physics- topic 6- waves
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
what do waves transfer
energy not matter
what are waves caused by?
vibrations/vibrating source
what’s a transverse wave?
where the oscillations of the wave are perpendicular to the direction in which the wave transfers energy
examples of transverse waves?
The ripples on the surface of the water.
The secondary waves of an earthquake.
Electromagnetic waves (light)
what are longitudinal waves?
the oscillations of the wave are parallel to the direction in which the wave transfers energy
examples of longitudinal waves?
sound waves.
ultrasound waves.
seismic P-waves.
what is frequency?
number of waves per second
what is the amplitude?
the maximum displacement of a point of a wave from its rest position
what is a wavelength?
distance covered by a full cycle of the wave. usually peak to peak or trough to trough
what are electromagnetic waves?
transverse waves made up of electric and magnetic fields
properties of electromagnetic waves (light)
transverse
can travel through a vacuum
can reflect/refract
transfer energy
travels at 300,000,000m/s through a vacuum


1- compression, high pressure
2- rarefaction, low pressure
what happens when light/waves pass from one medium to another and why?
it bends or refracts
because different materials have different densities, thus affects the speed of the wave causing it to change direction
how do waves transfer through a solid?
The particles in the solid vibrate and transfer kinetic energy through the material.
What technique is used to detect objects in deep water and measure water depth?
Echo sounding
High frequency sound waves are emitted, reflected and detected
Time difference between emission and detection, alongside wave speed, are used to calculate distances
what does the law of reflection state?
angle of incidence=angle of reflection
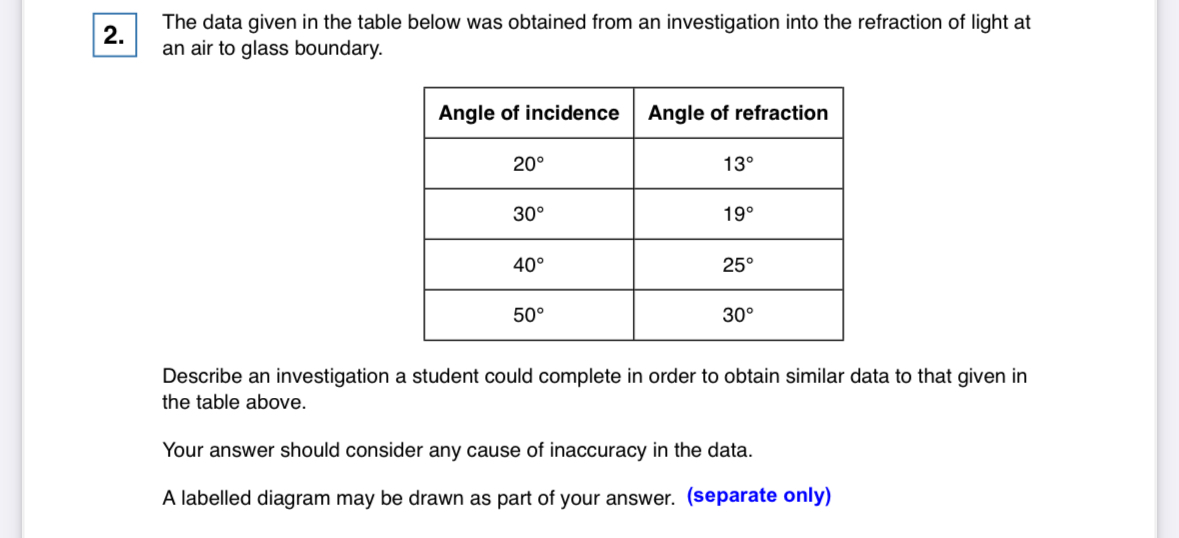
•place a glass block on a piece of paper
draw around the glass block and remove it
draw a line at 90° to one side of the block (this is the normal line)
use a protractor to measure and then draw a line at an angle of 20° to the normal
put the glass box back
using a ray box and split, point the ray of light down the drawn line of 20°
mark the ray of light reflected from the block and the refracted ray
remove the block and draw the reflected and refracted ray
measure the angle of refraction with a protractor
repeat the procedure for a range of values of the angle of incidence
possible sources of inaccuracy:
the width of the light ray which makes it difficult to judge where the centre of the ray is (make the ray as narrow and precise as possible)
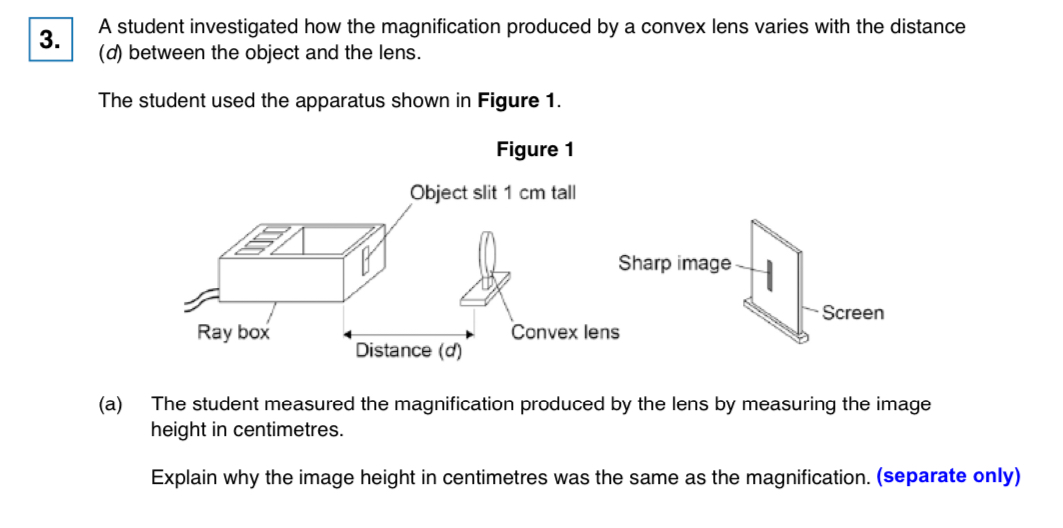
magnification= image height/object height
dividing by an object height of 1cm gives the same (numerical) value
what is an ultrasound?
