meteo 201 final (quiz questions)
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Sixty-Eight (68) degrees Fahrenheit is how many degrees Celsius?
20
If today is 5oC warmer than yesterday, by how many degrees Fahrenheit is today warmer than yesterday?
9
If you know the temperature and pressure of a gas, and know the value of the Gas Constant R, what other fundamental weather variable can you then calculate?
air density
Give the last name of the U.S. president whose friendship with a Penn State faculty member played an instrumental role in the early years of the department
Eisenhower
Assume the local time in State College is 6:30 PM on August 30, 2024. What is this time in UTC? Give your answer as simply four digits
2230
The two most important variable gases in the atmosphere are water vapor and ____________________.
carbon dioxide
Which map projection (that was mentioned in class) has latitude lines as arcs, tends to distort both high and low latitudes, and does not preserve direction?
polar stereographic
What is the general name given to any atmospheric layer in which temperature INCREASES with height?
inversion
Which of the following is the correct ordering of scales of atmospheric motion, from largest to smallest?
synoptic scale, mesoscale, microscale
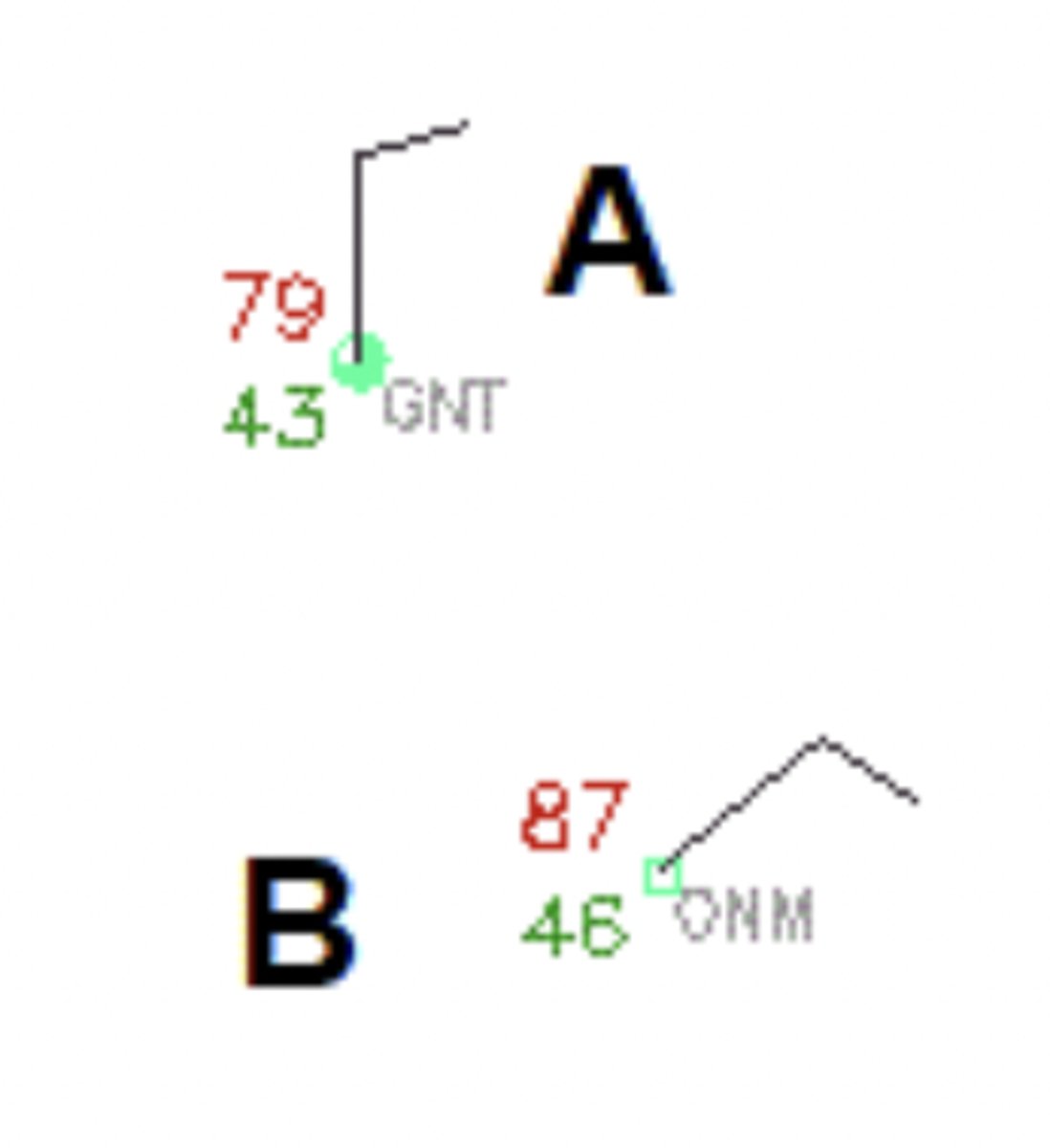
The dew-point depression is defined as the temperature minus the dew point. What is the dew-point depression in the station model labeled B? For your answer, just enter a number.
