Homeostasis and an Introduction to Body Systems
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Homeostasis
The ability of a system to maintain a steady state
Negative Feedback
System in which the stimulus and response are opposite
Negative Feedback Example
The thermostat is set to 70 degrees. Stimulus would be the room getting warmer. Response would be to turn on the air conditioner to cool down the room
Positive Feedback Example
The temperature rises above 70 degrees. Stimulus would be the warm getting warmer. Response would be to turn on the furnace to make the room even warmer
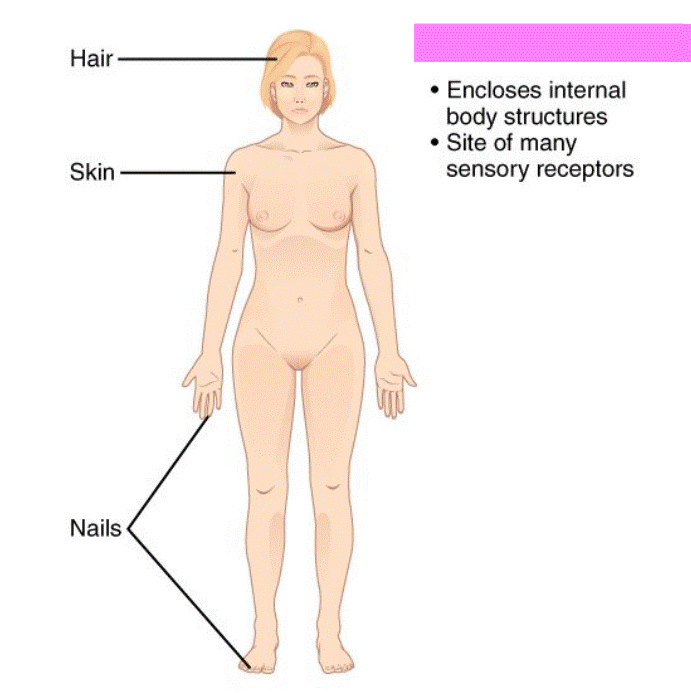
integumentary System
Consist of the hair, skin, nails, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands. Its function is protection of the body, secretion of waste products, production of vitamin D, and regulation of body temperature. Also supports sensory receptors that send information to the nervous system
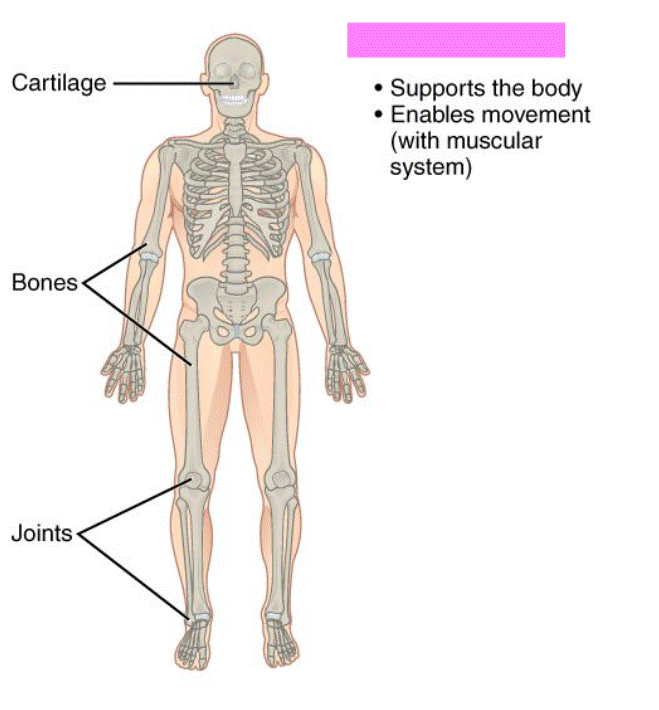
Skeletal System
Consist of bones, ligaments, and cartilage. It provides protection and support and produces red blood cells. It also stores chemical salts.
