Planetary Astronomy
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Celestial Sphere
An imaginary gigantic sphere that surrounds earth made up of all the surrounding planets and stars that surround earth. Doesn’t account for the actual distances of these objects. It is just a visualization tool.
Of all visible objects in the celestial sphere today, which one appears to move the least? Why?
Polaris because it is located on a celestial axis. Therefore, the earth’s rotation does not affect the location of Polaris in the night sky.
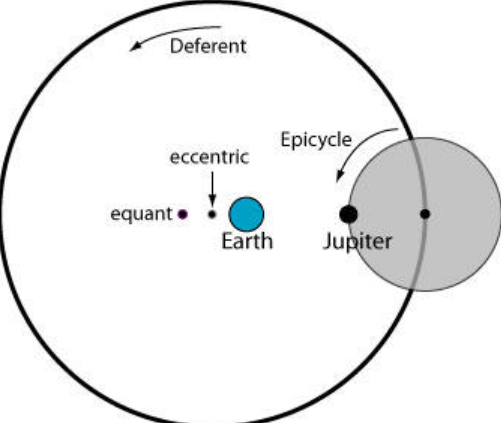
Basic structure of the Geocentric Model
Earth is at the center
Each planets moves in two distinct circular orbits.
The smaller orbit is the epicycle.
The larger orbit is the deferent.
Basic structure of the Ptolemaic Model
Similar to the geocentric model (Earth at center, epicycles, deferent)
What is the earliest model of the solar system
The Geocentric model
What is the most complex model of the solar system
The Ptolemaic model
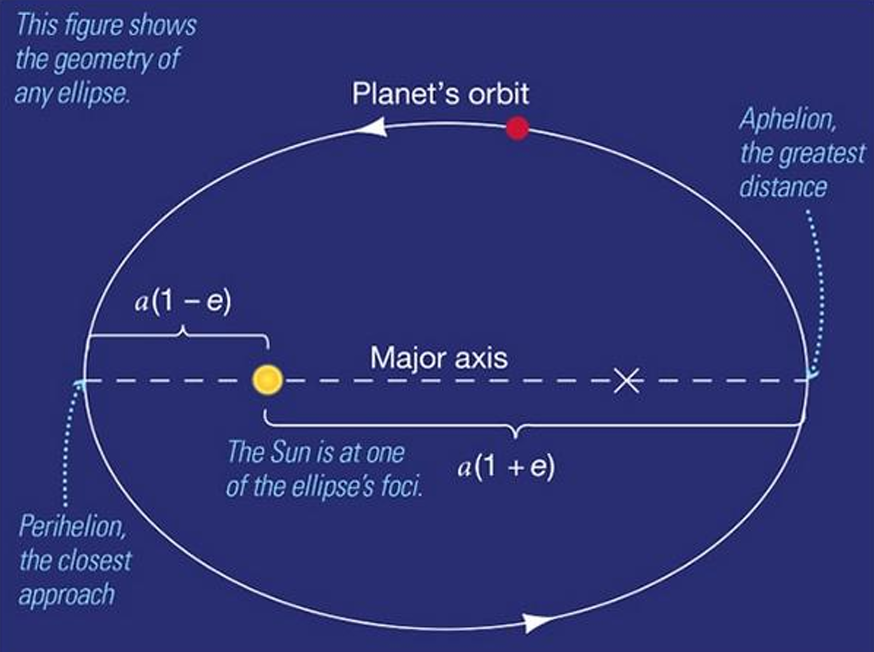
Kepler’s 1st law
The orbital paths of the planets are not perfect circles there are ellipticals with the sun at one Foci.
