Anatomy Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/108
Last updated 3:28 PM on 12/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
anatomy
study of th structures in the body
2
New cards
physiology
study of the function of structures in the body
3
New cards
Complementarity of Structure and Function
anatomy and physiology have to be studied together because a structures function depends on its form
4
New cards
Gross Anatomy
large-scale studying of anatomy
5
New cards
Microscopic Anatomy
small-scale studying of anatomy
6
New cards
Regional Anatomy
studies structures in a specific area
7
New cards
Systemic Anatomy
studies structures by the system they are functioning in
8
New cards
order of: Structural Organization
chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal
9
New cards
Would we be able to have properly functioning organs without “tissues” in our body?
no tissues are what make up muscle
10
New cards
Can organs of differing tissue structures still work together for a common purpose?
different tissue can still be working to achieve a common purpose
11
New cards
Why is it important for our body to maintain boundaries?
so that the internal environment remains distinct/separate from the external environment
\
Need boundaries protecting our organs to keep them from drying out and losing their function
\
Need boundaries protecting our organs to keep them from drying out and losing their function
12
New cards
Metabolism
all chemical reactions that occur within body cells
13
New cards
Catabolism
breaking things down
14
New cards
Anabolism
simpler structures building into more complex
15
New cards
Which two systems are primarily responsible for communicating and maintaining homeostasis in our bodies?
nervous and endocrine
16
New cards
superior
above the hips
17
New cards
inferior
below the hips
18
New cards
anterior
towards the front of the chest
19
New cards
posterior
towards the back of the chest
20
New cards
proximal
closer to the joint
21
New cards
distal
further from the joint
22
New cards
lateral
away from the middle of the body laterally
23
New cards
medial
towards the middle of the body laterally
24
New cards
CHAPTER 2
.
25
New cards
organic compound always have...
what 4 things are included
what 4 things are included
always have a carbon atom
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
26
New cards
inorganic compounds
do not contain a carbon atom in them
water, salts, and inorganic acids and bases.
water, salts, and inorganic acids and bases.
27
New cards
Monosaccharides
single chain
28
New cards
Disaccharides
double chain
29
New cards
Polysaccharides
linked simple sugars
great for storage
great for storage
30
New cards
function of carbs
to provide a ready, easily used source of cellular fuel
31
New cards
Dehydration Synthesis
the creation of larger molecules from smaller monomers where a water molecule is released
32
New cards
Dehydration Hydrolysis
a water molecule is added to each bond that is broken, thereby releasing its building blocks
breaking down similar substances by adding water.
breaking down similar substances by adding water.
33
New cards
Phospholipid Structure
Has polar heads (hydrophilic) and non polar tails (hydrophobic)
34
New cards
Saturated Fats
solid @ room temp
no double bonds between carbons
no double bonds between carbons
35
New cards
Unsaturated Fats
liquid at room temp/fatty acid chains have kinks and can’t solidify
there is a double bond between carbons in one of the fatty acids
there is a double bond between carbons in one of the fatty acids
36
New cards
6 Functions of Proteins
Structure/support
Enzyme/catylyssis
Transport/moving substances
Contractile/movement
Communication/transporting signals
Defensive/protect against disease
Enzyme/catylyssis
Transport/moving substances
Contractile/movement
Communication/transporting signals
Defensive/protect against disease
37
New cards
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
CHAPTER 3
38
New cards
functions of integumentary system
protection: to tissues and organs
protection: against infection
maintains temperature
prevents dehydration
disposes of waste
stores: water and fat
receptor: touch, pressure, pain, and heat
protection: against infection
maintains temperature
prevents dehydration
disposes of waste
stores: water and fat
receptor: touch, pressure, pain, and heat
39
New cards
parts of integumentary system
hair
skin
nails
nerves
glands
blood vessels
skin
nails
nerves
glands
blood vessels
40
New cards
3 layers of the skin
epidermis
dermis
hypodermis
dermis
hypodermis
41
New cards
what is the epidermis made up of?