41
Consider the following three cities which are all at about the same latitude: Olympia, WA (on the West Coast, right on the Pacific Ocean), Pierre, SD, and Portland, ME (on the East Coast, right on the Atlantic Ocean). Which probably has the LEAST seasonality (that is, difference between temperatures in summer and winter)? For your answer, just give the state abbreviation (that is, WA, SD or ME).
WA
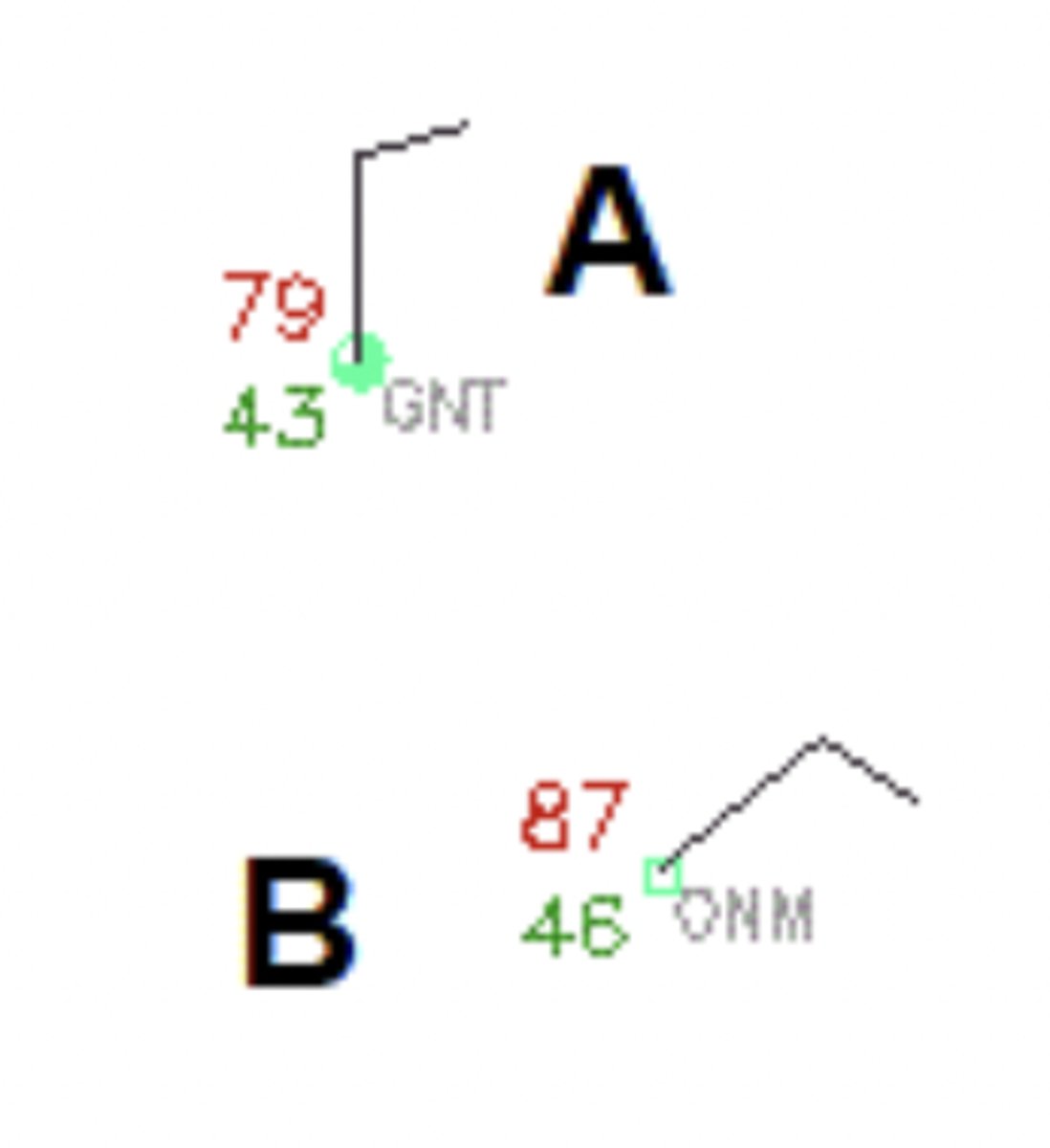
Again, consider the station models. Assuming the standard directions (that is, up is north, right is east, down is south, and left is west), which of the following is the best description of the wind direction in station model A?
