special senses
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
3 layers of the eye
fibrous external, vascular layer, inner
Fibrous external layer has?
sclera and cornea
Sclera is a __ _ tissue designed for? what is contained?
dense CT, protection and muscle insertion, type I collagen, fibroblasts, ground substance
3 functions of cornea
protection and support: collagen fibrils type I
helps focus light
enables light to enter (transparant)
how does corena focus light
what endothelium?
it is curved. simple squamous on bototm, stratified on top (epithelim)
Cornea epithelium: keratnized or not> how many layers? shape and feature?
non keratinized, 5 or 6, smooth or flat (transparancy), bowman’s membrane: thick basmeent membrane
The stroma is composed of
uniform layers of ?
This does what and makes it what
what blood suplly
what cell
parallel fibrils, minimizes light scattering, transparanet, avascular, keratocytes
where do cells in cornea get nutirents (3)
oxygen from air, aqueous humor underneath, tears on top
The __ is important for maintaining transparaency with aquaous humor and stroma. how?
water pumped into humor, keeps it transparaent
What produces aqeuous humor, where?
ciliary process in ciliary body
How does aquous humor exit eye
schlemms canal (scleral venous sinus)
trabecular meshwork (holes of endothelium and CT)
Another function of the ciliary body is to ?
keep lens in place: suspensory ligaments
Near and far vision is controlled by the?
ciliary body/muscle
near vision is: muscle contract or relax? ligament contract or relax?
muscle contract, ligament relaxes
Two functions of iris and what acheives it>
control size of pupil: smooth muscle/contractile cells
prevent light from entering fissure: pigmented (melanin absorbs light)
2 muscles taht control dilation/constriction of pupil
dilator pupillae (myoepithelial cells) and sphincter pupilale (smooth muscle)
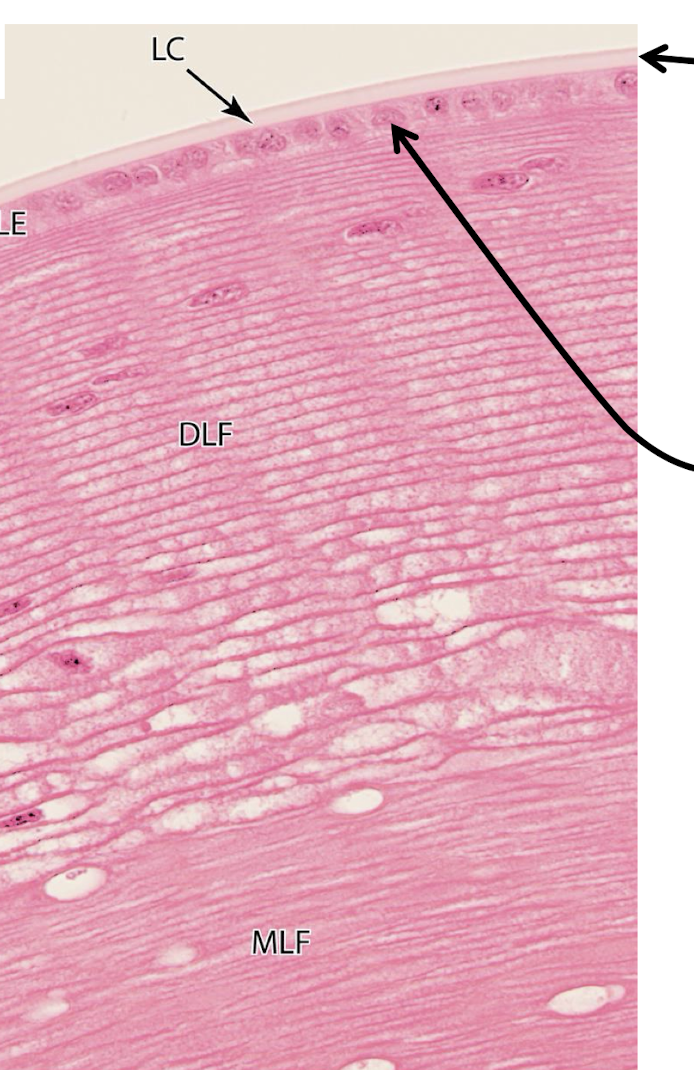
lens capsule: CT type IV
lens epithelium: simple cuboidal
starting at lens capsule: differentiation:
differentating fibers, elongate lose nucleus, gain cyrstallins, mature lens
choroid is?
CT with melanocytes and blood supply for retina
retina has two layers:
retinal pigemented epithelium (melanin), neural retina
cell types in neural retina
rods, cones, bipolar neurons, gnaglion cells, axons to optic nerve
What helps limit the uncontrolled reflection of light within eye
melanin