4.5 marketing mix
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
excluded HL topics + specific promotion strategies' adv/disadv
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
marketing mix
key decisions that must be taken in the effective marketing of a PRODUCT
influences if a business can sell it profitably
coordinated marketing mix
key marketing decisions that complement each other and work together to give customers a consistent message about the PRODUCT
these should be interrelated and fit together in an integrated marketing plan to target clear marketing objectives
product
end result of production process sold on the market to satisfy a consumer need or industrial need (purchased by businesses, not final consumers)
important to sell the right product to customers based on their expectations: quality, durability, performance, appearance
consumer durables
manufactured products that can be reused and are expected to have a reasonably long life
opposite: single-use
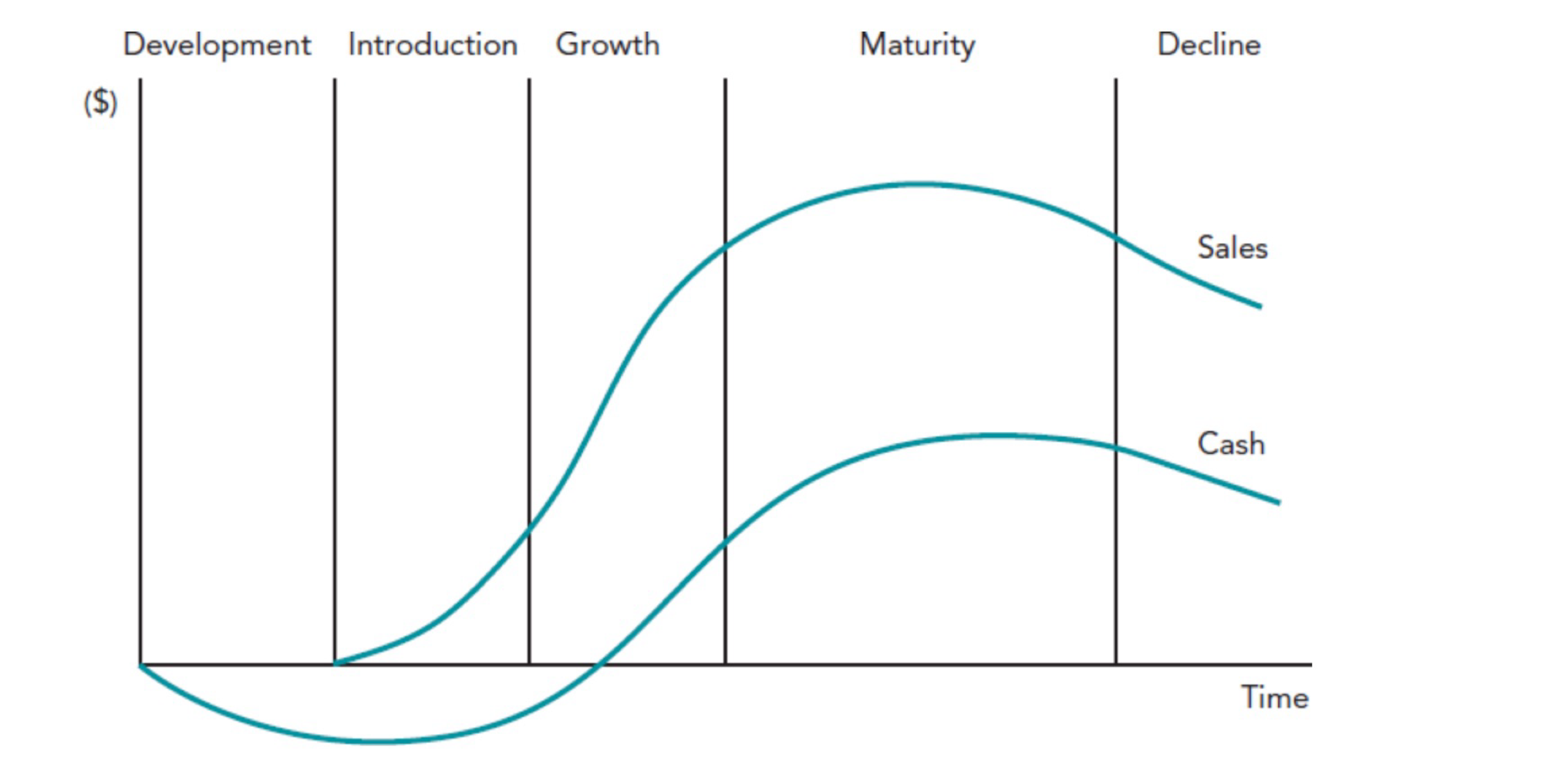
product life cycle
pattern of sales recorded by a product from launch to withdrawal from market
helps business know when to launch a new product/update existing product
product life cycle stages
introduction
growth
maturity/saturation
decline
product life cycle introduction
product: new model
promotion: high → above the line, informative to make customers aware of new product
pricing: depends → premium or penetration pricing
place: few
sales: low
product life cycle
product: make improvements to maintain consumer appeal
promotion: high → create brand identity, encourage customer loyalty and repeat purchases
pricing: increase (especially if initially used penetration pricing)
place: increase → due to increased consumer demand
sales: increase significantly but growth slows down to maturity
product life cycle maturity/saturation
product extension strategies used
promotion:
brand reinforcement → stress that product is different from competitors
below the line → aimed at target markets
pricing: lower → competitive pricing because competitors entering market
place: maximum geographical range of outlets, introduce new kinds of outlets
sales: stop growing but don’t decline significantly
increased competition, competitors copying growth strategies
technological advancements make existing less appealing
change in consumer tastes
saturation of market: people who want already have it, will only buy if existing breaks or there is newer technology
product life cycle decline
product: withdraw from market, replace with new product
promotion: minimal, only to inform about lowered prices
pricing: lowered to clear stock OR if product has cult following, can increase price to create exclusivity
place: eliminate unprofitable distribution outlets
product life cycle affects
investment
decline: invest heavily in R&D of new products to replace
profit margins
cash flow
product life cycle affects profit margins
growth/maturity: high sales → high gross/net profit margins
end of maturity: using competitive pricing → low gross/net profit margins
decline: sales fall → negative gross profit margins BUT if fixed costs already covered, might still have net profit
product life cycle effect on cash flow
development: negative because only cash outflow
unused factory capacity
high R&D costs
no sales
introduction: negative because revenue from sales < cost of sales + promotion
unused factory capacity
high promotional costs
penetration pricing
low sales
growth: increasing because sales increasing
when it is positive depends on length of consumer credit
maturity: most positive
high sales
