A&P Unit 1 vocabulary
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:59 AM on 8/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
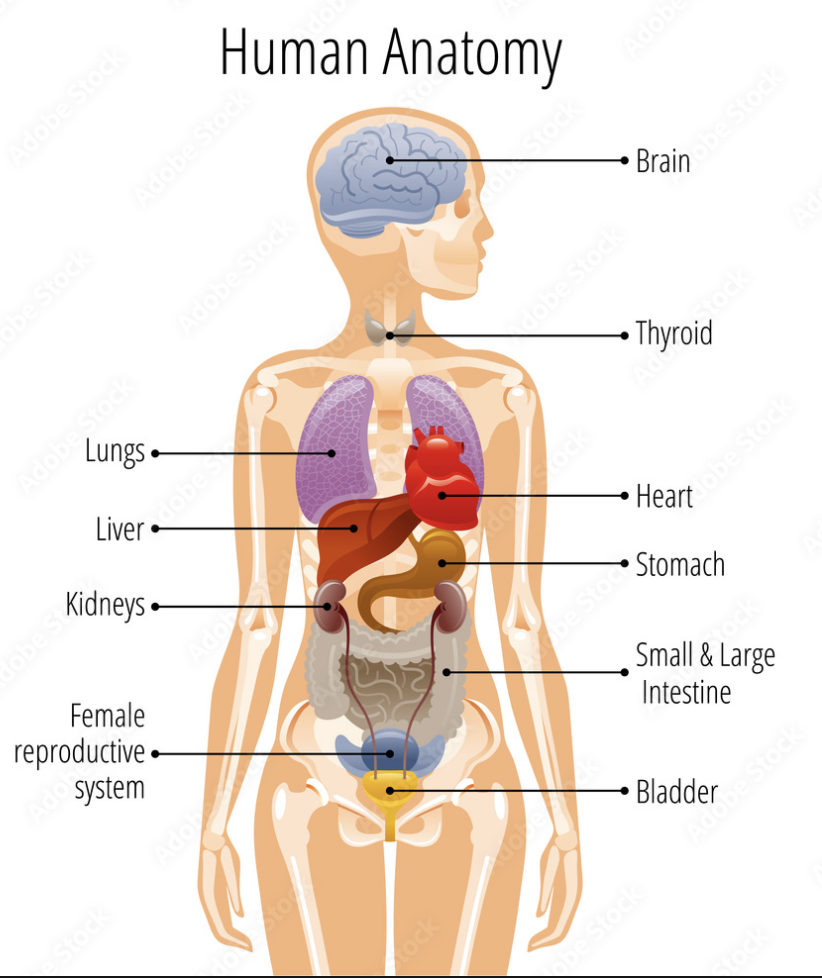
Anatomy
the science of the structure of living organisms
2
New cards
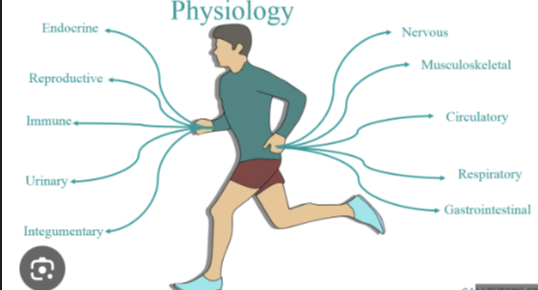
physiology
the science of the functioning of living organisms
3
New cards
atoms
the smallest part of an element; indivisible chemical means

4
New cards
cells
the basic biological unit of living organisms, enclosed by a limiting membrane; cells in more complex organisms contain a nucleus and a variety of organelles
5
New cards
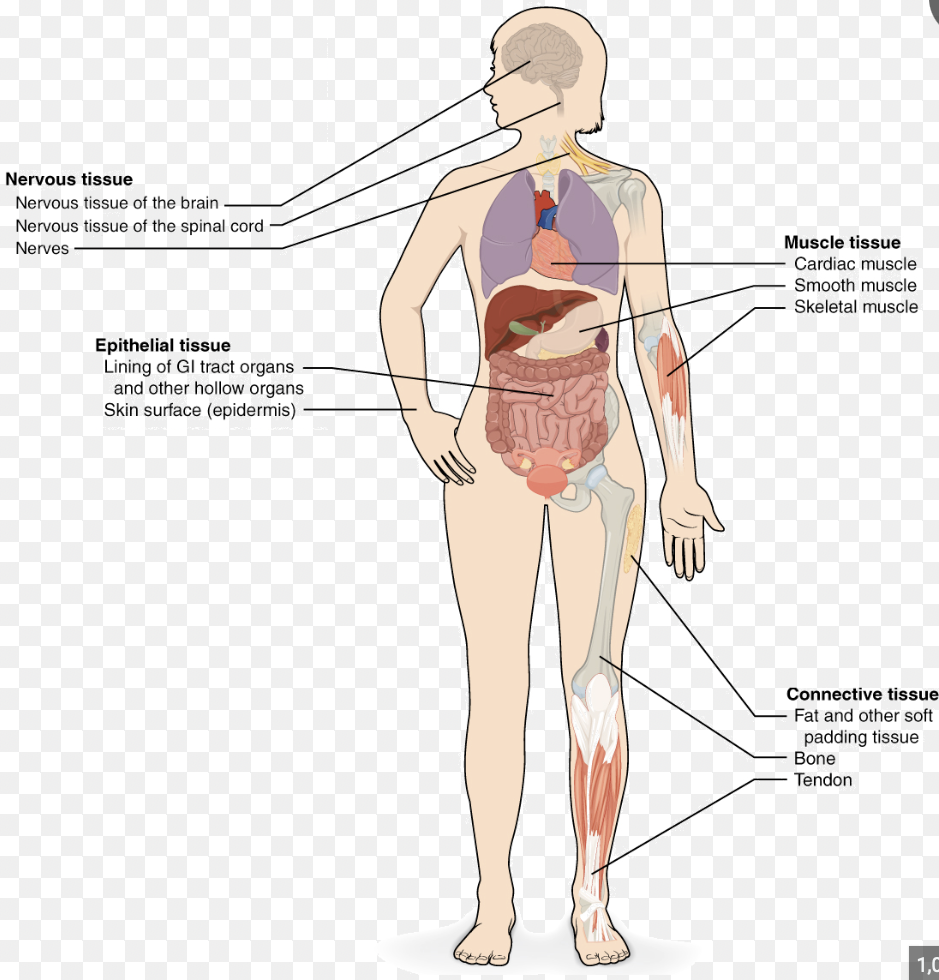
tissues