North
______________________ are lines on a map that are parallel to the wind and allow you to visualize the flow of the air at a given time.
streamlines
Assume you are isoplething a map of temperature. The temperature at point A is 48oF. The temperature at point B is 78oF. What do you assume is the value of temperature halfway between Point A and Point B? Just enter a number as your answer
63
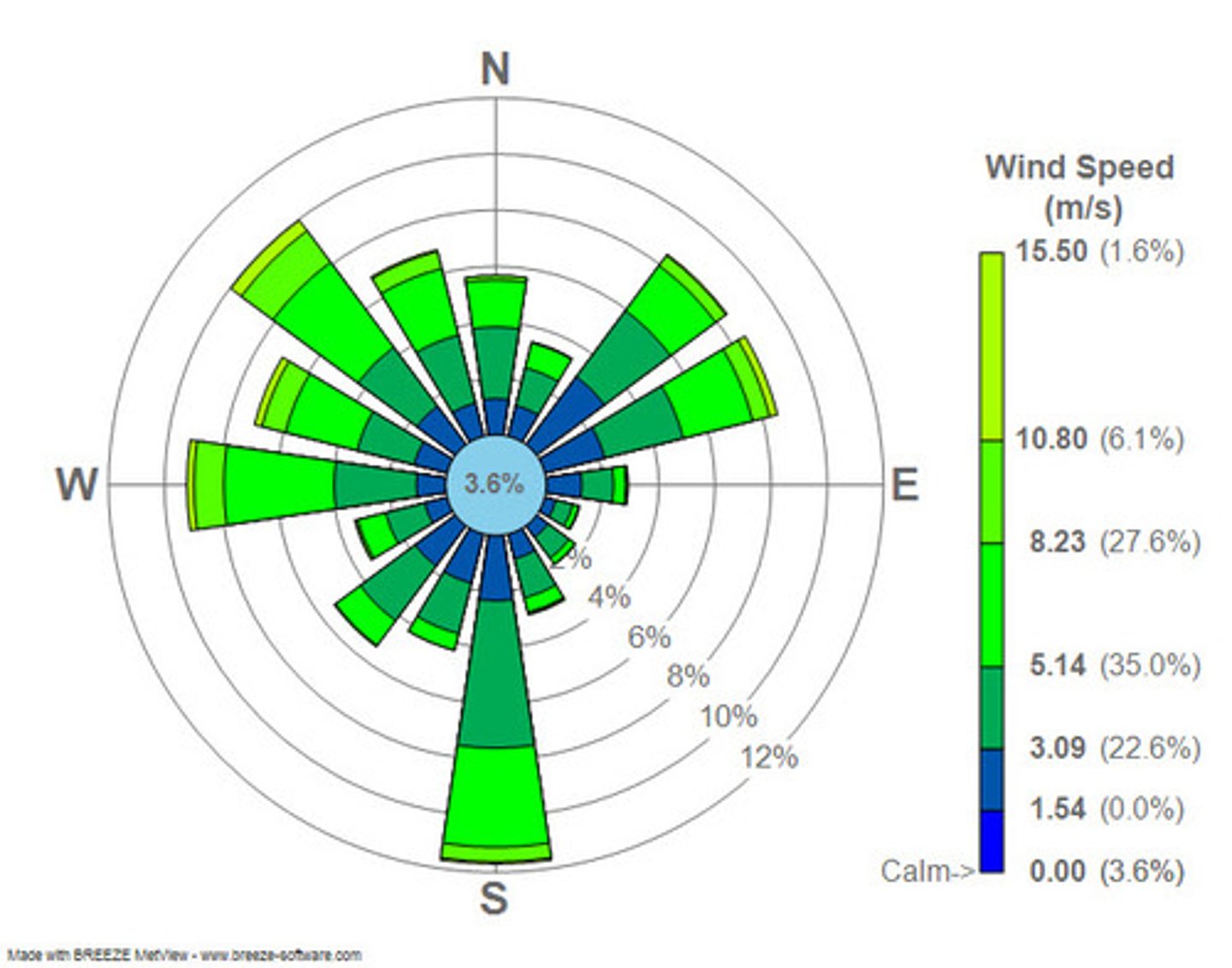
Based on this wind rose, what is the LEAST frequently observed wind direction?