stacked epithelial cells
42
New cards
Keratinocyte
creates the protein, keratin which make sskin tough and water resistant
43
New cards
Melanocyte
produces melanin; the skin's pigment
protects against UV rays and sunburn
protects against UV rays and sunburn
44
New cards
How does epidermis get nutrients?
diffusion through the dermis
45
New cards
dermis contains:
connective tissue
blood vessels
glands
hair follicles
nerves
blood vessels
glands
hair follicles
nerves
46
New cards
dermis layers
papillary
reticular
reticular
47
New cards
papillary layer
contain nerves and blood vessels
help feed dermis
help feed dermis
48
New cards
reticular layer
structure: collagen and elastin
helps skin sense pressure and pain
helps skin sense pressure and pain
49
New cards
When do scars occur?
when the dermis is damaged
50
New cards
What is a scar?
a formation of disrupted collagen
51
New cards
scar tissue vs. normal tissue
scar tissue does not contain hair nor sweat glands
52
New cards
hypodermis' structure and function
Form: loose connective tissue and fat
Function: insulate and pad
Function: insulate and pad
53
New cards
What type of immune cells are in the hypodermis?
macrophages
54
New cards
what is hair?
dead keratinocytes
55
New cards
Hair is everywhere except:
palms, feet soles, lips, and genitalia
56
New cards
hair's purpose:
heat regulation and protection of sun rays
57
New cards
what are nails made of?
keratinocytes
58
New cards
nail's purpose:
protect finger and toe tips
59
New cards
what type of organ is the skin?
sensory
60
New cards
what do nerve endings sense?
pain, heat, cold, and touch
61
New cards
What is Tactile Location?
ability to determine which parts of the skin have been touched
62
New cards
What is receptor adaptation?
touch receptor slowing down their response rate
63
New cards
Sweat glands (A&E)
Apocrine: secrete oil along hair shaft
Eccrine: secretes water and salt (sweat)
Eccrine: secretes water and salt (sweat)
64
New cards
sebaceous glands
produces sebum: oil that covers skin/hair
65
New cards
ceruminous glands
produces earwax
66
New cards
how does sweat cool off the body?
the water excreted evaporates > cools down the body
67
New cards
Immune system
skin's first line of defense
68
New cards
Digestive system
skins absorbs vitamin d which helps our body absorb calcium
69
New cards
circulatory system
skin contains blood vessels
70
New cards
Skin cancer
caused by uv radiation
melanoma: cancer in melanocytes
basal cell: occurs in lowest epidermis layer
melanoma: cancer in melanocytes
basal cell: occurs in lowest epidermis layer
71
New cards
what causes warts?
HPV
72
New cards
CHAPTER 7
the skull
73
New cards
what bones make up the skull?
cranium and facial
74
New cards
what is the vertebral column?
spine
75
New cards
what is the throacic cage?
rib cage
76
New cards
Appendicular skeleton
bones connecting to the middle of the body; limbs
77
New cards
Axial skeleton
bones in the midline of the body; spine, hips, rib cage
78
New cards
4 bone types
long, short, irregular, flat
79
New cards
7 functions of the bones:
S,P,M,M,B,T, H
S,P,M,M,B,T, H
support
protection
movement
mineral and growth storage
blood cell formation
triglyceride storage
hormone production
protection
movement
mineral and growth storage
blood cell formation
triglyceride storage
hormone production
80
New cards
long bones:
longer than they are wide
ex: femur, humorous, radius, tibia
ex: femur, humorous, radius, tibia
81
New cards
short bones:
cube shaped
ex: wrist and ankle bones
ex: wrist and ankle bones
82
New cards
Irregular bones:
complex shapes
ex: hips, vertebrae
ex: hips, vertebrae
83
New cards
Flat bones:
flat
sternum, ribs, skull bones
sternum, ribs, skull bones
84
New cards
compact bone:
dense, smooth outer layer of the bone
85
New cards
spongy bone:
honeycomb patterned flat bones; trabeculae
helps bone resist stress
helps bone resist stress
86
New cards
3 cartilage types
hyaline, elastic, fibro
87
New cards
hyaline cartilage:
provides support, flexibility, and resilience
ex: joints, ribs, nose tip
ex: joints, ribs, nose tip
88
New cards
elastic cartilage:
similar to hyaline but contains elastic fibers
ex: external ear and epiglottis
ex: external ear and epiglottis
89
New cards
fibrocartilage:
thick collagen fibers
ex: meniscus and vertebral discs
ex: meniscus and vertebral discs
90
New cards
MUSCLE MOVEMENTS
.
