g1,g7
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
how do g1 ,metals react with oxygen
g1 metals react very rapidly with oxygen
explaint rend in g1
as you go down g1 ,reactivity increases and mp and bp decrease
explain trend in g7
as you go down in g7,reactivity decreases and mp and bp increasee
why _ is more reactive than iodinee for e.g
(chlorine’s) outer electrons closer to the nucleus,(so) the chlorine nucleus has greater attraction for outer electrons ,(so) chlorine gains an electron more easily
why _ is LESS reactive than iodinee for e.g
less reactive,
chlorines nucleus has smaller attraction for outer electrons
so chlorine gains an electron less easily
less sheilding of outer electron
(b) Explain the trend in boiling points of the halogens shown in Table 1.
(boiling point) increases (down the table / group) 1 (because)
(because) the size of the molecule increases 1 (so) the intermolecular forces increase in strength allow
(so) the forces between molecules increase (in strength) 1
(so) more energy is needed to overcome the intermolecular forces
) Explain why the reactivity of the halogens decreases going down the group.
) (going down the group) the outer electrons become further from the nucleus,
(so) the nucleus has less attraction for the outer electrons
(so) an electron is gained less easily
as we move ____ g1 metals react more ____
as we move down g1 metals react more rapidly
describe what happens when g1 for e.g lithium reacts with water with green indicator to purple
lithium reacts with water - effervesence meaning a gas produced ,universal indicator is purple so its alkaline solution
state equation for metals reacting with hydrogen and a e.g
metal + water + metla hydroxide + hydrogen
sodium + water → sodium hydroxide + hydrogen
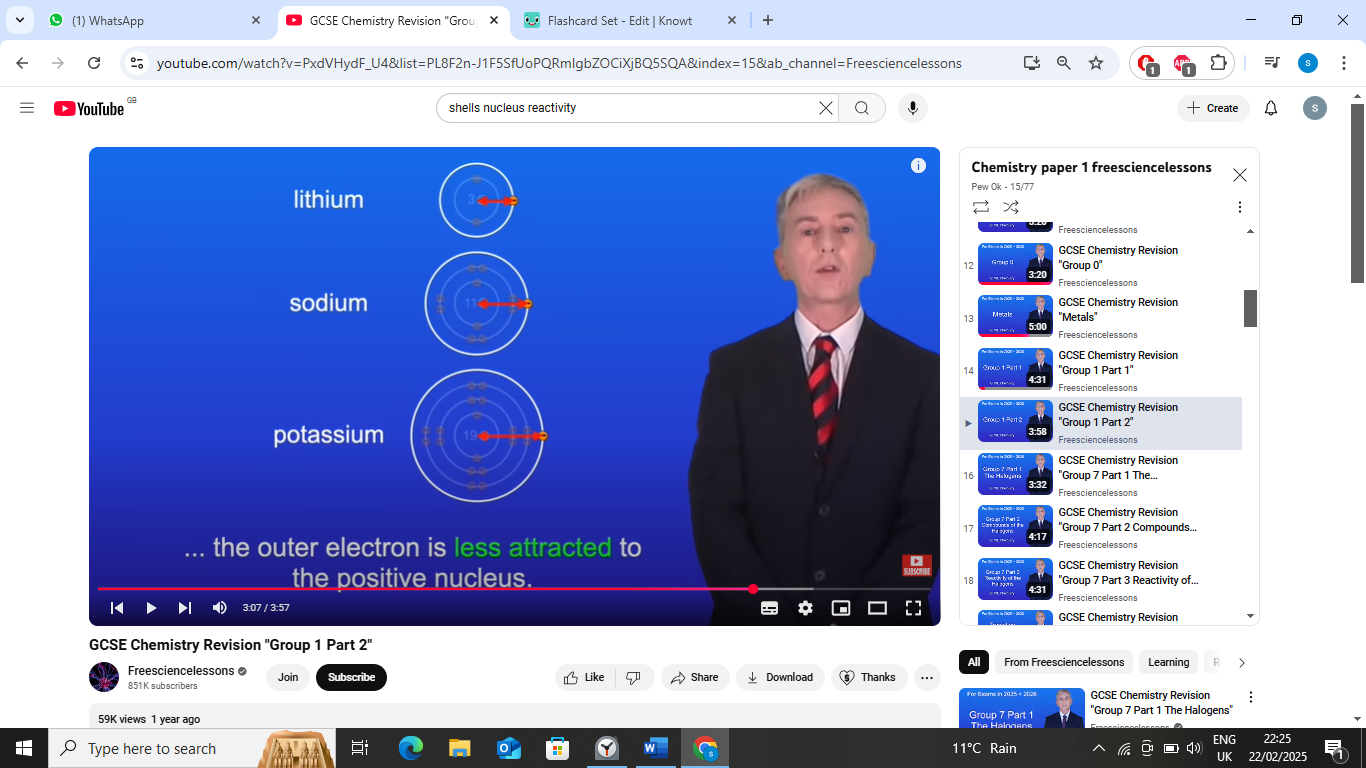
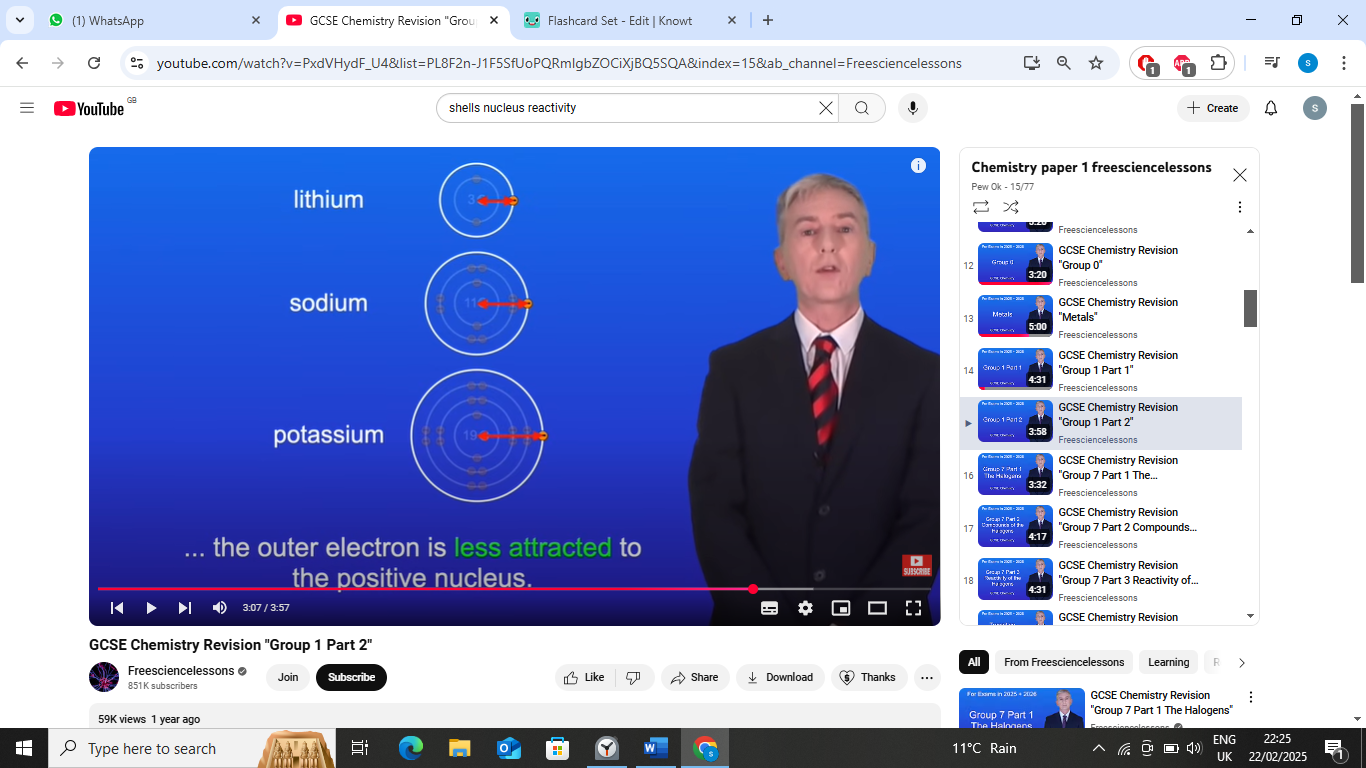
one reason
as we go down g1, the radius of the atoms increase so theres a greater distance between the positive nucleus and negative outer electron
the outer electron is less attracted to the positive nucleus
2nd reason
sheilding: the outer electron is repelled by the electrons in the internal energy levels,decreasing the attraction between the nucleus and outer electron
as we move ___ g1 elements have ___ electrons in the __ ____ ____
as we move down g1 elements have more electrons in the internal energy levels meaning sheilding inc as we move down group 1 making the outer electron easier to loose
as we move down g7 what happens to the mp and bp and molecules size
as you go down reactivity decreases,mp and bp increase as we move down g7,molecules get bigger moving down g7
when halogens react with metals they form ?
