Lecture 15: pre-formulation of solid dosage 2
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what does the functionality of pharmaceutical products depend on?
the physical form of the drugs
their performance depends on understanding the physical properties
what are the phyiscal forms of a drug and what does it affect?
only applied when a drug is in a solid state
affects preformance, development, patentability, manufacturing and profitability of a compound
A drug can have many different solid-state forms:
Crystalline (Polymorphs, Hydrates and Solvates)
Chiral
Habits
Amorphous
crystalline form has ---- solubility, amorphous form has ---- solubility
low
high
examples of amorphous and crystalline

what properties are determined by the nature of the crystalline structure?
Solubility and dissolution rates(amorphous is highly soluble)
Crystal hardness (compressibility for tablets)
Chemical stability (enthalpy of solution, enthalpy of transition, hygroscopicity, melting and sublimation temperatures)
some chemically unstable drugs change forms from active to inactive during storage
Others include: Colour and refractive index, heat capacity, conductivity, volume, density.
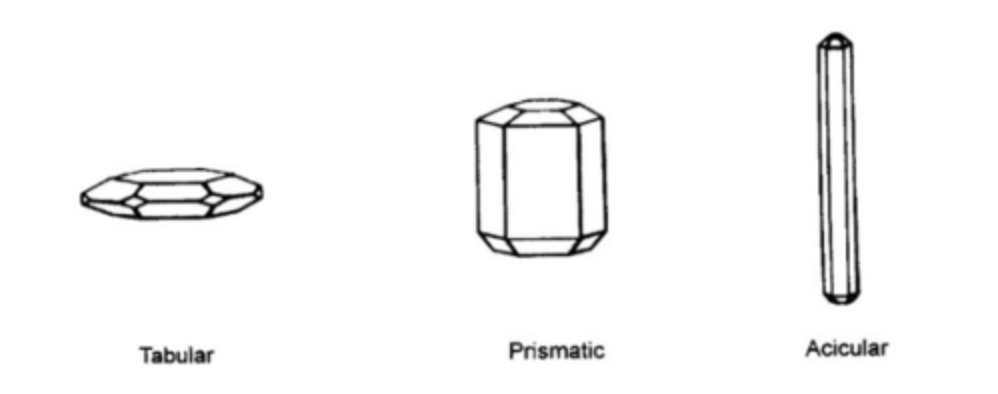
what are crystal habits?
the external shape of a crystal
what are crystal habits associated with?
the way solute molecules orientate themselves when growing.
The general shape of a crystal is related to the growth of individual crystal faces.
The slowest growing face dominates.
Crystal habit influences flow, compaction, stability and solubility.
what is crystal face identification?
Each crystal face has a designated index plane
These are known as Miller indices
what does the miller index do?
Miller index provides information about the molecular ordering of the surface of a crystal face
pharmaceutical effects of habit:
Injectables: Plate-like crystals pass through needles better than long needle-like crystals(poor flow, can clog, unstable)
Tableting: Plate-like tolbutamol crystals do not flow and have poor compressibility.
Needle-shaped paracetamol crystal powder shows poorest compression properties, showing greater capping and lamination, than the plate- or cube-shaped crystals.
Dry powder inhaler (DPI) formulations: Needle-like crystals usually have better fine particle fraction.
what is the definition of a crystalline structure?
A crystal is composed of periodical aligned building blocks called unit cells
These unit cells reveal the crystal structure and symmetry specific for each substance (Requires X-ray diffraction to elucidate).