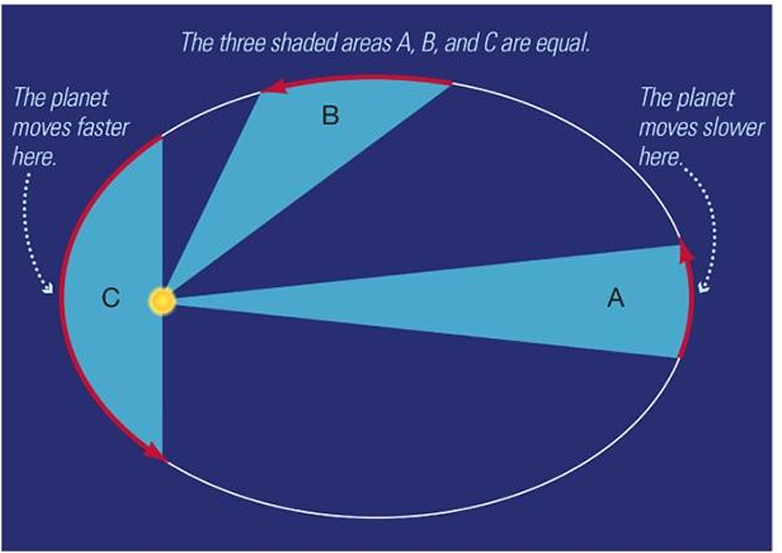
Kepler’s 2nd law
An imaginary line connecting the Sun to any planet sweeps out equal areas of the ellipse in equal intervals of time.
(A planet moves faster closer to the sun)
Kepler’s 3rd law
The square of a planet’s orbital period (earth years) is proportional to the cube of its semimajor axis (AU).
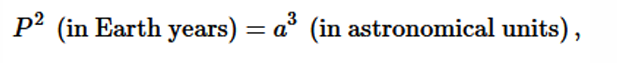
Semi major axis
The average distance between an orbiting body and the center of its orbit. (For an elliptical orbit)
What are the three parts that form the foundation of the scientific method?
Observation
Prediction
Theory
What is an astronomical unit (AU)
1 AU = the average distance between the earth and the sun.
Eccentricity
The ratio of the distance between the foci to the length of the major axis.
A measure of how flat an ellipse is a higher eccentricity = flatter ellipse.
Diffraction grading
A sheet of transparent material with closely spaced parallel lines on it. The spaces act as many tiny slit openings and light diffracts as it goes through them.
Ex) CD

What do absorption lines represent?
Wavelength’s of light that have been absorbed by an element.
T/F Each gas has its own emission lines?
True
T/F Absorption lines correspond to the emission lines of the same element?
True
Kirchhoff’s Laws
Luminous solid, liquid or dense gas emits light of all wavelengths.
Low density-hot gas emits light whose spectrum consists of a series of bright emission lines.
Cool, thin gas absorbs certain wavelengths from a continuous spectrum.
Explain the photo electric effect
Whether or not an electron is emitted from a sheet of metal depends on the light frequency not it’s intensity.
The speed of an ejected electron depends on wavelength/frequency
(So Frequency = Energy)
The explanation for this phenomenon is that sometimes light acts like a particle.
What scientist studied the photo electric effect
Einstein
Light moving away from the observer will be ______________.
Light moving towards the observer will be _______________.
Red shifted - longer wavelength.
Blue shifted - shorter wavelength.
Which of the following has a fundamentally different nature than the other four?
proton, electron, neutron, atomic nucleus, photon
The photon
The wavelengths of emission lines produced by an element are identical to ___________
identical to the absorption lines
If a light source is approaching you it’s wavelength will be shifted ________
shorter (higher f)
Analyzing a starts spectral lines can tell us all of theses except:
its composition, its surface temp, its transverse motion, it’s rotation, it’s density
Transverse motion
(The doppler effect only applies to light traveling away or towards you not parallel)
Rigel appears as a blue-ish start where Betelgeuse appears as a red-ish star, why?
Rigel is hotter than Betelgeuse.
(frequency of light is proportional to its energy) (E=hf) (Hotter objects give off photons of higher energy)
Why is a solar day longer than a sideral day?
Because while Earth rotates, it also moves along its orbit, so it must rotate a bit more than 360° for the Sun to return to the same position.