when halogens react with metals they form ionic compounds
when a halogen reacts with a metal the halogen atom gains what forming what ion
when a halogen reacts with a metal the halogen atom gains 1 electron forming 1- ion
why chlorine is less reactive than flourine
less reactive,
gains an electron less easily
(cuz of a greater distance between nucleus and outer electron so electrons less attraactedd to positive nucleus in cl atom comp to f atom
grater sheilding of outer electron
(more electrons in internal energy levels,electrons in internal energy levels repel the outer electrons than in fl atom)
a more ___ ______ displace a___ ____ from an ____ _____ of its salt
more reactive halogen displace a less reactive halogen from an aqeous solution of its salt
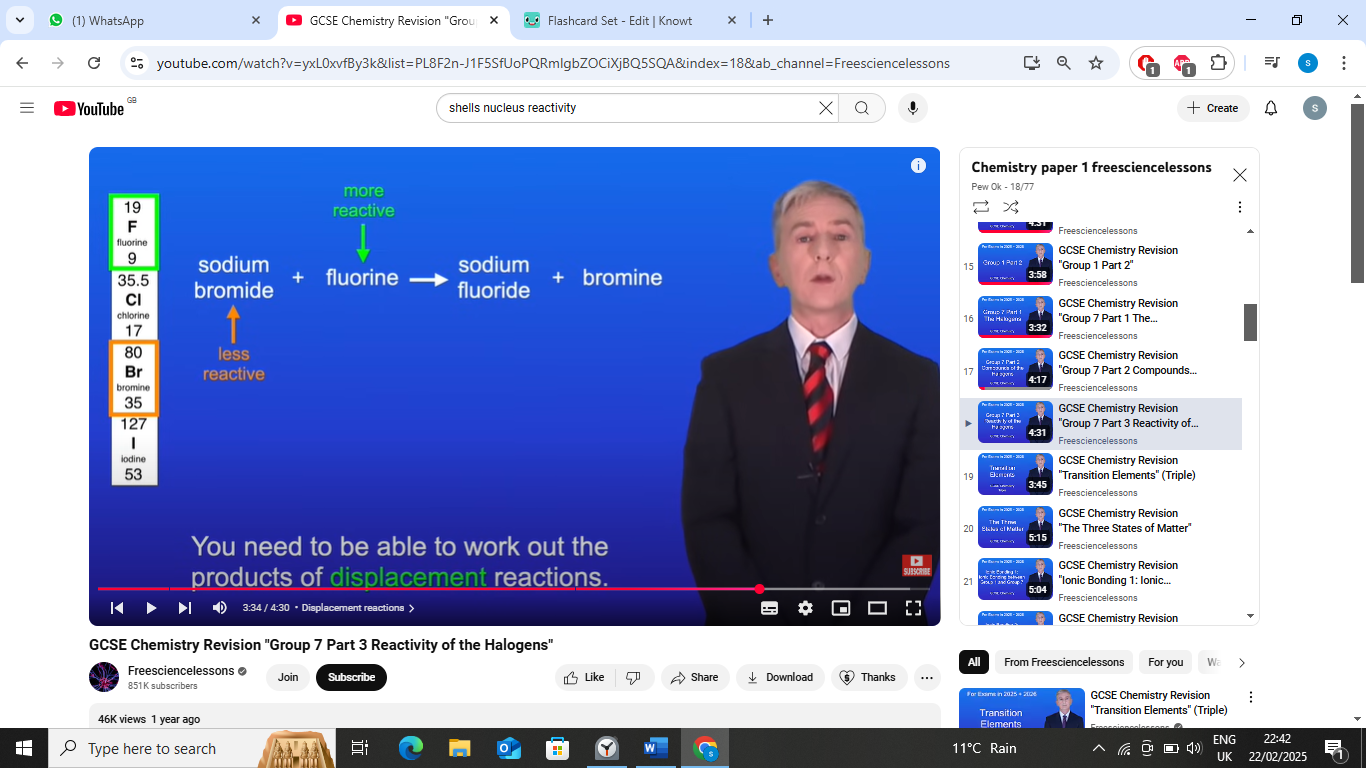
e.g of displacement reaction sodium bromide + flourine →
sodium bromide + flourine → sodium flouride + bromine
flourine is higher then bromine so its more reactive,displacing it
bromine less reactive
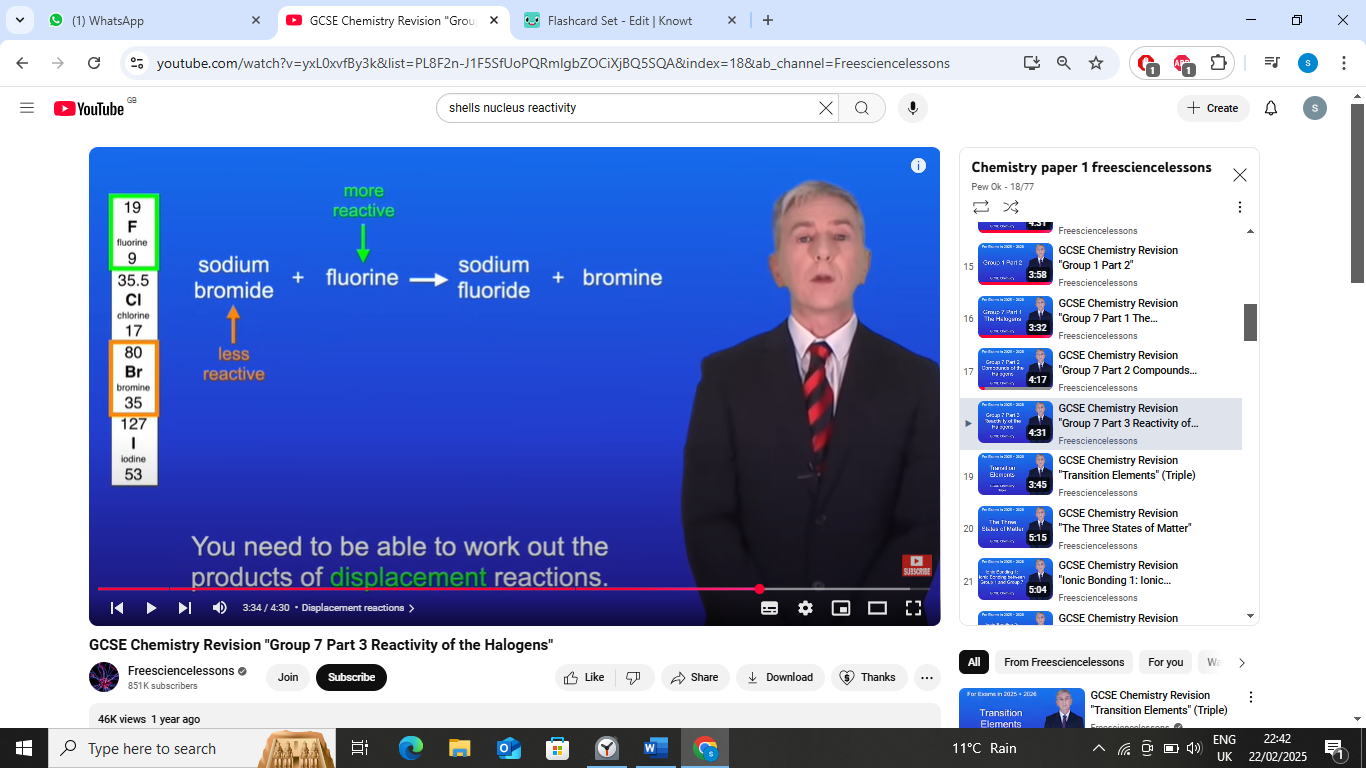
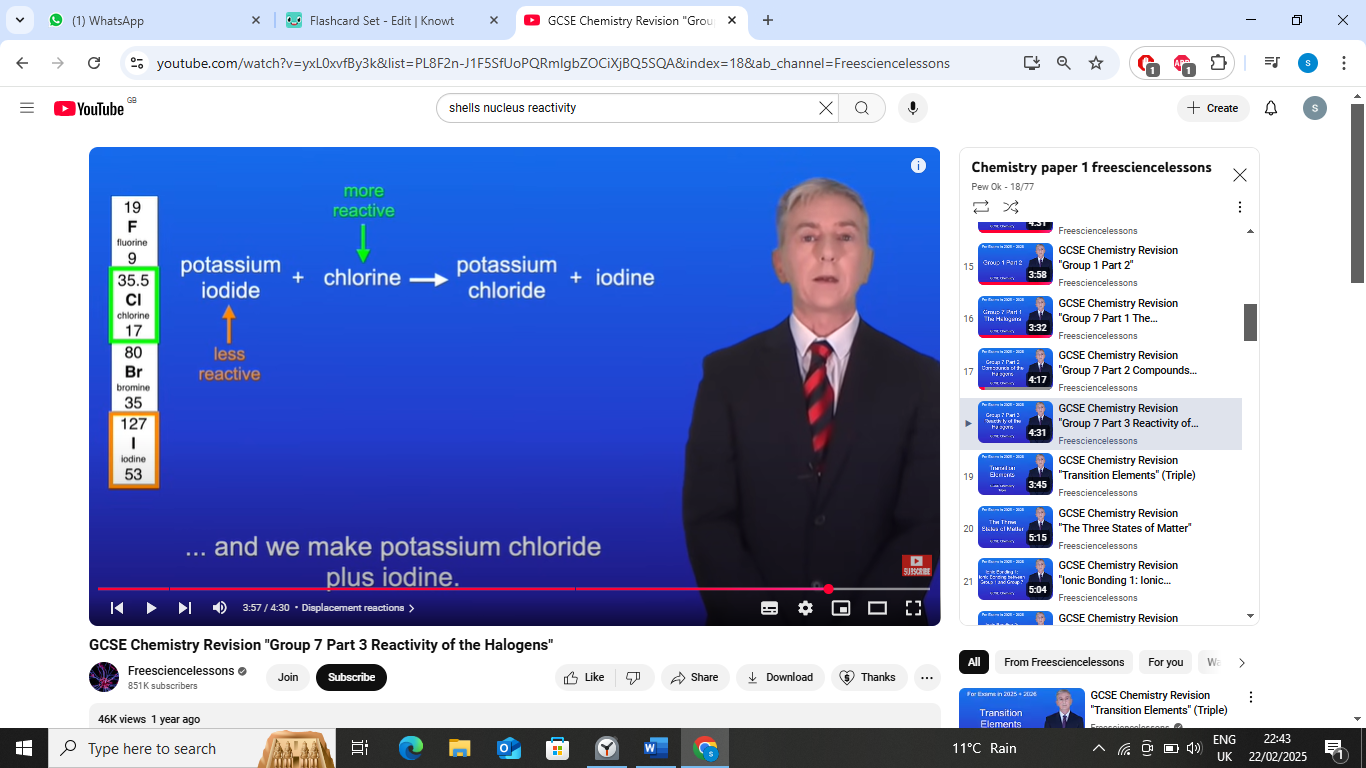
pottasium ioidide + chlorine ->
pottasium ioidide + chlorine → pottasium chloride +iodine
g1 properties
soft realtively
low metals,
low density,
react rapidly with oxygen,chlorine,water,
forms 1+ ions charge
trans metals prop
hard,strong emtals
.high mp
,high density
,much less reactivity than g1 metals with oxygen ect,
forms colorless compounds
,froms ion with diff charges
catylysts
rule for reactivity
the more further the electron shells are from the nucleus,the least reactive it is ie chlorine is less reactive than flourine as more shells making it hard to gain electron and more down in the group