a group of similar cells socialized to perform a specific function; primary tissue types are epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues
6
New cards
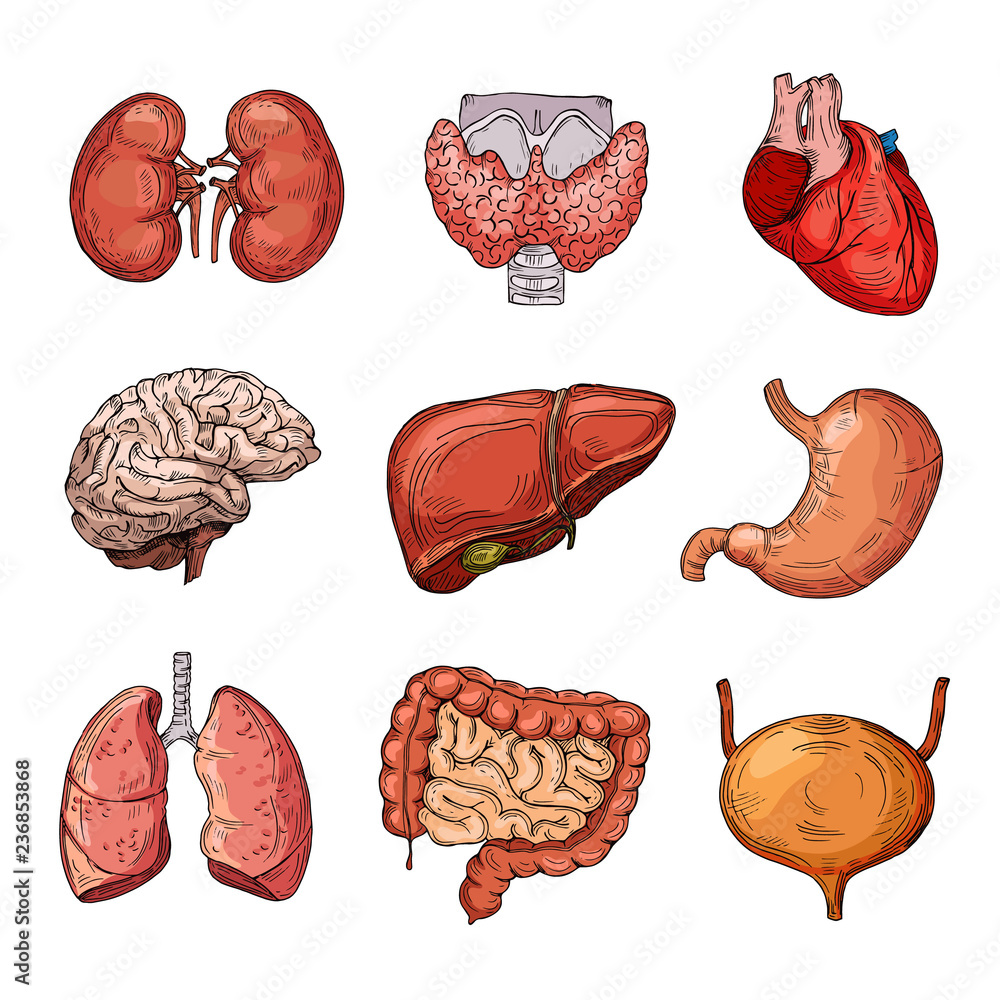
organ
a part of the body formed of two or more tissues that performs a specialized function
7
New cards
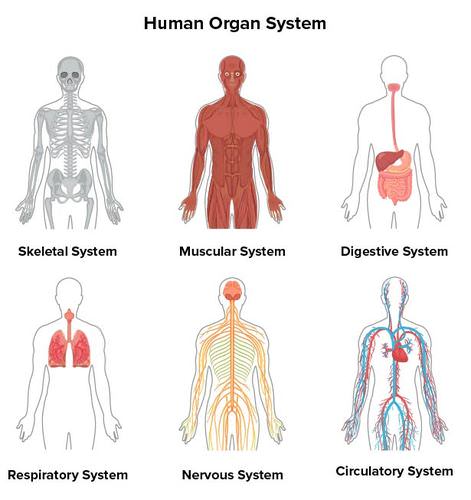
organ system
a group of organs that work together to perform a vital body function
8
New cards
organism
an individual living thing

9
New cards
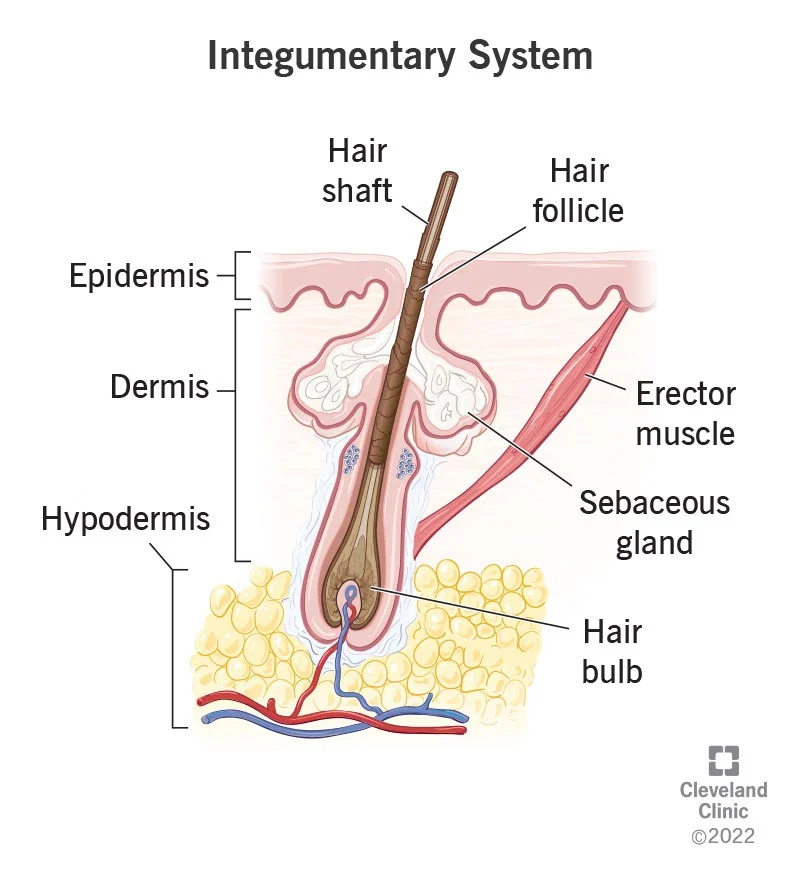
integumentary system
the skin and its accessory organs
10
New cards
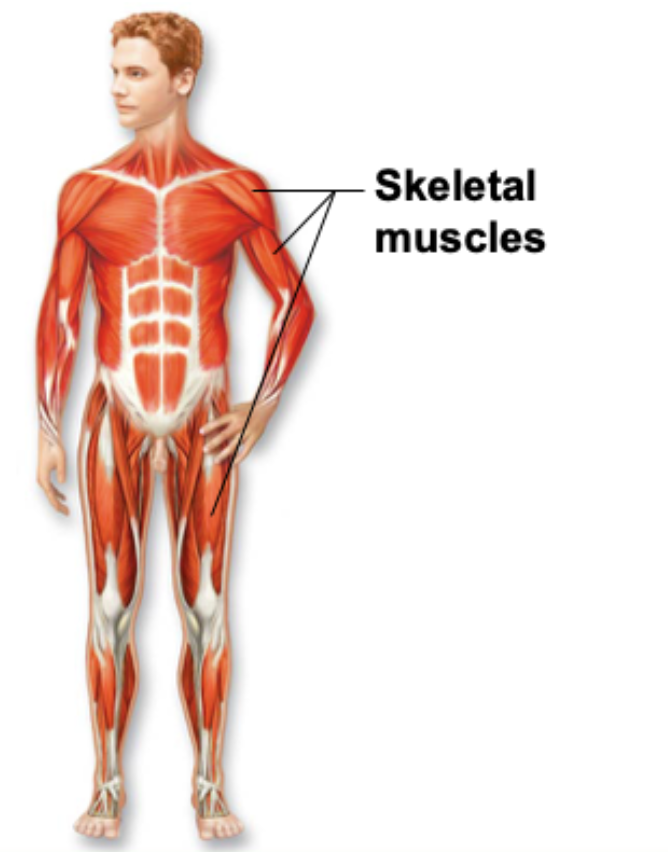
skeletal system
system of protection and support composed primarily of bone and cartilage
11
New cards
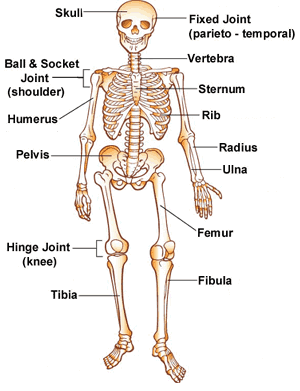
