Lecture 14 - Development coalitions
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Developmental coalitions (2)
A broad coalition w concentrated enforcement power that directs rents to invest in development
Depends on rel between pol + econ elites
Characteristics of developmental coalitions (3)
Broad coalitions - the broader the better
Concentrated power - of one person within the coalition
Rents directed to investment
Broad coalitions (5)
Key econ + pol elites are part of coalition
So institutions are inclusive, not extractive
So there's 'Embededness' between bureaucracy + pv sector
So losers are credibly compensated + don't resist
So Collective action is able to shift equilibrium
Concentrated power (6)
The leader can discipline members of coalition
So institutions are enforced
Accountability limits corruption + clientelism
Autonomy of bureaucrats is protected
Not eliminating corruption
Ensuring corruption/favoritism 'buys' development by protecting investments + compensating loser
Rents directed to investment (2)
A Developmental State: "Centralizing management of econ rents"
‘Embedded' autonomy coordinates + protects investments
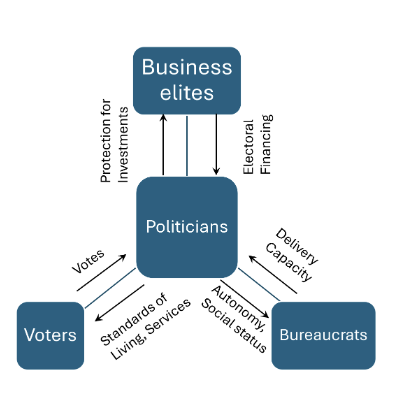
Developmental coalitions do not avoid politics (4)
They make development politically successful:
Business elites get investment opportunities + protection if they provide electoral financing
Bureaucrats earn professional + social praise from delivering services, not corruption
Voters reward politicians for development
Unlike other coalitions that make development politically unattractive (3)
Narrow coalitions
Extractive
Benefit from keeping competing groups poor
Developmental coalitions need to be politically successfull (4)
Structural constraints still exist; the critical juncture is only temporary
How do they change politics?
How do they escape bad equilibrium?
Definition: policy feedback
Policy Feedback (6)
Policies + inst reforms change future politics
Policy design is not qs of technical cost-benefit analysis - Or measuring 'pro-poor' impact
But anticipating how policies can raise pol pressure for future development through:
Accountability
Collective Action
Representation
But anticipating how policies can raise pol pressure for future development - E.g. (4)
Bolsa Família cash transfers in Brazil created strong vested interest defending program
Accountability: A programmatic policy giving voters econ security to reject clientelism
Collective Action: A new collective id + pride among poor beneficiaries
Representation: Benefits go to mothers, strengthening their pol power
Bolsa Família cash transfers in Brazil created strong vested interest defending program - Impact (3)
People that received Bolsa Família benefits more likely to vote for party that created policy
All pol parties now compete to extend program
'Inclusion of outsiders’
Developmental Coalitions in Rwanda (2)
Rwanda faces many structural constraints
Yet it has succeeded in implementing development where others have failed
Rwanda faces many structural constraints (3)
Geography: Landlocked, tropical
History + Culture: Colonialism, slavery + genocide damage trust
Institutions: Authoritarian pol institutions
Yet it has succeeded in implementing development where others have failed (5)
Institutional rules have been strengthened
The state has been centralized + given autonomy
External aid has been absorbed successfully
Low corruption, low clientelism
Limited resistance to change by losers/winner
How have developmental coalitions been successful in Rwanda (3)
Broad coalition
Concentrated Power
Directing rents to investment
Broad Coalition - Rwanda (4)
Politicians
Business, military elites
Tutsis and Moderate Hutus
Women
Concentrated Power - Rwanda (2)
The Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF) is dominant party
Grounded in the military
Directing rents to investment (3)
Tri-Star Investments / Crystal Ventures (100%RPF controlled)
>3% GDP; 9% of national revenue
Pol protection from RP
Development is politically beneficial - Rwanda example
RPF electoral campaigns financed by Tri-star/Crystal profits (50% of the 2010 campaign)
Type of state - Rwanda (6)
A 'Developmental Patrimonial' state
Developmental: Directing + disciplining resources for investment
Patrimonialism: Centralized + personalized power
Reflects agency of Kagame
Surprising + risky!
What guarantees Kagame won't changehis mind
What conditions permitted the emergence of a developmental coalition in Rwanda
Structural conditions
Critical juncture - 1994 genocide + RPF’s victory (not work for Cambodia even if genocide)
Agency
Structural conditions (4)
A history of Weberian bureaucracy + indigenous state-building
Disempowerment of large landowners
A dom, cohesive elite
External threats that align elite interests w development - from DRC
Agency (8)
The agency of Kagame in forming a coalition
Forging a broad coalition
Inviting Hutu moderates into gov
Convening pv sector investors, exiles, diaspora
Using concentrated power
Steady stream of officials at all levels of gov have been criminally or administratively sanctioned"
HR violations, arrest of journalists,+ assassinations of opponents to retain power
Increasing representation for pro-development groups → 30% quotas for women since 2003
Agency of Kagame in forming a coalition - critics (6)
The sustainability of the regime is unclear
Dependent on Kagame
Econ crisis may undermine coalition
Reciprocal financing can easily become corruption
Dominant parties lack credibility
Violence/invasion discourages investment
What does the role of agency and coalitions imply for the role of donors and external aid? (3)
Understand motivations of leaders + nature of coalitions (Do poli science)
If coalition is not developmental → limit support
If coalition is developmental → support it with very few conditionalities
If coalition is not developmental → limit support (2)
At best, finance civil society instead
Try stimulate developmental coalition
If coalition is developmental → support it with very few conditionalities (3)
Local actors are already motivated to enforce rules + accountability
Risks of aid (corruption, lack of ownership, isomorphic mimicry) are less of a concern
Eg. Rwanda one of only 2 countries receiving an 'A' in the OECD 2010 evaluation of Paris Agenda forAction