3. Profit max and competitive firms
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Which 3 settings do we cover profit maximisation?
using most general expression for profits
SR with 2 factors - one is fixed - can only change x1 and not x2
LR - both factors variable
What do we assume is a firms motivation?
to maximise its profit
What is profit and what is the equation
Profit is simply the difference btw revenue and costs
= TR- TC
= total rev - total costs
How do we write a firms profit if it has m inputs and produces n goods?
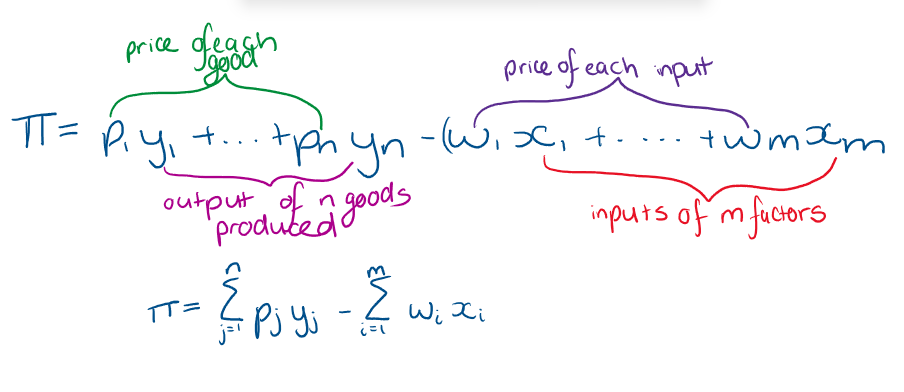
What is the equation for a firms profit if it has 2 factors and one output
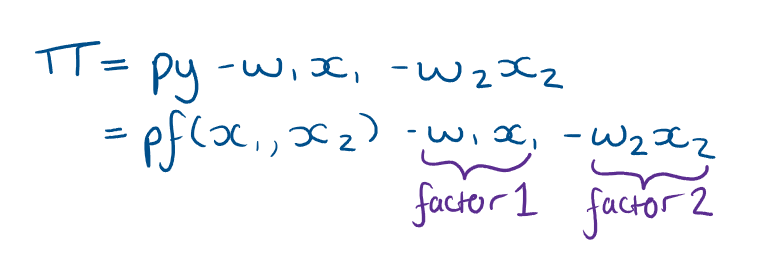
How do we maximise a firms profit?
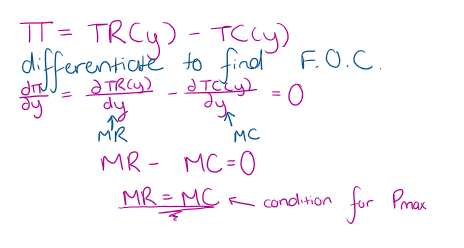
How do we Profit maximisation in the SR?
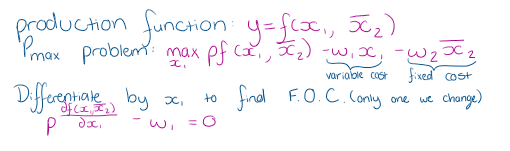
What does pMP1 = w1 mean?