muscular system
organ system consisting of skeletal muscles and their connective tissue attachments
12
New cards
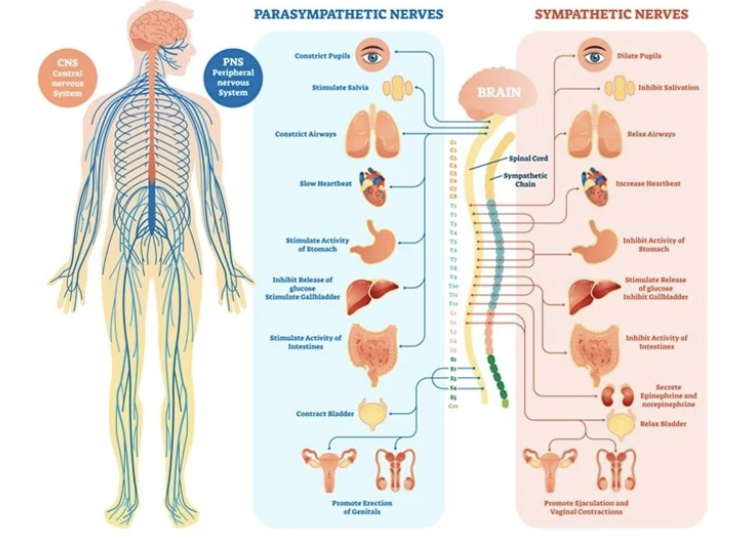
nervous system
fast-acting control system that employs nerve impulses to trigger muscle contraction or gland secretion
13
New cards
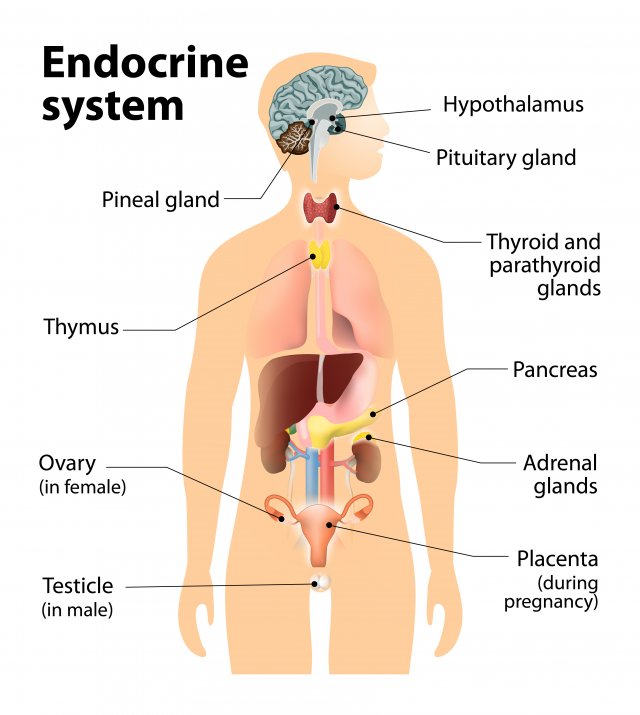
endocrine system
body system that includes internal organs that secrete hormones
14
New cards
cardiovascular system
organ system that distributes blood to all parts of the body
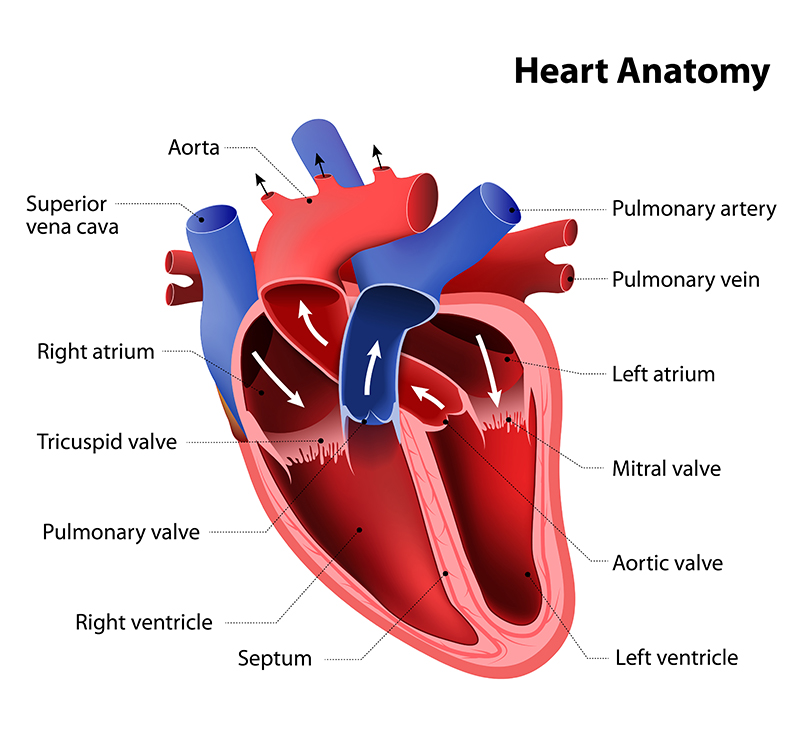
15
New cards
lymphatic system
the lymphatic vessels, and the lymphoid tissues and organs including lymph nodes
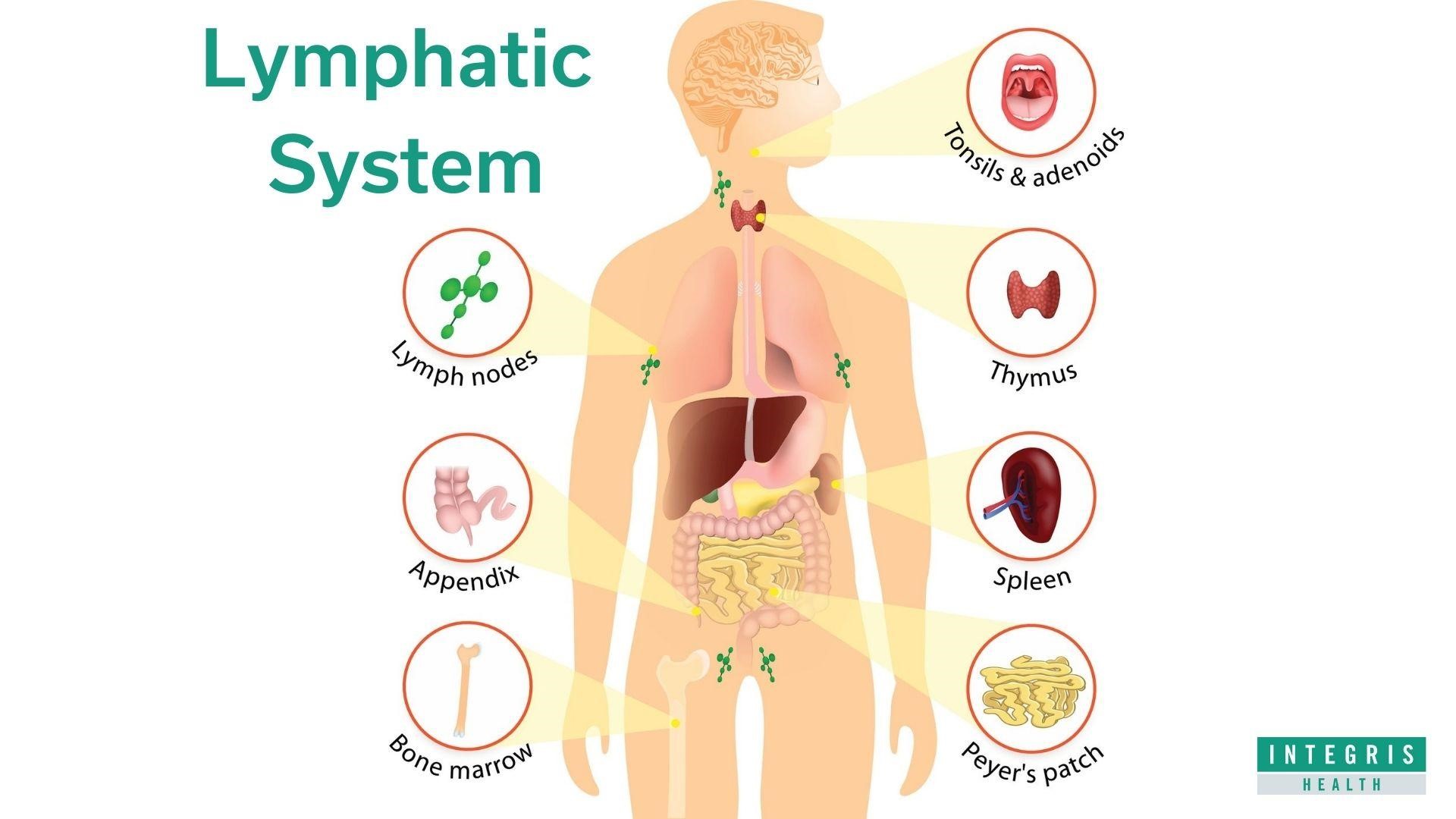
16
New cards
respiratory system
