chap 16: navigating the accreditation, certification, or licensure process
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
accreditation: Voluntary process by which the performance of an organization is

measured against nationally accepted standards of performance
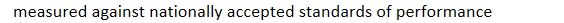
accreditation: many accrediting bodies require healthcare organizations to have a plan that
explains their method of fulfilling quality management activities
accreditation: Frequently change based on government regulations and
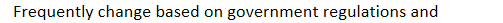
input from individual groups in the healthcare industry

accreditation: the past decade has seen as
explosion of quality metrics
standards and requirements of QM plan: some standards and regulations have explicit requirements
regarding plan and structure of improvement activities

standards and requirements of QM plan: examples: TJC does not require written plan, but does require
organizations take systematic approach to performance improvement
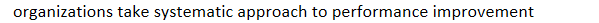
standards and requirements of QM plan: examples: DNV states
“the org shall clearly outline its methodology, practice, and related policies for addressing how quality and performance are measured, monitored, analyzed, and continually improved (DNV 2020, 12)

standards and requirements of QM plan: examples: PA hospitals require a patient safety committee that includes
two residents of community who are served – but not agents, employees, or contractors of – the facility (Commonwealth of PA 2006)

payment models: continue to evolve from traditional fee-for-service to
value-based payment models in which payments are modified based on the achievement of measure-based quality goals

payment models: hospitals that participate in the
Value-Based Purchasing Program have a percentage of Medicare payment at risk, depending on comparative quality performance
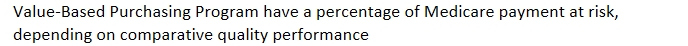
payment models: physician office services are increasingly being tied to the
achievement of quality goals and the submission of quality metrics

payment models: want to go from fee-for-service to
value-based purchasing program
ACA: all federal plans offered through ACA
must be accredited
ACA: overall accreditation status is calculated based on:
. Clinical performance
1. Healthcare Effectiveness and Data Information Set (HEDIS scores)

ACA: overall accreditation status is calculated based on:
Member satisfaction
1. Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (CAHPS Survey)

If a healthcare organization chooses to meet multiple standards and/or regulations, which requirements should they follow?

Go with the one that is most stringent, one with the highest bar (meet this, the rest will be met)

certification: facility = must meet conditions of participation (CoP) to
receive Medicare or Medicaid funding
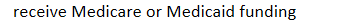
certification: facility: grants approval for healthcare organization to
provide services to specific group of beneficiaries
certification: practitioners = american board of medical specialities (AMBS) is
recognized as leader in setting gold standard for physician specialty certifications

certification: practitioners: show significant achievement of
being skilled and knowledgeable in specific area
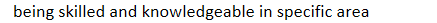
certification: being certified is
voluntary
licensure: act of granting a healthcare organization of an individual healthcare provider permission to
provide services of a defined scope in a limited geographical area

licensure: state government issue licenses based on
regulations specific to healthcare practices
licensure: facilities evaluated on an annual basis by the
state health department
Many publish “report cards”

licensure: is illegal for organizations and professionals to
provide healthcare services without
licensure: is
not voluntary
accreditation and licensure surveys: preparation for accreditation and licensure processes
cannot be accomplished a few weeks before the organization is due for review
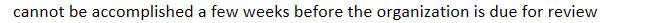
accreditation and licensure surveys: solid accreditation and licensure infrastructure must be
built and maintained so that the organization is ready for an inspection at any time

accreditation and licensure surveys: some are scheduled;
others are unannounced
survey process: surveyors want to be assured the facility’s leadership and staff can successfully
execute organizational policies and procedures

survey process: surveyors want to be assured the facility’s leadership and staff are continuously
monitoring and improving performance in the organization and that those improvements are tied to the organization’s strategic plan

survey process: no standard review process, voluntary processes are more
flexible and tailored to the organization

survey process: no standard review process governmental processes tend to be
more bureaucratic
JC accreditation standards: assesses the alignment of an institutions practices,
policies, procedures, and documentation with its standards of performance
Is quality of care being monitored for continual improvement

JC accreditation standards: 270 standards and
~2,000 elements of performance
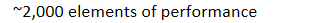
JC accreditation process: site visit every 3 years with midpoint
self-assessments that include correction action plans
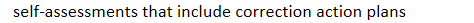
JC accreditation process: unannounced surveys
began in 2006
JC accreditation process: shifts organization focus from
survey preparation to continuous survey readiness
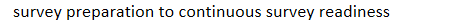
JC accreditation process: surveyors will come with knowledge of the organization =
Midpoint assessment action plan
Any consumer complaints