price of the factor equals the value of its marginal product
how much extra revenue u get for it
How do we show the Short run profit maximisation graphically
Using production function and isoprofit lines
single isoprofit line shows all combinations of input x1 and output y that give the same level of output
to find the equation for isoprofit line, we rearrange the SR profit expression to find, for a given level of profit, a relationship between y and x1
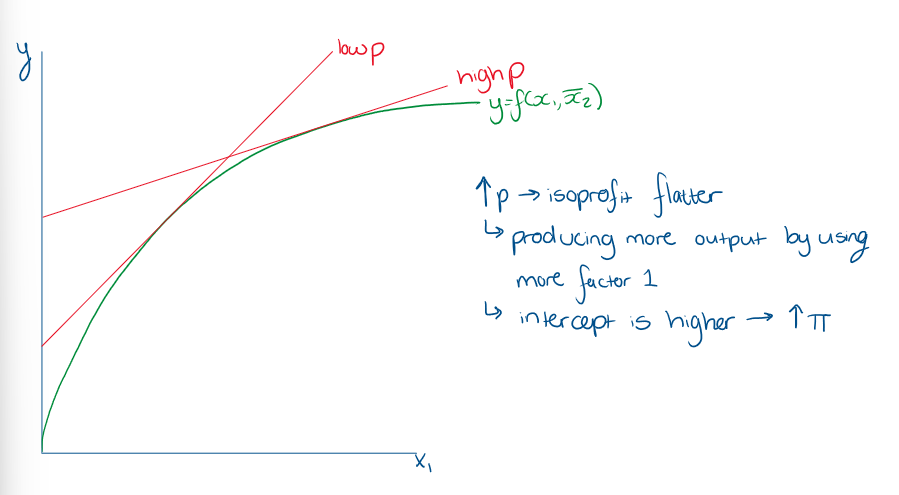
What is the equation for an SR isoprofit line? what is the intercept and slope
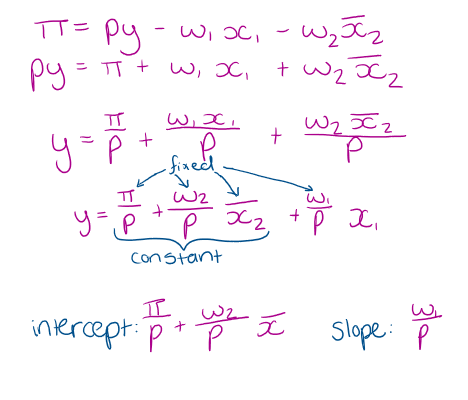
What does SR isoprofit graph look like?
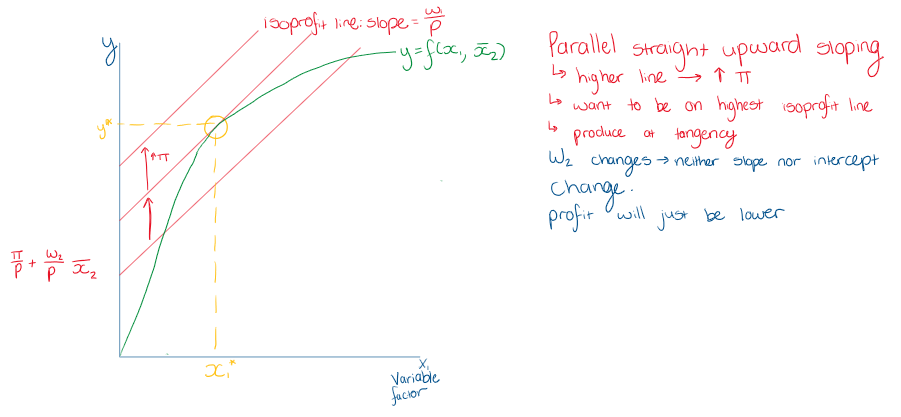
What is the point of tangency of the SR isoprofit line and the SR production function?
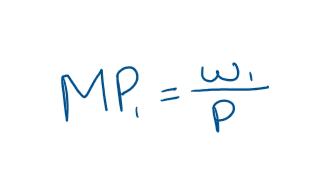
What happens in SR profit maximisation if the price of the fixed factor changes?
the firm cannot change the quantity it uses
slope of the isoprofit line doesn’t change, so the equilibrium point stays the same
However, the level of profit earned at this point will change:
a fall in w2 will leed to higher profit
rise in w2 will lead to lower profit
What effect does ncreasing or decreasing w1 on the isoprofit graph?
