MCB 32 Midterm 1
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
organ system that provides communication within the body by releasing hormones into the bloodstream
endocrine
organ system that provides communication between cells in the body via electric signals
nervous
organ system that supports the body and allows voluntary and skeletal body movement
muscoskeletal
organ system that transports molecules throughout the body and is responsible for moving material
cardiovascular
organ system that takes in oxygen and expels carbon dioxide
respiratory
organ system that filters the blood to regulate acidity, blood volume, and ion concentrations; as well as excreting waste
urinary
organ system responsible for breaking down and absorbing food
gastrointestinal
materials in the external environment must pass through ? cells (? # of membranes) to enter the internal environment
epithelial, 2
the most total body water (internal) is in the
intracellular fluid (inside the cell)
two categories of extracellular fluid
plasma (most of ECF) and interstitial fluid
fluid that is not in the blood, but that surrounds cells
interstitial
the phospholipid bilayer can easily be permeated by which kind of molecules
nonpolar (hydrophobic)
an important storage polysaccharide found in animal tissues
glycogen
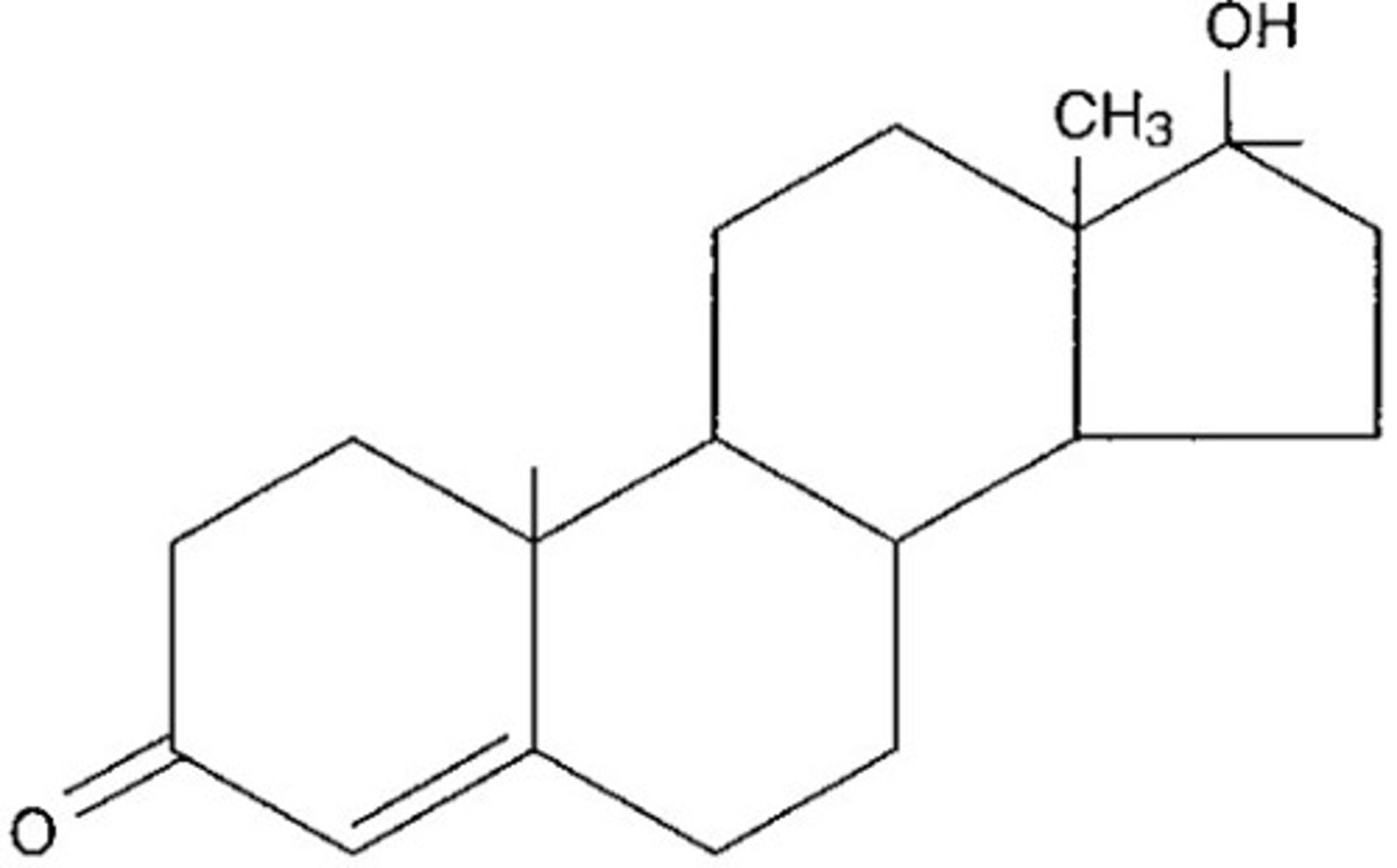
steroid structure
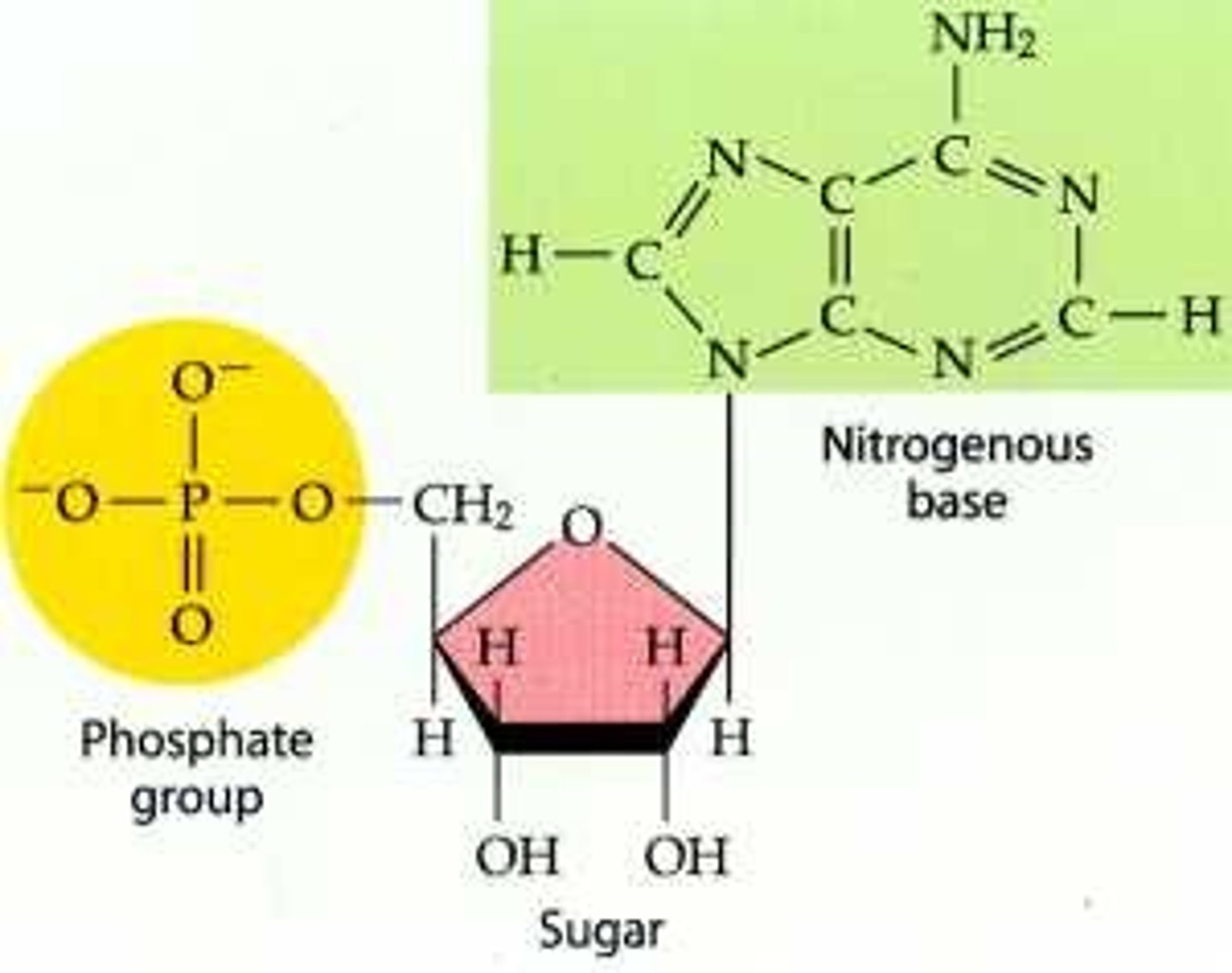
nucleotide structure
nucleotide: 5 carbon sugar + phosphate group + base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, or uracil)