east-southeast
A(n) is the weather instrument used to measure wind direction, while a(n) is the weather instrument used to measure wind speed.
wind vane, anemometer
A circular ring of currents in an ocean basin, driven primarily by the wind, is called a _________________
gyre
The wind direction most frequently observed, on average, during a specified period at a location is known as the ________________________
prevailing wind
Given that it is defined as the weight, per unit area, of an air column, _______________________ always decreases with height.
pressure
Assume that a meteorologist says that "the temperature gradient is very small in Pennsylvania." If you looked at a map of Pennsylvania at that time, which of the following would be true?
Isotherms in Pennsylvania would be very far apart
If you ask me to forecast the high temperature in State College tomorrow, and I tell you "80" because that's what the high temperature was today, what very simple forecasting method am I using?
persistence
The time scale of forecasting that falls between "Weather" forecasting (which generally refers to a week or two into the future) and "Seasonal" forecasting (which generally refers to several months in the future) is called _____________________ forecasting.
subseasonal
The two primary types of numerical weather prediction models are models and models.
gridpoint, spectral
What is the last name of the British mathematician who tried to do numerical weather prediction by hand in the early 1900s?
Richardson
The values of all the variables that are given to a numerical weather prediction model at the beginning of a run are collectively known as the _________________________ (Hint: I'm looking for a two-word answer here).
initial conditions
The idea of using a set of numerical weather prediction model forecasts rather than just one model is known as __________________ forecasting.
ensemble
Which of the following statements about isoplething meteorological variables IS NOT TRUE?
It's possible for two isopleths of different values to cross.
The brown lines on this map from the National Weather Service show pressure, but not the actual pressure measured at the observing sites, but rather a "corrected" pressure known as ____________________ pressure.
sea-level pressure
Assume you have a sample of air with 1000 water vapor molecules in it. Suddenly, the number of water vapor molecules is cut in half (that is, now you only have 500). Which of the following characteristics of the air WILL NOT change?
equilibrium vapor pressure
The lowest temperature to which air can be cooled by evaporating water into it is called the _____________________ temperature.
wet bulb
Which of the following does not represent saturation?
mixing ratio=specific humidity
A precipitation minimum on the leeward side of a mountain is called a ___________________________.
rain shadow
During a typical day, when is relative humidity a minimum?
at the warmest time of the day
When the __________________ gets to about 70oF, the air feels quite muggy - in fact, some might say it feels "gross."
dew point
Which of the following are always about the same numeric value?
mixing ratio and specific humidity
Microscopic particles of dust, dirt, soot, salt and other particles in air onto which water vapor condenses to form cloud drops are called what?
condensation nuclei
Name any process from the energy staircase that RELEASES energy.
condensation
freezing
deposition
The idea that all matter emits radiation constantly, and at all wavelengths, is known as __________________ Law.
Plancks
Order the following types of radiation from shortest to longest wavelength: visible, infrared, ultraviolet.
ultraviolet, visible, infrared
Object A has a temperature of 1 K. Object B has a temperature of 2 K. As a result, Object B emits ______________ times as much energy, per unit area, as Object A. Your answer should just be a number.