high frequency sound waves that has over 20,000 Hz
explain how ultrasound can be used to produce a picture of an unborn baby?
the ultrasound reflects from boundaries between different tissues. the computer used the time taken to receive the reflection to calculate the distance to the tissue boundary
how do we hear from sound waves?
sound waves in the air are funnelled into the ear where they hit the eardrum(a thin membrane). the sound wave causes the ear drum and other parts of the inner ear to vibrate. this causes the sensation of sound.
what is the frequency of normal human hearing?
20-20,000Hz
why do sound waves travel faster in solids?
the particles in solids are much closer together so the vibrations can pass more easily between them?
what happens to the frequency when a wave changes medium?
doesn’t change because that would mean waves would have to be created or destroyed at the boundary which isn’t possible
why can sound waves not travel through a vacuum?
because sound waves move by particles vibrating and a vacuum has no particles
what is a reflected sound wave called?
echo
what do seismic waves do?
carry energy away from the earthquake, they pass through the earth and can be detected by seismometers
what are primary waves?
longitudinal waves, can pass through solid and liquid, causes structures to shake up and down so not too damaging and they are faster than secondary waves
what are secondary waves?
transverse waves, travel only through solids and cause structures to shake side to side so they are damaging. they are slower and arrive later than primary waves
why do seismic waves travel in curved paths?
due to density changes in the earth
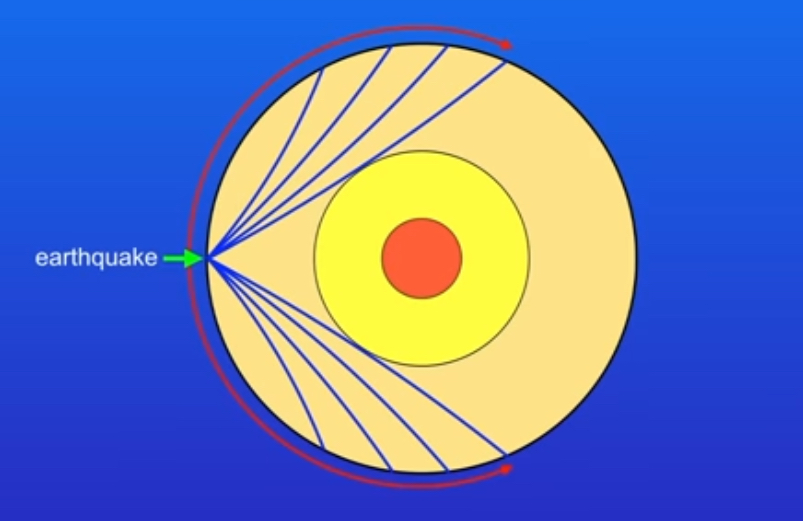
what type of wave does this image show?
secondary waves, can’t pass through liquids
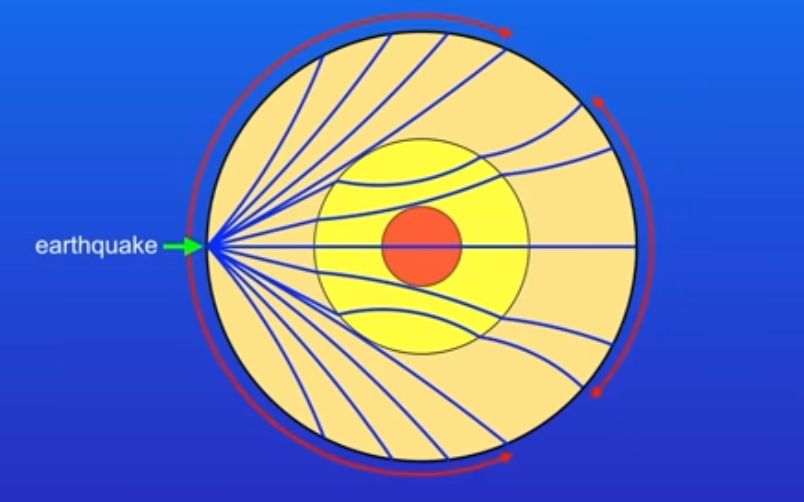
what type of wave does this diagram show?
