pk-pd synchronous
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pharmacology week 3 lecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
weak acids
best absorbed in the stomach
what are weak acids best absorbed in the stomach?
bc in the highly acidic stomach, the acids are in their unionized form
what diffuses more readily through cell membranes?
non-ionized substances
weak bases
best absorbed in the intestines
why are weak bases best absorbed in the intestines?
weak bases have enough in the unionized form for absorption in the intestines
carboxylic acid groups on drugs and change with pH
acidic pH (stomach):
when in an acidic state, driven to unionized form
alkaline pH (intestine):
when in a basic state, driven to ionized form
less tendency to be absorbed
amino groups on drugs and change with pH
acidic pH (stomach):
will go into ionized form
alkaline pH (intestines):
will go into unionized form
what is the main form of absorption?
oral
other forms of absorption
intramuscular, subcutaneous, transdermal, inhalation, sublingual, rectal, inhalation, topical
when does absorption occur?
with any administration that leads to the drug getting into the systemic circulation
does absorption occur with IV admin?
NO
bc the medication is injected directly into the systemic circulation
bioavailability
fraction of drug that reaches the systemic circulation
absorption: passive diffusion
transport through a cell membrane
drug MUST be in aqueous solution at absorption site
drug dissolves into and out of the lipid material of the membrane
follow’s Fick’s first law of diffusion
Fick’s first law of diffusion
movement will occur from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration
can ions permeate the lipid material of the membrane?
no, since they have no lipid solubility
can electrolytes permeate the lipid material of the membrane?
yes
can weak acids or bases permeate the lipid material of the membrane?
yes
what are most drugs?
electrolytes, weak acids or bases
why are most drugs electrolytes, weak acids or bases?
bc the ionized moiety is usually lipid soluble
absorption: active transport
involves energy
drug binding to a carrier
often does against concentration gradient OR electrochemical gradient
where can active transport of drugs in the body be found?
active transport mechanisms can be found in many barrier membranes and help modulate the concentration of drug in an organ
first pass metabolism
drug gets metabolized/inactivated prior to reaching the site of action for the drug
where does first pass metabolism occur?
in the liver
but it can occur in other organs too
when does first past metabolism occur?
during and after absorption
one-compartment model
used for drugs which rapidly equilibrate with the tissue compartment
two-compartment model
used for drugs which slowly equilibrate with the tissue compartment
systemic circulation volume
~4.5 L
body water volume
~ 40 L
what is volume of distribution related to?
systemic circulation volume and body water volume
what affects volume of distribution?
physiology
drug characteristics
physiologic changes that affect Vd?
cardiac output, proteins binding
drug characteristics that affect Vd?
lipophilic, intracellular, low molecular weight
high molecular weight, high protein binding
for high Vd
higher concentration in tissue than in plasma
relatively lipophilic, intracellular, low molecular weight
for low Vd
confined to plasma and interstitial fluids (not tissues)
high molecular weight (mAb drugs), high protein binding
what is the main organ for metabolism?
the liver
what does most metabolism take place with?
CYP450 isoenzymes
what is metabolism?
the conversion of the administered drug into another substance by chemical reaction
what are the outcomes of metabolism?
active drug to inactive metabolite
active drug to active metabolite
inactive drug to active metabolite
prodrug
the metabolism of an inactive drug to active metabolite
how many phases does hepatic metabolism have?
2 phases
phase I of hepatic metabolism
biotransformation
drugs undergo oxidation, reduction or hydrolysis to become more hydrophilic
phase II of hepatic metabolism
conjugation
drugs receive a molecular attachment that facilitates transport within the body
can drugs be subjected to either or both phases of hepatic metabolism?
yes!
but often undergo phase I followed by phase II
CYP450 drug interactions
substrate
inhibitor
inducer
substrate
drug is metabolized by that CYP isoenzyme
inhibitor
drug decreases the activity of that CYP isoenzyme
inducer
drug increases the activity of that CYP isoenzyme
what happens if you inhibit metabolism?
increase concentration of drug in plasma
what is the main organ for elimination?
kidney
elimination: renal
the net of three mechanisms within the kidneys:
glomerular filtration
tubular secretion
tubular reabsorption
what is used as a marker of renal function?