91
New cards
During contraction, muscles…
shorten
92
New cards
During relaxation, muscles…
lengthen
93
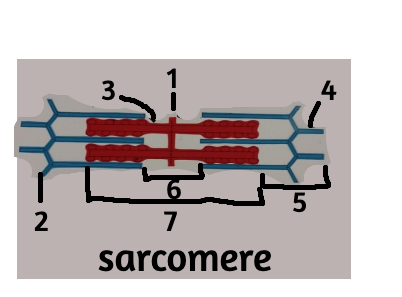
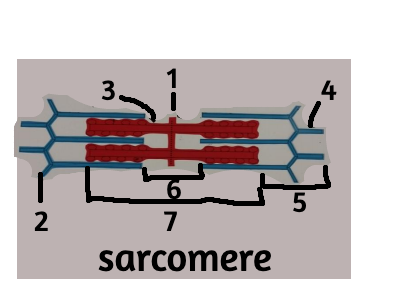
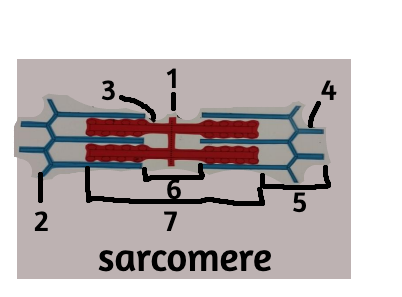
New cards
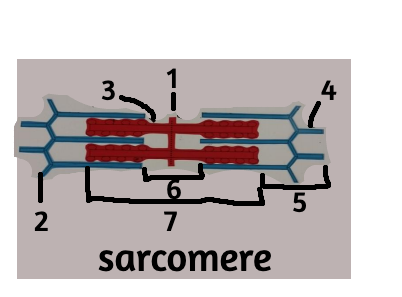
1
M line
94
New cards
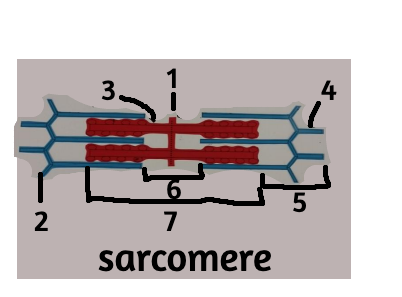
2
z disc
95
New cards
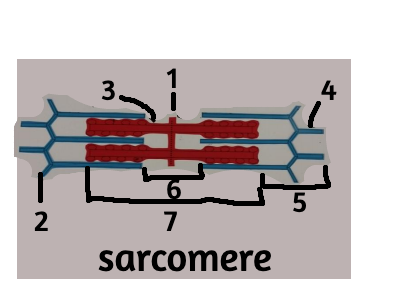
3
thick filament
96
New cards
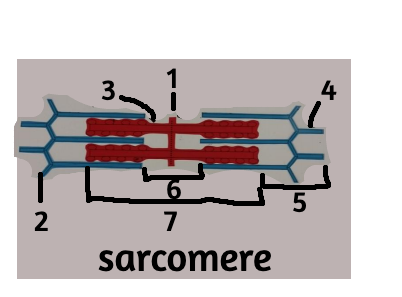
4
thin filament
97
New cards
5
i band
98
New cards
6
H zone
99
New cards
7
A band
100
New cards
Which parts (sarcomeres) move during muscle contraction?
blue lines: thin filaments/z lines