lowest promotional costs
max factory capacity
decline: decreasing because price low and sales low
market saturation
demand for a particular product or service has reached its peak, competitors entered market
people who want the product already have it, will only buy if existing breaks or there is newer technology
product portfolio
made up of all product lines offered for sale by a business
can be analysed using BCG matrix
why need range of products in portfolio + what contributes to range
why need range?
reduced risk: less exposed to market changes (changes in consumer tastes/demand) → not dependent on performance of main products
balance → diversification
steady cash flow/profit performance
what contributes to range
new products
international adaptations (international marketing)
mergers and takeovers
balanced product portfolio
when one product reaches decline, should have other products in growth or introduction stage of product life cycle
ensures balanced risk profile, smoother cash flow and profits
extension strategies
introduced in maturity/saturation stage of product life cycle → to lengthen product life cycle
add features to original product
+ R&D and promotion for slightly revised product is less expensive than new product
- consumers may not be interested in a slightly revised product
repackage product
+ cheap and fast
- consumers feel misled once realise
discounted price
+ can reach new market segment of consumers with low spending power
- impacts brand image → better to replace earlier to avoid discounting
rebrand
+ can reach new market segments
- expensive
market development
+ increases sales
- need to adapt product/promotion to local laws/culture
brand
an identifying name/symbol that distinguishes a product from competitors’ product
aspects
awareness
loyalty
development
equity/value
importance of branding
instant recognition from logo
differentiate from competitors
employee motivation increases
customer referrals increase through social media
customers have expectations
customers have emotional attachment → customer loyalty
brand equity gives value to business beyond its tangible assets
internationally consistent, recognisable and transferrable → can exploit marketing EOS + sales increase
BUT international branding might not connect with local culture/tastes
brand awareness
extent to which consumers recognise product by name and special characteristics
usually due to logo/trademark associated with the brand
effects
increased sales (familiar, more likely to buy)
competitive advantage (differentiated)
is the primary goal of promotional activity in introduction phase
brand loyalty
tendency of consumers to choose a brand over others
seen by repeat purchases regardless of marketing pressure from competing brands
likely to promote through word of mouth
effects
reduced price sensitivity
repeat purchases (predictable and stable sales revenue)
reduced marketing costs (recommend through word of mouth)
increases the likelihood of successful product launches (more willing to try new offerings)
is the primary goal of promotional activity in growth phase
brand development
long-term strategy that involves strengthening the name and image of a brand to resonate with its target audience. (eg values, mission, vision)
features
visual identity (logos, designs)
tone and style of communication
values, mission, vision
alt: measures the infiltration of a products sales, usually per thousand population
if 100 people out of 1000 buy, brand development = 10
brand equity/value
estimation of how much a brand is worth. recorded on the balance sheet under non tangible assets.