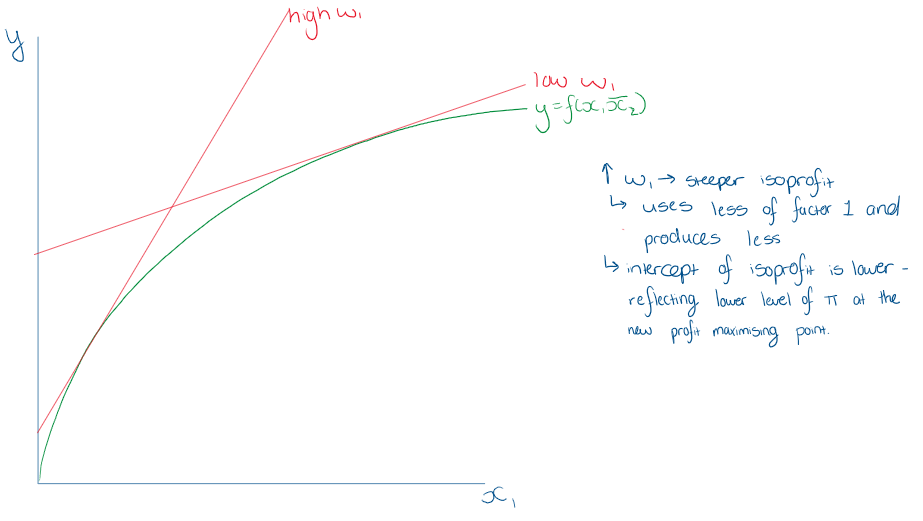
What effect does increasing or decreasing p have on the isprofit graph?
What is a firms LR profit maximisation problem
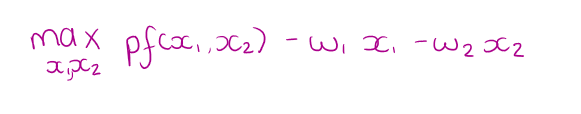
How to solve a Lr profit maximisation
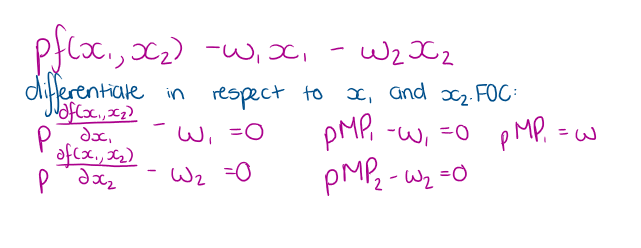
What does pMP1 =w1 and pMP2 = w2 tell us
firm should keep hiring more of each factor until the amount added to revenu equals the amount added to costs
What happens if we have Cobb-Douglas function, how do we find the profit maximisation? What are our optimal choices

What does constant returns mean in Cobb-douglas?
a+b = 1
doubling input doubles output
if a firm doubles the amount of both factors it uses it doesn’t just double output but also profit
What are the 3 different stages of constant returns to scales?
any positive level of output is profitable → increasing output will always increase profits; there is no maximum
any one positive level of output leads to a loss, increase output → increase loss → the firm will chose in LR not to produce
any one positive level of output means the firm breaks even→ be true at every positive level of output; the firm is indifferent between all output levels
What is the only feasible outcome with CRS
0 profits. why might this not be reality?
Have assumptions that might not hold:
CRS may not apply for all output levels
large firms may have price-setting power
high output may lead to lower price
factor demand may affect factor prices
Is it reasonable to assume CRS for all output levels?
may think producing v small or v large quantities will be inefficient
there is large range of output over which we have CRS, we are still likley to find the only possible outcome is 0 profits
If we have CRS over the whole range of output, a firm may become so big that it has price-setting power
assumption of fixed p might not hold
Firms output may become so high that it cant sell it all at the assumed price p
may need to move down the demand curve by dropping price → fixed p may not hold
Assumption of fixed factor prices must mean the firms demand for these inputs doesn’t affect their price
if the firm produces very high levels of output, this may not hold. the firm may need to offer higher payment to attract the required amount of at least one factor
What is the key feature of a competitive market? When does this arise?
each firm is price taker
arises when:
there are many firms in the market, with each individual firm only selling a very small part of total market sales
and firms all sell identical products
Why does price takers happen?