16
Assume that 100 units of energy arrives at the top of the Earth's atmosphere from the Sun. Let A be how many of those units are back-scattered to space. Let B be how many of those units are directly absorbed by the atmosphere. Let C be how many of those units reach the surface and are absorbed. Order A, B and C from smallest to largest.
B,A,C
The process whereby energy is transferred via molecular collisions is known as , while the process by which energy is transferred vertically via rising parcels of warmed air is known as
conduction, convection
The two most important greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are and . No formulas, please - write out the names of the gases
water vapor and carbon dioxide
Fill in the blanks in this statement with words that refer to sky cover: All else being equal, nights are usually warmer than nights.
cloudy, clear
When thinking about the three "fates" of radiation when it encounters an object, radiation can be transmitted, back-scattered, or ______________________.
absorbed
The Bergeron-Findeisen process, also known as the --- process, depends on the notion that all three phases --- of co-exist in a cloud and that water vapor molecules will tend to migrate from the vicinity of the liquid to the vicinity of the solid.
ice crystal, water
The general name for a mid-level layered cloud is --- , while the general name for a high-altitude cloud with some vertical development ("puffiness") is ---
altostratus, cirrocumulus
consider three weather observing networks in the United States, Cooperative Climate Network, ASOS/AWOS, Upper-Air Observing Network. put in least to most locations
Upper Air, ASOS/AWOS, Cooperative
Which of the following is NOT an example of a method or instrument that makes an in-situ observation
satellite radiometer
Which of the following is NOT measured by ASOS
snow depth
Order those three sources from the one that contributes the Largest percentage of initial conditions for computer models to the smallest
satellites, aircraft, radiosondes
what word in a cloud name indicates that it produces rain
nimbus
---- satellite imagery is tuned to the temperature of clouds, while ---- satellite imagery is tuned to the thickness and water content of clouds
infrared, visible
Indicate if its geostationary (G) or polar orbiting (P)
Orbits at same speed as Earth rotates
Provides best view of tropics
Closer to Earth
Image the Earth in swaths
G, G, P, P
What is the general name of the instrument on a weather satellite that measures the intensity of radiation emitted by or back scattered from an object at various wavelengths
radiometer
Three types of satellite images reduced to two
Visible and Infrared
If you're given a map of isobars, what would you look for in order to determine where the wind is likely blowing the fastest?
isobars closest together
The hypothetical wind that results from a balance between the pressure gradient force and the ________________ force is known as the geostrophic wind.
coriolis
Fundamentally, the force that sets air in horizontal motion (and thus is responsible for the wind) is the __________________________ force.
pressure gradient force
What is the impact of friction on the wind?
slows the wind and causes the wind to cross isobars towards lower pressure
An elongated zone of high pressure is called a --- , while an elongated zone of low pressure is called a --- .
ridge, trough
The two main operating states of the WSR-88D are precipitation mode and _______________________ mode.
clear air
A ________________________ is a curlicue appendage on a reflectivity image of a thunderstorm that indicates the presence of rotation. This feature typically only appears in highly organized supercell thunderstorms that tend to produce the strongest tornadoes.
hook echo
Three of the following situations would result in a radar reflectivity image that looks like precipitation was occurring, even though precipitation was not actually occurring at the ground. Choose the one that doesn't fit that description
Radar beam overshoots shallow clouds that are far from the radar
Assume that a hurricane is approaching the Louisiana coast from the south (that is, the hurricane is moving north). On what side of the hurricane would the storm surge be greatest?
east
Radar reflectivity cannot be negative, given that it's an amount of radiation. Yet the scale on some radar reflectivity images has negative values. Why is this?
negative value means that the wind is moving towards the doppler
Formally, what would a meteorologist call an air mass that is relatively warm and relatively moist? No abbreviations accepted.
maritime tropical
Consider the four primary air mass types. The largest density difference would be found between a --- air mass and a --- air mass. No abbreviations please.
continental polar, maritime tropical
The ____________________ tends to decrease as a front approaches, reach a minimum as the front goes through, and then increase as the front moves away.
