3.8- equilibrium constants
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Dynamic equilbrium

Reversible reaction where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, so the quantities of each substance stay the same
le chateliers principle
If a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change, the equilibrium tends to shift so as to minimize the effect of that change
Kc and Kp
Kc- the equilibrium constant in terms of concentration and is usually used for reactions in solution
kp- the equilibrium constant in terms of partial gas pressures and is used for reactions only involving gases
Equilibrium constants in solutions
equation kc
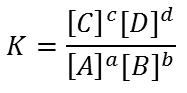
Products over reactants
equilibrium constants in gases
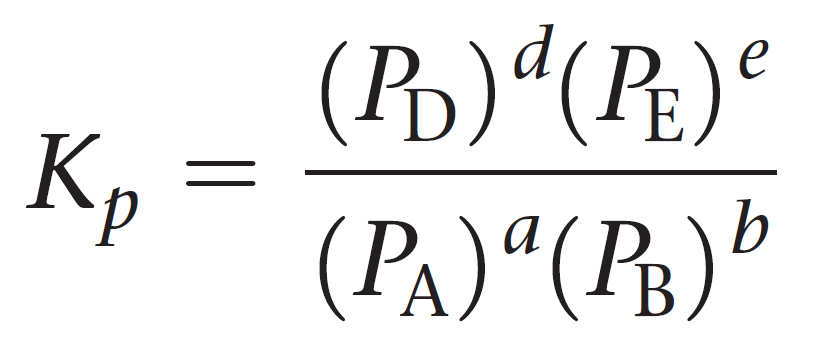
each represent their partial pressure
Products over reactants
Partial pressure
The pressure that the gas would exert if it alone occupied the volume
sum of the partial pressures = the total pressure of the system
Interpretating equilibrium constants
kc small/bigger than 1
If Kc is <1: very few products are formed and most of the mixture is starting material, typically the case when free energy change is positive and reaction doesn’t occur spontaneously
if Kc is >1, then most reactants have been converted into products
equilibrium data
tells us about the relative stability of reactants and products, and the changes that occur between them
reaction rate
Gives us information about the changes that occurred between the reactants and transition state
allows us to deduce what's happening during the reaction and the order in which individual bonds are broken and made- called the reaction mechanism
Changing equilibrium yield
Buy altering concentration, pressure or temperature
equilibrium constant will allow us to identify which concentration or pressure values favour high yield
the energetics can allow us to identify what temperatures will favourite higher yield
Maximising rates
Buy increasing temperature pressure and adding catalyst
these factors would be altered to increase rate unless the factor decreases yield
Identifying energy calculations
Energy calculations will identify how much energy needs to be the input into the system for reaction to occur minimizing the input of excess energy
the energy generated by an exothermic reaction may be calculated and this allows a company to decide whether it's economical to harness this energy or needs to be removed as waste
Equilibrium constants and temperature
exothermic
Temperature is the only thing that affect equilibrium constants
for an exothermic reaction and increasing temperature will cause the equilibrium to shift in the endodermic direction (left) reducing the amount of products and increases the amount of reactants
decreasing the value of the equilibrium constants
Equilibrium constant and temperature
endothermic
For an endothermic reaction and increasing temperature will cause the equilibrium to shift in the exothermic direction (right) increasing the amount of products and decreasing the amount of reacants
this increases the value of the equilibrium constant
Increase and decrease in Kp and Kc
exothermic and endothermic
Exothermic reaction: increasing temperature decreases Kc and Kp
endothermic reaction: increasing temperature increases Kc and Kp