when another company purchases, brand value = purchase price – net book value of the acquired brand.
alt: brand value = assets – liabilities
premium that a brand has because customers willing to pay more than they would for a non-branded product
if high awareness + development, will have high equity
trademark
form of intellectual property that is a distinctive name, symbol, motto or design that distinguishes a business/its products.
can be legally registered and cannot be copied.
value is under balance sheet intangible assets.
price
amount paid by consumer for product
will affect
demand
brand image
revenue and profits
depends on
cost of sales
competitors prices
market conditions
stage of product life cycle
marketing objectives
PED
pricing strategies
cost plus
penetration
predatory
loss leader
premium
competitive
dynamic
contribution
cost plus pricing
all direct costs + some indirect costs + fixed or % mark-up
mark up depends on demand, number of competitors, stage of product life cycle
advantages
easy to calculate for single-product business
price covers all costs of production
suitable for market leaders: they set the market price
disadvantages
difficult to calculate for multi-product businesses: difficult allocate indirect (fixed) costs
inflexible: could possibly charge higher
doesn’t consider market conditions
if sales decrease, average fixed costs increase, cost-plus price increases
penetration pricing
used for new products. initially set a low price to attract customers, then raise price.
accompanied by heavy promotion because aim to increase volume of sales
advantages
low cost → high demand → high sales
high sales volume → economies of scale → can lower price
can increase price later
disadvantages
low profit margins + if increase price might have customer resistance
price war: competitors with more resources can survive longer
perceived as low quality
loss leader
product that is sold at a loss and advertised to attract customers into the store → hope customers will purchase other products, which are priced to make a profit.
OR loss leader paired with complimentary product (eg printer cheap but ink expensive)
advantages
low price → high demand → high market share
complementary products’ profit compensates for loss from loss leader
disadvantages
customers may choose cheaper complementary product from competitors → overall loss since did not buy complementary product
predatory pricing
deliberately undercutting competitors prices to eliminate them from the market
illegal, creates monopoly
advantages
short term benefit customers → lower prices → demand increase
eliminates competitors
disadvantages
long term creates monopoly → when increase prices customers no other option
illegal → heavy fines
perceived as low quality
premium pricing
price is higher than needed
create impression that it is higher quality or value
advantages
customers perceive as high quality/stronger brand image → demand increase
price covers all costs
disadvantages
needs coordinated marketing mix
high price → lower demand if PED high → lower sales since choose competitors
dynamic pricing
demand is tracked in real time and prices are adjusted accordingly
demand high and capacity low → increase price to maximise revenue
demand low and capacity high → prices lowered to increase demand and maximise capacity utilisation
adv
maximises revenue
adapt to market conditions
disadv
advanced IT systems needed
consumers feel exploited
consumers alienated if find out that others bought at lower price
competitive pricing
matching/undercutting competitors’ prices → aim to increase sales
price matching
discounts for new customers → attract away from rivals
refund difference
adv
customer loyalty since can be assured that getting a competitive price
able to increase/maintain market share since remain competitive
disadv
reduces profit margins
may have higher costs than competitors → making loss will risk long-term survival
contribution pricing
set prices based on direct cost per unit and some allocation of total indirect costs (no markup, unlike cost-plus)
adv
ensures that each product does not make a loss
lower price than cost-plus → more competitive
disadv
need sell minimum quantity
unable to accurately allocate indirect costs
does not account for changes in quantity affecting unit cost of production (EOS/disEOS)
PED
PED = % quantity demanded / % change in price
always negative
if numerical value >1 → elastic: demand is more responsive to a change in price (eg luxury goods)
increasing price will decrease total revenue
decreasing price will increase total revenue
use competitive pricing:
if 0<numerical value<1 → inelastic: demand is less responsive to a change in price (eg necessities)
increasing price will increase total revenue
decreasing price will decrease total revenue
use price-skimming: set as high as possible then reduce over time. used when strong brand image.