organ system that carries out gas exchange; includes the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs
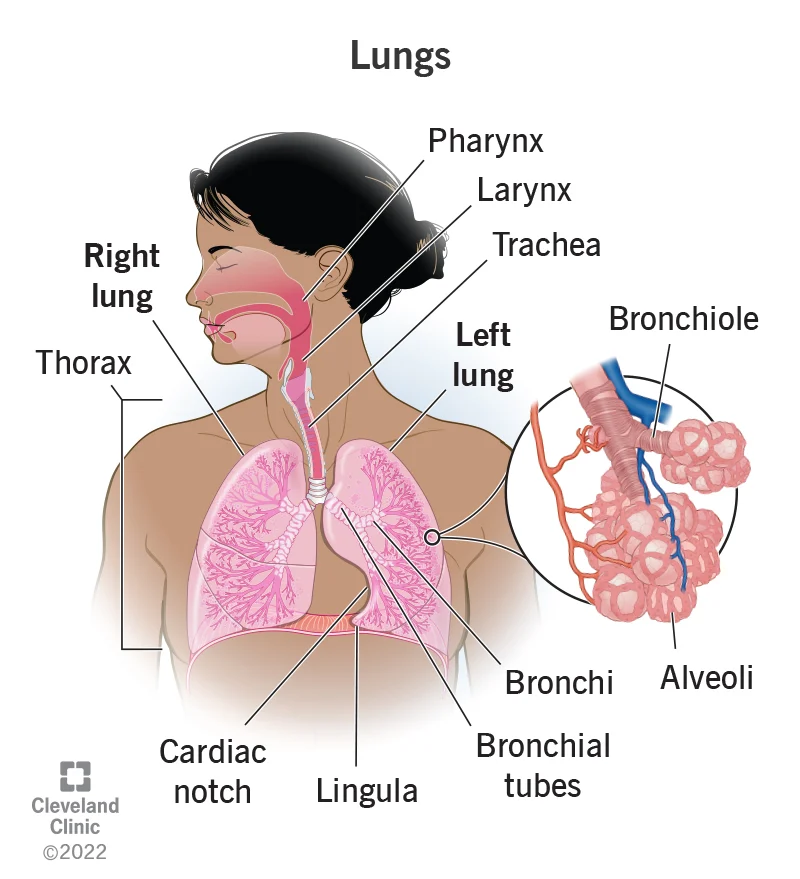
17
New cards
digestive system
system that processes food into absorbable units and eliminates indigestible wastes
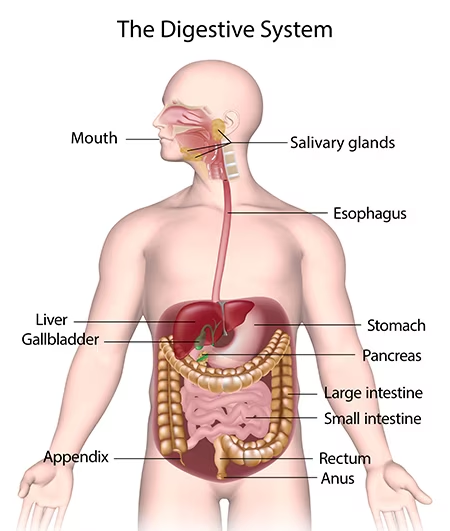
18
New cards
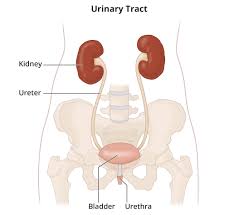
urinary system
system primarily responsible for water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance and the removal of nitrogen-containing wastes from the blood
19
New cards
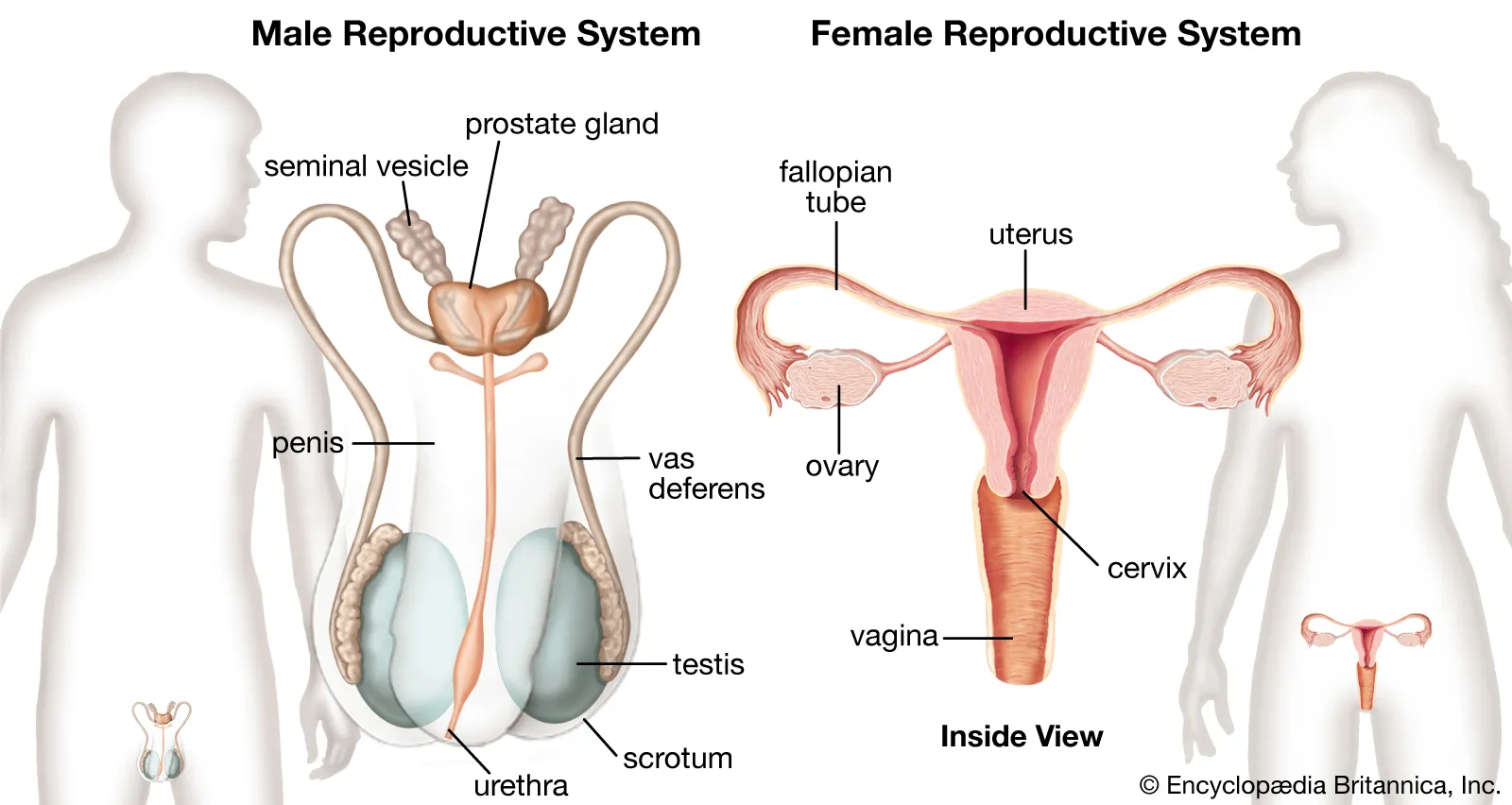
reproductive system
organ system that functions to produce offspring
20
New cards
movement
an act of changing physical location or position or of having this changed