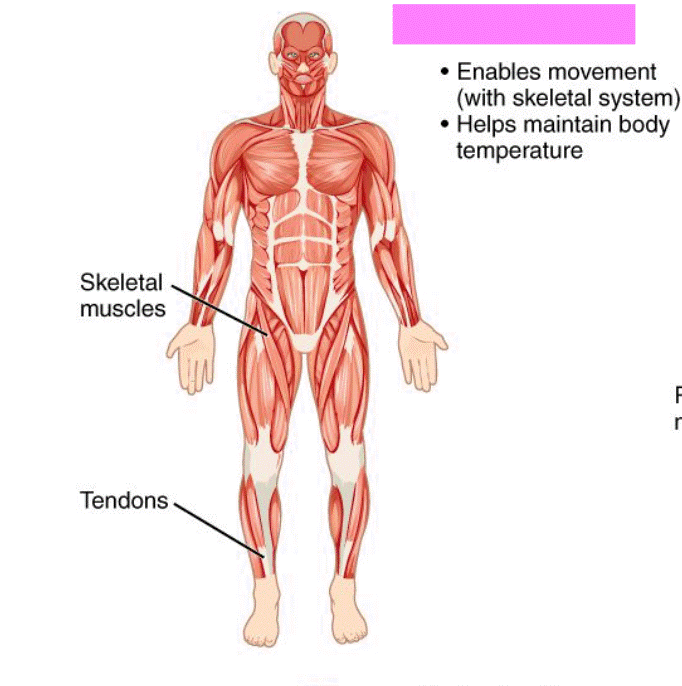
Muscular System
Produces movement, helps to maintain poster and produces heat
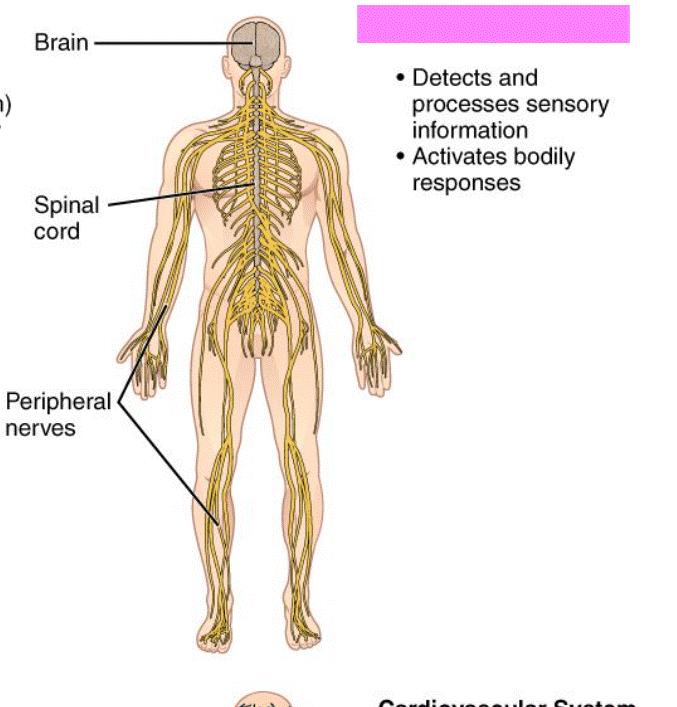
Nervous System
Consist of the brain, spinal cord, and receptors. It receives sensory information and detects changes and in response. stimulates muscles and glands
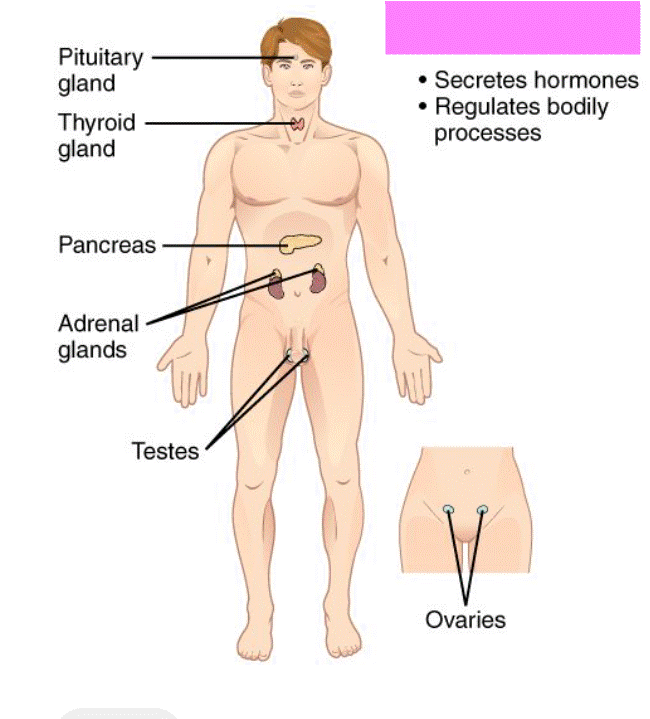
Endocrine System
A series of glands that secrete hormones. Contains many feedback systems to help maintain homeostasis
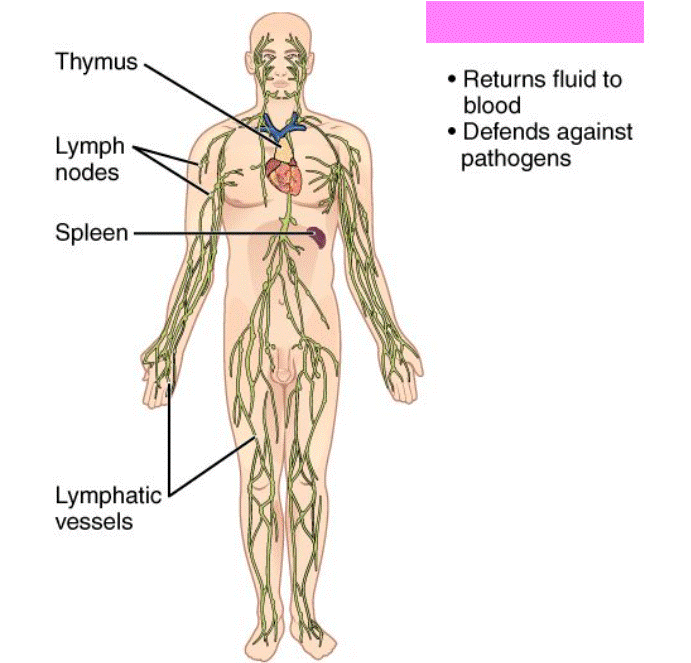
Lymphatic System
