A&P unit 4 - CNS
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
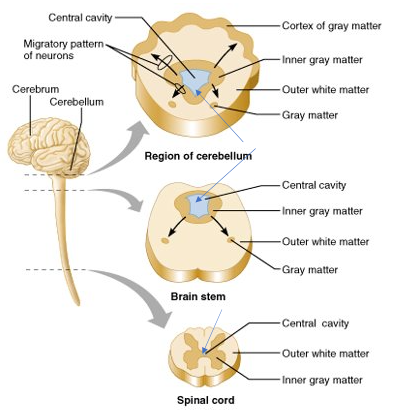
basic pattern organization of CNS
-central cavity surrounded by gray matter core (nuclei)
-external to grey matter is white matter (myelinated axons)
-cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum have an outer "bark" or cortex of gray matter
cranial meninges
-3 CT layers
-separate and support brain & BV
-help contain and circulate CSF
-in brain AND spinal cord
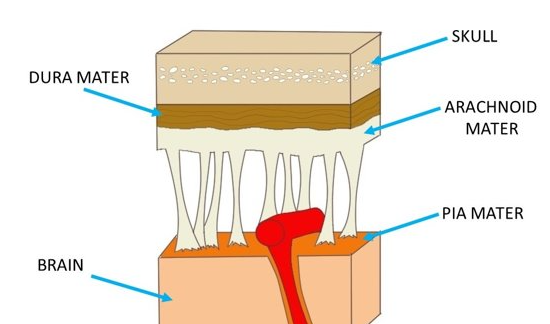
pia mater
-adhere directly to brain surface
-thin layer of areolar CT
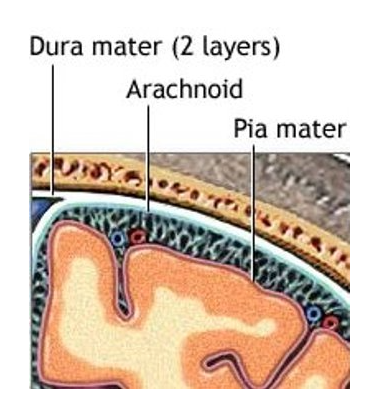
arachnoid mater
-in middle
-arachnoid trabeculae - lines that extend to pia mater
-subarachnoid space - contains CSF
-made of collagen & elastic fibers
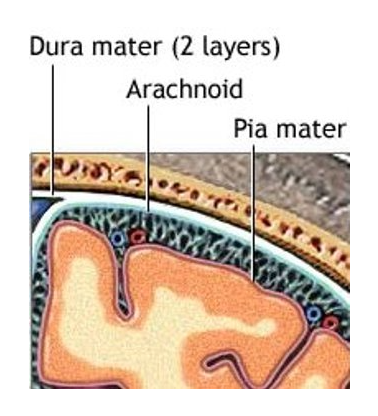
dura mater
-tough outer layer, closest to bone
-made of dense CT in 2 layers
-layers usually fused, but in some areas they separate to form dural venous sinuses that drain excess CSF from brain
