EARTH SCI. 11: Energy, Resources, & Waste Management
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Resource
It is any material, substance, or organism found in nature that is useful to satisfy a need, provided it is technologically accessible, economically feasible, and culturally acceptable.
Renewable Resources
These are sources of energy that can be replenished or renewed over time.
Nonrenewable Resources
These are resources that do not renew themselves at a sufficient rate within a human time frame.
RA 9513
This is also known as the Renewable Act of 2008, which governs the development, utilization, and commercialization of energy resources in the Philippines.
Hydro Energy
It is the process of generating electricity by utilizing the kinetic and potential energy of moving or falling water. This energy is typically harnessed by channeling water through turbines in dams, rivers, or tidal flows, causing the turbines to spin and drive generators that convert the mechanical energy into electrical energy. Additionally, this is a renewable energy resource.
RA 7156
This is also known as the Mini-Hydroelectric Power Incentive Act, wherein incentives and privileges are granted to mini-hydroelectric power developers and entrepreneurs to develop potential sites for hydroelectric power in their localities.
Ocean Power
It is a renewable energy resource that harnesses the natural energy found in the oceans through various processes such as waves, tides, ocean currents, and thermal or salinity gradients.
OTEC (Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion)
This is another way of producing energy using the ocean water. It uses the temperature difference between surface water (25°C) and deep ocean water (5°C). The surface temperature vaporizes a low-boiling point fluid like ammonia. The vapor expands and spins a turbine. The vapor is then condensed by deep ocean water into liquid so that it can be reused.
Geothermal Energy
This is a renewable energy resource that harnesses heat from within the Earth—typically from hot rocks, reservoirs of steam, or hot water deep below the surface—to generate electricity.
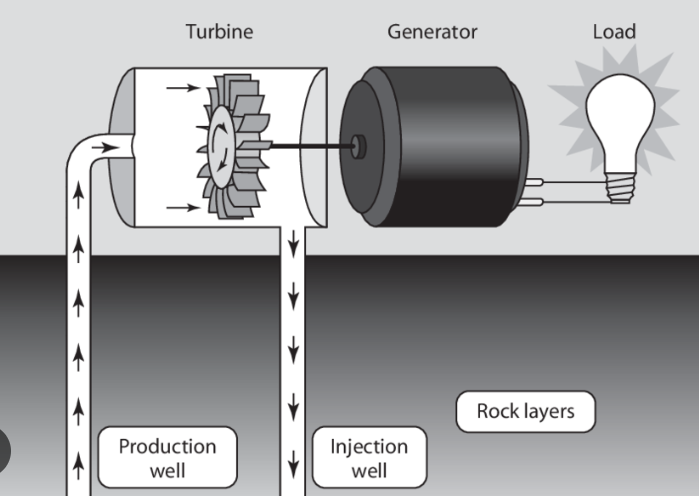
Dry steam power plants
The simplest and oldest design of a geothermal power plant.
This directly utilizes geothermal steam, which is sent directly to the turbine that drives the generator, producing electricity. The steam is cooled in the condenser, turns into cool water, and is then returned to the reservoir.
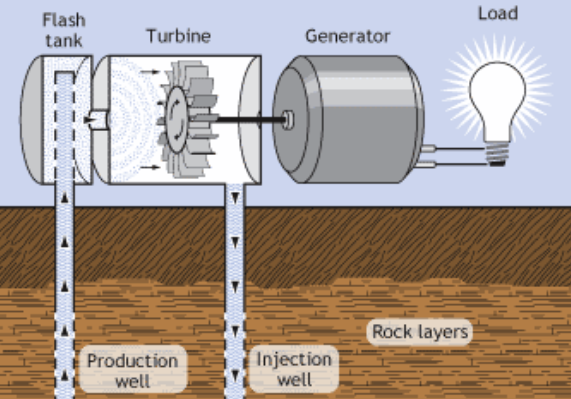
Flash steam power plants
The most widely used type of geothermal power plant today.
The hot water is pumped to the surface under great pressure. When it reaches the surface, the pressure is reduced, causing the water to boil rapidly or “flash” into vapor. The vapor in the flash tank drives the steam turbine. After passing through the turbine, the steam is cooled in the condenser. The cooled water is returned to the reservoir and heated by geothermal rocks.
