Government intervention and government failure
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
What is the main reason for government intervention in markets?
To correct market failure and improve economic efficiency and equity
Name three main ways governments influence the allocation of resources.
Public expenditure — direct provision of goods/services (e.g. education, healthcare).
Taxation — raising revenue and discouraging harmful activities (e.g. tobacco tax).
Regulation — setting legal limits or rules (e.g. pollution standards, safety laws).
What are the 7 key ways of government intervention to correct market failure?
indirect taxation
subsidies
price controls
state provision
regulation
extension of property rights
pollution permits
What is an indirect tax?
tax on goods or services e.g VAT
What is the purpose of an indirect tax?
To reduce consumption/production of goods with negative externalities (demerit goods) by increasing the production costs of producers e.g cigarettes
Draw the indirect tax graph.
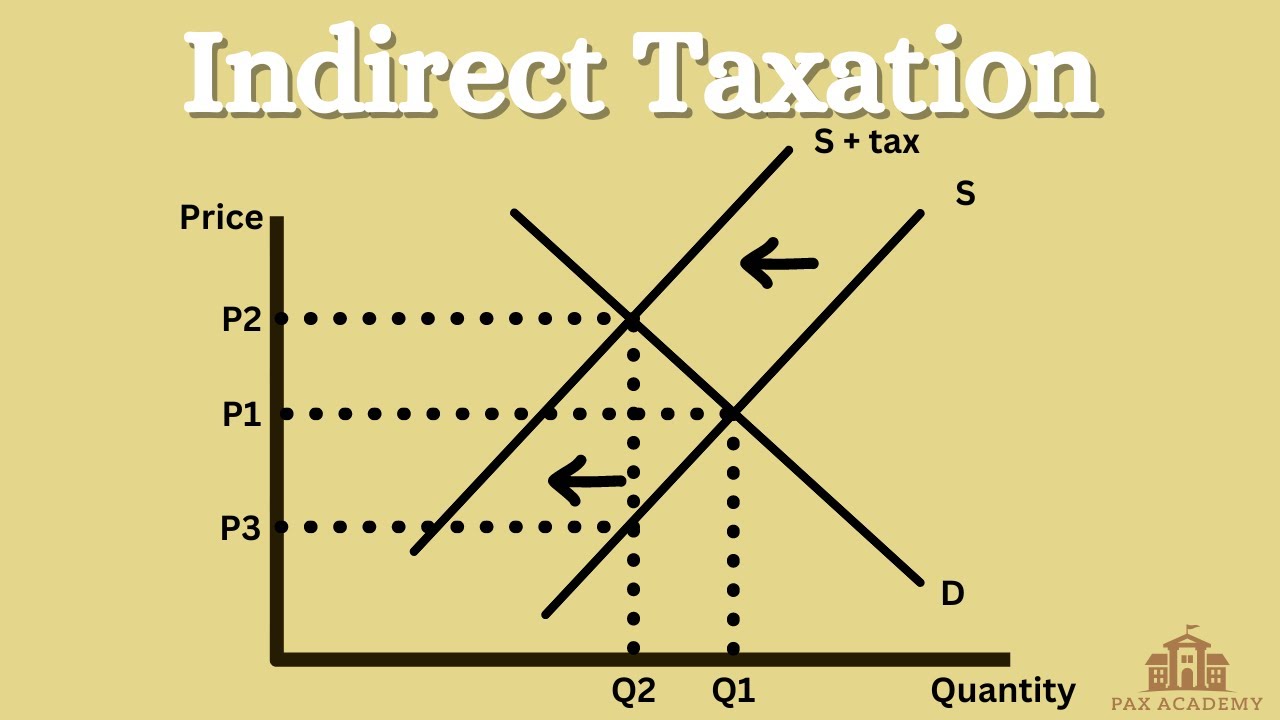
What are the strengths of indirect tax?
internalises external costs
raises government revenue (can fund public goods)
consumers still have a choice
What are the weaknesses of indirect tax?
Regressive → hits low-income households harder.
Hard to set right tax level (imperfect info about external cost).
May lead to black markets or tax evasion if set too high.