CrCl
glomerular filtration
passive diffusion; impacted by:
molecular size
protein binding
glomerular integrity and total number of functioning nephrons
tubular secretion
transports drugs from the blood to the lumen of the nephron
active transport
tubular reabsorption
either via passive diffusion or by active transport systems
clearance
getting drug out of the body
expressed as volume/time
NOT the amount of drug removed, but the volume of plasma (or blood) from which drug is removed in a given time
total body clearance
the sum of all clearances by various mechanisms
Cl total= Cl renal excretion + Cl hepatic metabolism + Cl biliary excretion + Cl other
what affects plasma drug concentrations?
rate of drug administered
volume of distribution
clearance
conversion of plasma concentration v. time curve to straight line (first-order elimination)
allows for extrapolation of drug concentrations at various times for a drug
half-life
t1/2
time necessary for the concentration of drug in the plasma to decrease by one-half (50%)
area under the curve
indicator of overall drug exposure
the greater the area → the more drug absorbed
transmembrane signaling
cascade of steps
most drugs act on receptors on the extracellular face of the cell membrane and modify the intracellular function of those receptors by transmembrane signaling
agonist drugs
full activation/full drug effect
partial agonist drugs
partial activation/partial drug effect
antagonist drugs
no activation/drug effect
can also block the effect of agonist drugs
example of an antagonist
antihistamines
graded dose-response curves (individuals)
response of a particular receptor-effector system is measured against increasing concentrations of a drug, the graph response versus the drug concentration or dose
Emax
maximum efficacy
EC50 (ED50)
concentration (dose) needed to achieve 50% of the maximal drug effect
the small the EC50
the greater the potency of the drug (potency on the ceiling effect of the drug)
what does the slope of the line in a graded dose response curve represent
the change in response per unit dose
therapeutic window
range of concentration between minimum effective and toxic concentrations
therapeutic drug monitoring
monitoring drug concentration levels in the plasma/blood to reach therapeutic dosing goals while avoiding toxicity
subtherapeutic
plasma concentrations too low
NOT effective
supratherapeutic
plasma concentrations too high
TOXICITY
plasma drug concentration
he measurement of the drug's concentration in the blood over time, which is represented by a plot known as the plasma concentration–time profile