Sideral vs Solar day
Sideral Day: The time it takes Earth to rotate once relative to distant stars (about 23 hours, 56 minutes, 4 seconds).
Solar Day: The time it takes Earth to rotate so the Sun appears in the same position in the sky (about 24 hours).
Ecliptic
The Suns apparent path around the celestial sphere due due the erart’s orbit of it.
Celestial pole
Where the earth’s axis intersects the celestial sphere
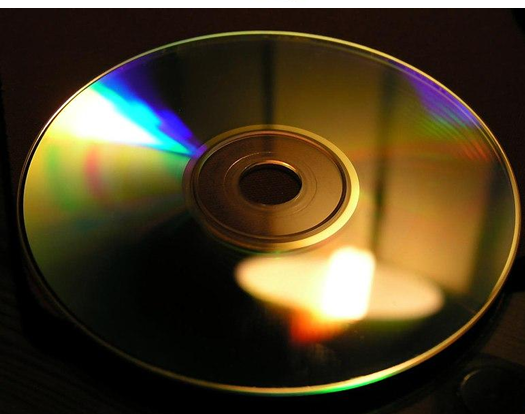
Why do we experience seasons?
Because the Earth’s axis is inclined to the ecliptic.
Summer in NORTHERN hemisphere (north pole of earth points to sun) when Earth is tilted towards sun (opposite for southern hemisphere)
Lunar Eclipse occurs when:
Moon enters earth’s shadow
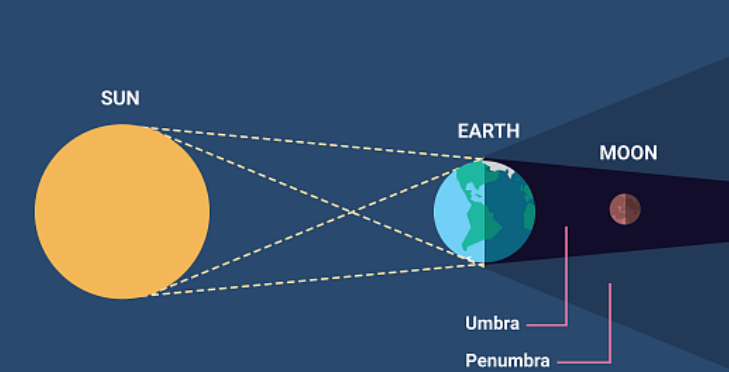
Solar Eclipse occurs when:
Moon passes between earth and sun.
Lunar eclipse: umbra
The darkest, central part of Earth’s shadow.
Lunar eclipse: penumbra
The lighter, outer part of the shadow.
What was the most successful Geocentric model?
The Ptolemaic model
How did the The Ptolemaic model account for retrograde motion?
The planet moved on a small circle (an epicycle), which itself moved along a larger circle around Earth (the deferent). The combined motion created the illusion of a loop.
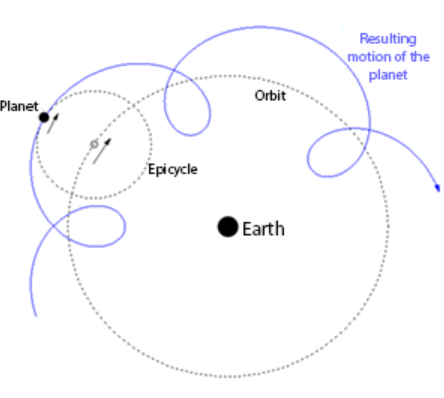
How does the Heliocentric model account for retrograde motion?
Attributes retrograde motion of the planets to the earth passing them in orbit.
What marked the beginning of the copernican revolution
The realization that the sun was the center of the solar system.
What were the two types of orbit in the Ptolemaic model?
Deferent: Planet’s orbit or earth
Epicycle: Planet’s smaller orbit within the deferent
What are Kepler’s Three laws of planetary motion?