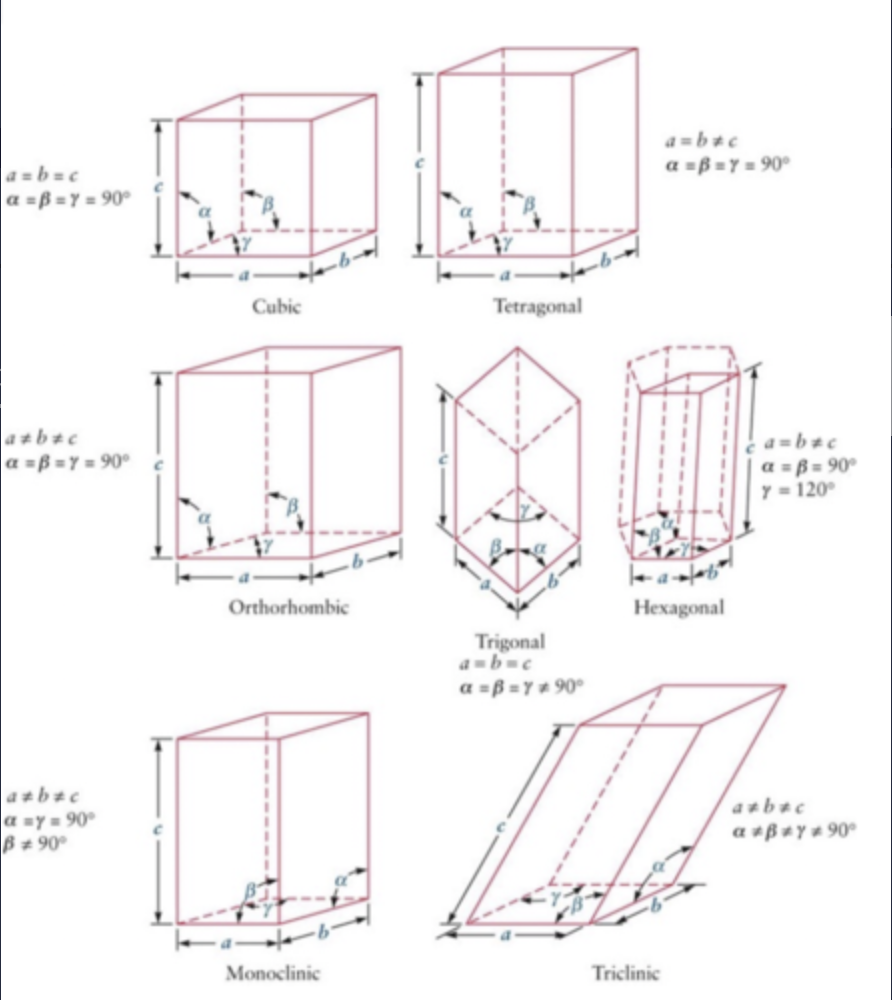
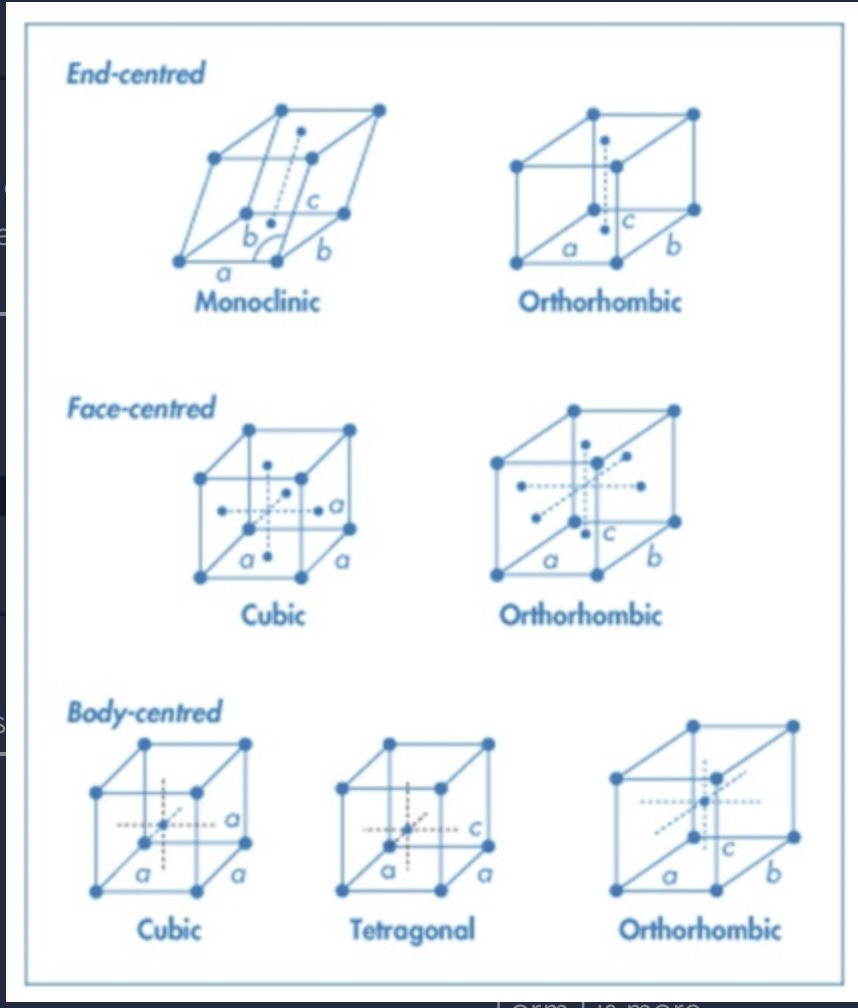
There are a total of 7 types of crystal structures and all can be defined by the lengths and angles between each side of the unit cell.
what are the 7 primitive unit cells
Cubic
Tetragonal
Orthorhombic
Trigonal
Monoclinic
Triclinic
Hexagonal
Drug molecules will typically form triclinic, monoclinic and orthorhombic unit cells
