total mass of two players if Player A has a mass of 94 kg and Player B has a mass of 76.7 kg?
Total mass = 94 kg + 76.7 kg = 170.7 kg.
What is the significance of impulse in sports physics?
Impulse relates to the change in momentum, which is crucial for understanding how forces affect motion during athletic performance.
What is the formula for calculating acceleration from force and mass?
Acceleration = Force / Mass.
What does a negative velocity indicate in the context of momentum?
A negative velocity indicates the direction of motion is opposite to the defined positive direction.
How is total momentum related to total mass and total velocity?
Total momentum = total mass x total velocity.
What is the total marks for the exam mentioned in the notes?
The total marks for the exam is 150 marks.
What is the structure of the exam as per the notes?
Section A: 90 marks (30 multiple choice questions, negatively marked); Section B: 60 marks (3 short answer questions).
What is the vertical velocity of an athlete at take-off if they apply a net impulse of 135 N.s?
The vertical take-off velocity is 1.71 m.s-1.
What does the term 'change in momentum' refer to?
Change in momentum refers to the difference between the final momentum and the initial momentum of an object.
How do you find the final velocity of an object using impulse?
Rearranging the impulse formula gives vf = (Impulse + m * vi) / m, where vi is the initial velocity.