3.6 (2.1.2) structure of proteins
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
define primary structure
The sequence/ order of amino acids in the polypeptide
describe secondary structure of proteins
The O, H, and N atoms of the amino acids interact in the formation of hydrogen bonds. This may twist the chain of amino acids into an alpha-helix. Or it may form beta-pleated sheets
why may secondary structure of proteins include beta-pleated sheets
parallel polypeptide’s hydrogen bonding
what is a peptide bond
a covalent bond which joins two amino acids by removing H2O from an amino group (–NH2) of one amino acid and a carboxyl group (–COOH) of the adjacent amino acid in a polypeptide chain
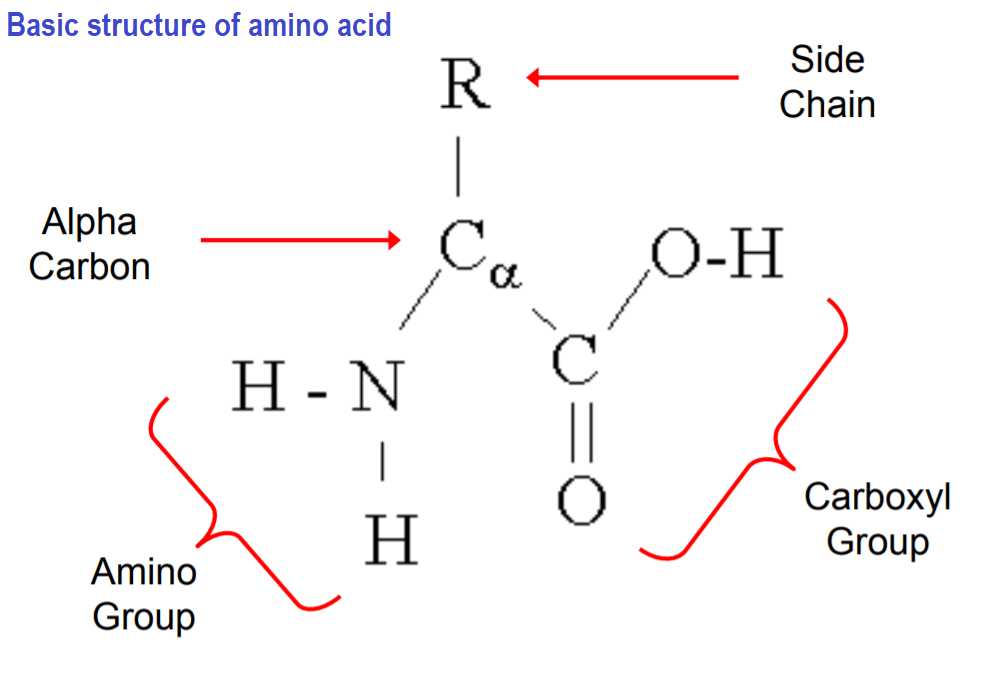
general structure of amino acid
includes a basic amino group (-NH2), an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH), and an organic variable group
define tertiary structure of protein
the folding of the protein into its final 3D shape
name 4 types of bonding in tertiary structure of protein
1) hydrophobic/ hydrophilic interactions 2) hydrogen bonding 3) ionic bonds 4) disulphide bridges
define disulphide bonds in protein
the strongest covalent of the forms which bonds one S atom with another S atom from a different amino acid
define quaternary structure of protein
more than one polypeptide
describe properties of globular proteins
compact. spherical. hydrophobic variable groups on amino acids. hydrophilic variable groups. soluble. important in reactions within aqueous medium
example of globular proteins
enzymes, insulin
define conjugated protein
globular proteins with a prosthetic group
describe haemoglobin as a conjugated protein
quaternary protein made of 4 polypeptide subunits. each subunit has a haem group. role is to transfer oxygen around the body
what does a haem group do
binds reversibly with oxygen
structure and function of catalase
contains 4 haem prosthetic groups. breaks down hydrogen peroxide in water + oxygen
describe properties of fibrous proteins
long. insoluble due to many hydrophobic variable groups within primary structure. limited type of amino acid. repetitive sequence of amino acids. not folded into 3D shapes
describe structure and properties of keratin
more cysteine= more disulphide bridges= stronger and inflexible
describe structure of elastin
made of tropoelastin. found in elastic fibres
describe structure and properties of collagen
there are 3 polypeptides wrapped around each other in rope-like structure. flexible but strong. in connective tissues in skin, ligaments, tendons
role of globular proteins
functional (catalysts, transport)
role of fibrous proteins
structural (strength and support)
solubility of globular proteins
soluble in water
solubility of fibrous proteins
insoluble in water
sequence of globular proteins
irregular amino acid sequence
sequence of fibrous proteins
repetitive amino acid sequence
stability of globular proteins
more sensitive to changes in temperature, pH
stability of fibrous proteins
less sensitive to changes in temperature, pH
examples of globular proteins
catalase, haemoglobin, insulin, immunoglobulin
examples of fibrous proteins
collagen, keratin, elastin, actin, myosin