21
New cards
responsiveness/irritability
the ability to sense changes (stimuli) in the environment and then to react to them; see also irritability
22
New cards
digestion
the body process of breaking down foods chemicals and mechanically
23
New cards
metabolism
the sum total of the chemical reactions that occur in the body
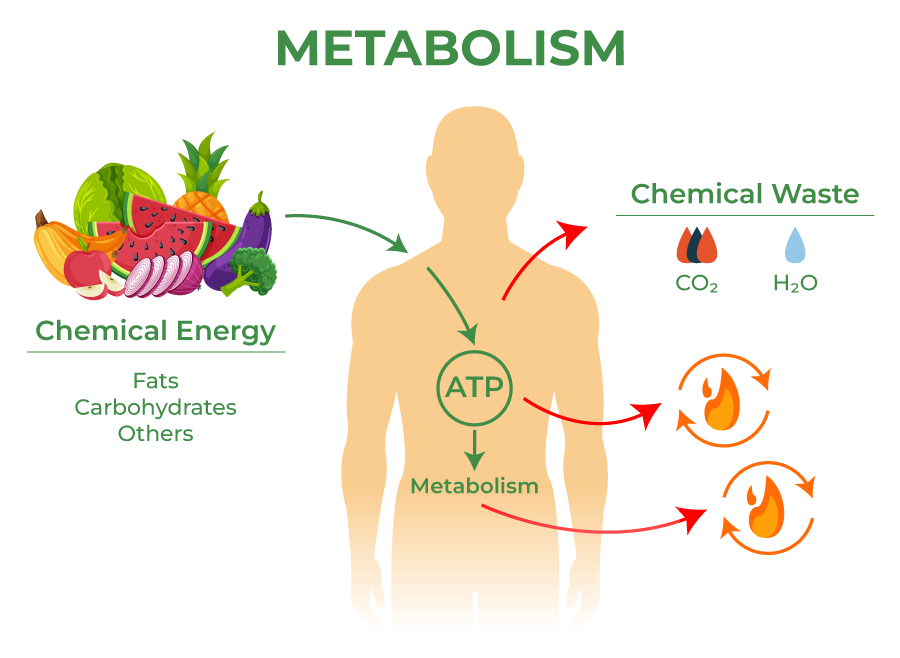
24
New cards
excretion
the elimination of waste products from the body
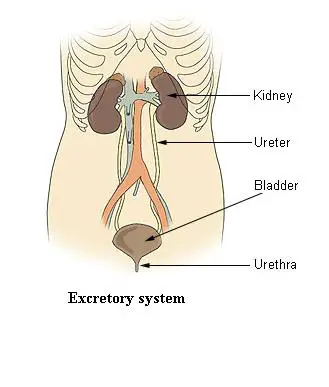
25
New cards
reproduction
the action or process of making a copy of something
26
New cards
growth
the process of increasing in physical size

27
New cards
nutrients
a substance that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life