Inelastic demand goods (e.g. petrol) → little behaviour change.
What are subsidies?
payments to producers or consumers to lower costs
What is a subsidy used for?
To encourage production or consumption of goods with positive externalities (merit goods) by lowering the producer’s of these goods production costs e.g education
Draw the graph for subsidies.
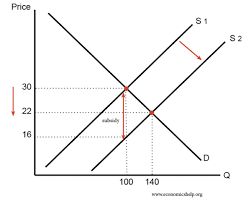
What are the advantages of subsidies?
Increases consumption of merit goods.
Can promote long-term growth and innovation.
Reduces underproduction
What are the disadvantages of subsidies?
High opportunity cost — taxpayer money.
Risk of dependency and inefficiency if firms rely on subsidies.
Hard to calculate true external benefit.
may be pocketed and not used for exact purpose
What are price controls?
Government-imposed limits on prices
What are the two-types of price controls?
maximum (price ceiling) or minimum (price floor)
What is a maximum price?
price set below equilibrium to encourage the consumption of a good e.g rent controls
Draw the maximum price graph.
lowers price, reduces incentive to supply but increases incentive to consume creating excess demand. Promotes equity.
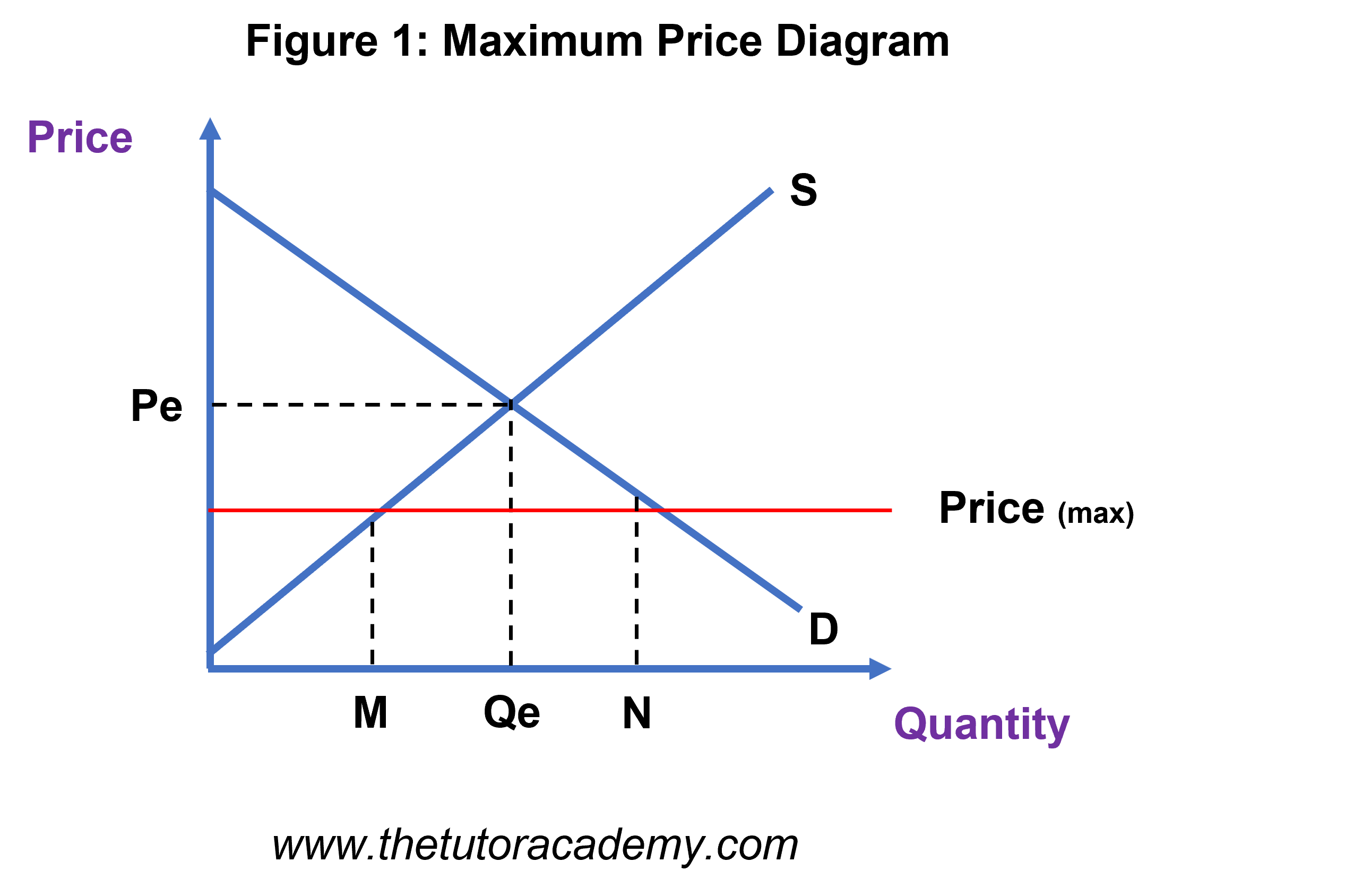
What are the strengths of maximum price?