Planetary orbits are ellipses
A planet moves faster as it’s closer to the Sun
The semimajor axis of the orbit is related to the planet’s orbital period by: P² = a³ (semi major axis is half of the longest diameter of an ellipse)
T/F all objects with a mass exert a gravitational force?
True
How does gravitational force decrease with radial distance?
1/r²
Escape speed
Escape speed is the speed needed for an object to escape the gravitational pull of another object.
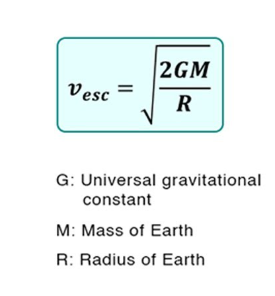
How can the mass of a distant object be measured?
Through determining the gravitational force needed to keep an object orbiting another.
All light is ________________________
Electromagnetic radiation
T/F all electrically charged objects are surrounded buy an electric field
True
What happens when a charged particle moves?
IT causes a change in the electric/magnetic field that travels at the speed of light as an em wave.
What are the two properties of radiation?
Diffraction - bending around corners
Interference - constructive/destructive
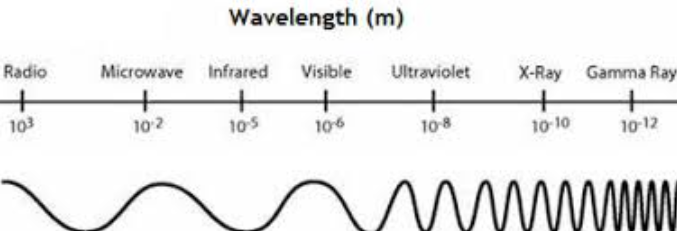
Emf spectrum order:
What is a Black Body curve?
A curve that depicts the intensity of radiation an object gives off based on its temp.
A hotter object emits _______ radiation than a cooler object
MORE
Hotter objects have a ______ where the most radiation is given off
shorter peak wavelength
Wiens law:
Wien's displacement law states that the peak wavelength of a blackbody's radiation is inversely proportional to its absolute temperature
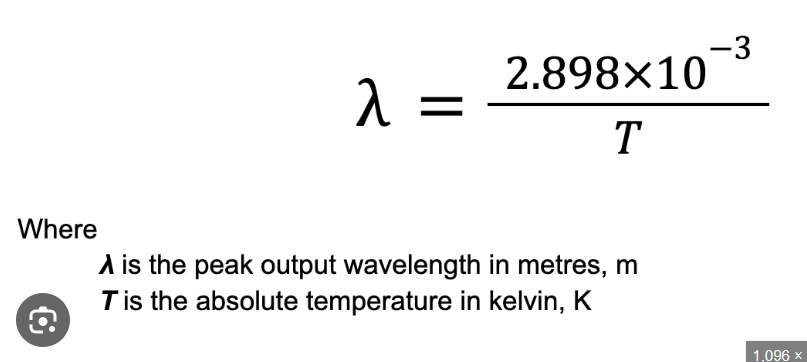
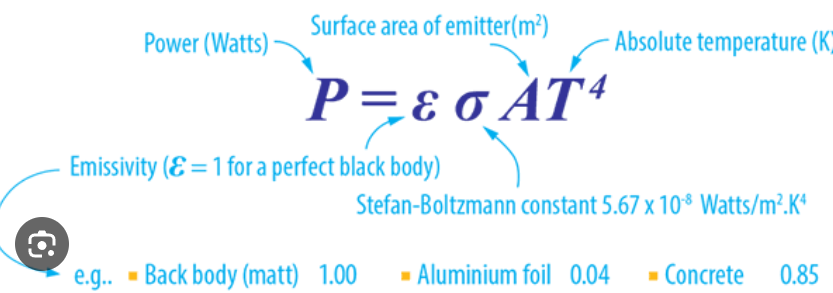
Stefan-Boltzmann law:
the total power radiated per unit surface area of a black body is directly proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature