Unit 4 Imaging Artifacts - DMU 3315
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
artifacts, anatomical, physiologic
Ultrasound ___ represent a wide range of misleading ultrasound appearances that do not accurately represent ___ structures of ___ exams.
real, sing, placed, brightness, shape, size
Artifacts can affect structures by making them…
Not ___
Mis___
Mis___
Incorrect ___
Incorrect ___
Incorrect ___
assumptions, straight line, same straight, constant, 1540 m/s, Attenuation rate, echo amplitude, height, axial, y, width, lateral, x, thickness, slice thickness, elevational, z, central axis, one echo, last, preceding, image acquisition, operator, system, system controls, transducer, electronic system
To create an image, the ultrasound system must have a set of rules/___ to process echoes
Ultrasound travels in a ___ ___ during transmission and echoes follow the ___ ___ path back
Speed of sound in the body is a ___ (___)
___ ___ is uniform and predictable
Two comparable tissue reflectors in a similar location will generate a comparable ___ ___
The beam dimensions are small in ___ (___, ___-axis), ___ (___, ___-axis), and ___ (___ ___, ___, ___-axis)
Echoes originate only from the ___ ___ of the beam
Each reflector only generates ___ ___
The arriving echo was generated by the ___ emitted ultrasound pulse, not by any ___ pulses
The rate of ___ ___ exceeds the rate of physiologic events and the rate of transducer movement
The ___ is using the ___ appropriately
All ___ ___ have been adjusted correctly
The ___ elements and the ___ ___ components are functioning normally and without interference from surrounding equipment
System, Operator, Acoustics, Patient
Anytime the assumptions on which the ultrasound equipment has been designed are violated, artifacts will occur (SOAP):
___
___
___
___
Acoustics
Is essentially the way sound works within the body
system, real, real echoes, absence, real structures, operator, operator’s
While ultrasound artifacts do not accurately reflect reality, to the ultrasound ___, artifacts appear perfectly “___”
Artifacts represent ___ ___ or the real ___ of echoes; however, they DO NOT represent ___ ___ the way the operator would expect these to appear
Alternatively, the ___ may misinterpret artifacts as real structures
It is the ___ responsibility to determine whether the image accurately represents reality or not
Equipment related, Propagation group, Attenuation group
What are the three classifications of artifacts?
Equipment related
This classification of artifacts occurs anytime there is a defective part of the ultrasound instrument
Propagation group artifacts
Comet tail
Grating lobe
Mirror image
Range ambiguity
Refraction
Reverberation
Ring-down
Slice (section) thickness
Speckle
Speed error
Attenuation group artifacts
Enhancement
Focal enhancement
Refraction (edge) shadowing
Shadowing
Propagation
What classification of artifacts is comet tail?
Propagation
What classification of artifacts is grating lobe?
Propagation
What classification of artifacts is mirror image?
Propagation
What classification of artifacts is range ambiguity?
Propagation
What classification of artifacts is refraction?
Propagation
What classification of artifacts is reverberation?
Propagation
What classification of artifacts is ring-down?
Propagation
What classification of artifacts is slice (section) thickness?
Propagation
What classification of artifacts is speckle?
Propagation
What classification of artifacts is speed error?
Attenuation
What classification of artifacts is enhancement?
Attenuation
What classification of artifacts is focal enhancement?
Attenuation
What classification of artifacts is refraction (edge) shadowing?
Attenuation
What classification of artifacts is shadowing?
electrical interference, electrical, interference
Strong ___ ___ from other nearby ___ devices can create ___ patterns
In the image, we see horizontal lines traveling through the image, especially at the bottom (far field)
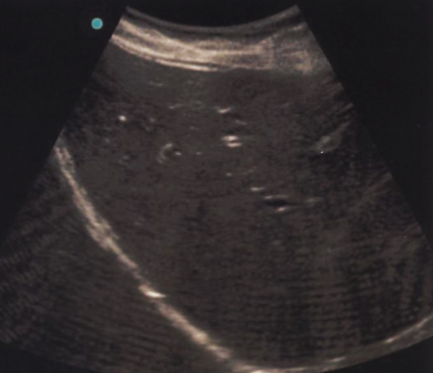
Faulty Elements
Piezoelectric crystals may become damaged or breaks in wiring can occur
Displayed as anechoic vertical lines
To confirm:
Use more gel
Change approach
Use on various patients
Confirmed if still appears in exact location
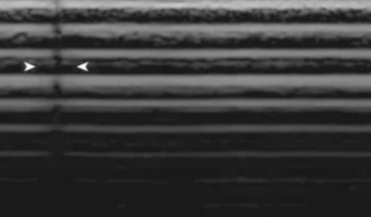
crystals, wiring, anechoic, gel, approach, patients, location
Faulty Elements
Piezoelectric ___ may become damaged or breaks in ___ can occur
Displayed as ___ vertical lines
To confirm:
Use more ___
Change ___
Use on various ___
Confirmed if still appears in exact ___
Focal Banding
Horizontal brightness at the level of the focus
Occurs because of the increased intensity in the focal zone
Results in increased amplitude of echoes
There’s increased intensity of the beam at the focal zone because the intensity equals power divided by area and since the area goes down at the focus, the intensity is increased.
Adjust TGCs to fix
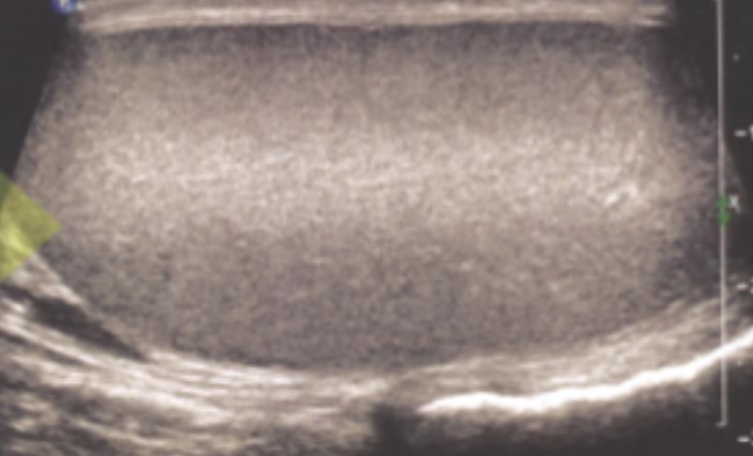
Horizontal brightness, focus, intensity, amplitude, focal zone, power, area, increased, TGCs
Focal Banding
___ ___ at the level of the ___
Occurs because of the increased ___ in the focal zone
Results in increased ___ of echoes
There’s increased intensity of the beam at the ___ ___ because the intensity equals ___ divided by ___ and since the area goes down at the focus, the intensity is ___.
Adjust ___ to fix
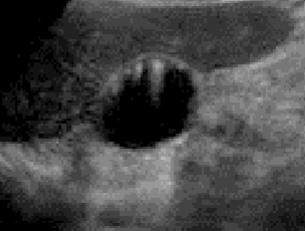
Side Lobes
Caused by echoes from a strong reflector outside of the central beam
Most of the intensity is in the main sound beam, but sometimes additional beams travel out in directions not included in the main beam
Occur with single element transducers
Reduced with harmonics
Results in a structure being shown as being laterally displaced or going out laterally
In the image, the gallbladder is located behind the bowel and is not visible. The black oval next to the bowel is this artifact mimicking the gallbladder.