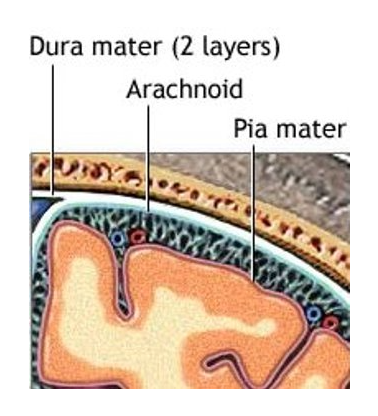
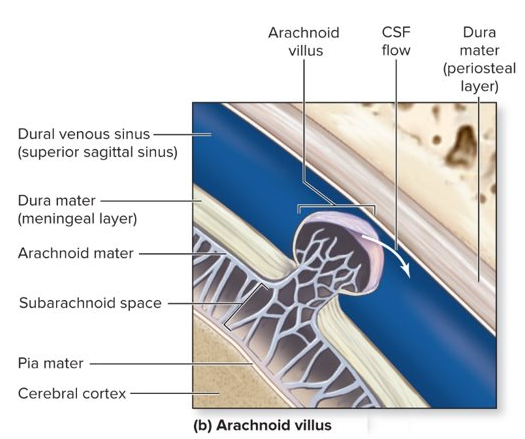
diagram 2 layers of dura mater
-periosteal layer - closest to bone
-meningeal layer - closer to brain
-CSF drained thru dural venous sinus
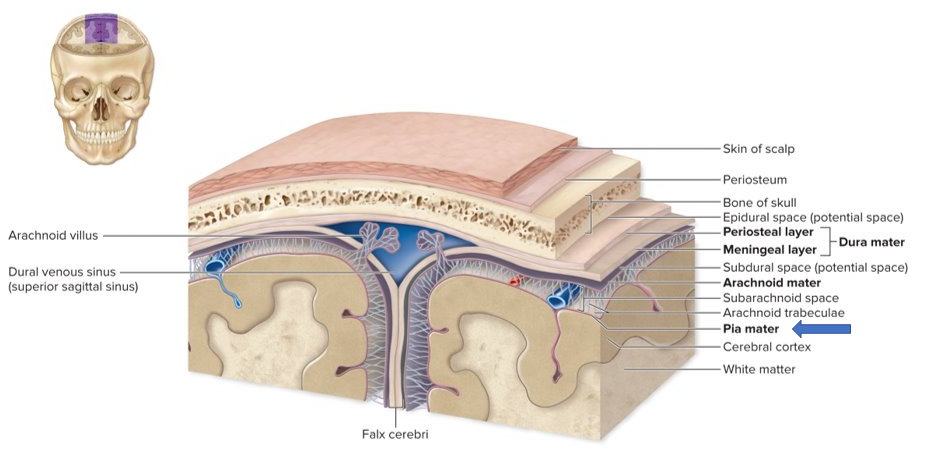
4 ventricles image
functions of CSF
-Buoyancy – reduces brain’s weight by 95%
-Protection – provides a liquid cushion
-Environmental stability – transport of nutrients / wastes and protects against fluctuations
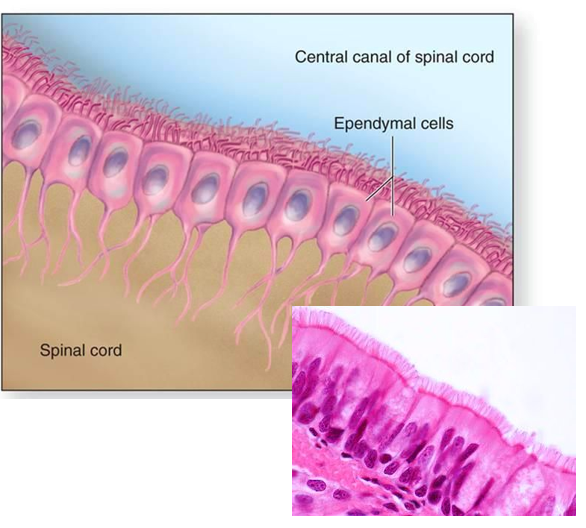
ependymal cells
-produce CSF
-have cilia
-line cavities in brain and spinal cord → each ventricle, choroid plexus capillaries
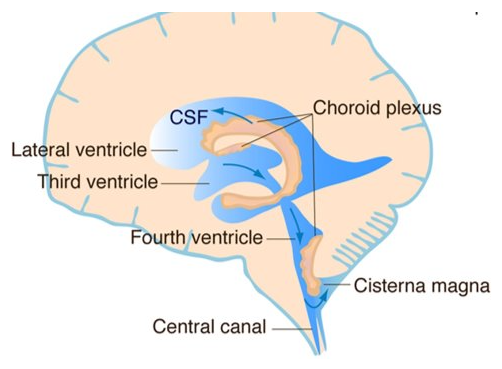
excess CSF
-flows into arachnoid villi, drains into dural venous sinuses
-arachnoid granulation = collection of arachnoid villi
→ if it is not drained properly, can cause edema of brain (meningitis)
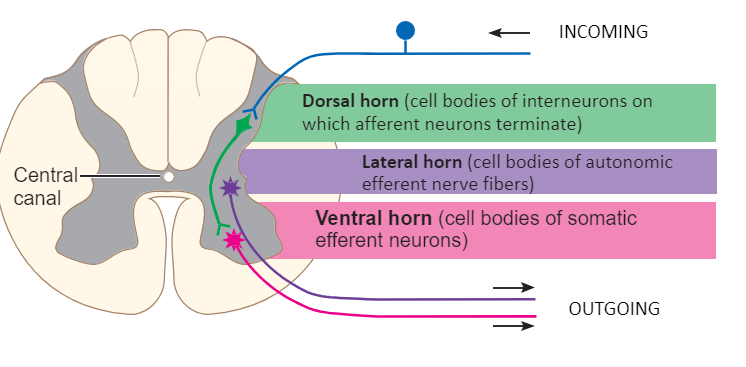
horns of the spinal cord
*made of gray matter
the brain runs caudal → rostral. What does this mean?
