Cell structure and Function Physiology
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Four basic types of biomolecules/macromolecules:
Carbohydrates → sugars
Lipids → fats
Proteins (made of amino acids) → protein components
Nucleotides → DNA, RNA
Functional groups
Contribute to molecules propensity to undergo specific chemical reactions
Intermolecular Forces
→ how molecules interact with one another in the universe
Carbohydrates are made up of
Composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Three types of Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides
simple sugar → most common is = glucose
Three types of Carbohydrates: Disaccharides
→ formed by covalent bond between two
monosaccharides
Sucrose
Three types of Carbohydrates: Polysaccharides
→ many monosaccharides joined together
Can be broken down into glucose via hydrolysis?
Glycogen
→ stored form of glucose in human body
*Functions of carbohydrates
Protects cell from mechanical damage → carbs in ECM = cushion
Lubrication → carbs present in mucus
Recognition → carbs on surface →unique cellular identity
Adhesion → formation of glycoproteins = cell to cell interactions
Energy source → primary source of energy
Lipids
mostly carbon and hydrogen
Nonpolar(no dipole) covalent bonds (strong &sharing electrons)
hydrophobic
5 classes of lipids
Triglycerides
Ketones
Phospholipids
Eicosanoids
Steroids
Triglycerides
glycerol (3-carbon alcohol → backbone of Triglycerides)
+ 3 fatty acids (long carbon acid chain)
Fatty acid chains
Nonpolar
Hydrophobic → do not mix with polar molecules
Saturated fatty acids → no double carbon bonds
Unsaturated fatty acids → has double bonds
Amphipathic → have polar and non-polar sections → Unique properties
Ketones
Organic compounds with a carbonyl group (C=O) between two carbon
Produced from fat breakdown
Serve as alternative energy sources in ketosis
Ketosis
metabolic state in which body relies on fats as primary fuel source as opposed to carbohydrates
Hydrolysis of triglycerides in adipose tissue
Causes release of FFA’s(Free Fatty Acids) into blood
FFA’s(Free Fatty Acids) are converted to…
ketone bodies in the liver
Acetoacetic acid
energy source during fasting
RBC’s (red blood cells) cannot use ketones
(require glucose)
Phospholipids
amphipathic molecules
Polar head + non-polar tail – amphipathic molecules
Contains two tails → attached phosphate group
Formation of phospholipid bilayer
Critical in establishment of electrochemical gradient
Needed to make ATP
ATP = molecular currency of biology
Eicosanoids
Modified fatty acids
Intracellular communication
Prostaglandins, thromboxane
types of eicosanoids: Prostaglandins
Potent
Act in low concentrations on local targets
Initiate a large array of downstream effects
Inflammation, pain, vasodilation
types of eicosanoids:Thromboxane
Synthesized from platelets
Involved in platelet aggregation (blood clotting)
Steroids
All steroids are derived from cholesterol
Contain four rings
Cholesterol
Important in cell membrane fluidity
Cholesterol = precursor molecule of bile salts
Bile salts
are formed in liver
Help digestion of fats
Ex. of steroids
Estrogen
Testosterone
Aldosterone
Amino acids
u Building blocks of proteins
u Twenty different kinds of amino acids
u Amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds
Polymers
(chains)/multiple of amino acids
Peptides
Generally 2-50 amino acids
Proteins
more than 50 amnio acids
have many functions
Levels of protein structure: Primary structure
Sequence of AAs(amino acids) connected via peptide bonds
Levels of protein structure: Secondary structure
α-Helixes
β-Pleated sheets
Levels of protein structure: Tertiary Structure
Formation of bends and loops in a polypeptide chain
hydrogen bonds
Ionic bonds (strong)
Van der Waals forces
Covalent bonds (sttong)