Assumes buyers and sellers have perfect information → no firm can sell anything above the market price
consumers will see they can buy the product at a lower price from someone else, and because products are all identical they are not prepared to pay extra from any seller
How does an inidvidual firm choose output in a competitive market? and at what point?
What is the MC AC AVC graph for an individual firm in a competitive market? where is profit max
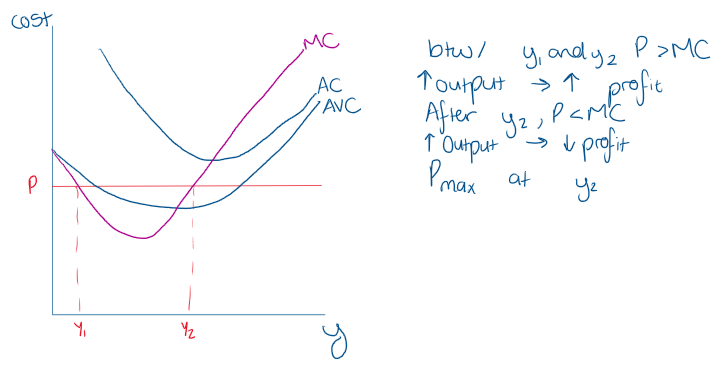
When will the firm choose not to produce?
should be based on comparing revenue and variable costs as they have to pay fixed costs anyway
firms supply curve is the part of its MC curve that lies abouve the bottom of the AVC curve
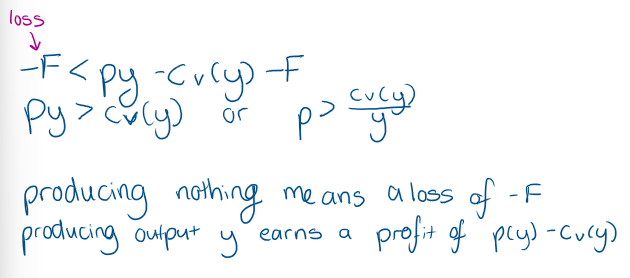
Show a graph where we derive the supply curve from
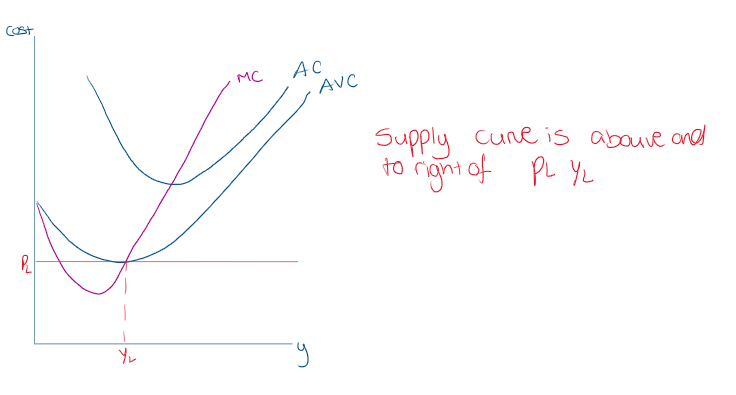
What is producer surplus?
the difference btw the amount a producer, or producers, receive for selling a quantity of a good, and the min they would be willling to accept
What section of the graph is producer surplus?