primary waves
why does the primary wave have shadow zones?
because p waves travel faster in solids than in liquids so they slow down as they enter liquid outer core which causes them to refract (change direction)
what happens if we pass white light through a prism?
it splits into a spectrum
what is the order of the electromagnetic spectrum?

how can we remember this order?

do electromagnetic waves need a medium to travel through?
no
What type of spectrum do electromagnetic waves form?
a continuous spectrum
what speed to electromagnetic waves travel at?
300,000,000m/s
why do watery foods (soup) heat up faster in a microwave?
microwaves are absorbed by foods which contain water molecules but microwaves are reflected by metals
what is the wavefront?
an imaginary line that connects all the same points in a set of waves
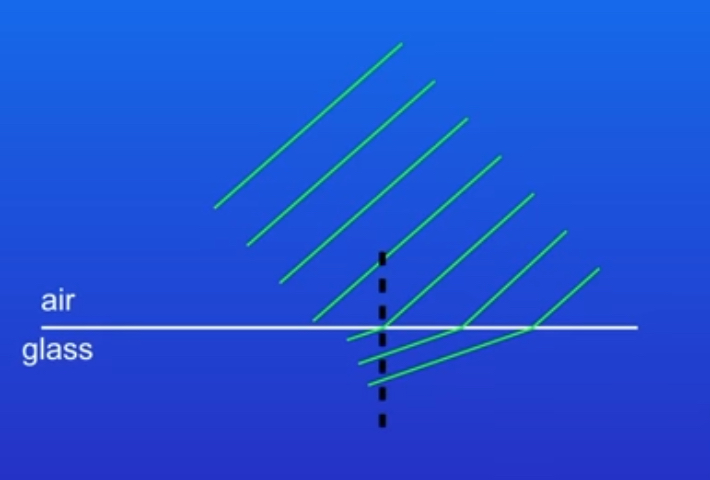
why do the waves change direction towards the normal when moving from air into glass?
because glass is denser than air so when the first wavefronts start to move into the glass those parts slow down and move closer together this causes the wave to change direction towards the normal
what happens to the electrons and energy levels when electromagnetic waves are absorbed (heated)?
electrons move to a higher energy level
what happens when the electron moves back to its original energy level?
it generates an electromagnetic wave (light)
what is another way that an electromagnetic wave can be generated?
a change to the nucleus (e.g gamma rays in radioactive atoms and the nucleus would have less energy)
what are the problems with ultraviolet waves?
increase the risk of skin cancer and causes the skin to age prematurely
what are the problems with X-rays and gamma rays?
ionising radiation (knock electrons off when they are absorbed) this can cause the mutations of genes and increase risk of cancer
what are radio waves used for?
to transmit radio and terrestrial TV signals
walked talkies
why are radio waves used?
they can travel long distances without being absorbed (e.g buildings and trees)
describe what happens in the electrical circuit when the car aerial absorbs radio waves?
an alternating current js induced in the electrical circuit (electrons vibrate in the circuit) with the same frequency as the radio wave
How can radio waves create an alternating current in a circuit?
when radio waves are absorbed, they can induce oscillations in a circuit with the same frequency as the waves themselves
what are microwaves used for?
heating food- because most food contains lots of water molecules and water molecules absorb the energy of microwaves the energy causes the temperature of the food to increase
communicate with satellites in space- because microwaves can pass through the earths atmosphere without being reflected or refracted
mobile phones
what is infrared emitted by?
any heated object (electrical heaters)
what is infrared used for?