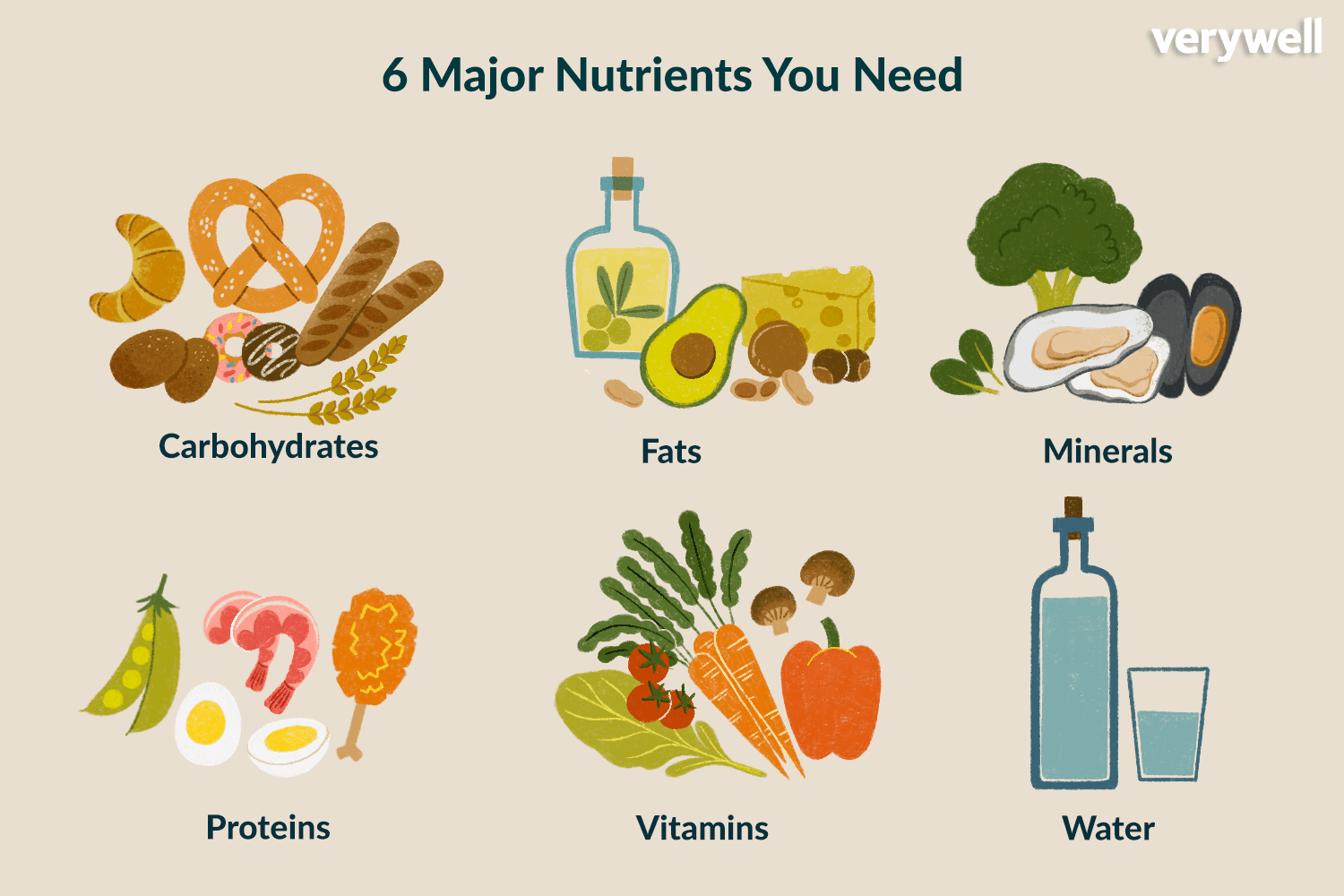
28
New cards
oxygen
the odorless gas that is present in the air and necessary to maintain life

29
New cards
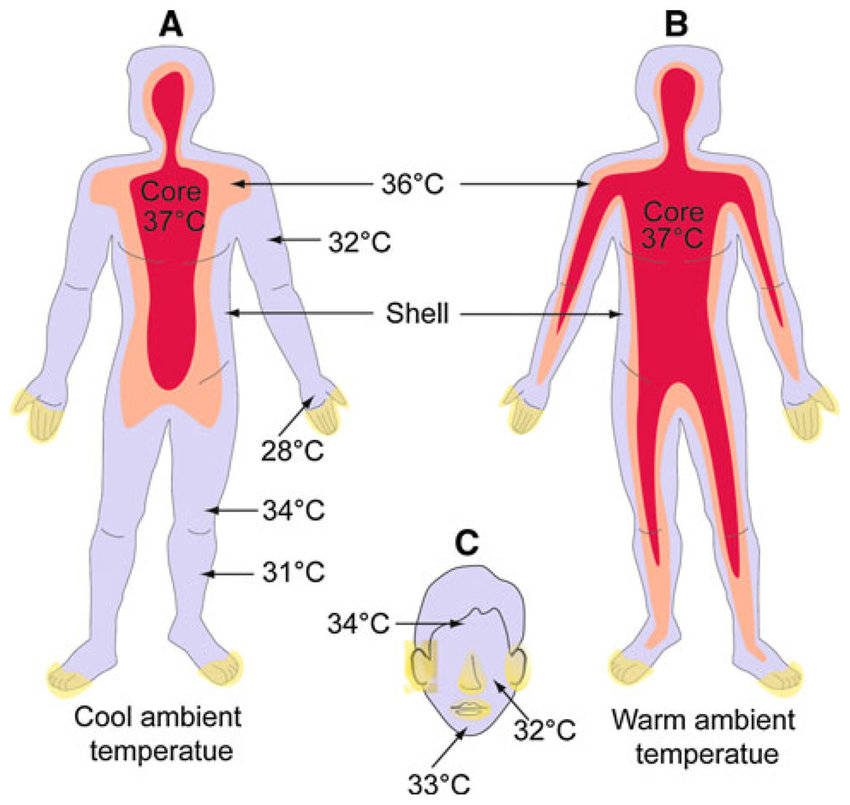
normal body temperature
the typical temperature range found in humans
30
New cards
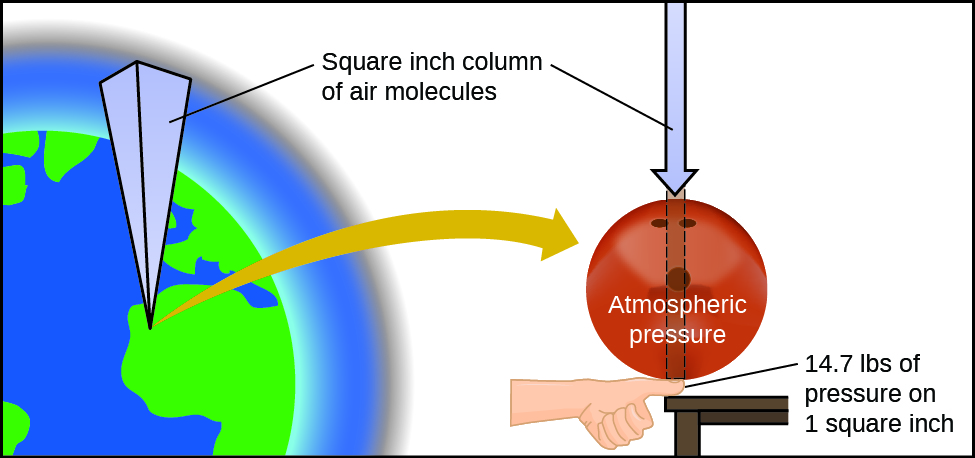
atmospheric pressure
the pressure of the air outside the body
31
New cards
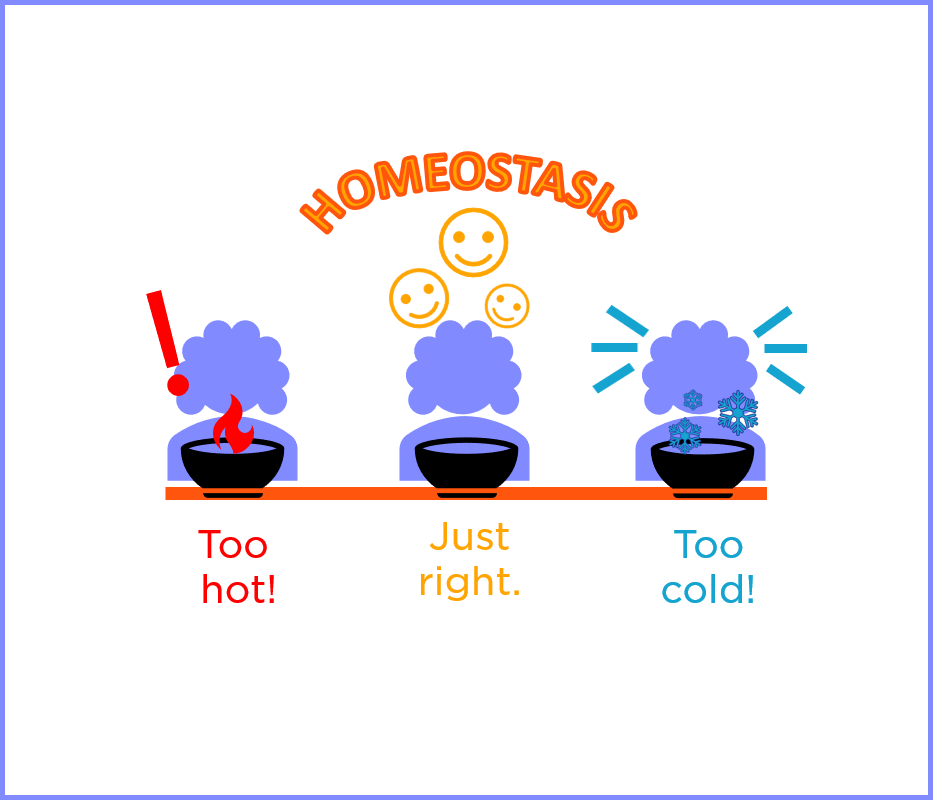
homeostasis
a state of body equilibrium or stable internal environment of the body
32
New cards
receptor
(1) a peripheral nerve ending specialized for response to particular types of stimuli; (2) molecule that binds spe- cifically with other molecules, e.g., hormones and neurotransmitters.