Includes the lymph vessels, lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen. It’s function is to return fluid to blood as well as transport some absorbed food molecules and defend against infection
Immune System
Consist of cells and antibodies that help the body to fight off pathogens. Some organs associated includes the thymus and spleen.
Blood
A fluid system that contains cells and plasma. These structures work to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide along with water, electrolytes, hormones, carbohydrates, fats and proteins and waste
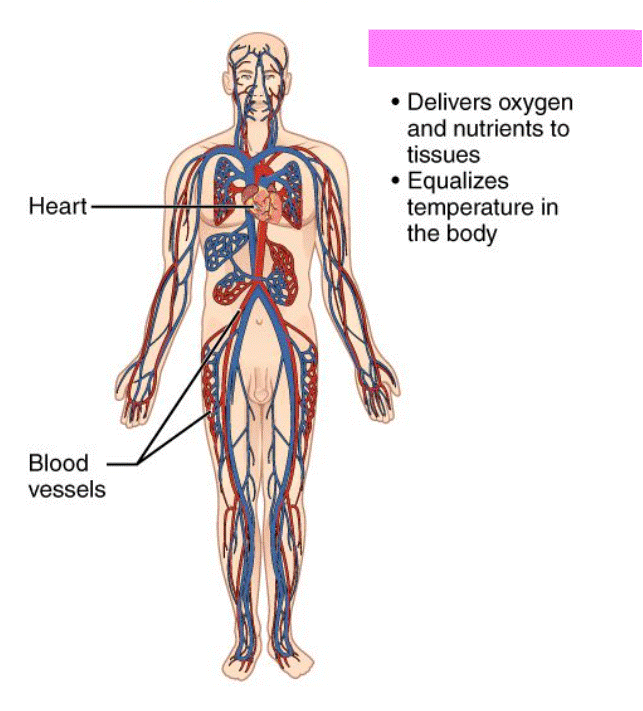
Cardiovascular System