tail → head
as you move up the brain it gets more complex functions & more evolutionarily advanced
gray matter vs white matter
gray = cell soma, holds nuclei
white = axons, myelinated
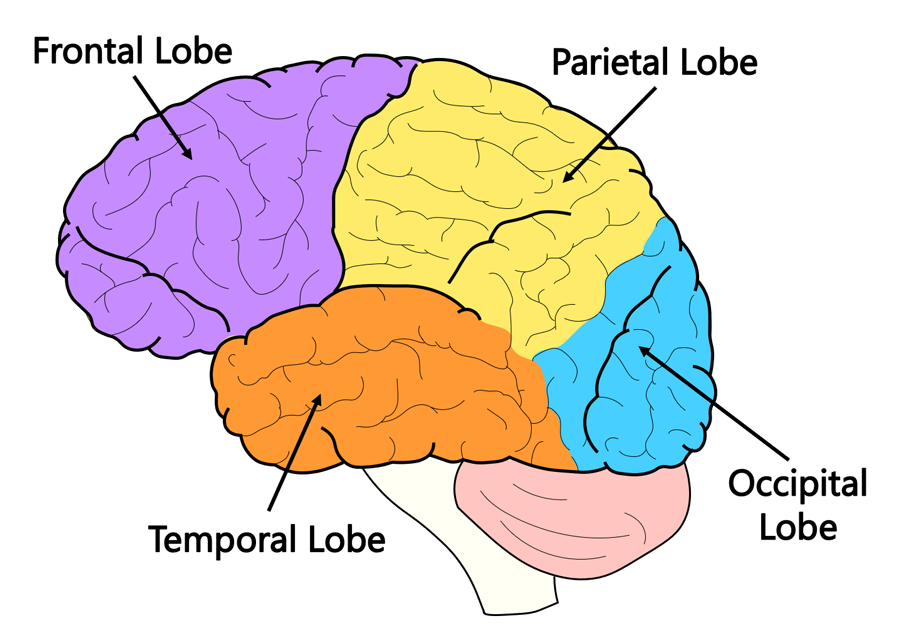
name each of the 4 lobes and what they control
frontal = voluntary motor & cognition
temporal = hearing
occipital = vision
parietal = somatosensory
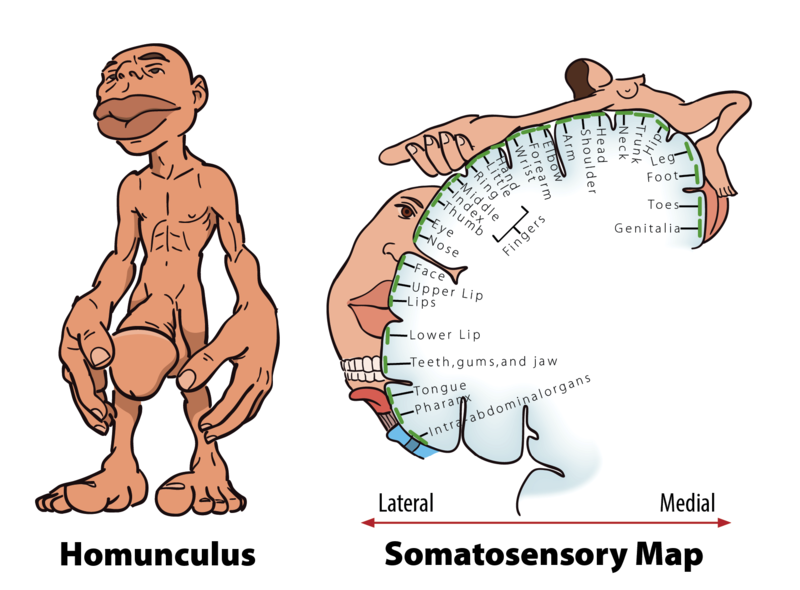
homonculus
term for human model showing how much space in the brain is given up to sensory regions for that specific area in the body
amygdala
location = diencephalon
function =
-negative emotions like fear and anger
-fight or flight
-link emotional reaction to memories
basal nuclei/basal ganglia
gray matter in cerebrum
function =
-initiate movement & suppress unwanted mvmt
-monitor & coordinate slow, sustained contractions
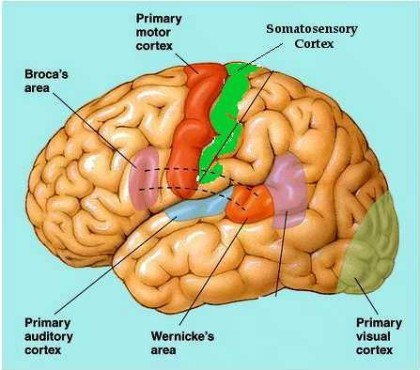
broca’s area
location = frontal lobe, left hemisphere only
function = motor speaking ability → form words
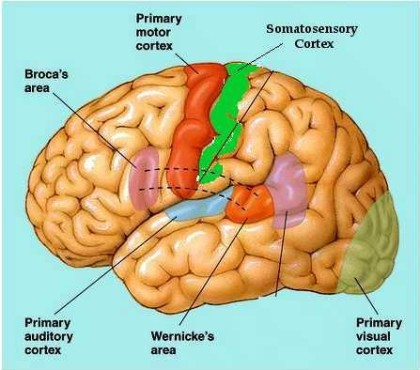
wernicke’s area
location = temporal & parietal lobe, left hemisphere only
function = language comprehension. receives visual & auditory input to understand
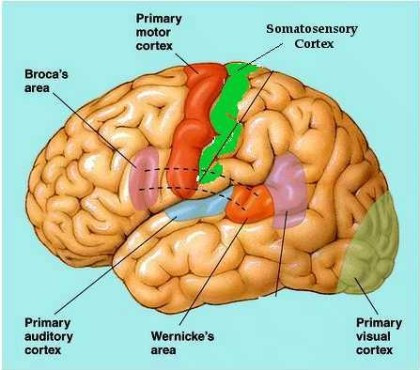
cerebellum
function =
-balance
-muscle memory
-execute voluntary motor mvmt
hippocampus
location = diencephalon
function =