molecules can arrange themselves into 14 different configurations and are known as bravais lattices
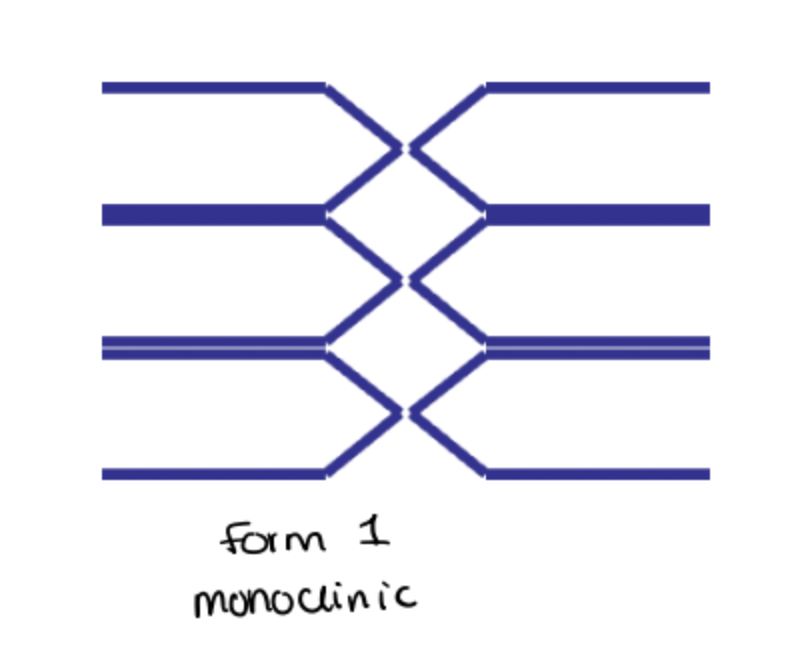
what forms does paracetamol exist?
Exists in two polymorphic forms, monoclinic. (Form 1) and orthorhombic (Form 2)
Form 1 is more thermodynamically stable at room temperature and is the commercially used form.
Form 1 not suitable for direct compression, has to be mixed with binding agents before tableting.