Includes the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins. The function is to transport blood
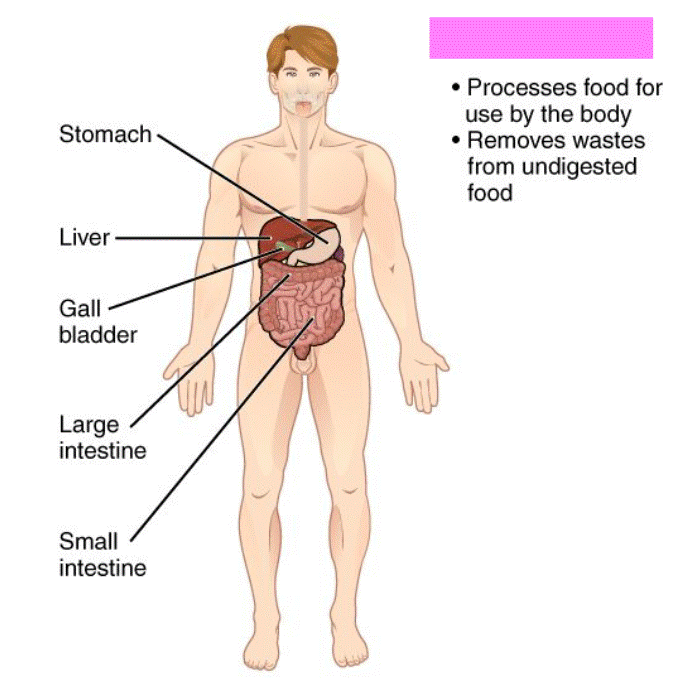
Digestive System
The function is to receive, break down, and absorb food. It also eliminates waste. It includes the mouth, tongue, teeth, salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and intestines.
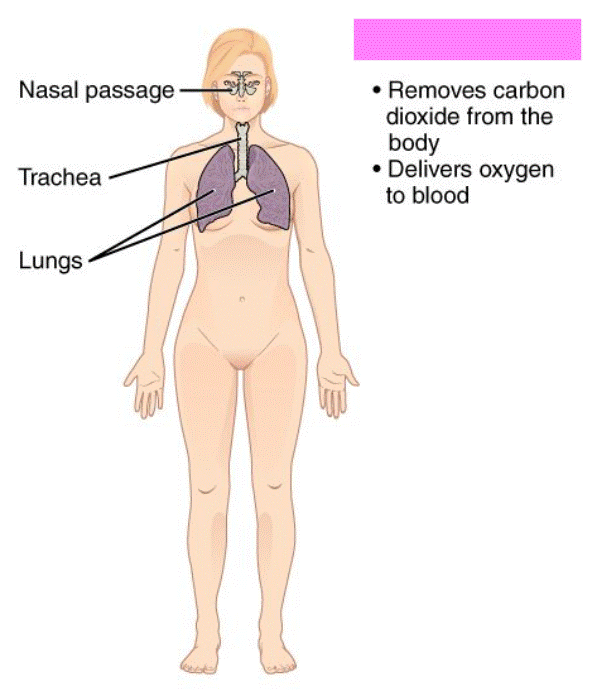
Respiratory System
Consist of the nasal cavity, lungs, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and bronchi. Supplies the body with oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide.