Can make essentials affordable
quick and visible form of intervention
stabilises the market in the short-term
promotes equity
What are the weaknesses of maximum price?
creates shortage (some consumers can’t buy either way due to shortage)
encourages black markets and exploitation
can distort market forces to create an inefficient allocation of resources
May require costly government rationing schemes
What is minimum price?
price set above equilibrium to discourage the consumption of demerit goods e.g alcohol
What else can minimum price do?
prevent workers from exploitation
Draw the minimum price graph.
higher prices incentivises supply but does the opposite to demand leading to a contraction - now there is excess supply

What are the advantages of minimum price?
Can raise incomes or reduce overconsumption
Quick and visible intervention
creates a decent wage increasing standard of living of the poorest people incentivising people to work
producers are protected from price volatility (degree of price variation over time)
reduces external costs
What are the limitations of minimum price?
creates excess supply (opportunity cost)
people may become over-dependent on the government’s help
could increase unemployment
Encourages black markets
What are regulations?
rules set by the government to be followed e.g ad restrictions
What does regulation aim to do?
Change behaviour by imposing rules and standards
What are the strengths of regulations?
positive externalities directly reduces harmful activity
disincentive to break rules
easy for the public to understand
can protect consumers where markets fail badly
What are the disadvantages of regulations?
Costly to enforce and monitor.
Risk of regulatory capture (firms influencing regulators).
Inflexible - doesn’t account for differences across firms.
Can stifle innovation and raise production costs.
What is state provision?
when the government directly provides goods or services
Give an example of state provision
The NHS or public education - public and merit goods
What are the advantages of state provision?
ensures universal access and equity
Corrects complete market failure (e.g. public goods)
What are the weaknesses of state provision?
Inefficient due to lack of competition and profit motive.
High opportunity cost - taxpayer-funded.
Risk of overuse or moral hazard (e.g. NHS waiting times)
What is meant by extending property rights?
Assigning ownership to resources so users bear responsibility for their use or misuse. It also prevents the tragedy of the commons
What are the strengths of extension of property rights?
Encourages responsible management and internalises costs.
Reduces overuse of common resources.
Can be flexible and market-driven
What are the weaknesses of extension of property rights?
Hard to assign property rights for global resources (air, oceans).
Monitoring and enforcement are costly.
May create inequality if rights are unevenly distributed
What are tradable pollution permits?
Allowances that let firms emit a certain amount of pollution, which can be bought and sold
What are the advantages of pollution permits?
Market-based - least-cost firms reduce pollution first.
Provides financial incentive to cut emissions.
benefits the environment in the long-run
raises revenue for greener firms
What are the disadvantages of pollution permits?
monitoring of emissions is expensive
firms may pass costs to consumers
competition is restricted as they raise barriers to entry
difficult to set correct cap (info problem)
risk of permit hoarding
Other than efficiency what are the four objectives of government policy?
Equity (fairness) – redistributing income via taxes and welfare.
Economic growth – encouraging productive investment.
Stability – reducing inflation and unemployment.