Cystine R group → formation of disulfide bridge
Levels of protein structure: Quaternary structure
Only exists when there is more than one polypeptide interacting
Ex) hemoglobin
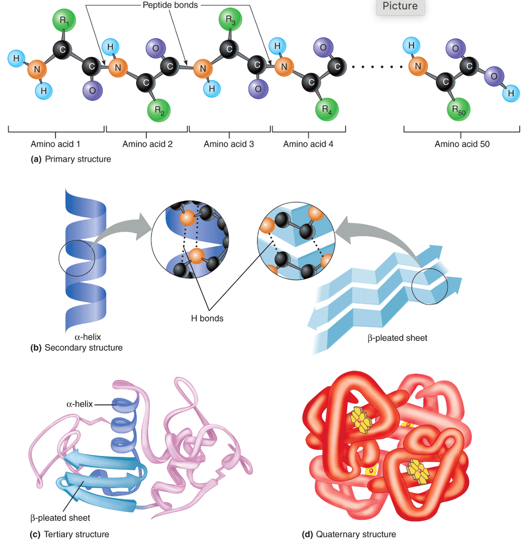
Image of Levels of protein structure
Nucleotide structure
Phosphate group
Five-carbon carbohydrate
Ribose
Deoxyribose
Nitrogenous bases
Pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, uracil)
Purines (adenine, guanine)
Nucleic acids
polymers of nucleotides
DNA
stores genetic code
double stranded
Helix
RNA
Needed for expression of genetic code
usually single stranded
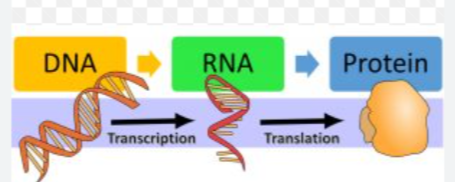
DNA→ RNA→ Protein
Bases: Purines
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
Bases: Pyrimidines
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T)
DNA carbohydrate
deoxyribose
Law of complementary base pairing
A-T (A-U)
C-G
For RNA Uracil instead of thymine (A-U)
RNA carbohydrate
ribose
Different functions of the cell: Movement
muscle cells → sliding filament theory
Different functions of the cell: Conductivity
nerve cells → depolarization
Different functions of the cell: Metabolic absorption
cells taking in nutrients → glucose
Different functions of the cell: Secretion
glands secreting mucus → hay fever
Different functions of the cell: Excretion
elimination of waste materials
Different functions of the cell: Respiration
biological fuel oxidized to make energy → ATP
Different functions of the cell: Reproduction
tissue growth, cells enlarge and reproduce themselves
Different functions of the cell: Communication
cells communicate to one another → chemical signaling
Nucleus
Largest membrane-bound organelle
Cell division → site of mitosis
Controls genetic Information
Cytoskeleton
→ give cells support
Cytoskeleton component: Microfilament
(made up of actin molecules) → smallest
Strands of actin, inter-twined
Actin are involved in → muscle contraction and cell division
Cytoskeleton component: Intermediate filaments
maintain cells structure (anchoring)
Stronger than microfilaments → structural proteins → keratin
Help anchor neighboring cells together, and anchor organelles within cell
Cytoskeleton component: Microtubules
largest
Made up of proteins → alpha and beta tubulin proteins
Involved intracellular movement movement, cell division
Cytoplasm
is an aqueous solution (cytosol)
fluid that fills all the space between all the organelles
Organelles → suspended in cytoplasm → enclosed in biologic membranes
Ribosomes
uRNA protein complexes → found of rough ER
uSite for protein synthesis
umRNA undergoes modifications → 5' cap = necessary for initiation of translation
uPoly-A tail → prevents mRNA degradation
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Network of tubular channels (cisternae)
Smooth ER
synthesis of phospholipids, fatty acids, cholesterol, and steroids
Detoxification of drugs
Rough ER
synthesis of membrane, secretory, and lysosomal proteins
Makes proteins
Packages newly synthesized proteins into vesicles → transport to golgi for processing
Golgi complex
Network of smooth membranes
Processing and packaging of proteins
Proteins get transported throughout cell
Site of post-translational modification
High traffic area of the cell
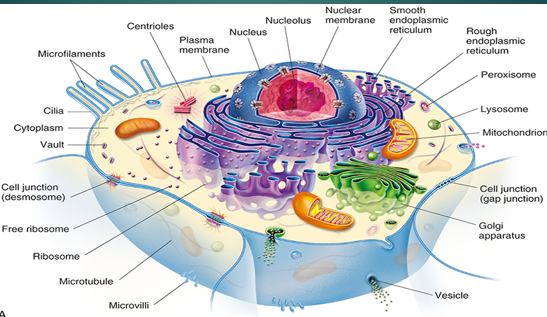
Lysosomes
recycling center of cells
Saclike structures
Contains degradative enzymes (acidic hydrolases) –active in acidic env.
Digest cellular substances into basic forms
Respond to cellular injury → enzyme release → leads to cellular self-destruction
Peroxisomes
Protective roll in cell
Break substances down into harmless products
Similar to lysosomes
Detoxify waste products
Contain oxidative enzymes
Protects cells from hydrogen peroxide → breaks it down
Contains enzyme catalyze
Mitochondria 1
Cellular energy metabolism
ATP generation!