JC accreditation process: surveyors will come with knowledge of the organization =
Previous accreditation data
Core measure data

JC survey process: survey team then develops
preliminary report of onsite survey, noting any deficiencies

JC survey process: exit conference: report probable
accreditation decision
JC survey process: exit conference: summarize findings and
explain any deficiencies
JC survey process: opening conference: outline the
schedule of activities
JC survey process: opening conference: identify individuals to be
interviewed
JC survey process: opening conference: leaders are expected to provide an overview of the organization’s mission and vision,
strategic goals and objectives, current experiences and outcomes, performance monitoring, and improvement activities

JC accreditation process: composition of survey team varies depending on the size of the organization =
Physician
Administrator
Registered nurse
Other masters-level clinicians

JC accreditation process: composition of survey team varies depending on the size of the organization =
State Licensing agency representative
Expert in environment of care and life safety issues
Length of the survey process also depends on the size of the organization (3-5 days)

tracer methodology: assess standards compliance and follows a number of patients through an
organization’s entire health care delivery process to identify performance issues in one or more steps of care process

tracer methodology: focuses on patient care at
the point of care
tracer methodology: patients selected based on current census of
patients that have a typical case mix
tracer methodology: high-risk process or systems areas:
Medical management
Infection control

tracer methodology: high-risk process or systems areas:
Data management
Restraints

JC accreditation categories =
accredited
accreditation with follow-up survey
contingent accreditation
preliminary denial of accreditation
denial of accreditation
CMS CoP certified: requires hospitals submit >60 measures in
addition to Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAPHS) survey results

CMS CoP certified: also require measures for long-term care,
physician services, dialysis centers, some ambulatory care settings

deemed status: demonstrates that an organization not only meets but
exceeds expectations for a particular area of expertise
deemed status: health care organizations that want to participate in and recieve payment from
CMS must be certified as complying with CoP, or have received accreditation through a national accrediting organization that CMS has provided with deemed authority standards, set forth in federal regulations

deemed status: CMS lists organizations with
deeming authority
deemed status: health care organization would be exempt from
federal inspections to ensure compliance with CMS requirements of participation
CMS conditions of participation: _________ surveys
unannounced
CMS conditions of participation: survey team drops in on an annual basis or in
response to complaints from patients or employees
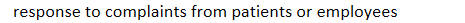
CMS conditions of participation: surveyors usually from state department of health,
however one to two Medicare officials from the regional office may be present

CMS conditions of participation: process like
state licensure surveys
certification and licensure of long-term care: usually,
scheduled reviews
certification and licensure of long-term care: two surveyors who came from
nursing, pharmacy, dietetic, or clinical laboratory background

certification and licensure of long-term care: look for evidence of three trigger issues: excessive percentage of
patients suffering from dehydration
certification and licensure of long-term care: look for evidence of three trigger issues: decubitus ulcers in
low-risk residents
certification and licensure of long-term care: look for evidence of three trigger issues: fecal
impaction
Psychiatric and rehabilitative care: CARF accreditation: commission on
Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities (CARF)
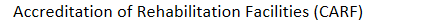
Psychiatric and rehabilitative care: CARF accreditation: three
surveyors
Psychiatric and rehabilitative care: CARF accreditation: flexible
survey process
Psychiatric and rehabilitative care: CARF accreditation: tailored to patient care services and
community of interest of the organization
CARF survey process: opening conference =
Must be accessible to all communities of interest
Payers
Staff members
Referring agencies
Members of the community
Patients

CARF survey process: document review =
Examines policies and procedures, administrative rules and regulations, administrative records, human resources records, and case records of patients

CARF survey process: interviews with program staff and patients =
Validate information gathered from the document review
Determine where staff or patients have any important issues regarding patient care services

CARF survey process: exit interview with organization leaders =
Identify any deficiencies
Present an overall summary of findings

DNV-GL healthcare accreditation: offers the national integrated accreditation for healthcare organizations (NIAHO),
which incorporates International Organization for Standardization (ISO 9001) quality management standards

DNV-GL healthcare accreditation: alternative option for
healthcare organizations because of its facility-friendly yet stringent accreditation philosophy
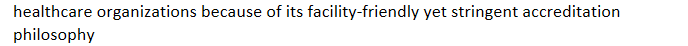
DNV-GL healthcare accreditation: granted deeming status from
CMS in 2008