Sustainability – protecting future generations and the environment
What is meant by a mixed economy?
An economy where markets allocate resources but the government intervenes to correct failures
What is government failure?
when the government intervenes in a market to correct market failure but the intervention results in a misallocation of resources even worse than before
How is government failure different from market failure?
Market failure is caused by market inefficiencies; government failure is caused by policy inefficiencies
What are the six main reasons why government failure occurs?
distortion of the price mechanism
law of unintended consequences
inadequate (imperfect) information
administrative costs
conflicting objectives
regulatory capture
How can intervention distort markets?
it solves one problem but causes another as price signals are distorted. Signalling function is artificially altered leading to an inefficient allocation of resources. For example, minimum price creates excess supply (surplus) and this is bad in things like farms with perishable stocks
When might a distortion improve welfare?
When it increases fairness or corrects serious inequality (e.g. minimum wage)
Why might long-term distortions worsen efficiency?
Firms may become dependent on support and stop innovating
What’s the evaluation judgement?
Distortion isn’t automatically bad — acceptable if equity or welfare gains exceed efficiency losses
What is the law of unintended consequences?
when consumers or producers change behaviour in ways the government didn’t predict to maximise their self-interest
Give an example of unintended consequences of policy.
Black markets after bans
How can policymakers reduce unintended consequences?
By testing policies (pilot schemes) and combining with education or enforcement
Why are they hard to avoid?
Human behaviour is unpredictable and incentives can backfire
What’s the evaluation judgement?
Risk is higher for behaviour-based policies — but can be mitigated with careful design and evidence
How does inadequate information cause government failure?
governments and regulators rarely have full knowledge about the extent of market failure or the right level of intervention leading to over-correction or under-correction
Give an example of inadequate information leading to government failure.
setting the wrong level of pollution tax as external costs are hard to measure
How can governments reduce the problem of imperfect information?
By using research, pilot schemes, or independent expert bodies (e.g. OBR) to improve accuracy
Why might government still intervene despite imperfect info?
Even partial correction can improve welfare compared to doing nothing
Why might imperfect information persist even with data?
Markets change quickly, and political pressures or bias may lead to poor decisions
What’s the evaluation judgement for this cause?
It limits precision but doesn’t always make intervention harmful — depends on data quality and adaptability
What are administrative costs?
The costs of implementing and enforcing policies. They can be expensive and it means that resources are diverted from other priorities
What factors can lower administrative costs?
Technology, automation, and efficient monitoring systems
When might high administrative costs still be justified?
When long-term social benefits (like better health or cleaner air) outweigh the costs
What’s the evaluation judgement?
Justified if benefits exceed costs; risk of failure if bureaucracy (complex administrative system of rules) grows faster than impact
What are conflicting objectives?
the government has multiple aims such as economic growth, low inflation and low unemployment. Government goals may clash and one policy may be implemented at the expense of another
How can governments manage conflicting objectives?
Through better coordination and long-term planning (e.g. aligning fiscal and environmental policies)
Why might political cycles worsen this issue?
Short-term electoral goals often override long-term welfare aims
What’s the evaluation judgement?
Conflicts are inevitable, but clear priorities and consistency reduce the harm
What is regulatory capture?
when regulators become influenced by the firms in the industry they oversee resulting in weak enforcement or policies that favour firms, not consumers
How can it be prevented?
Independent agencies, transparency, and public accountability
What’s the evaluation judgement?
Capture risk can be reduced but not eliminated — needs strong institutions and oversight
What is competition policy?
Government action to promote competition and prevent abuse of market power by making markets more competitive
What is the core objective of competition policy?
to ensure markets work efficiently and to prevent monopoly abuse, collusion and anti-competitive mergers
What are the main principals of competition policy?
Promote competition
Prevent abuse of dominant position
Protect consumer welfare
Encourage efficiency and innovation
What does competition policy make sure but generally accept?
it makes sure that there is competition so consumers have cheaper and more options and that excessive profits aren’t made and that prices reflect costs of production.
it accepts that in some cases, economies of scale and barriers to entry means that monopoly power will be enjoyed but will deliver more efficient outcomes than in perfect competition
What is the role of the UK’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA)?