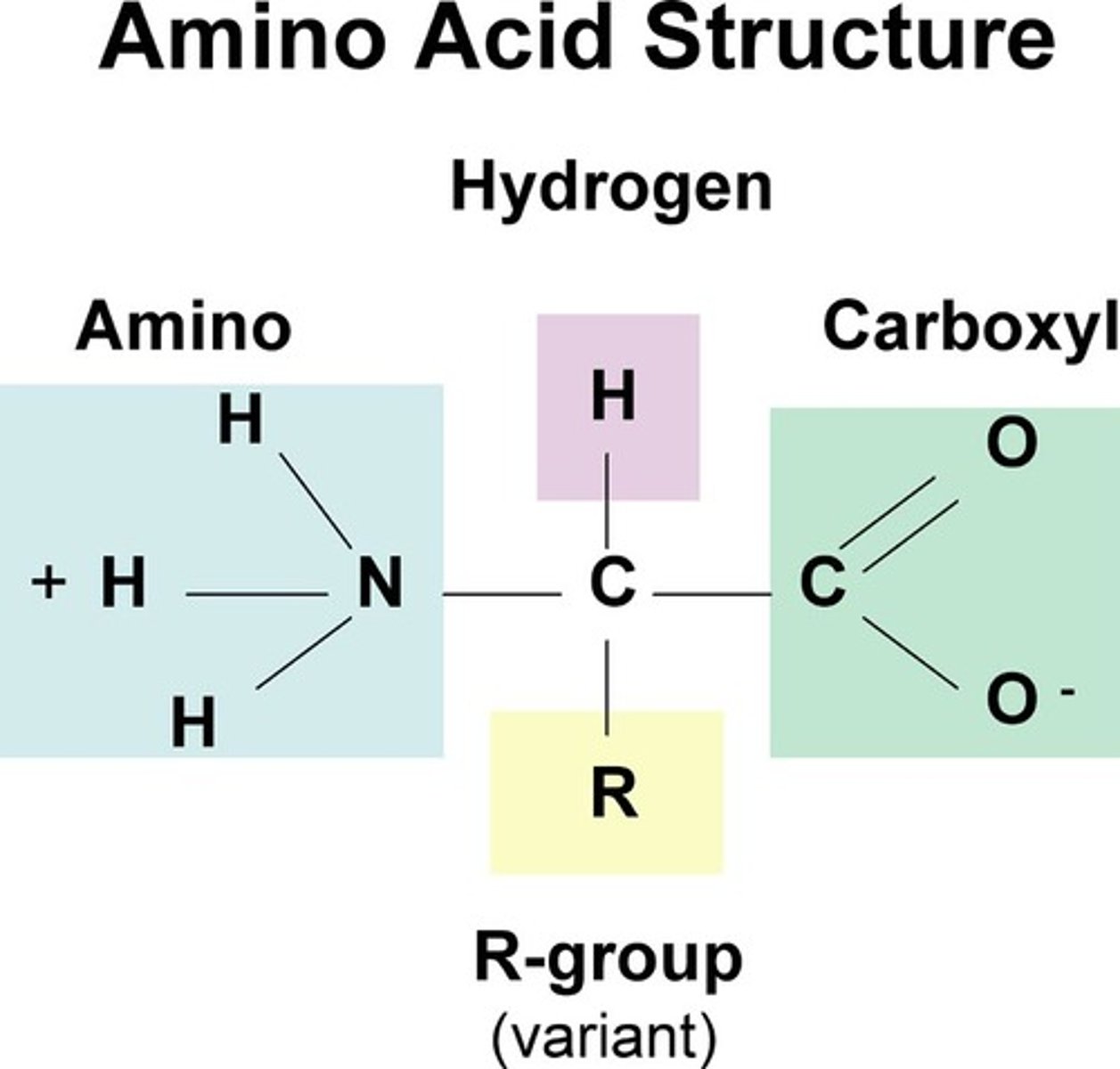
amino acid structure
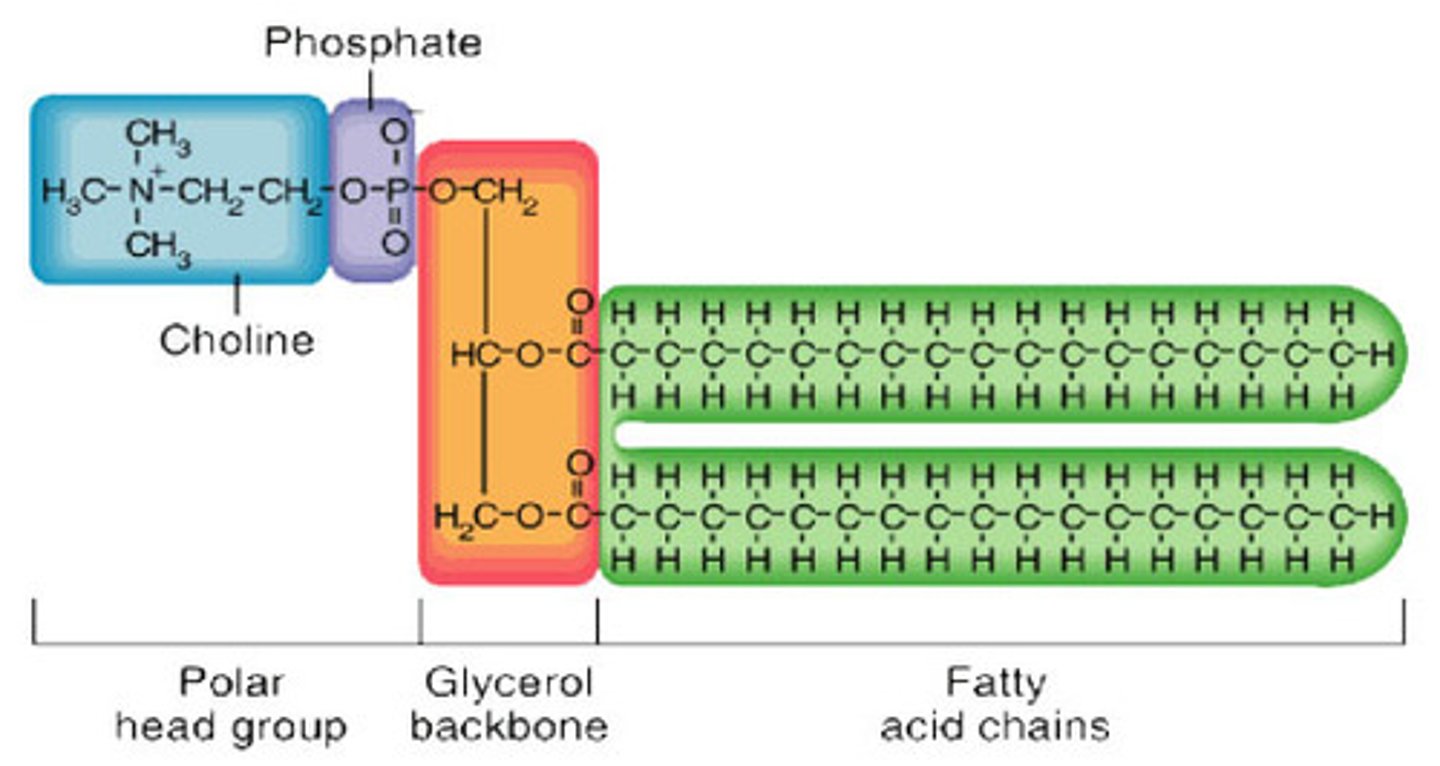
phospholipid structure
reactions that require energy input
endergonic
what type of reaction is the breakdown of polysaccharides into monosaccharides
hydrolysis, catabolic
T/F - enzymes are consumed in a reaction
FALSE (enzymes are NOT consumed in a reaction)
enzymes are what biomolecule
proteins
what does it mean to say that an enzyme is saturable
the rate at which an enzyme catalyzes a reaction depends on substrate concentration until a threshold concentration is reached
movement of ions across a membrane
neuronal signalling
molecules that release H+ ions when dissolved in water
acids
ph below 7
acids
ph above 7
bases
important characteristic of phospholipids
amphiphillic (polar and nonpolar)
what characterizes a peptide
less than 50 amino acids
function of nucleic acids
store and express genetic information (i.e. directions for making proteins)
proteins are made up of
amino acids
proteins act as ? to catalyze chemical reactions
enzymes
T/F: proteins can provide structural support for cells
true
nucleic acids are polymers of ?
nucleotides
the sum of all chemical reactions in cells
metablism
breakdown of large molecules into smaller ones
catabolism (exergonic)
production of larger molecules
anabolism (endergonic)
what type of reaction is disaccharide --> monosaccharide
catabolism (exergonic)
why are anabolic reactions able to happen in cells?