peak concentration
highest concentration that will occur in the plasma
typically drawn 30 minutes after IV admin to allow for distribution
trough concentration
lowest concentration in the plasma between doses
typically immediately before the next dose is to be administered
random concentration
drawn at any point during the dosing interval
concentration/time curves for oral administration
time for medication to transit to gut and be liberated from tablet
gradual rise in concentration over time due to needing to be absorbed into the plasma
Cpk
peak concentration
amount of drug being absorbed is equal to amount being eliminated
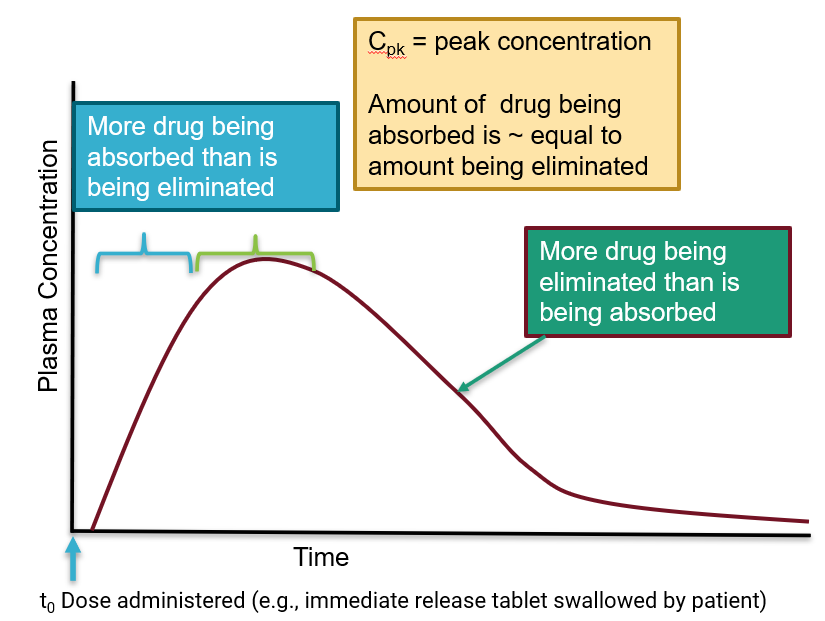
oral administration
concentration/time curves
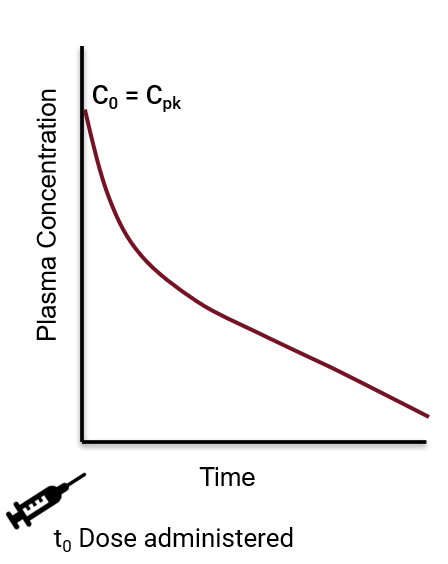
intravenous bolus dose
concentration/time curves
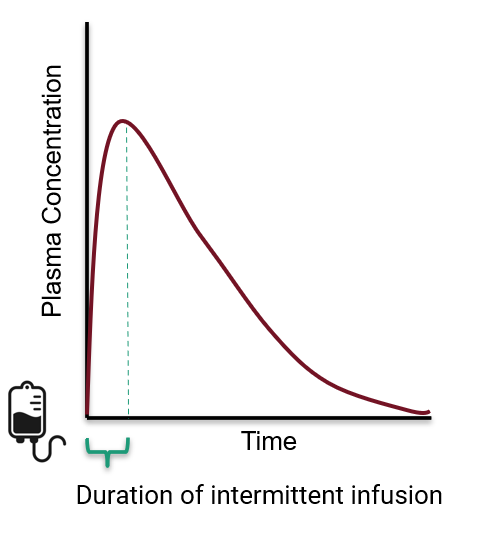
intermittent infusion
concentration/time curves
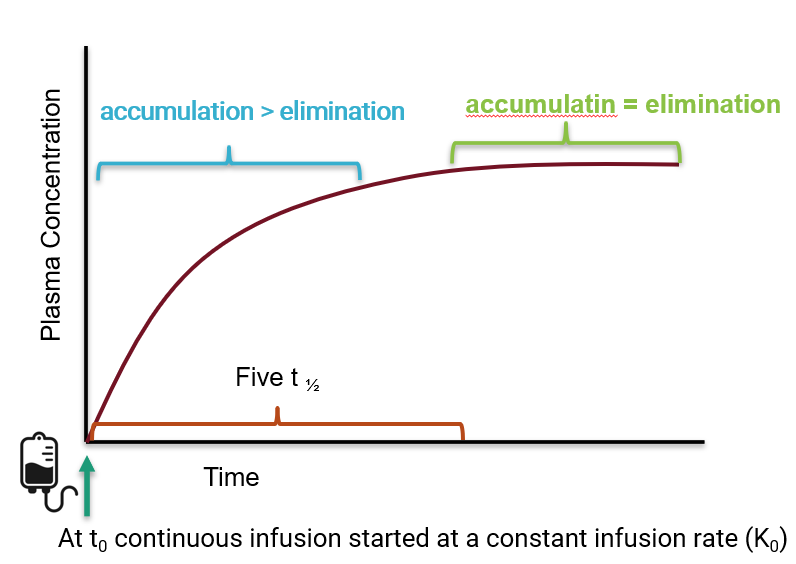
continuous infusion
concentration/time curves
concentration/time curves for IV bolus dose
C0=Cpk
Cpk occurs instantaneously
IV bolus dose
medication is administrated directly into the bloodstream
no need for absorption
IV bolus dose (IV push)
typically administered over 10-30 seconds
C0
concentration at time0
concentration/time curves for intermittent infusion
Cpk does NOT occur instantaneously
Cpk occurs at the end of the infusion
intermittent infusion
medication administered directly into the bloodstream
no need for absoprtion
intermittent infusion administered over
10, 30, or 60 minutes
concentration/time curves continuous infusion
usually for drugs with a short half-life
continuous infusion
small amount of drug is administered to patient every second/minute
steady state
when accumulation rate=elimination rate
what is steady state?
a function of the drug’s half-life
how many half-lives does it take to reach steady state?
5
principle of superposition
continuous to build until reaches steady state→ will still have ups and downs
when a pt receives a subsequent dose of a medication and there is still drug present in the plasma, there is an additive effect on the plasma concentrations
Css ave
average concentration at steady state
IR v ER medications
extended release medications are formulated to release drug over a longer period of time
results in less variability in Cmax and Cmin
physiologic factors affecting pharmacokinetics
elderly
kidney failure/dysfunction
hepatic dysfunction
obesity
pediatrics
pregnancy