cook food in ovens- because the energy of infrared is easily absorbed by the surface of objects (for example, infrared from a heater is absorbed by objects in the room)
infrared cameras- to check buildings for heat loss
remote controls
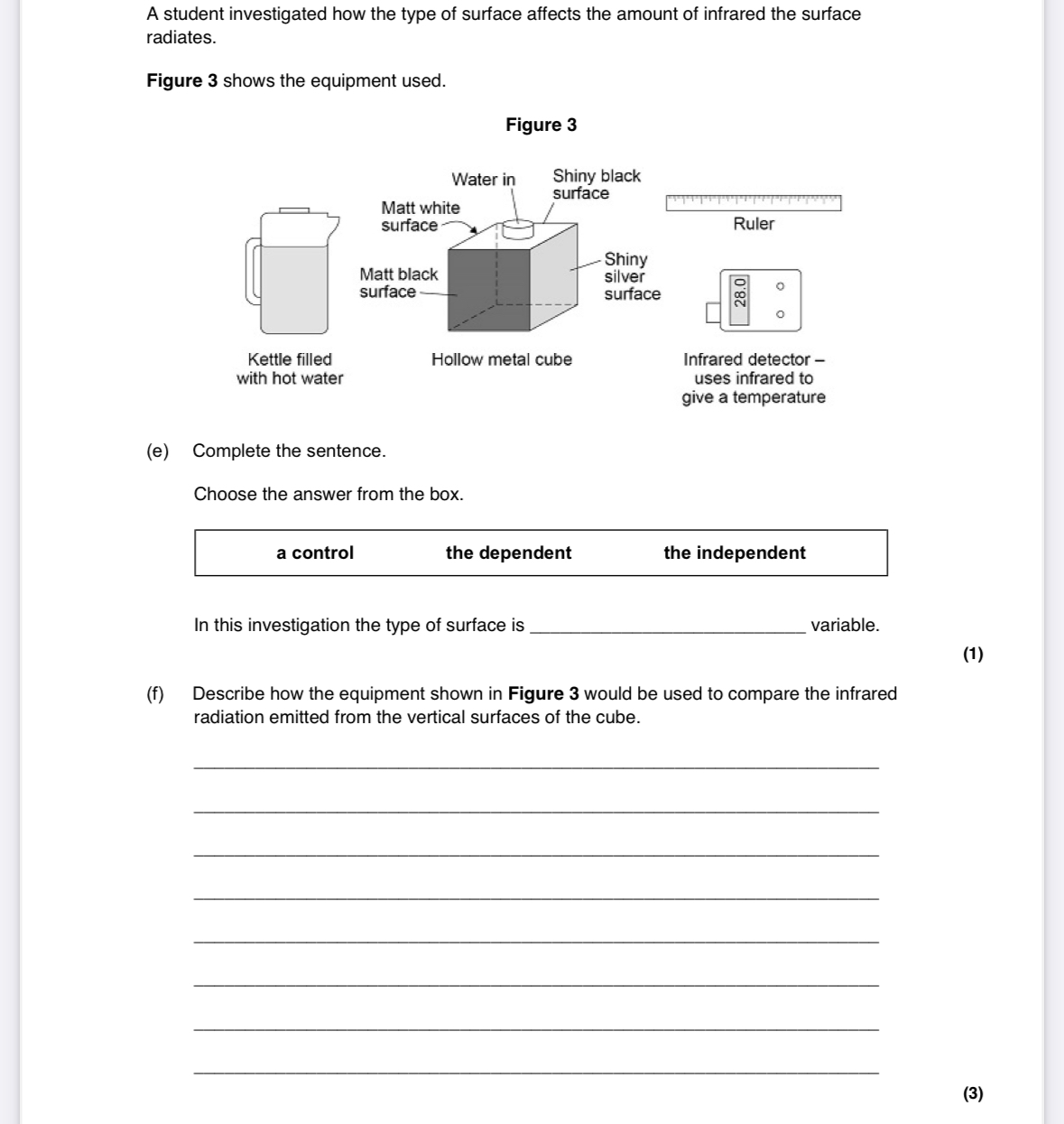
pour hot water into the metal cube
point the IR detector at a side and take a reading
repeat with each different side (surface) but keep the detector the same distance away
what is the use of visible light?
communication using optical fibres
photographs
what are optical fibres?
very thin strands of glass and we can transmit pulses of lights down the fibres and use these pulses to carry information
used to carry telephone and cable TV signals

flexible
what is ultraviolet light used for?
nails
sun tanning
energy efficient light bulbs- Uv light is created inside the bulb and because it has short wavelengths it carries more light than visible light- the energy of the UV light is absorbed by the internal surface of the bulb and is converted to visible light (this requires much less light than a normal bulb)
bright clothing- certain chemicals can absorb UV radiation and re-emit it as visible light
what are X- rays/ gamma rays used for?
medical imaging- both very penetrative so they can easily pass through body tissue, however x- rays are absorbed by bones
X- rays: used to visualise broken bones
Gamma rays: used to detect cancers
also both used in medical treatments
what are properties of objects that reflect light well?
smooth, shiny surfaces
pale colours
give clear images because they reflect light regularly
what are the properties of objects that do not reflect light well?
rough, matt surfaces
dark colours
give diffuse images of no image
What is meant by the term 'specular reflection'?
reflection from a smooth surface in a single direction
What is meant by the term 'diffuse reflection'?
reflection from a rough surface who can causes scattering
white objects reflect _______
all colours
red objects only reflect ______ and _______ all other colours
red part of light
absorbs
a book observed in daylight has a blue front cover with its title white. describe and explain its appearance in a red light?
the blue front cover would appear black as it absorbs the red light but the title would appear red because it reflects red light
a red filter absorbs all the colours of the white light spectrum except red, which is transmitted by the filter m. a blue filter does the same with blue light. they are both positioned so that light passes through one filter then the other filter. if the light is directed at the first filter is white light, describe and explain what colours are transmitted through both filters.
red light would pass through the red filter and when it reaches the blue filter, the red light gets absorbed so no light is passed through (appears black)
What do all bodies (objects) emit and absorb?
infrared radiation
What happens to the quantity of infrared radiation emitted by an object as temperature increases?