because they are coupled with catabolic reactions
the rate of a catabolic reaction can be increased/decreased by altering the ...
activation energy barrier
proteins that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy
enzymes
substrates bind to enzymes in the ?
activation site
enzymes are NOT ? by reactions
CONSUMED
T/F: enzymes can catalyze multiple reactions
true
an enzyme that has a higher affinity for substrate A than for substrate B, will ??
bind faster to substrate A than B, however eventually both will bind to saturate all enzymes
how can you increase the rate of an enzymatic reaction when all enzymes are saturated?
add more enzymes
allosteric regulation binding is
reversible and noncovalent
allosteric regulators alter
enzyme affinity for substrates
where do allosteric regulators bind to enzymes
anywhere but the activation site
covalent modification (i.e. phosphorylation of enzymes) can alter
enzyme activity and affinity
a collection of cells with a related function
tissue
4 types of tissues:
epithelial, connective, nervous, muscular
a single layer of cells that act as selective barriers connected by tight junctions
epithelial tissue cells
transmembrane proteins that hold epithelial cells together preventing molecules from passing in between cells
tight junctions
side of epithelial cell facing the lumen
apical
side of epithelial cell facing the blood vessel
basolateral
on the apical side of an epithelial cell, there are ? that increase the surface area
microvilli
two types of epithelial glands
endocrine and exocrine
glands that secrete hormones into the blood stream
endocrine
glands that secrete products into the external environment (i.e. tears, sweat, digestive track materials)
exocrine
3 types of muscle tissue
smooth, cardiac, skeletal
only muscle tissue that is voluntary
skeletal
tissue that lines blood vessels and the digestive tract
smooth muscle tissue (pushes food through the body)
a lysosomal storage disease that causes a mutation of the nuclear envelope and accelerated aging
progeria
plasma membrane is made of
sugars, proteins, and lipids
two types of nervous tissues
neurons and glia cells
two organelles surrounded by TWO membranes
nucleus and mitochondria
transcription (DNA copied into RNA) occurs where
nucleus
the nucleus contains genetic information in the form of
chromatin (DNA + proteins)
the cytoplasm is made up of
cytosol and organelles
the ? structure surrounds the nucleus
endoplasmic reticulum
function of the rough ER
protein synthesis
function of the smooth ER
synthesizes lipids
translation occurs where
in the rough ER
process where RNA is read by ribosomes and used to make proteins
translation
organelle that receives synthesized proteins from the ER and finishes processing them, then packages them and delivers them to their final destination
golgi apparatus
how does the ER deliver proteins to the plasma membrane (exocytosis)
secretory vesicles
process in which the membrane of a secretory vesicle and the plasma membrane fuse to release contents outside of a cell
exocytosis
lysosome is surrounded by ? membrane(s)
1
function of lysosome
contains enzymes to digest debris/old organelles
T/F: mitochondria has its own DNA and can make cellular energy (ATP) via cellular respiration
true
chemical reaction that breaks down sugars/fats/proteins to yield ATP/water/carbon dioxide
cellular respiration (occurs in the mitochondria)
anaerobic respiration (glycolysis) occurs where?
cytoplasm
the cytoskeleton is made up of ? that provide cell structure/support
proteins
T/F: the cytoskeleton is not rigid/fixed
true (the proteins in the cytoplasm reassemble all the time!)
two components of the cytoskeleton
microtubules and microfilaments (actin)
component of the cytoskeleton that is usually found near the cell membrane, and involved in cell movement and muscle contraction (also found in microvilli)
microfilaments (actin)
largest filament of the cytoskeleton, provides a track for transporting vesicles
microtubules
makes up cilia/flagella
microtubules
involved in cell movement / muscle contraction
microfilaments
RBC's perform
anaerobic respiration (glycolysis)
number of glucose molecules produce in aerobic respiration
36
number of glucose molecules produced in glycolysis
2
the Na+/K+ pump is an example of what type of transport
primary active transport
sodium-linked glucose transport (couples the inward flow of sodium with the inward flow of glucose) is an example of what type of transport
symport (cotransport)
diffusion distance increases - what happens to the rate of simple diffusion?
decreases
can neurotransmitters diffuse across the plasma membrane
NO
intercellular communication occurs at
chemical synapses and gap junctions
the a ligand binds a GPCR, the gprotein releases a ? and binds a ?
GDP, GTP
a chemical messenger that acts on a nearby cell is functioning as a
paracrine signal
hypersecretion of ACTH would lead to the following
increased cortisol levels, decreased CRH levels