-memory formation → learning
-retrieval of long-term memories
thalamus
location = diencephalon
function = sensory relay station before info is sent to cortices
hypothalamus
location = diencephalon, below thalamus
function =
-hormone secretion, sleep/wake cycle (melatonin)
-regulate autonomic internal processes → homeostasis
brainstem
pons, medulla, midbrain
function = autonomic behaviors, and control cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive systems
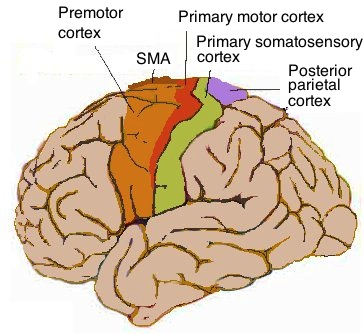
primary motor cortex
location = precentral gyrus
function = motor control in body
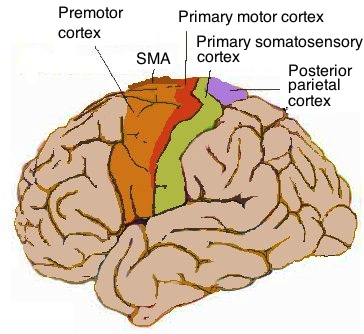
premotor cortex
location = in front of precentral gyrus/PMC
function =
-orient body to specific target
-plan mvmt before sending to PMC
-coordinate skilled mvmts
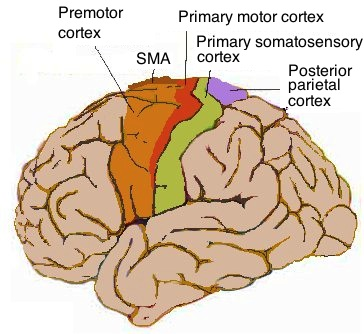
primary somatosensory cortex
location = postcentral gyrus
function = relay and process somatosensory info
primary visual and auditory cortices
location = occipital (visual), or temporal (auditory)
function = process visual/auditory info
prefrontal association cortex/PFC
location = frontal lobe
function =
-higher cognition
-thinking, brainstorming, weigh consequences
-working memory
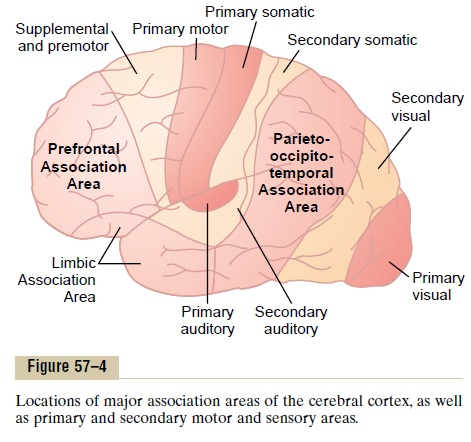
parietal-temporal-occipital association cortex
location = parietal, occipital, temporal lobes