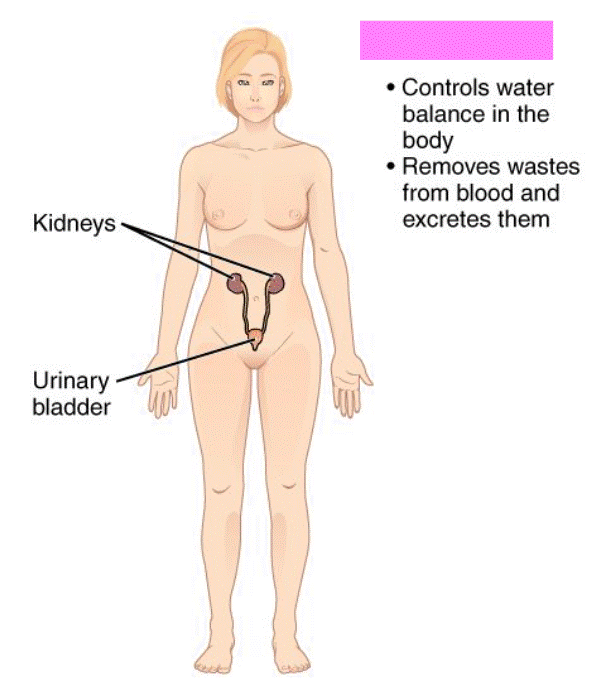
Urinary System
Function is to remove wastes, maintain water and electrolyte balance, and store and transport urine. Includes the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra
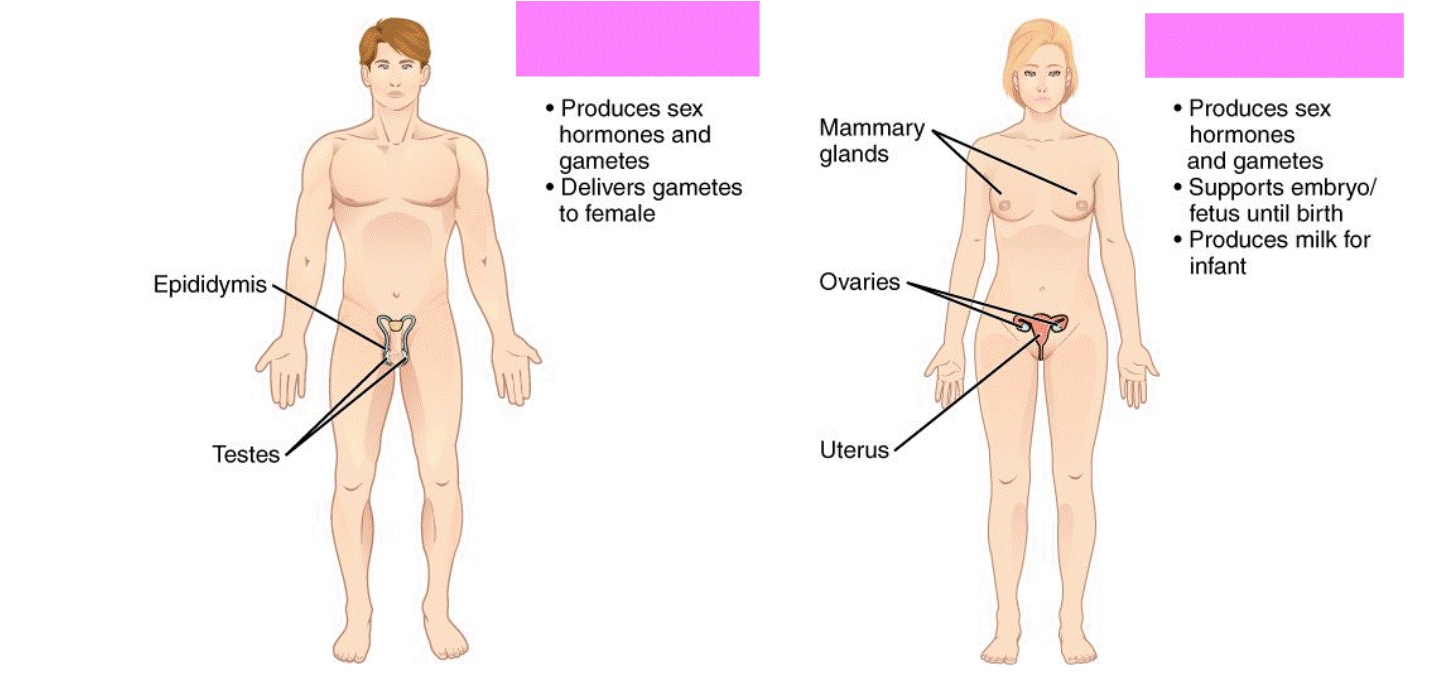
Reproductive System
Passes genetic information down to future generations as well as produce hormones that help the body to mature.