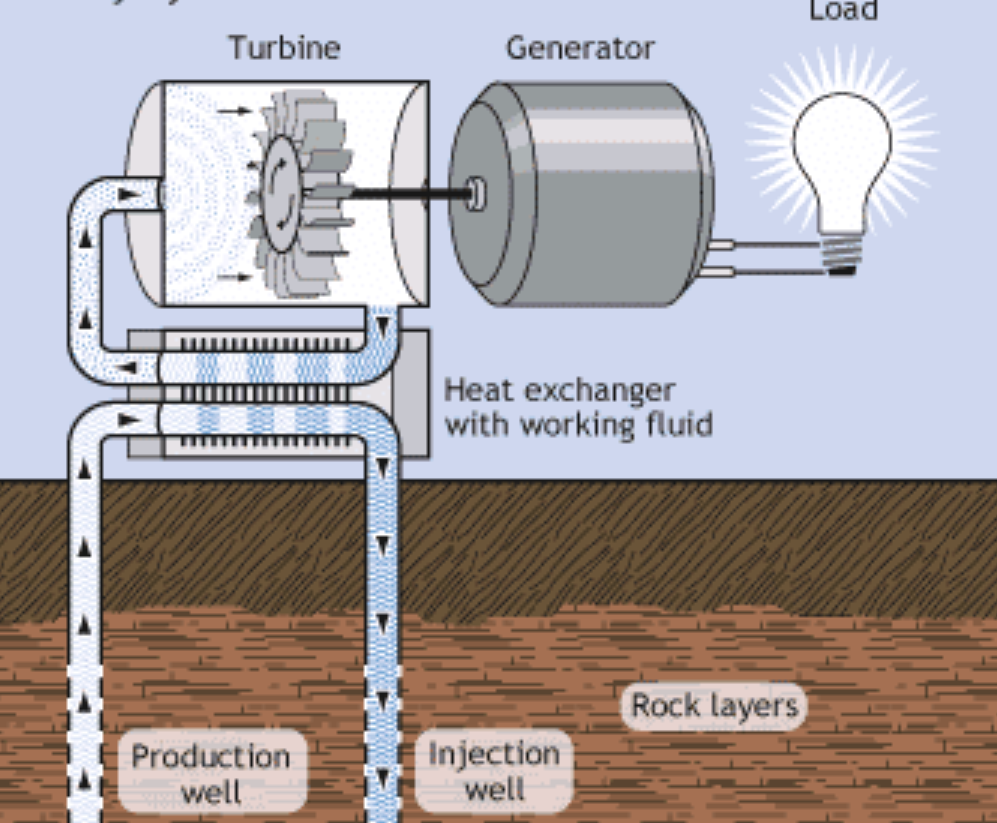
Binary cycle power plants
A type of geothermal power plant that is used if the water that reaches the surface is not hot enough to produce steam. The hot geothermal water alongside a secondary fluid with a much lower boiling point (such as isopentane) is passed through a heat exchanger. The heat from the hot water causes the secondary fluid to flash vapor. The vapor drives the turbine that produces electricity. Isopentane condenses back and is reused again.
Solar Energy
It is a renewable resource that utilizes the sun’s radiation to provide electricity, heat, and other energy services for a wide range of applications.
Sun
It is considered as the largest source of energy.
Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Energy
Converts sunlight directly into electricity using solar panels made of semiconductor materials like silicon. When sunlight hits the solar cells, it excites electrons and generates electric current. The electricity produced is direct current (DC), which is then converted to alternating current (AC) for use in homes and businesses. PV systems can range from small rooftop setups to large solar farms and provide clean, renewable energy without greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
Wind Energy
It is a form of renewable energy that harnesses the natural movement of air in the Earth's atmosphere to generate electricity. It works by converting the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical energy using large turbines with blades that spin when the wind blows. This mechanical energy is then converted into electrical energy by a generator inside the turbine.
Fossil Fuels
It is a natural energy source formed from the decomposed remains of ancient plants and animals buried millions of years ago under layers of soil and rock. Over time, heat and pressure transformed these organic materials into carbon- and hydrogen-rich substances like coal, petroleum (oil), and natural gas.
Coal
It is a solid fossil fuel that is primarily composed of carbon, along with varying amounts of hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. It is a black or brownish-black sedimentary rock formed from the remains of ancient plants.
It is known as the most polluting source of energy and its combustion produces products that contribute to the formation of acid rain.
Natural Gas
A nonrenewable energy resource that is a mixture of naturally occurring, light hydrocarbons composed mostly of methane. They form from the remains of ancient microorganisms, as well as plant and animal matter. It is known as the cleanest of all the fossil fuels.
This is usually trapped in rock formations. To get it out of the ground, experts will drill straight down to where it is thought to be deposited.