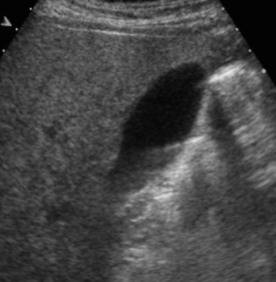
strong, central beam, intensity, single element, Side, Single, Strong, harmonics, laterally
Side Lobes
Caused by echoes from a ___ reflector outside of the ___ ___
Most of the ___ is in the main sound beam, but sometimes additional beams (side lobes) travel out in directions not included in the main beam
Occur with ___ ___ transducers
(___ lobes = ___ element = ___ reflector)
Reduced with ___
Results in a structure being shown as being ___ displaced
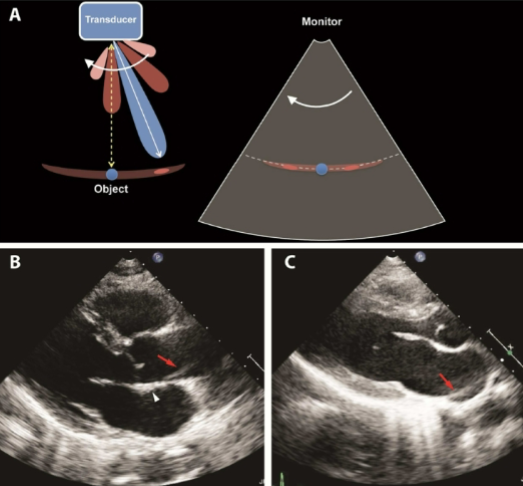
Grating Lobes
Echoes from weaker beams outside the main beam from an array transducer
Appears as duplicated structures laterally
Seen a lot with echo
Reduced with harmonics
weaker, array, laterally, echo, harmonics
Grating Lobes
Echoes from ___ beams outside the main beam from an ___ transducer
Appears as duplicated structures ___
Seen a lot with ___
Reduced with ___
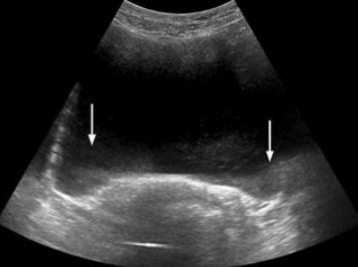
Slice (Section) Thickness
AKA Partial Volume Filling
Beam is too thick in the elevation plane
Gives the appearance of debris in an echo-free structure
Partial Volume Filling, thick, elevational, echo-free
Slice (Section) Thickness Artifact
AKA ___ ___ ___
Beam is too ___ in the ___ plane
Gives the appearance of debris in an ___ structure
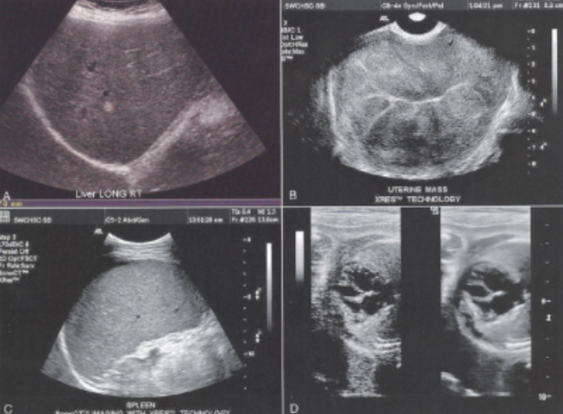
Speckle
The granular appearance of images that is caused by the interference of echoes from the distribution of scatterers in tissue.
The generation of this artifact can be compared to throwing a handful of marbles into a pond. Each marble generates a circular propagating wave. These waves combine together through the effects of constructive and destructive interferences.
The location of the highest wave does not necessarily represent the location where the marble impacted the water, but rather where the marble waves come together to form a larger wave.
Reduced by using:
Spatial compounding
Persistence
granular, interference, scatterers, circular propagating, constructive, destructive, larger, Spatial compounding, Persistence
Speckle
The ___ appearance of images that is caused by the ___ of echoes from the distribution of ___ in tissue.
The generation of speckle can be compared to throwing a handful of marbles into a pond. Each marble generates a ___ ___ wave. These waves combine together through the effects of ___ and ___ interferences.
The location of the highest wave does not necessarily represent the location where the marble impacted the water, but rather where the marble waves come together to form a ___ wave.
Reduced by using:
___ ___
___
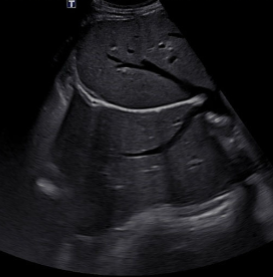
Mirror Image
Occurs when the beam encounters a large specular reflector
Appears as duplication of objects opposite of a highly reflective structure
May be reduced by changing approach
Common behind the diaphragm
specular reflector, mirror, reflective structure, approach, diaphragm
Mirror Image
Occurs when the beam encounters a large ___ ___ that acts as a ___
Appears as duplication of objects opposite of a highly ___ ___
May be reduced by changing ___
Common behind the ___
Reverberation
Occurs between two strong reflectors
Sound waves bounce back and forth between structures
Appears as equally spaced extra reflectors on the image
Commonly occurs in the anterior portion of the bladder
Reduced with harmonics (but can’t be completely eliminated)
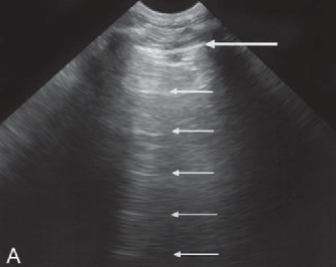
strong reflectors, Sound waves, equally, bladder, harmonics, can’t
Reverberation
Occurs between two ___ ___
___ ___ bounce back and forth between structures
Appears as ___ spaced extra reflectors on the image
Commonly occurs in the anterior portion of the ___
Reduced with ___ (but ___ be completely eliminated)
False
True or False: Reverberation can be completely eliminated
Comet Tail
Type of reverberation artifact
Small focal reflectors cause a narrow reverberation artifact
Often seen with and useful in the diagnosis of:
Adenomyomatosis/cholesterolosis of the gallbladder (GB)
Colloid thyroid nodules
reverberation, reflectors, reverberation, Adenomyomatosis, cholesterolosis, gallbladder, Colloid thyroid nodules
Comet Tail
Type of ___ artifact
Small focal ___ cause a narrow ___ artifact
Often seen with and useful in the diagnosis of:
___/___ of the ___ (GB)
___ ___ ___
Ring-down
Type of reverberation artifact
Associated with gas – commonly seen in bowel
Appears as high amplitude streaks (bright white)
Can be helpful to identify gas in conditions such as:
Pneumobilia – air in the bile ducts
Pneumo = lung, air
Emphysematous cholecystitis – gas in the gallbladder wall
Abscesses containing air
An abscess is a collection of pus that forms in a localized area of the body
reverberation, gas, bowel, Ring, Gas, high, bright, Pneumobilia, Pneumo, Emphysematous cholecystitis, Abscesses, abscess
Ring-Down
Type of ___ artifact
Associated with ___ – commonly seen in ___
___ = ___
Appears as ___ amplitude streaks (___ white)
Can be helpful to identify gas in conditions such as:
___ – air in the bile ducts
___ = lung, air
___ ___ – gas in the gallbladder wall
___ containing air
An ___ is a collection of pus that forms in a localized area of the body
Comet tail, ring down
___ ___ artifacts are short, tapering trails from highly reflective surfaces like metal or stones, which quickly fade with depth, while ___ ___ artifacts are long, continuous bands of echoes from gas bubbles causing fluid resonance, persisting further into the image.
Refraction
AKA Duplication or Ghost Artifact
Change in beam direction when the beam encounters a boundary between two materials with different propagation speeds
Causes object to be projected laterally
Appears as:
Widening (of object)
Duplication (of object)
Can be reduced by sliding the transducer laterally
Happens quite frequently at the midline of the body, especially in the abdomen, because of the rectus abdominis muscles
This often affects the aorta in transverse, so you would just slide the transducer laterally
Duplication, Ghost Artifact, direction, propagation speeds, laterally, Widening, Duplication, sliding, laterally, midline, abdomen, rectus abdominis, aorta, laterally
Refraction
AKA ___ or ___ ___
Change in beam ___ when the beam encounters a boundary between two materials with different ___ ___
Causes object to be projected ___
Appears as:
___ (of object)
___ (of object)
Can be reduced by ___ the transducer ___
Refraction happens quite frequently at the ___ of the body, especially in the ___, because of the ___ ___ muscles
This often affects the ___ in transverse, so you would just slide the transducer ___
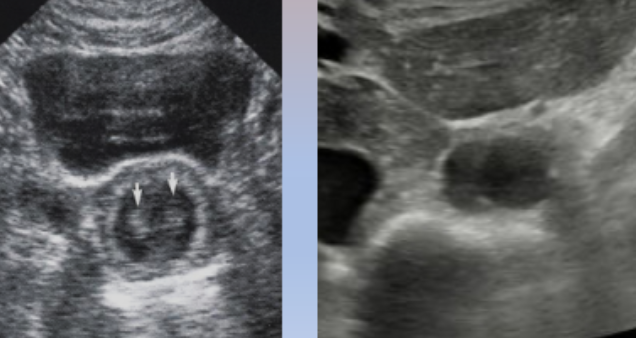
Edge Shadowing
Type of refraction artifact
Caused by a combination of reflection and refraction at the margin of a well-defined object
The beam is being bent because of refraction and because of attenuation in the area next to the bent beam, we end up with the shadow as shown in the diagram
Appears as a shadow originating from the edge of a structure
Reduced with spatial compounding
…because spatial compounding takes different averages/different frames of the beam shot at different angles. So, we’re actually able to angle the beam behind the structure and area that causes the refraction to help reduce those shadows.
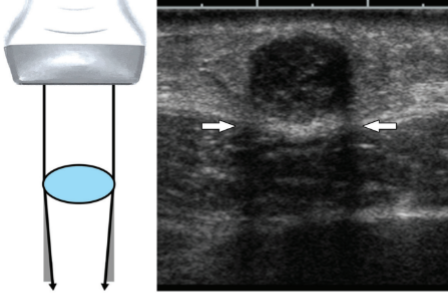
refraction, reflection, refraction, well, bent, refraction, attenuation, shadow, shadow, edge, spatial compounding, spatial compounding
Edge Shadowing
Type of ___ artifact
Caused by a combination of ___ and ___ at the margin of a ___-defined object
The beam is being ___ because of ___ and because of ___ in the area next to the bent beam, we end up with the ___ as shown in the diagram
Appears as a ___ originating from the ___ of a structure