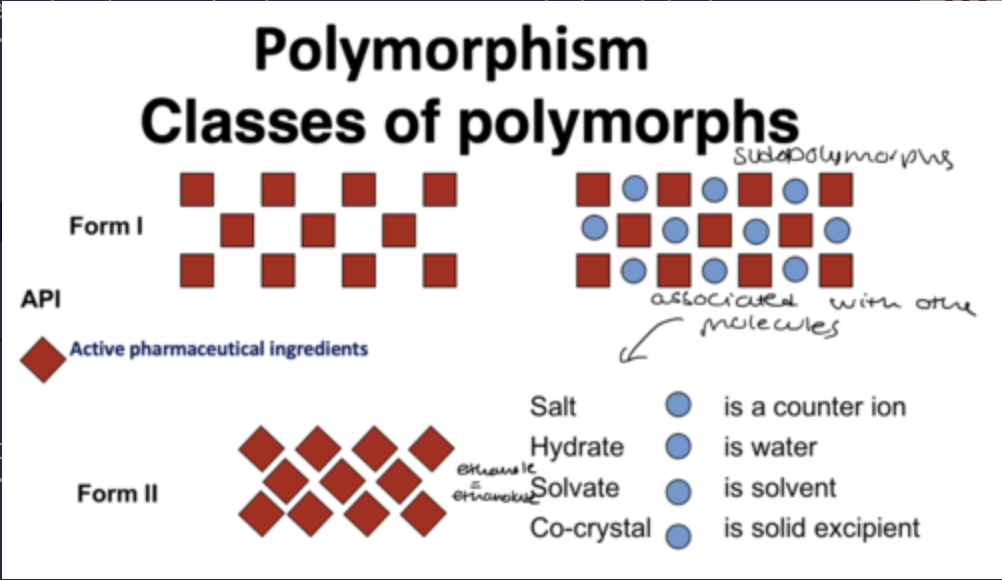
classes of polymorphs diagram
what does crystal form mean?
ordering of atoms and molecules to form crystal structure
it does not mean outer appearance (habit) of the crystals/particles.
What are polymorphisms?
When the same chemical compound exists in different crystal forms
what are pseudopolymorphs?
Special cases of polymorphs are pseudopolymorphs like solvates (solvent molecules in crystal lattice) or hydrates (water molecules in crystal lattice
what is enantiomorphism?
Chiral molecules can crystallise as mirror images of each other. This is known as enantiomorphism. A mixture of D (dextro) and L (levo) crystal forms are known as a racemic mixture.
basic overview of solid forms:
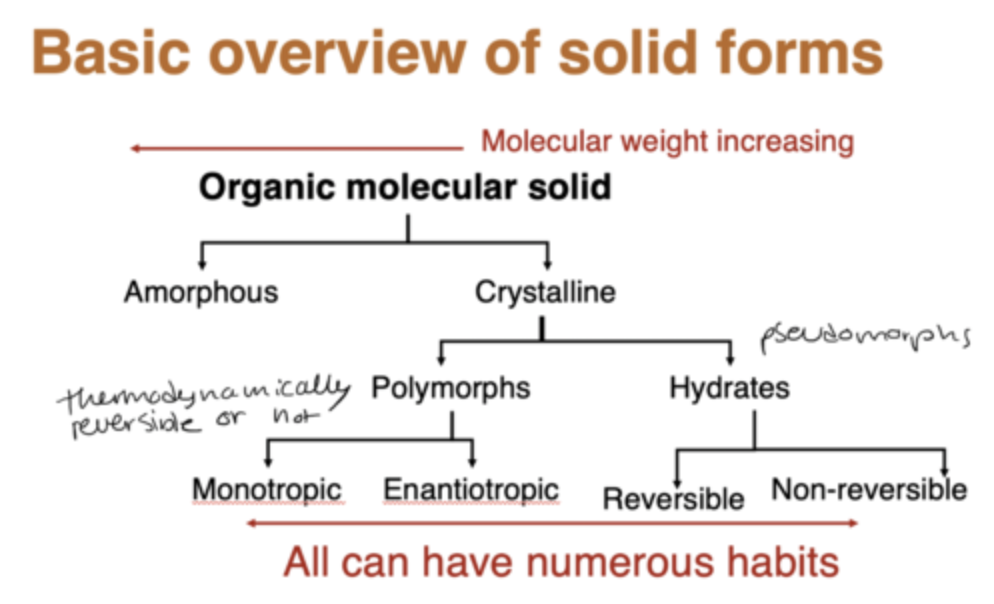
what does enantiotropic and montropic mean?
