Non-gravid Uterus Pathology
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are the 4 most common categories of diseases affecting the uterus?
Anomalous
Infectious
Metabolic
Neoplastic
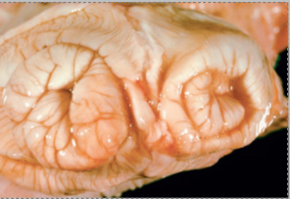
What is this condition in a cow?
Anomalous- double cervix
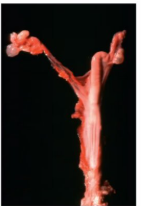
What is this condition? Describe it.
Anomalous - segmental aplasia of a uterine horn
Genetic condition (White heifer disease most common, but also in dogs)
Blind ended portion continues producing fluid
What is the route of most non-gravid uterine infections?
Ascending
How does the uterus defend against infection
IgA produced locally in mucousa = prevents bacterial attachment to uterine wall
Hormonal changes:
oestrogen stimulates neutrophils, macrophages and T-cells
progesterone downregulates the immune response
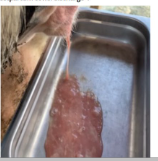
What condition does this indicate in a cow?
Metritis
Cause of post-partum metritis in sheep and goats
Clostridium tetani and perfringens
Risk factors of metritis in cattle (6)
Stillbirth
Twins
Retention of foetal membrane
Reduced feed intake before calving
Hypocalcaemia
Dystocia
Causative agent of contagious equine metritis and what are its clinical signs?
Taylorella equigenitalis
highly contageous venereal disease of mares
stallions do not develop disease but can transmit it. they are an important reservoir
endometritis
transient infertility
abortion (rare)
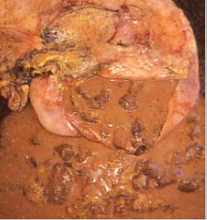
Give a morphological diagnosis
Acute, severe, diffuse, purulent metritis
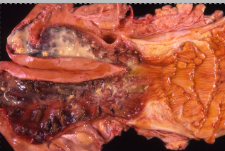
Give a morphological diagnosis
Moderate, diffuse, suppurative and haemorrhagic endometritis
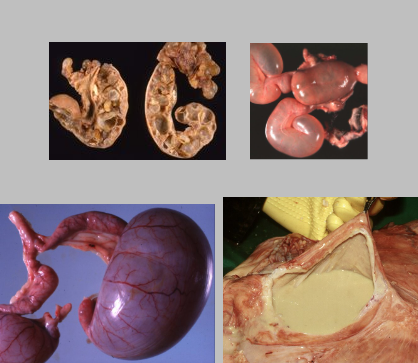
What is this condition?
Pyometra
What occurs during cystic endometrial hyperplasia in dogs
Influenced by prolonged oestrogen exposure and no progesterone (metabolic cause)
Common in dogs
Endometrial hyperplasia with cystic distention of endometrial glands
Chronically hyperplastic glands leads to accumulation of mucoid fluid
mucometra
hydrometra
May increase susceptibility for uterine infection (E.coli), resulting in pyometra
Clinical signs of endometriosis
Idiopathic condition
Chronic pelvic pain
Infertility
Ectopic endometrial-like tissue (glands/stroma) that induce chronic inflammatory response and adhesions, and scar tissue
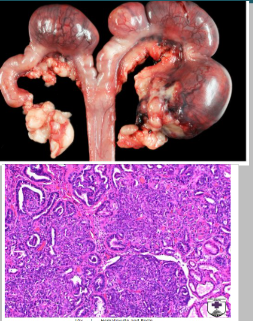
What is this condition in the rabbit?
Uterine endometrial adenocarcinoma
80% metastasis rate, often to lungs
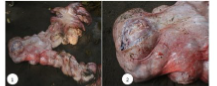
What is this condition - the most common female reproductive neoplasm across domestic mammals?
Leiomyoma/Leiomyosarcoma