pressure
The word _______________________ doesn't actually mean "rain", as many people think, but instead means "seasonal reversal of the wind."
monsoon
Sometimes in summer, an area of high pressure develops over the North Atlantic Ocean, centered around 30 degrees latitude. Meteorologists often refer to this area of high pressure as the "Bermuda High". Given the position of this area of high pressure, the Bermuda high would be considered a specific example of a _______________________ high (these highs are considered a part of the general circulation in that part of the world).
subtropical
What is the sign of omega if air is sinking? Choose between "positive", "negative", or "zero".
positive
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) is basically the meeting ground of the ________________ winds that blow in the Northern and Southern Hemisphere.
trade
It's fair to say that, generally speaking, there are three main precipitation "mechanisms": _______________, convective, and frontal.
orographic
Of the following latitude bands, which tends to get the least precipitation, on average?
30 degrees north
The movement of the air on the _____________________ side of a front determines the type of front (I'm looking for a word that is related to temperature)
cold
One motivation for studying upper-air weather patterns is that in order for surface low-pressure systems to survive, there must be upper-air--- to compensate for the low-level convergence. Similarly, in order for surface high-pressure systems to survive, there must be upper-air ---to compensate for the low-level divergence.
divergence, convergence
Pressure levels at which radiosondes always report data are called --- pressure levels, while other pressure levels at which data is observed during a balloon launch are known as--- pressure levels.
mandatory, significant
The standard height (in meters) of the 300-mb pressure surface is ___________________ meters. Just enter the number.
9000
In meters, what is the average thickness of the layer between the 700-mb pressure surface and the 500-mb pressure surface? Just enter the number.
2500
What mandatory pressure level is often used to assess vertical velocity and also relative humidity, because most clouds that produce precipitation will pass through this level? Give your answer in millibars, and just write the number.
700
Fill in the blanks with word that refer to temperature: Pressure decreases faster in ---air than in--- air.