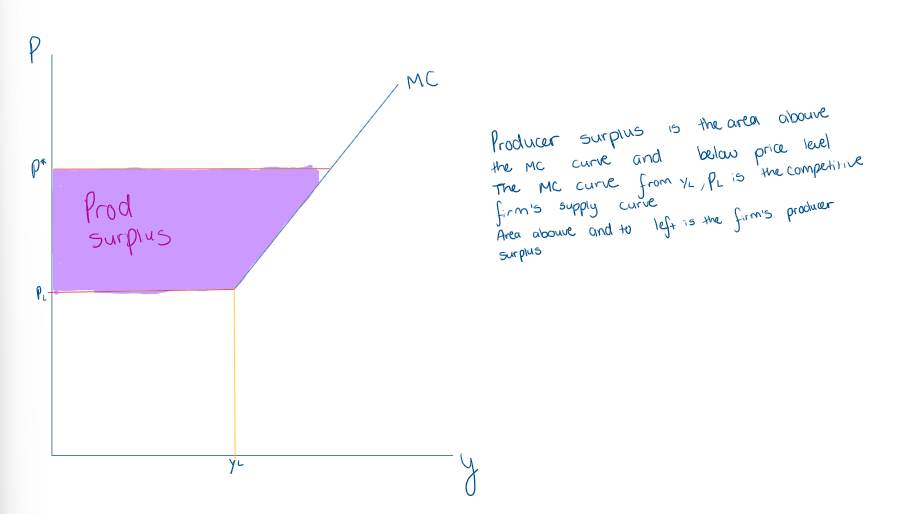
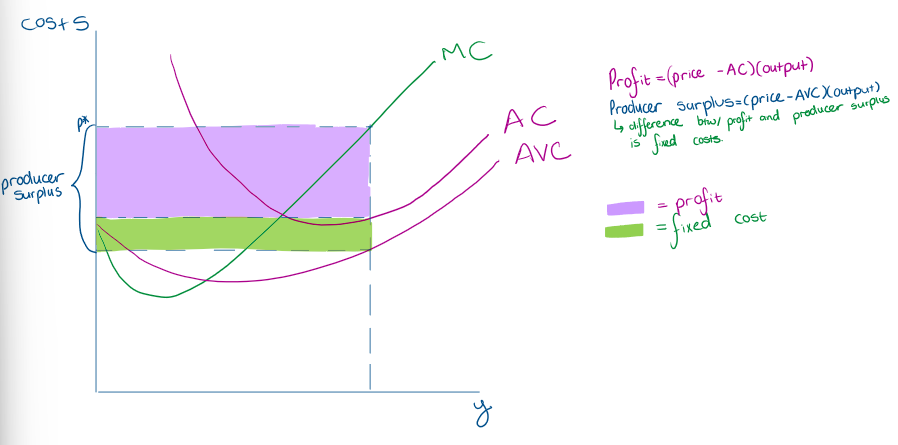
What is the difference between profit and producer surplus
profit = producer surplus - fixed costs
What does producer surplus look like broken into profit and fixed costs?
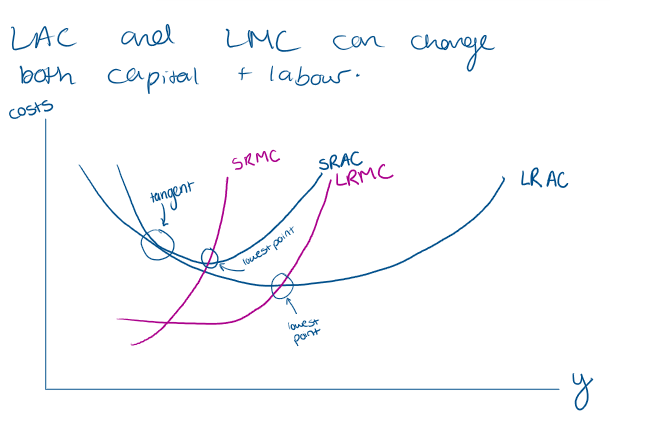
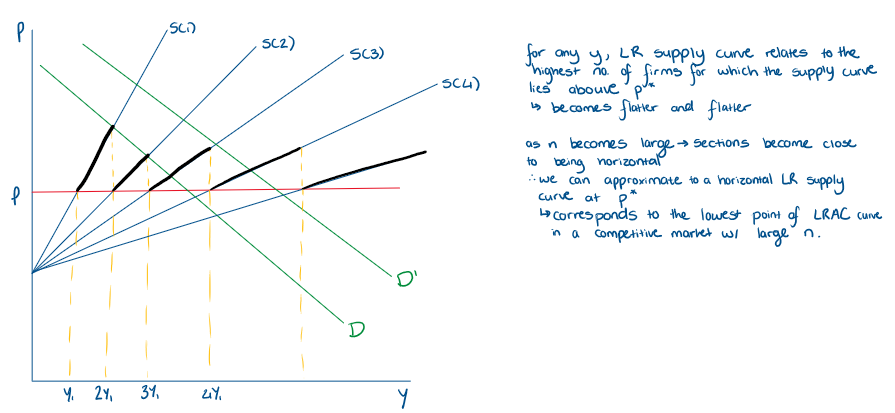
What part of the LRMAC, LRAC, SRAC, SRMC is the LR supply curve