Reduced with ___ ___
…because ___ ___ takes different averages/different frames of the beam shot at different angles. So, we’re actually able to angle the beam behind the structure and area that causes the refraction to help reduce those shadows.
Multipath
Beam reflects off the structure at an angle
The reflection then bounces off another structure before heading back to the transducer
Displays object deeper than it really is because the beam traveled longer
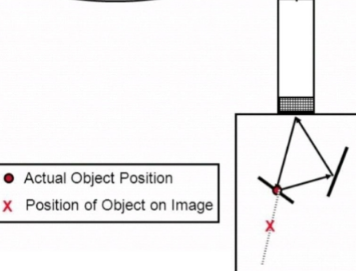
angle, another, deeper, longer
Multipath
Beam reflects off the structure at an ___
The reflection then bounces off ___ structure before heading back to the transducer
Displays object ___ than it really is because the beam traveled ___
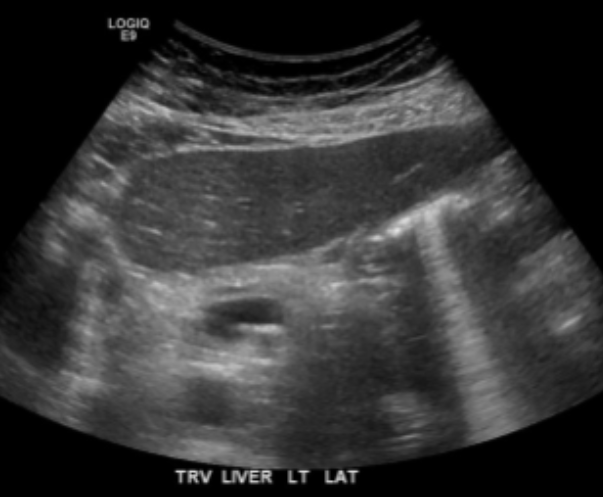
Propagation Speed Error
Caused by a structure of lower or higher velocity than 1540 m/s (what the machine assumes)
Appears as:
Vertical displacement behind area of non-1540 m/s
Faster = shallower
Slower = deeper
Distortion of shape of the object
Cannot be eliminated
The image shows a hemangioma that causes a slower velocity and therefore makes a part of the diaphragm appear deeper than it really is
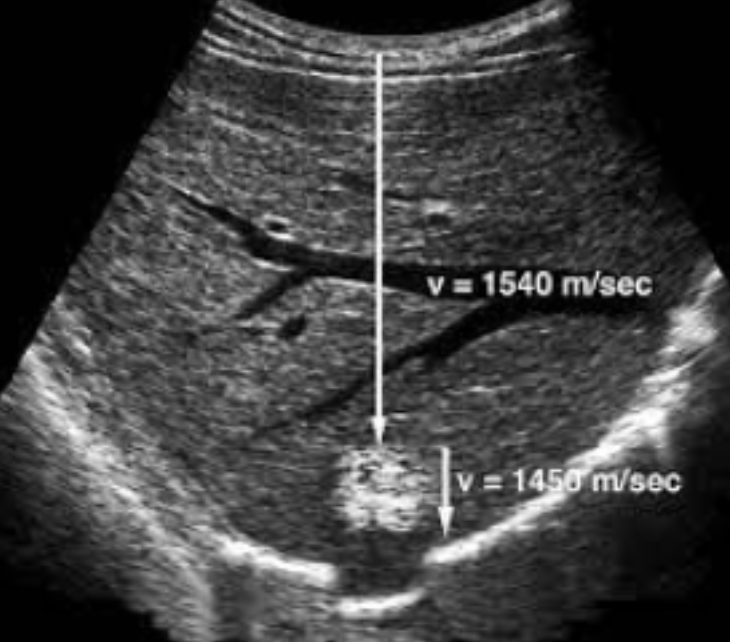
1540 m/s, Vertical, 1540, shallower, deeper, shape, Cannot
Propagation Speed Error
Caused by a structure of lower or higher propagation speed than ___ (what the machine assumes)
Appears as:
___ displacement behind area of non-___ m/s
Faster = ___
Slower = ___
Distortion of ___ of the object
___ be eliminated
True
True or False: Propagation speed error cannot be eliminated
Range Ambiguity
Occurs when echoes from the preceding pulse arrive at a time when another pulse has been emitted
Causes:
Depth is relatively shallow and a low attenuating structure lies beyond the field of view (FOV)
Multiple focal zones - because image is stitched together
Reduce:
For structure beyond FOV - decrease output power or gain
Switch to one focal zone
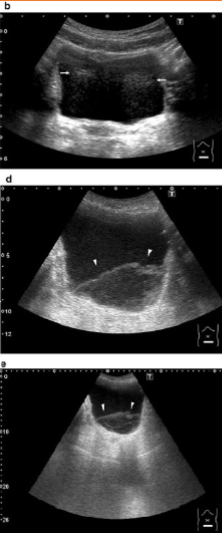
preceding, emitted, shallow, low, field of view, FOV, focal zones, output power, gain, focal zone
Range Ambiguity
Occurs when echoes from the ___ pulse arrive at a time when another pulse has been ___
Causes:
Depth is relatively ___ and a ___ attenuating structure lies beyond the ___ ___ ___ (___)