Investigates mergers
Investigates anti-competitive behaviour
Can block mergers or impose fines
What is the focus of EU competition policy?
Preventing cartels, abuse of dominance, and anti-competitive mergers
What is an example of EU and UK competition policy in action?
Google (EU)
Fined for abusing dominant position in search
Shows regulation of market dominance
UK supermarket mergers
CMA investigates impact on prices and consumer choice
What are the 3 key elements of competition policy in the UK?
monopoly policy
merger policy
restrictive trading practices policy
Tell me about monopoly policy
the CMA conducts a cost-benefit analysis with information such as concentration ratios and complaints from consumers or other firms in the market tell them where to investigate further
What are some alternative approaches to the problem of monopoly?
price controls to restrict monopoly abuse
taxation of monopoly profits
state ownership of monopoly to act in public interest
compulsory break up of all monopolies - ‘monopoly busting’
Tell me about merger policy
it targets mergers that reduce competition and the creation of monopolies or oligopolies. This because few firms means less competition, high prices and less choice
Tell me about restrictive trading policy
it can be divided into 2 kinds: those undertaken independently by a single firm, and collective restrictive practices that involve either a written or implied agreement between 2 firms
What are some examples of independently undertaken restrictive practices?
decisions to charge discriminatory prices
the refusal to supply to a particular resale outlet
What is a key example of collective restricting trading practice?
a cartel agreement, in which firms come together to fix the price of a good
Define public ownership
when firms or industries are owned and run by the government on behalf of the public e.g NHS, BBC etc
What is nationalisation?
The transfer of ownership of assets or firms from the private sector to the public sector (the state).
What are advantages of public ownership/nationalisation?
Equity and universal access - ensures essential services are accessible to all
long-term investment can happen without short-term profit pressure
cheaper for consumers - benefit from economies of scale and allocative efficiency
reduces externalities as things are provided at socially optimum, not private
What are the disadvantages of public ownership/nationalisation?
productive inefficiency - lack of profit motive
poor incentives - weak management and limited innovation (X-inefficiency)
political interference - decisions based on electoral concerns
decrease quality of goods and services
very costly and burden falls on tax payers - could further indebt us
can lead to diseconomies of scale if industry gets too large
What can happen instead of nationalisation/public ownership?
a public private partnership (PPP). The UK is the current leader of this - has efficiency of private sector but interest of the public at heart e.g St Bartholemew’s hospital
What is privatisation?
the transfer of ownership of a firm or industry from the public sector to the private sector e.g British Gas
What are the arguments for privatisation?
increased efficiency - profit motive encourages cost reduction
greater competition - incentives improve performance
reduced government burden - raises revenue and reduces public sector borrowing
What are the arguments against privatisation?
short-termism - focus on profits over long-term investment
equity concerns - higher prices, reduced service in unprofitable areas
private monopoly risk (without competition)
less allocative efficiency
lack of strategic direction - focuses on dividends for shareholders
What is economic liberalisation?
opening up markets to private ownership and competition, and reducing government intervention in the economy. Closely related policies include deregulation and PPP
Define regulation
the imposition of rules and other constrains which restrict freedom of economic action
What are some other examples of regulatory bodies other than the CMA?
Ofwat for water
Ofcom for broadcasting
Ofgem for British gas
What are the strengths of regulation?
prevents market abuse - controls monopoly power
protects consumers - ensures serve quality and safety (e.g FSA for food)
corrects market failure - environmental protection
What are the weaknesses of regulation?
depends on how regulated a market is
regulatory capture
reduced innovation - limits pricing freedom
compliance costs - raises costs for firms e.g administrative costs
What is deregulation?
the removal or reduction of previously imposed regulations e.g bus services
What are the arguments for deregulation?
increased competition - lower prices and greater choice
improved efficiency - reduced bureaucracy (administrative systems, rules, procedures etc)
innovation
What are the arguments against deregulation?
inequality - services may focus on profitable customers
reduced consumer protection - lower safety or quality standards
market instability - risk of failure or crises