function =
-integrates sensory output from the 3 lobes
-important in language understanding
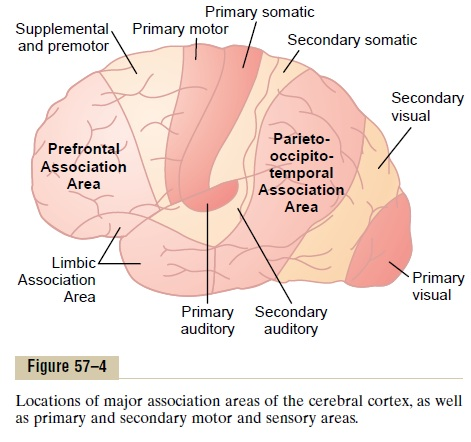
limbic association cortex
location = temporal, some in the frontal
function = motivation, emotion, memory
functional systems
term for a collection/network of neurons that work together, but span large distances in the brain
→ reticular formation
→ limbic system
reticular formation/reticular activating system
functional system involving the brainstem to thalamus
functions = alert cerebrum of incoming sensory info → promotes alertness and directs attention to events
→ sensory overload occurs with too much info in the RAS being sent
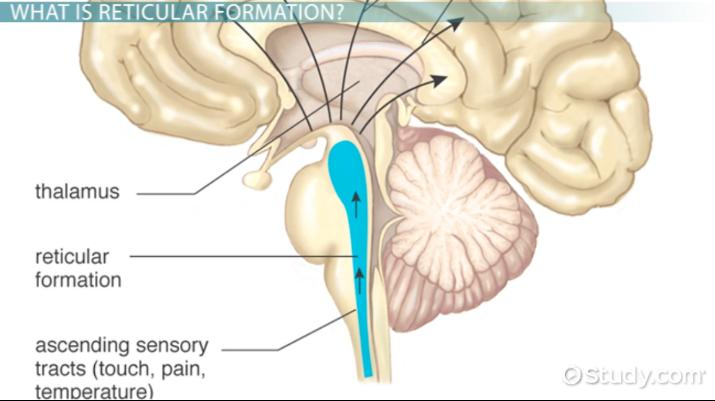
limbic system
functional system involving hippocampus, hypothalamus, thalamus, amygdala
functions =
-emotional activation
-associate emotion to a perceived event
-integrate emotion with memory
short and long term memory
short term = temporary modification to preexisting synapse function
-working memory in PFC
long term = permanent modification to preexisting synapse function
-procedural memory in cerebellum
-involves PFC and hippocampus
LTP
“long term potentiation”
process of strengthening synapse by using the connection more
→ strengthen memories, with LTP we can turn short term to long term or strengthen short term