the part of LMC that lies above the LAC
How do we get the LR supply curve look like? including LRMC
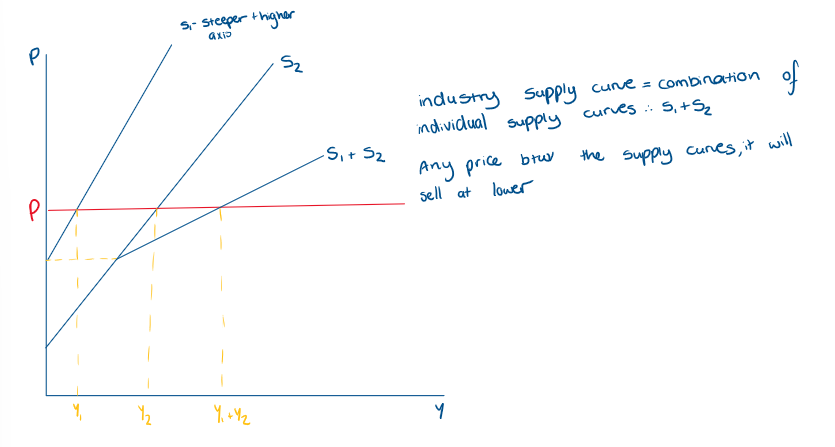
how do we find the industry supply?
sum horizontally across supply curves
What does industry supply curve look like if the individual curves are different?
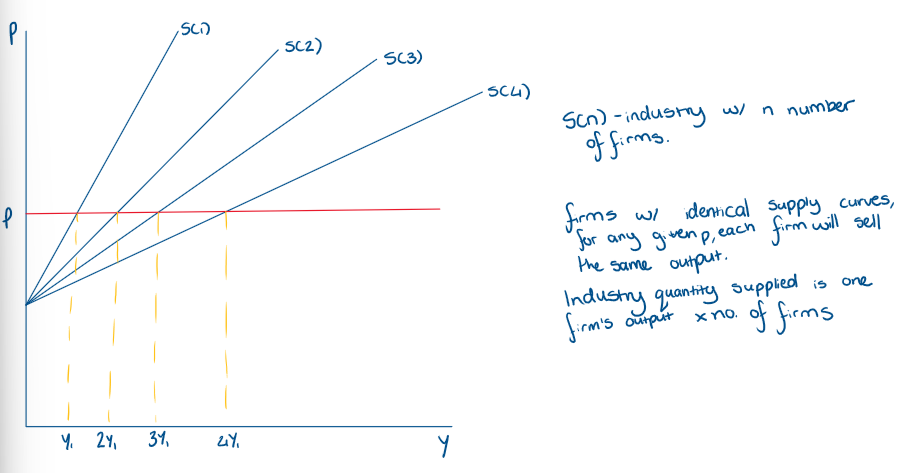
What does an industry supply curve look like for firms with identical supply curves?