Ranks second in its utilization in the Philippines.
Liquefied Natural Gas
The liquid form of natural gas. It takes up less space than its gaseous form and can be easily stored and used for various purposes.
Petroleum
This comes from the Latin words petra and oleum.
It is a natural liquid found deep underground in rock layers. It is mainly made of hydrocarbons, which are compounds of carbon and hydrogen, and include gases like methane, ethane, propane, and butane. It formed millions of years ago from the remains of tiny sea plants and animals that were buried under layers of sediment.
Petra
Rock
Oleum
Oil
RA 8749
Also known as the Philippine Clean Air Act of 1999, it is based on the principle of the right of the people to a balanced and healthy ecology. It focuses primarily on pollution prevention rather than control and provides a comprehensive management program for air pollution.
Ocean
It is a vast body of salt water that covers about 71% of Earth's surface and contains around 97% of all Earth's water. Oceans are continuous and include the major ones: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans.
Freshwater
It is water that has very low concentrations of dissolved salts and is found in rivers, lakes, streams, groundwater, and glaciers.
Groundwater
It is water that seeps into the ground and fills up the open spaces in rocks, sediments, and soil beneath the Earth’s surface.
Zone of Saturation
The zone where all pore spaces are filled with water.
Zone of Aeration
The zone where pore spaces contain air and water.
Water Table
Separates the zone of aeration and the zone of saturation.
Porosity
Refers to the volume percentage of open spaces called pores.
Permeability
It is the ability of solid materials like rocks to transmit water through the pore network.
Spring
It forms when the water table meets the land surface, allowing groundwater to flow naturally.
Hot spring
It is formed when hot groundwater flows to the surface.
Running water
This is surface water that moves from a higher area to a lower area due to gravity.
Surface water
It is the water visible above ground and is an important source for drinking, irrigation, recreation, and habitat for many species.
Stream
Refers to all water flowing into a channel, regardless of its size.
River
It is a large stream that comes from smaller streams called tributaries. They flow towards oceans, seas, lakes, or another river.
Lake
A large inland body of standing water.
Domestic Use
Refers to the use of water for household needs such as drinking, cooking, bathing, washing, gardening, and raising small animals.
Agricultural Use
Refers to the use of water for household needs such as drinking, cooking, bathing, washing, gardening, and raising small animals.
Power Generation
The use of water to produce electrical or mechanical power, such as in hydropower plants.
Industrial Use
The use of water in manufacturing or producing goods and other industrial products.
Aquaculture
The use of water for raising and propagating aquatic organisms such as fish, shrimp, and crabs for commercial purposes.
Livestock raising
The use of water for maintaining and raising herds or flocks of animals for commercial production.
Water scarcity
A condition wherein the demand for water exceeds the available supply.
Water Pollution
The reduction of the quality of water.
RA 9275
Also known as the Clean Water Act of 2004, it provides comprehensive water quality management of all water bodies. It primarily applies to the abatement and control of pollution from land-based sources, such as industrial and commercial establishments, agriculture, and community or household activities. It mandates the protection, preservation, and revival of the quality of fresh, brackish, and marine waters.
Soil
It is formed by the interaction of the parent material (bedrock), climate, time, plants and animals, and topography. It consists of minerals, organic matter, water, and air. It supports the growth of plants. The basic types of this include clay, silt, and sand.
Loam
It is a type of soil made up of a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay particles.
RA 9003
Also known as the Ecological Solid Waste Management Act of 2000. It provides systematic, comprehensive, and ecological waste management policies that ensure the protection of human health and the environment and maximizes the utilization of valuable resources, among others.
Agricultural waste
Includes waste generated from the planting and harvesting of crops, trimming or pruning of plants and wastes, or runoff materials from farms and fields.
Reduce
It means limiting the amount of generation of waste.
Reuse
Refers to the recovery of materials with the intention of using it either in the same or for a different purpose, without changing its physical or chemical properties.
Recycle
It means converting any used material or waste material into a new product that is useful.
Segregation
A phase in recycling that is defined as the practice of separating solid wastes at the point of origin.
Collection
A phase in recycling that is defined as the removal of solid waste from the source.
Composting
Refers to the controlled decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms into a humus-like product.
RA 9512
It is also known as the National Environmental Awareness and Education Act of 2008. The act promotes environmental awareness through environmental education. It mandates the integration of environmental education in the school curricula at all levels—public, private, formal, nonformal, technical-vocational, professional, indigenous learning, and out-of-school youth courses or programs.