33
New cards
control center
the body structure that determines the normal range of the variable, or set point
34
New cards
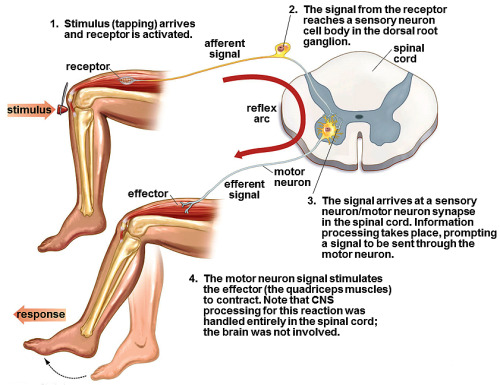
effector
an organ, gland, or muscle capable of being activated by nerve endings
35
New cards
negative feedback
occurs when a system’s output acts to reduce or dampen the processes that lead to the output of that system, resulting in less output
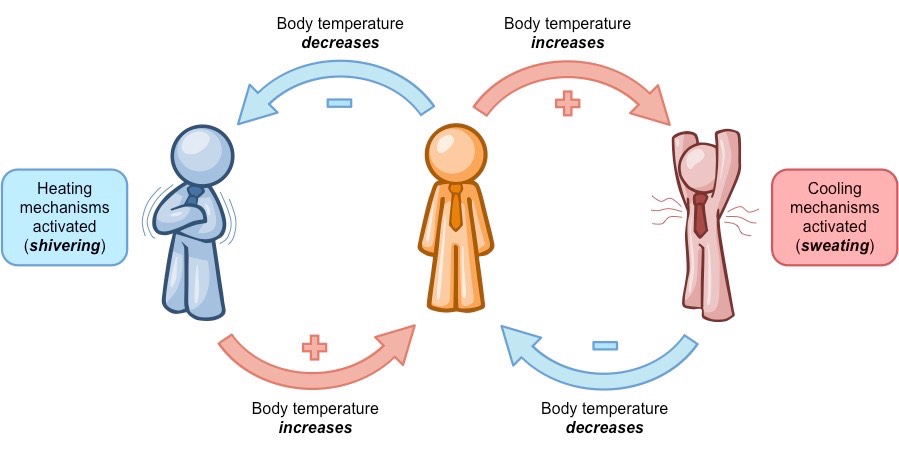
36
New cards
positive feedback
intensifies a change in the body’s physiological condition rather than reversing it
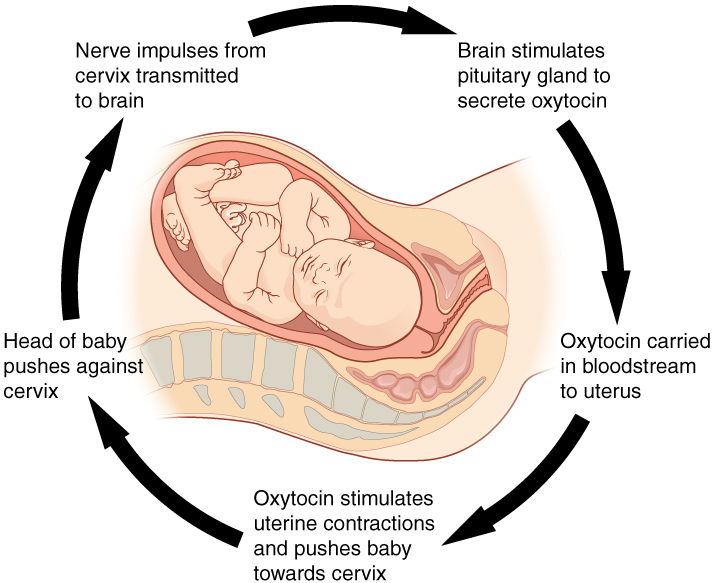
37
New cards
homeostatic imbalance
an inability of the body to restore a functional, stable internal environment
38
New cards
anatomical position