Occurs within inner membrane of mitochondria
Powerhouse of cell
Osmotic regulation
Modulates movement of water and ions
Mitochondria 2
pH control
Buffering capacity → H+ gradient
Contains various buffering molecules (bicarbonate)
Calcium homeostasis
Calcium transport systems → VDCAS (voltage-gated calcium channels)
Regulate intracellular calcium levels
Plasma Membrane Functions
Cell-to-cell recognition → receptors on cell surface
Cellular mobility → fluid mosaic model
Cellular shape → cytoskeletal components
Movement of molecules → protein channels
Plasma Membrane Composition
Basic structure of plasma membrane = lipid bilayer
Various proteins + carbohydrates
Bound to membrane proteins (glycoproteins) and lipids (glycolipids)
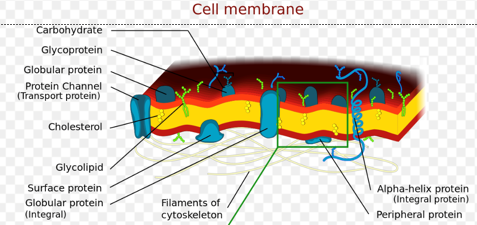
Protein regulation (proteostasis)
Main role is minimize protein misfolding and protein aggregation
Protein regulation (proteostasis) Regulated by:
Ribosomes (makers)
Chaperones (helpers)
Proteolytic systems → set of enzymes and mechanisms involved in protein breakdown
Lysosomes
Ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS)
Helps regulate protein homeostasis
Proteostasis malfunction
associated with human disease
Kuru
Mad disease
Tight Junctions
intracellular adhesion complexes
Connects to adjacent cells together
Limit movement of molecules between intracellular spaces (paracellular movement)
Found in epithelium
Occludins
proteins which link cells together
Integral proteins = permanently attached to membrane
Formation tight junctions
Force special type of transport → transepithelial transport
Transepithelial transport
Direct movement through the cells, rather than between them (paracellular movement)
Desmosome
filamentous junction between cell
Binds cells together for strength
Found in tissue subject to mechanical stress
Enable stretching
Cadherins → proteins within desmosomes
Help make connections within desmosome
Gap Junctions
Channel protein
Permits electrical and chemical communication between cells
Enables ions to move between two adjacent cells
Intracellular signaling
Cells are connected via → connexon → made of connexins = proteins
Gene
Portion of DNA holding genetic code → codes for a proteins
Codons
Genes are read in triplets = Codons
code for specific amino acids
Initiator codon (AUG)
found in every mRNA
AUG
Codes for methionine
Enable translation to start
Termination codons
(stop codons)
UGA, UAA, UAG
Translation stops
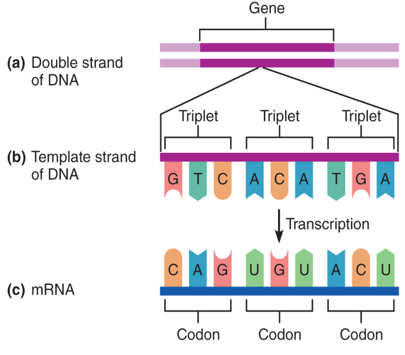
The Genetic code
DNA
Transcribed into mRNA
mRNA translated into protein
A triplet is transcribed into a codon
Code for 20 amino acids
Transcription
DNA is transcribed into mRNA
Primarily Three types of RNA are transcribed:
mRNA: Messenger
rRNA: Ribosomal
tRNA: Transfer
Promotor sequence (Transcription)
DNA sequence before the gene
Initiates transcription of gene
RNA polymerase binds promoter sequence
Initiation of transcription
RNA polymerase catalyzes bonds between nucleotides
mRNA strand is synthesized
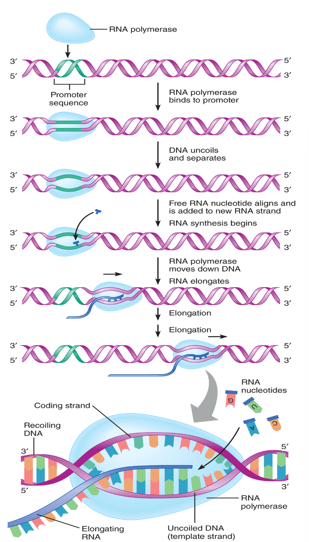
Transcription
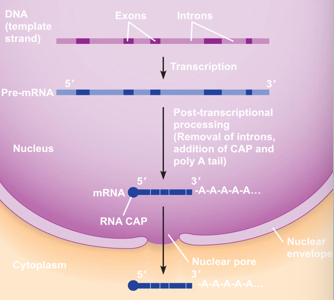
mRNA Processing: Introns
Non-coding regions of mRNA
Excised out of mRNA
mRNA Processing: Exons
Coding sequences
Spliced together
add 5' CAP → necessary for initiation of translation
add 3' poly A tail → protects mRNA from degradation
Mature mRNA
Transported outside of nucleus
Translation in cytosol
Translation
Process of synthesizing proteins
Occurs in cytoplasm
DNA → RNA → Protein
mRNA → carrying code from DNA template
tRNA → transfer RNA → brings amino acid to ribosome during translation
rRNA → ribosomal RNA → makes up ribosome needed for translation
Transcription →
Translation →
Replication →
Transcription → making mRNA from DNA
Translation → making protein from mRNA
Replication → making copies of DNA
Replication
copying DNA
Chromosome
one complete DNA molecule plus associated proteins
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes
One paternal, one maternal
All 23 chromosome pairs make up the human genome
Chromosomes are coiled around histones = proteins
DNA = net
(-) charge