factors
brand loyalty
availability of alternatives
% of consumer income that is taken up by the good
luxury/necessity
time period to adjust: longer time period, more elastic since more time to search for alternatives
promotion
communicate with customers with aim to
raise brand awareness → increase sales
remind about existing product + promote new product
encourage repeat purchases + attract new customers
above-the-line promotion
forms of communicating with potential customers that are aimed at mass market, not targeted
aims to increase brand awareness
types of advertising
informative → raise awareness of new product/communicate major changes
persuasive: creating distinct brand image → especially when little difference from competitors
advantages
raises awareness in wide-ranging audience → useful if product has mass appeal
disadvantages
high cost
unable target specific market
below-the-line promotion
forms of communicating with potential customers that are aimed at specific market segment
NOT DIRECTLY PAID FOR
examples: sales promotion, money-off coupons, customer loyalty schemes, BOGOF, POS displays, public relations, sponsorship
advantages (general)
direct communication with consumers
based on specific marketing objectives → can measure results against
through-the-line promotion
integrates both above and below the line elements
aim to convert customers into measurable and targetable sales
example: social media
use online marketing to communicate and directly sell
use influencers with high social-networking potential to create appealing messages that are likely to be passed on to many people
advantages
no-cost
global audience reach
target specific market segments
interactive
performance metrics
speed of transmission
disadvantages
lack of skill
time investment
negative feedback is public → damage brand image
security issue
performance metrics are not immediate
not everyone uses social media
influencer may not align with brand image
place
distribution channels: chain of intermediaries product passes through from manufacturer to consumer
companies may have multiple, depending on type of product and needs of consumers
players
manufacturers: produce goods → need widest geographical range of market BUT need maintain brand image
wholesalers: buys in bulk from manufacturer and holds goods, sells to retailers in smaller quantities
retailers: sell goods to final consumer → will sell goods but demand mark up to make profit
consumers: want ease of access to try before buying + ease of return
direct selling
manufacturer → consumer
example: online sales → reaches wide market
advantages
no markup, no profit margin taken by other business
complete control over marketing mix
faster
direct contact with consumer → market research
disadvantages
no outlets for consumers to try
need pay for all promotional costs + no after sales service since no intermediaries
need space for + pay cost of holding stock
delivery costs high since need deliver to consumer
manufacturers need focus on both producing and selling
single intermediary channel
manufacturer → retailer → consumer
usually for consumer goods/industrial goods to businesses
advantages
retailer has space for + pays cost of holding stock
retailer has outlets to display products and allow consumers try
retailer’s location is more convenient for consumer
manufacturers can focus on production
disadvantages
retailer makes profit through markup → more expensive for consumers
loss of control over marketing mix
no exclusive outlet: retailers sell competitors’ products too
manufacturer pays cost of delivery to retailer
two intermediary channel
manufacturer → wholesaler → retailer → consumer
advantages
wholesaler buys in bulk then sells to retailer (‘breaking bulk’)
wholesaler pays for cost of delivery to retailer
wholesaler has space for + pays cost of holding stock
best option when entering foreign market: since wholesaler has direct contact with retailers
disadvantages
two intermediaries who need to make profit → price for final consumers increase
slowest
manufacturer loses more control over marketing mix
people
employees/managers and how customers communicate with them
influenced by
who/how business is represented to customers → affects brand image and customer loyalty
if genuine → performance increase → honest feedback from customers
interpersonal skills, trained with service knowledge, high efficiency → customer satisfaction increases
process
procedures and policies put in place to provide service to customer
how it influences customer satisfaction
fast, efficient, avoid delays → brand image improved
clearly defined and everyone knows how → consistent customer experience
remain competitive, embrace new technology, up to date → meets customer expectations
physical evidence
how business and products are presented to customers
goods: product packaging
services: location, appearance, employee behaviour and appearance
important in coordinated marketing mix → justifies premium pricing
impacts customer experience and satisfaction
should be customer-tested and updated