What does free entry and exit mean?
firms respond to profit incentives
if existing firms in a market earn profits, new firms are free to enter the market
if firms are making losses, they are free to exit the market - in SR if the loss is bigger than the fixed cost or in the LR for a smaller loss
for free entry and exit what do we assume in equilibrium
firms earn 0 profits
not exactly the case - unless firms are infinite which isn’t accurate
What do we assume in free entry and exit?
all firms have the same cost curves → same supply curves
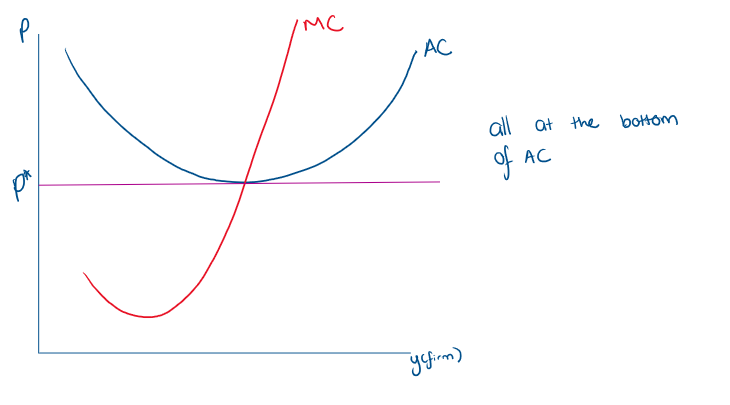
LR, the lowest price at which any firm will remain in the market is equal to their minimum average cost which we call p*
What happens if the market price is greater than minimum average cost?
p>p*
firms are earning profits and there may be an incentive for new firms to enter
if price is below p*, at least one firm will in LR leave the market
What happens if the market price is below the minimum average cost?
if p<p*,
at least one firm will in LR leave the market
What happens if the market price is equal to minimum average cost?
p=p*
they will be earning exactly
Using an industry supply curve, how many firms would operate in the market? If demand interests P btw 3 the supply curve for 3 and 4?
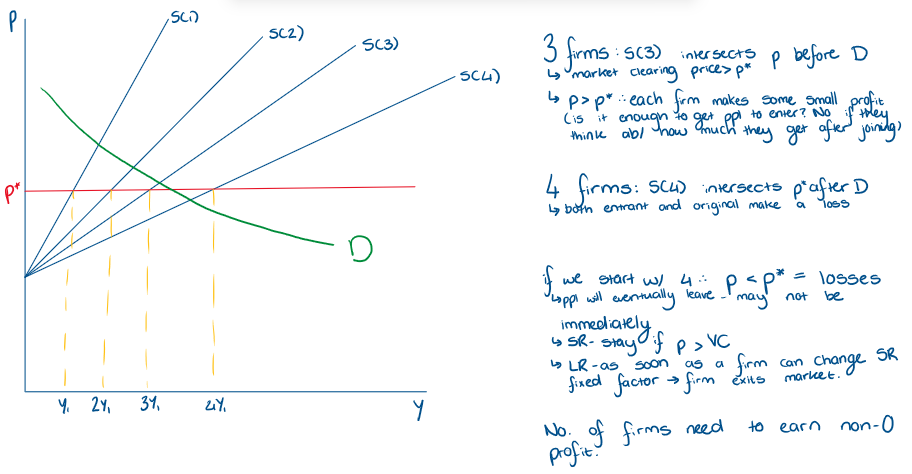
Using an industry supply curve, how many firms would operate in the market if demanded shifted upwards?
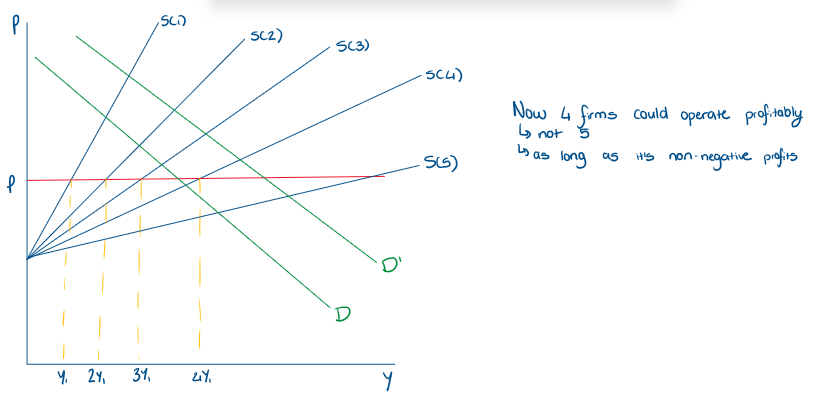
Using previous knowledge, how does it appear that we will get 0 profits as an approximation?