Solid phase transitions which transform reversibly without passing through the liquid or gaseous phases are called enantiotropic.
If these are not achieved prior to a phase change then they are called monotropic
any transition from one polymorph to another below melting point will be irreversible

what are the features of form 1 polymorph?
Lower density
Lower lattice energy
Lower melting point
Faster dissolution rate
Possible fracture line
what are the features of form 2 polymorph?
Higher density
Higher lattice energy
Higher melting point
Slower dissolution rate
Lower bioavailability
what are properties that may change with polymorphic forms?
Melting point
Dissolution rate
Compressibility
Density
Flowability
Surface properties (surface energy and morphology)
Habit and crystal shape
Hygroscopicity
Hardness
Stability
why is polymorphism important?
It is essential during the preformulation stage that the most thermodynamically stable polymorph is formed, since a more favourable form may be obtained upon scaling-up.
Moisture-mediated and solid-state phase transformation from one polymorph to another can occur during processing and storage.
Regulatory: "What assurance can be provided that no other crystalline forms of this compound exist?" -
Requires the manufacturer to indicate the characterisation of the various forms of the drug
Patents - Subsidiary patents for desirable forms
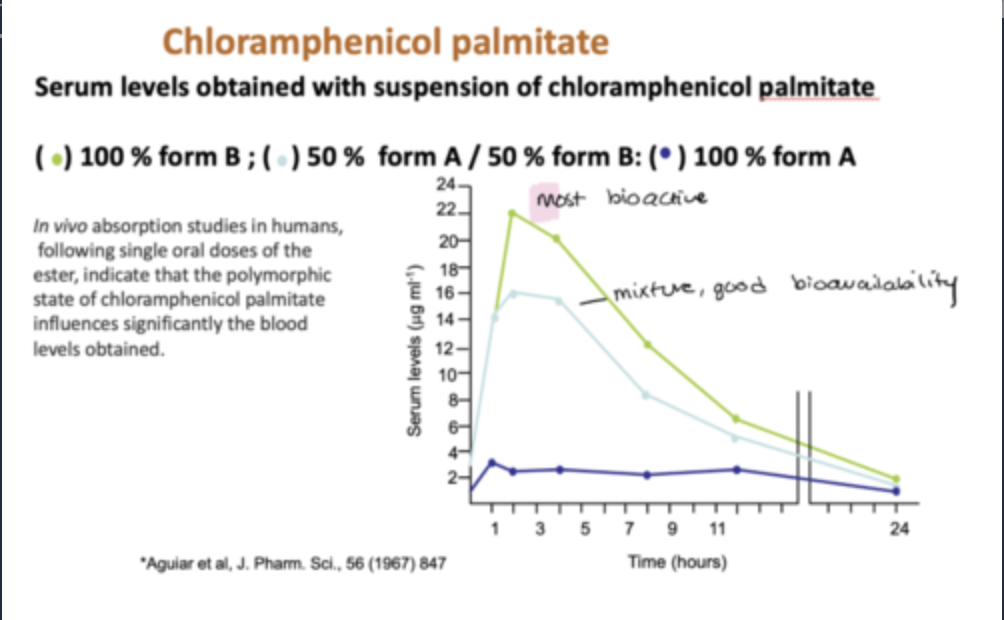
e.g. Chloramphenicol-3-palmitate (CAPP)
CAPP is a broad spectrum antibiotic.
Can crystallise in at least three polymorphic forms.
The most thermodynamically stable form A, is marketed.
Form B, however, has an eightfold higher bioactivity than form A.
Can create the danger of fatal dosages when the unwanted polymorph is unwittingly administered because of alterations in process or storage conditions (interconversion).