Multiple ___ ___ - because image is stitched together
Reduce:
For structure beyond FOV - decrease ___ ___ or ___
Switch to one ___ ___
Shadowing
Caused by a highly attenuating structure
Reflection
Scattering
Absorption
Refraction
Combination of any of these
Complete absence of echo information behind attenuating structure
Can be reduced by spatial compounding
Different angles can angle behind these attenuating structures
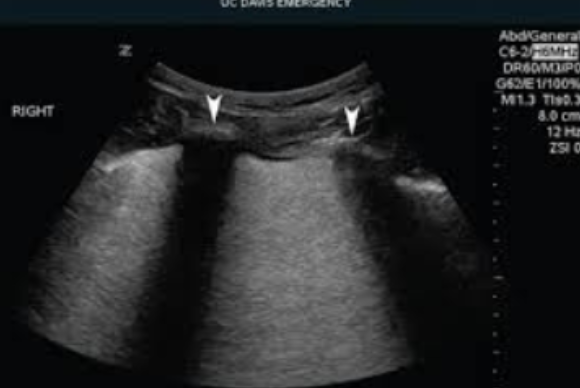
highly, Reflection, Scattering, Absorption, Refraction, absence, spatial compounding, angles
Shadowing
Caused by a ___ attenuating structure
RSAR:
___
___
___
___
Combination of any of these
Complete ___ of echo information behind attenuating structure
Can be reduced by ___ ___
Different ___ can angle behind these attenuating structures
Dirty Shadowing
Also behind a strongly attenuating structure, but the structure produces some echoes but is highly attenuated in the process
Appears as a hypoechoic shadow behind a structure
Commonly seen with bowel
Can be reduced by spatial compounding
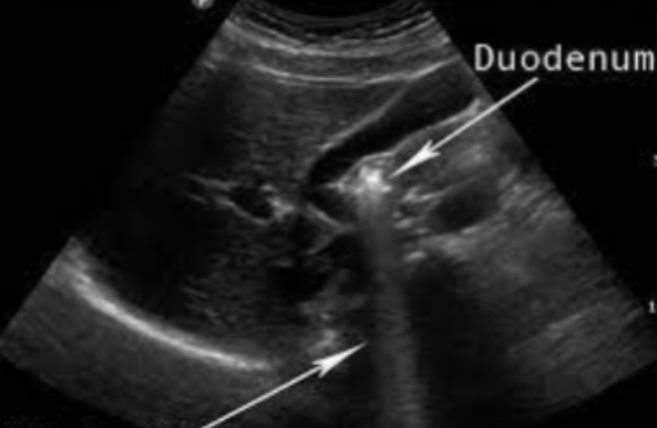
strongly, echoes, hypoechoic, bowel, spatial compounding
Dirty Shadowing
Also behind a ___ attenuating structure, but the structure produces some ___ but is highly attenuated in the process
Appears as a ___ shadow behind a structure
Commonly seen with ___
Can be reduced by ___ ___
Enhancement
Caused by a structure of low attenuation adjacent to a structure of normal attenuation
Appears as a band of increased echogenicity behind an area of low attenuation
Reduced by:
Gain & TGCs
Spatial compounding
Can be diagnostically useful to distinguish fluid-filled from solid objects
Fluid filled objects have this artifact
Solid objects DO NOT have this artifact
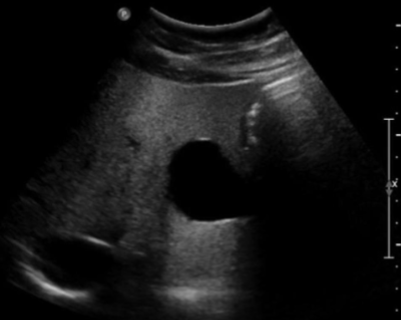
Posterior Acoustic Enhancement, low, normal, increased, attenuation, Gain, TGCs, Spatial compounding, Fluid-filled, Solid
Enhancement
AKA ___ ___ ___
Caused by a structure of ___ attenuation adjacent to a structure of ___ attenuation
Appears as a band of ___ echogenicity behind an area of low ___
Reduced by:
___ & ___
___ ___
Can be diagnostically useful to distinguish fluid-filled from solid objects
___ objects have enhancement
___ objects DO NOT have enhancement