describes the body in standing position when feet and head are facing forward; arms to the side with palms facing the front
39
New cards
directional terms
describes the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body

40
New cards
regional terms
describe the different parts of the body by the structures and functions of a specific region
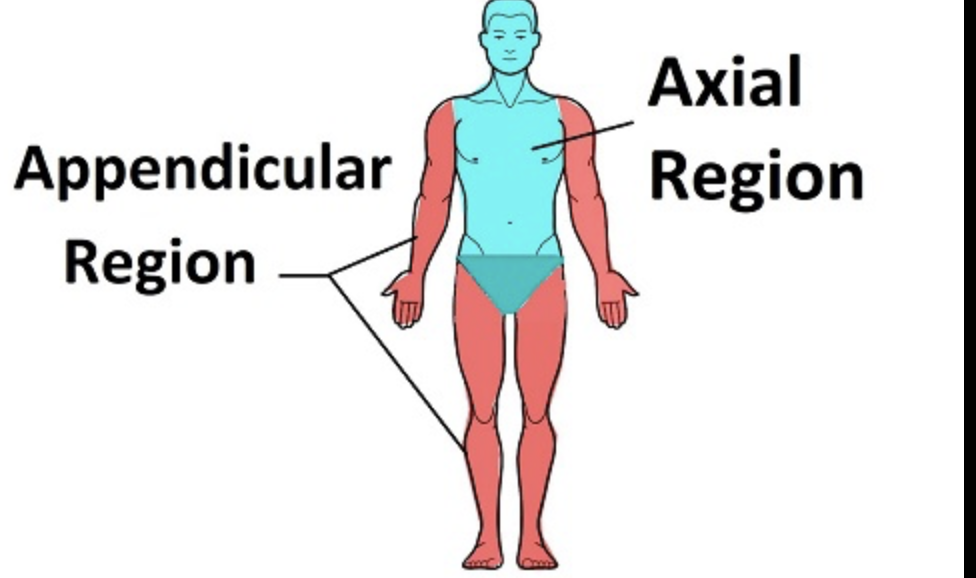
41
New cards
section
a segment or subdivision of an organ
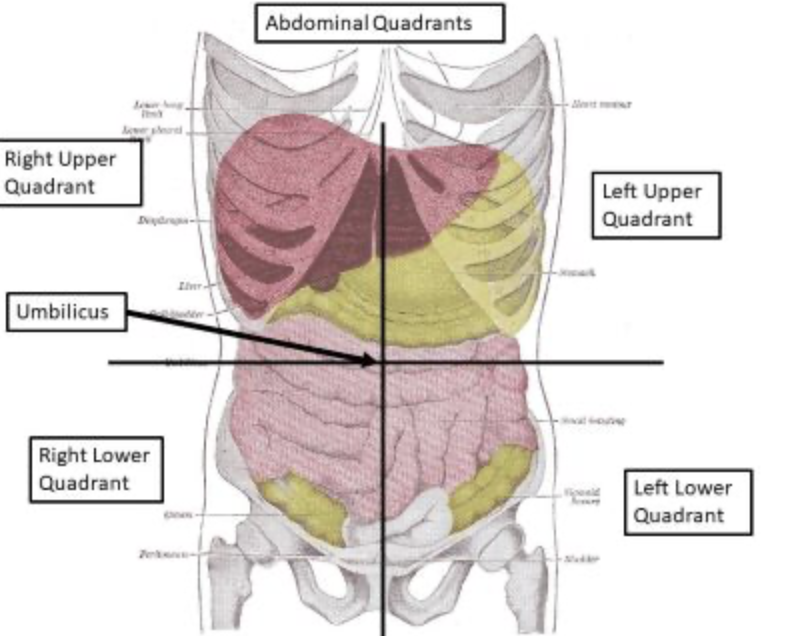
42
New cards
plane
an imaginary vertical and horizontal line used to divide the body into sections for descriptive purposes
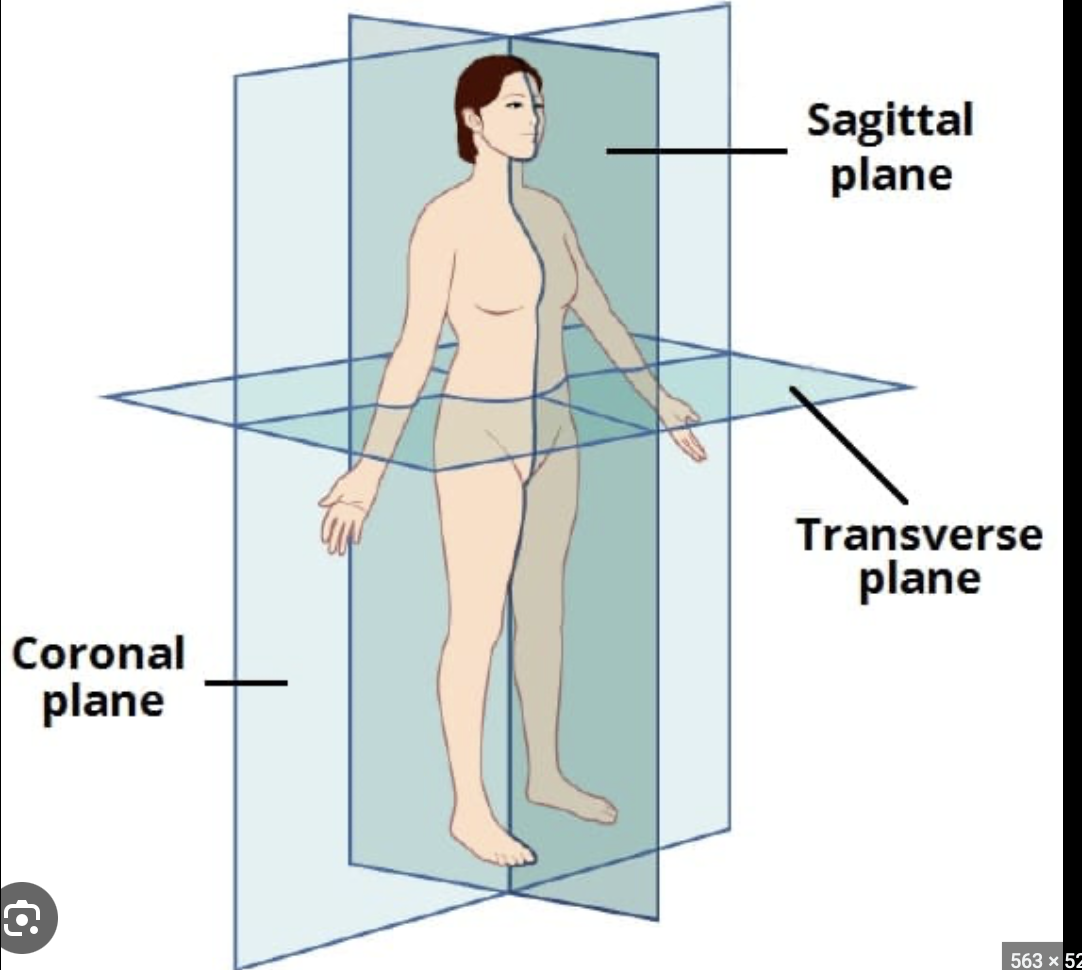
43
New cards
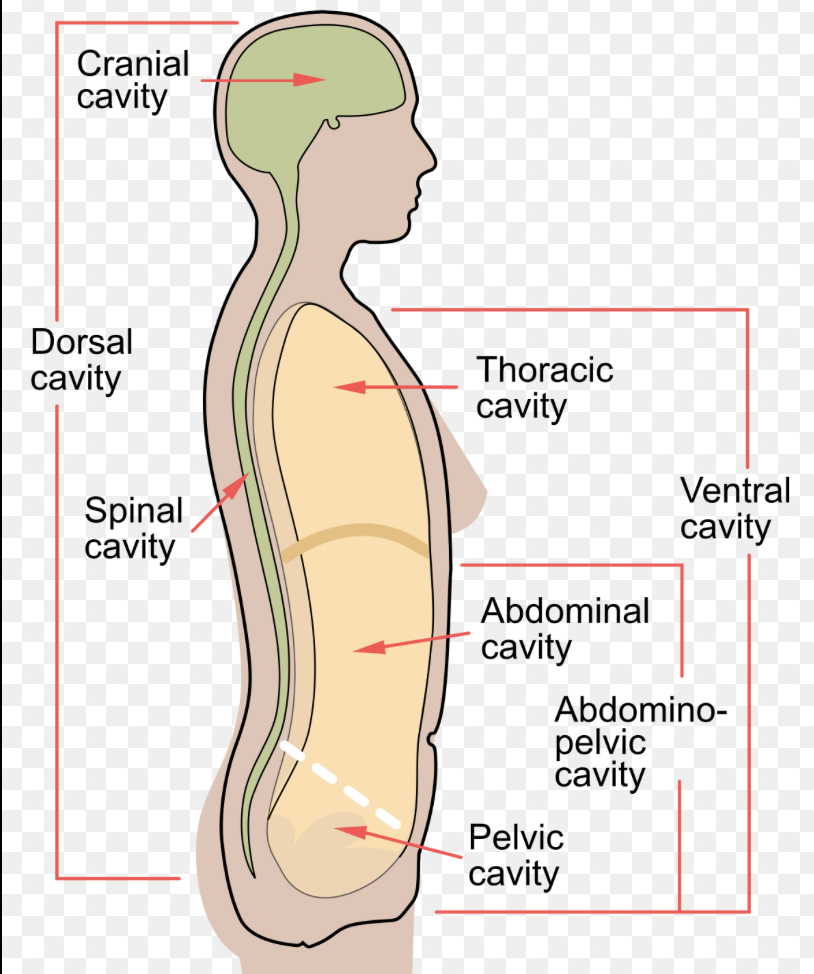
body cavities
spaces within the body that contain and protect special organs