The hotter the object, the more infrared radiation it will emit.
how do lenses form images?
refracting light
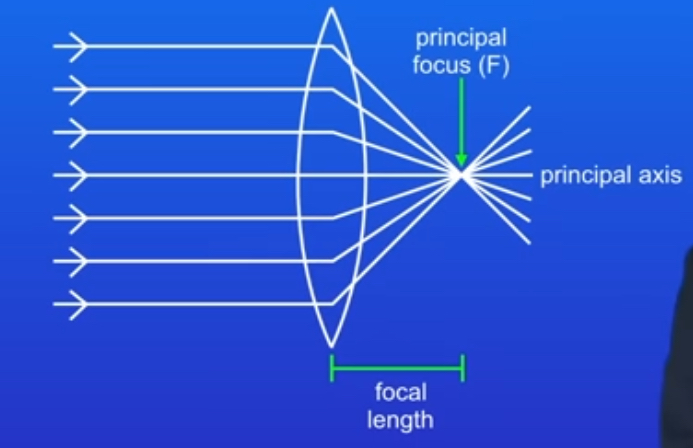
what’s a convex lense?
converging lense- bulges outwards, causes a rays of light parallel to the axis to be brought together (converge) at the principal focus
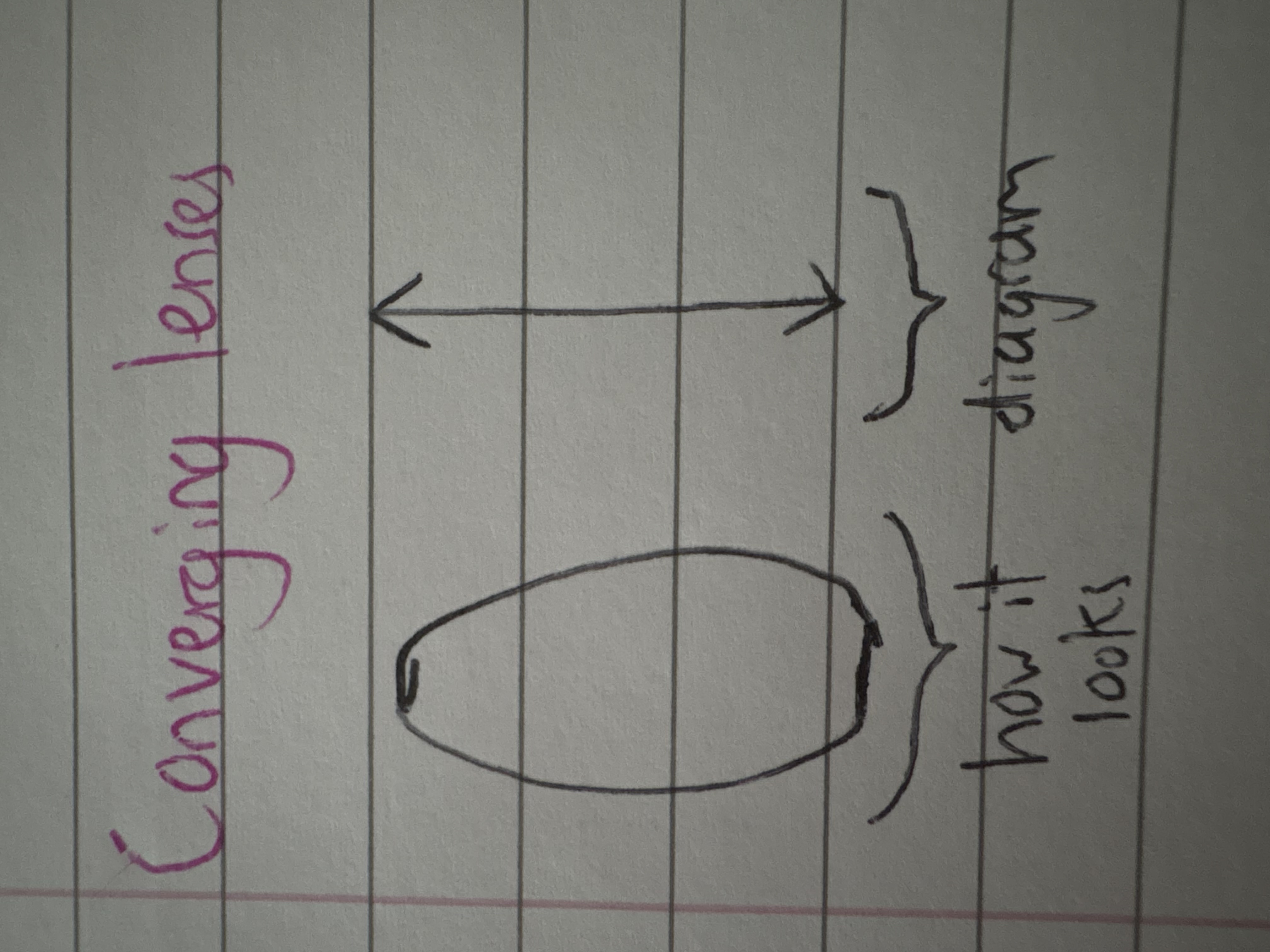
what will a ray diagram through a convex lense look like (if the object is more than 2 focal lengths away)?
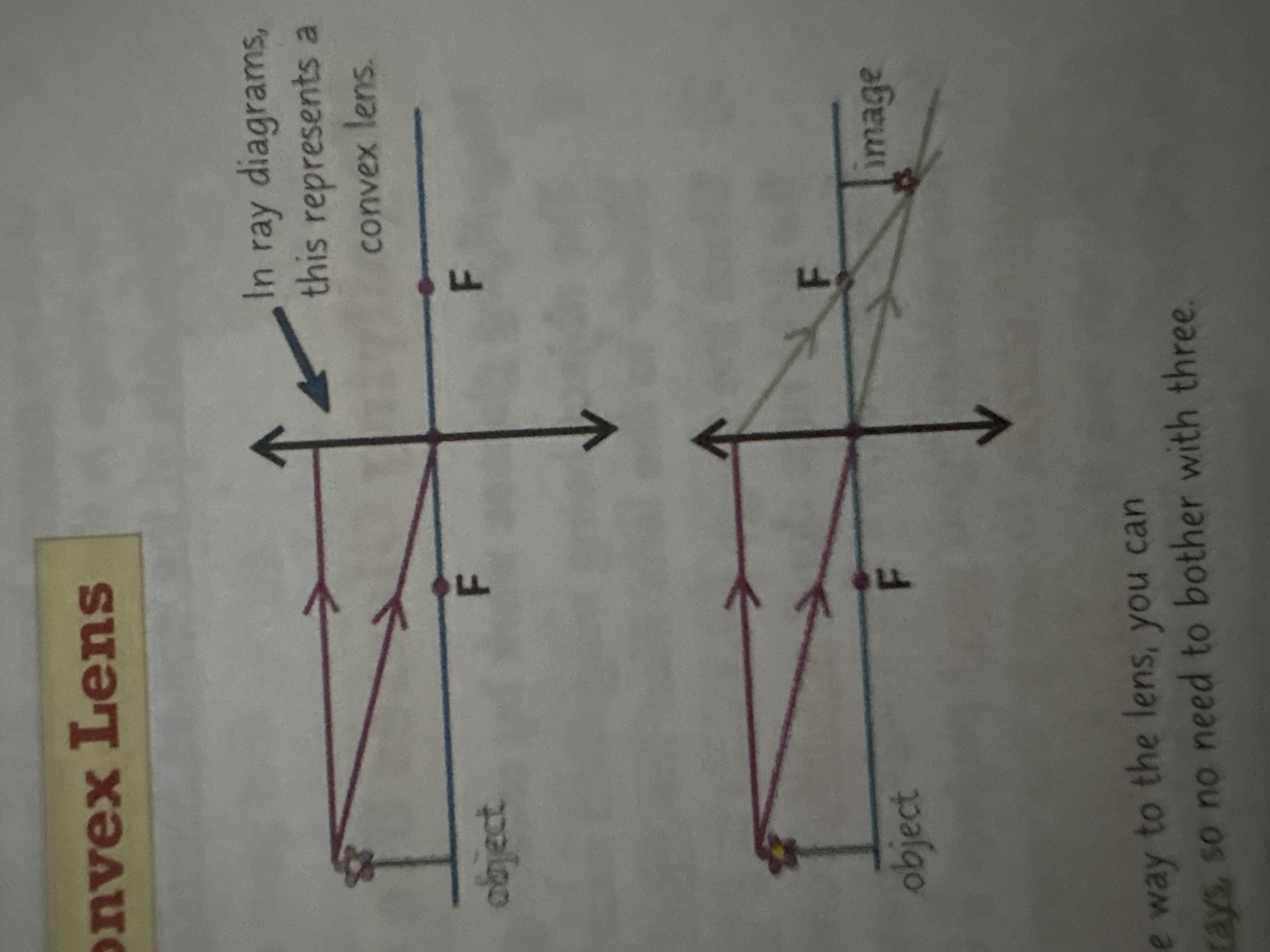
what are 3 features of the image produced through a convex lense if it’s more than 2 focal lengths away?
smaller, inverted, real (lines meet at a point)
what are 3 features of the image produced through a convex lense if it’s between 1 and 2 focal lengths away?
larger than the object (magnified), inverted (upside down), real
what will a ray diagram through a convex lense look like (if the object is less than 1 focal length away)?

what does it look like when days of light his a convex lense?
what’s a concave lense?
diverging lense- caves inwards, cause parallel rays of light to spread out (diverge)
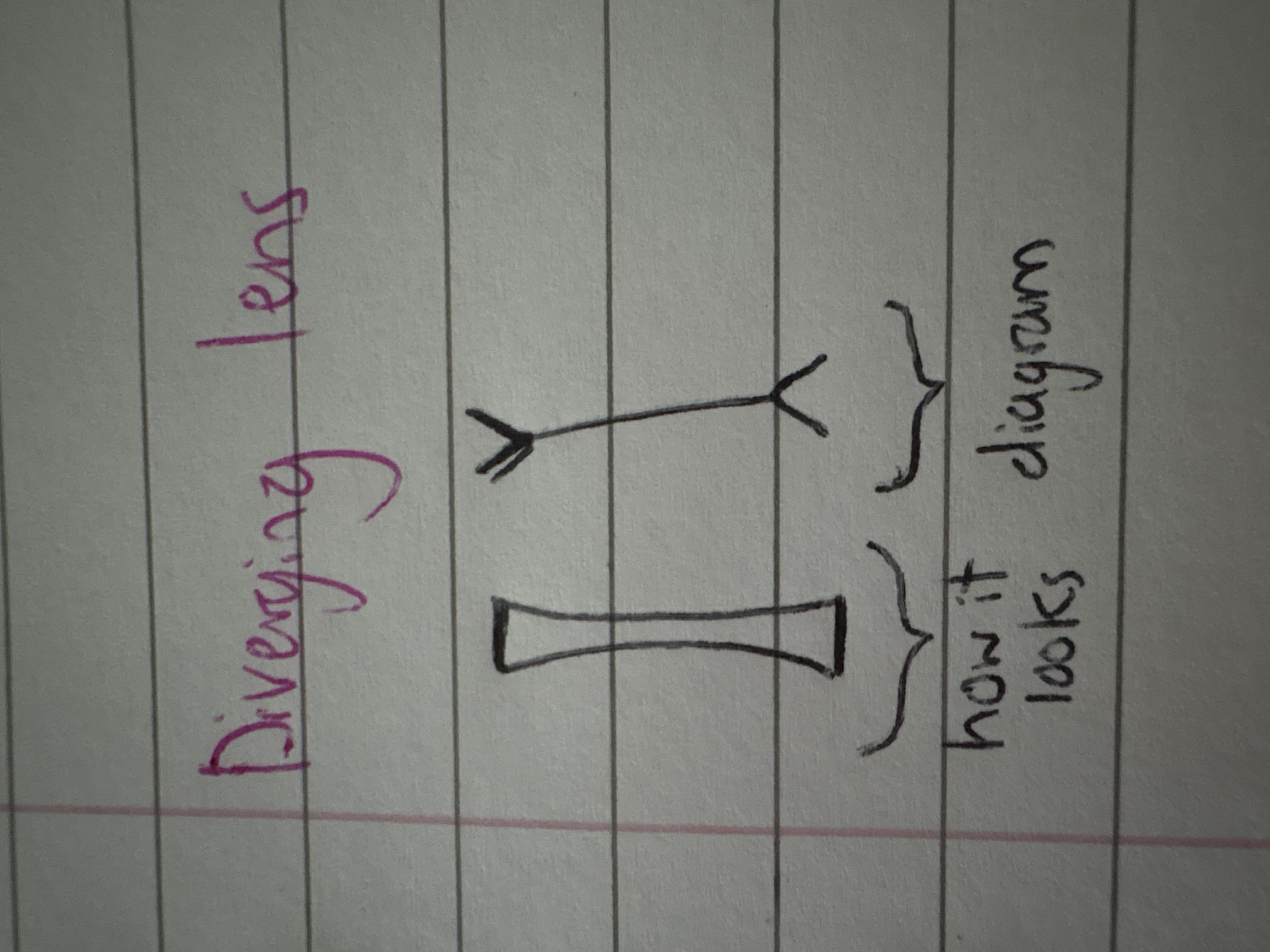
what will a ray diagram through a concave lense look like?
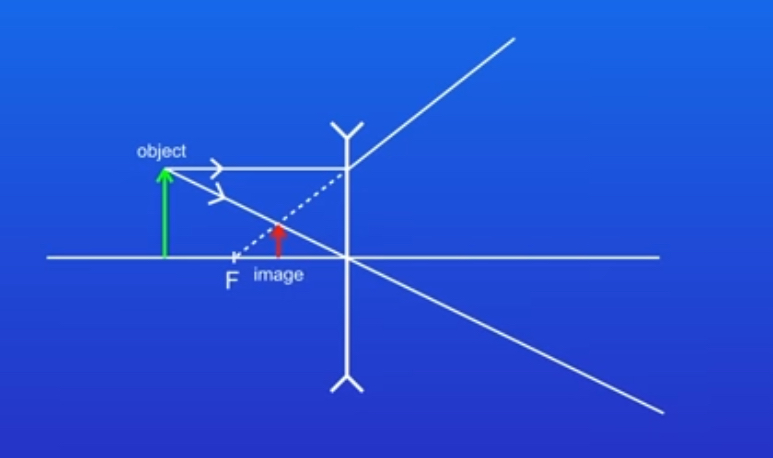
what are 3 features of an image produced through a concave lense?
smaller, upright and virtual
what does it look like when rays hit a concave lense?