when n* is large → price will be close enough to p*
technically we are only guaranteed 0 profits as n* approaches infinity
What does the LR supply curve look like for a competitive market?
What does a standard representation of a firm and market in LR competitive equilibrium look like
What happens if there is either a physical limit to entry or a legal restriction?
firms are free to bid to enter the industry, but not all will be successful
e.g. licence is required to enter an industry and issued to the highest bidder
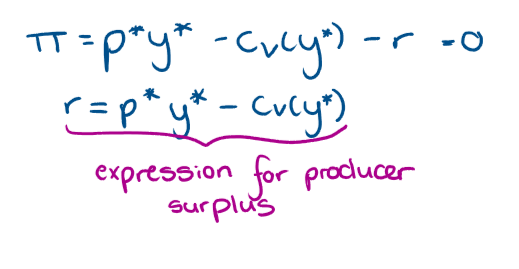
What is economic rent?
the amount of a F.o.P is paid in excess of the minimum payment required for it to be supplied
assume it is costless to produce/administer licences → they have a 0 cost
assume all other costs of production are variable costs
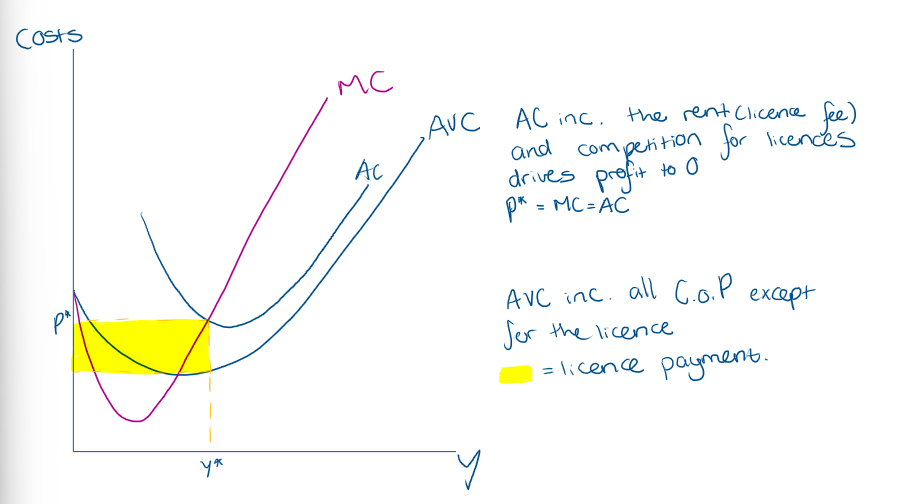
What will profit be if we have to include the cost of a licence?
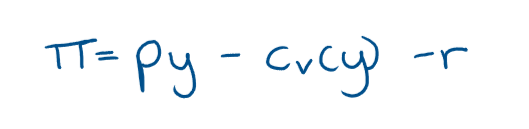
What is equilibrium in a market with cost for licence?
large number of firms wanting to enter competing for licences -? effectively creates a competitive market for licences
cost of licence will be determined by the firms’ willingness to pay → comes from profit incetive
In eq, cost of licence will be the cost that results in firms making 0 profits
What will r be in in an equilibrium market?
On a graph, show what would be the licence payment?
What is rent seeking behaviour?
activity aimed at creating or extending opportunities to gain economic rents
may lead to artificially creating scarcity purely bc/ someone will benefit from the associated rents
(example - licenses for g/s restricting supply without good reason)