cold, warm
Isopleths of--- on a constant pressure surface can be interpreted the same as isopleths of--- on a nearby constant height surface.
height, pressure
An elongated area of high pressure on a constant height surface (such as a map of sea-level pressure) is called a ridge. What do we call an elongated area of high height on a constant pressure surface?
ridge
A 1000-500 mb thickness of __________________ meters is considered a "first-guess" at the rain-snow line - that is, the boundary between liquid and solid precipitation in a storm. Just enter the number.
5400
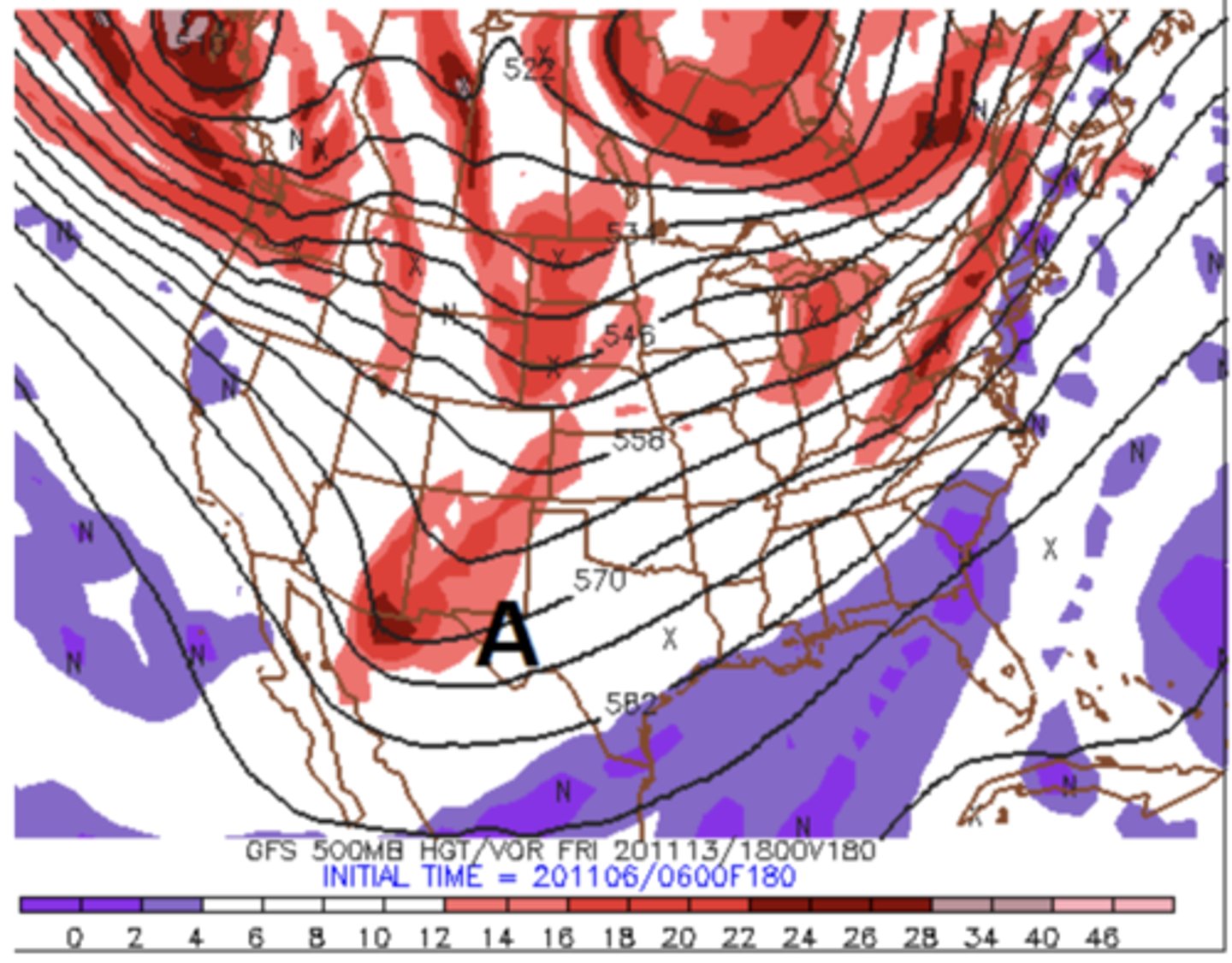
The solid black lines on the map below are 500-mb heights. What is the best estimate of the wind direction at Point A?
southwest
Assume you're in the Northern Hemisphere. If you go high enough in the atmosphere, the temperature gradient will eventually reverse -- that is, it'll become warmer to the north and colder to the south. That's because the __________________ , which is the boundary between the troposphere and the stratosphere, is lower in colder air than in warmer air, so you reach the stratosphere at a lower height in the colder air than in the warmer air.
tropopause
The mid-latitude jet stream is typically found between the --- millibar level and the --- millibar level (please just enter the numbers - you do not have to type "millibar" or "mb").
250, 300
You are given a map of heights on a high-altitude pressure surface. If you wanted to find the mid-latitude jet stream, you would look for the zone with the largest height _______________.
gradient
Absolute vorticity is the sum of --- vorticity, shear vorticity, and --- vorticity.
earth, curvature
In terms of divergence and convergence on a 500-mb chart, areas where a parcel of air increases its spin are associated with--- , while areas where a parcel of air decreases its spin are associated with--- .
convergence, divergence
In terms of the sign (positive or negative) of vorticity, counterclockwise spin is considered---vorticity, while clockwise spin is considered---vorticity.
positive, negative
Isopleths of vorticity are called __________________ (I did not use the word in class, but it's in the Powerpoint).
isovorts
Consider the map below. Based solely on the vorticity pattern, would you expect upper-level divergence or upper-level convergence at Point A? Just answer "divergence" or "convergence".