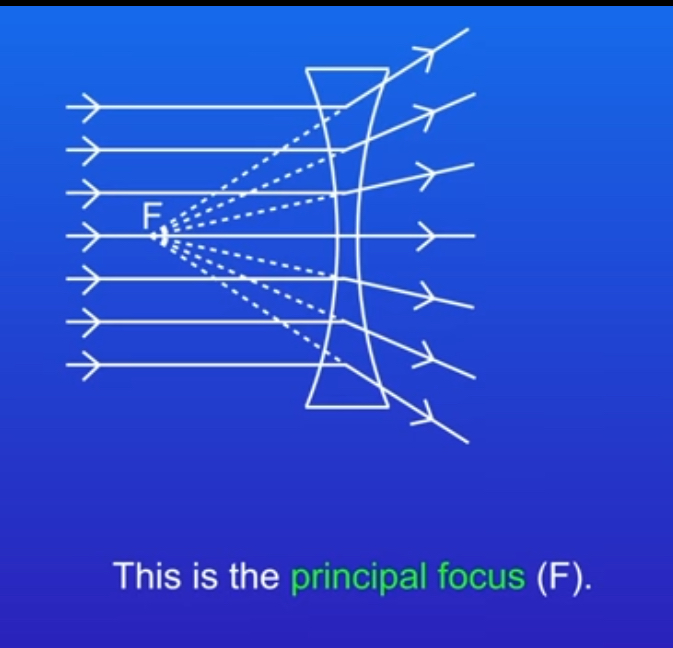
What is the difference between the image produced by a convex and a concave lens?
Convex lenses can produce real or virtual images
Concave lenses can only produce virtual images
a camera uses a converging lenses to form an image
describe how the image formed by the lens in a camera is different rom the image formed by a lens used as a magnifying glass
when an object is placed close to a magnifying glass (closer than focal length) it will appear bigger than the actual object it is virtual and will be formed right way up. where as in a camera its smaller, real and inverted
Why does magnification not have a unit?
it’s the ratio between image height and object height
ratios do not require units
what can be used to see how much infrared is emitted from different surfaces?
leslie cube

(2.2-1.4)/2=0.4


what’s the unit for wavelength
metres
what is the function of a microphone?
to covert sound waves into variation in current/p.d
explain how a moving coil microphone works?
sound waves cause the diaphragm to vibrate
the diaphragm causes the wire/coil to vibrate
the coil cuts through the magnetic field
a potential difference is induced across the ends of the coil
explain why the car has maximum speed.

Explain how the properties of x-rays make them suitable for the medical imaging of bones.
they pass through soft tissue but are absorbed by bone
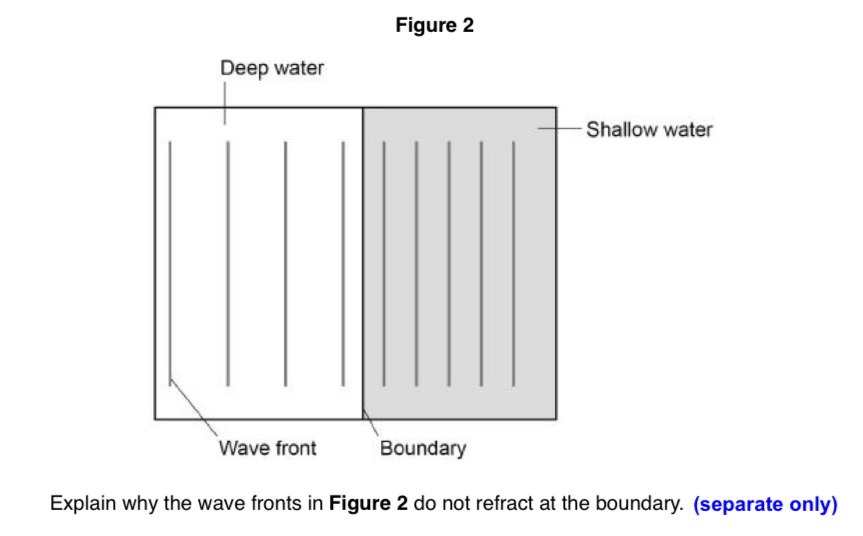
every point on the wavefront hits the shallow waters at the same time. so every point slows down at the same time