Chapter 4: Dynamics: Force and Newton's Law of Motion
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
acceleration
the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over a period of time
carrier particle
a fundamental particle of nature that is surrounded by a characteristic force field; photons are carrier particles of the electromagnetic force
dynamics
the study of how forces affect the motion of objects and systems
external force
a force acting on an object or system that originates outside of the object or system
force
a push or pull on an object with a specific magnitude and direction; can be represented by vectors; can be expressed as a multiple of a standard force
force field
a region in which a test particle will experience a force
free-body diagram
a sketch showing all of the external forces acting on an object or system; the system is represented by a dot, and the forces are represented by vectors extending outward from the dot
free-fall
a situation in which the only force acting on an object is the force due to gravity
friction
a force past each other of objects that are touching; examples include rough surfaces and air resistance
inertia
the tendency of an object to remain at rest or remain in motion
inertial frame of reference
a coordinate system that is not accelerating; all forces acting in an inertial frame of reference are real forces, as opposed to fictitious forces that are observed due to an accelerating frame of reference
Newton’s First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)
a body at rest remains at rest, or, if in motion, remains in motion at a constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force
mass
the quantity of matter in a substance; measured in kilograms
net external force
the vector sum of all external forces acting on an object or system; causes a mass to accelerate
Newton’s Second Law of Motion
the net external force Fnet on an object with mass m is proportional to and in the same direction as the acceleration of the object, a , and inversely proportional to the mass;
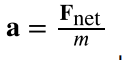
Newton’s Third Law of Motion
whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the first body experiences a force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force that the first body exerts
Normal Force
the force that a surface applies to an object to support the weight of the object; acts perpendicular to the surface on which the object rests
System
defined by the boundaries of an object or collection of objects being observed; all forces originating from outside of the system are considered external forces
Tension
the pulling force that acts along a medium, especially a stretched flexible connector, such as a rope or cable; when a rope supports the weight of an object, the force on the object due to the rope is called a tension force
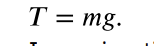
Thrust
a reaction force that pushes a body forward in response to a backward force; rockets, airplanes, and cars are pushed forward by a thrust reaction force
Weight
the force w due to gravity acting on an object of mass m ; defined mathematically as: w = mg, where is the magnitude and direction of the acceleration due to gravity
Components of an object at rest on an inclined plane
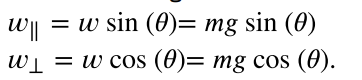
Steps to Solve Problems Involving Newton’s Laws of Motion