divergence
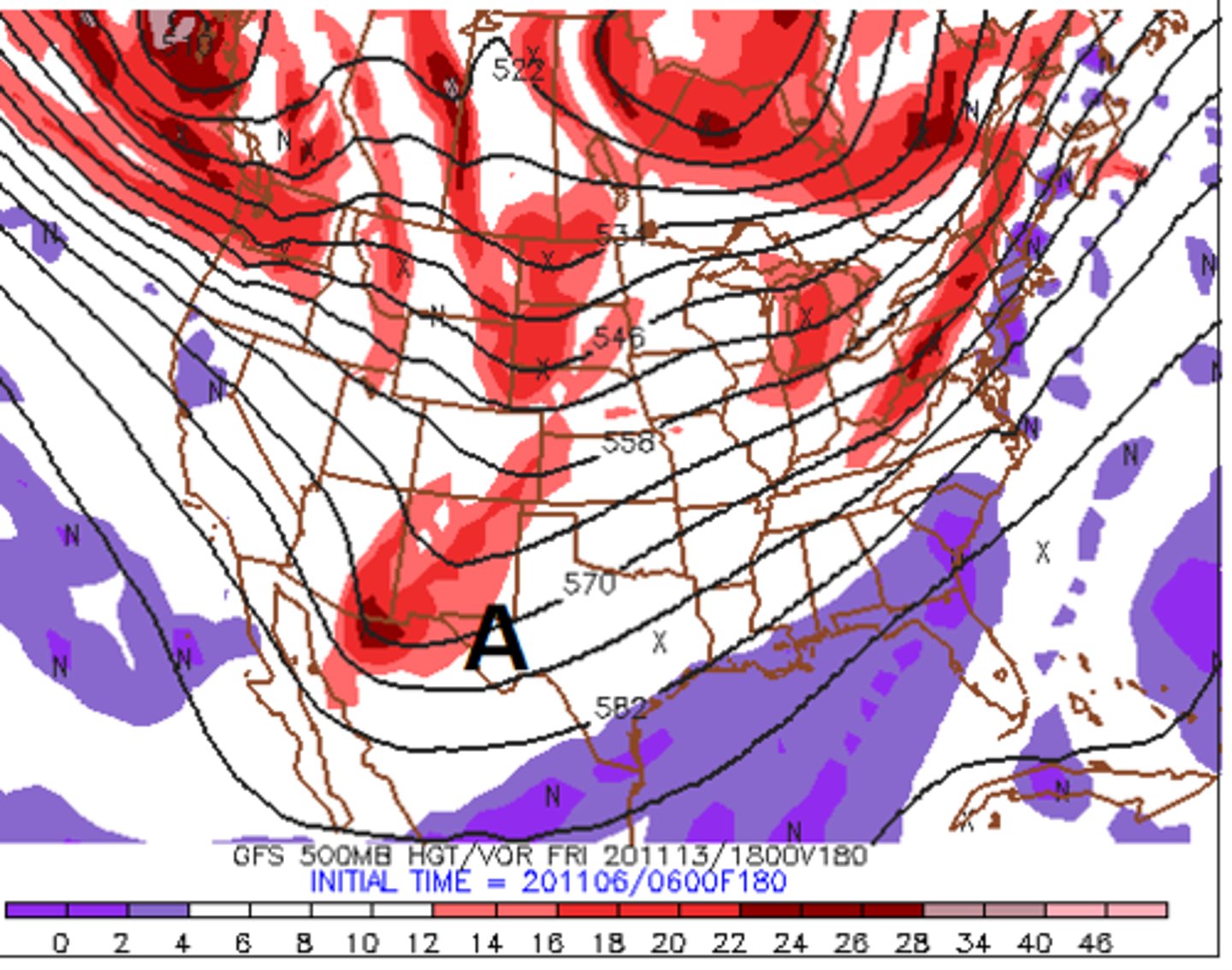
If you were on a planet where, on average, it was warmer to the west and colder to the east, and all other principles of meteorology worked the same as they do on Earth, what wind direction would you expect to find on an upper-level pressure surface on this planet?
north
In what type of 500-mb flow pattern -- zonal or meridional -- would you expect absolute vorticity values to be larger, on average?
meridional
The moist adiabatic lapse rate is less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate because condensation is occurring in a saturated parcel, releasing _____________________ and slowing the cooling rate (I'm looking for a very specific two-word answer here).
latent heat
If a parcel of air is given a nudge upwards in a layer, and the parcel is warmer than the environment regardless of whether the parcel is saturated or unsaturated, we say the layer is --- and the parcel is --- buoyant.
unstable, positively
A layer of the atmosphere in which the environmental lapse rate is between the moist adiabatic lapse rate and the dry adiabatic lapse rate is called a(n) ______________________ unstable layer.
conditionally
What Greek letter is used by meteorologists as a symbol for a lapse rate? Please spell out the name of the letter.
gamma