(Parts 9 and 10) Animal Spatial Distribution, Dispersal, and Navigation Mechanisms in Ecology
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
What is Natal Philopatry?
Natal Philopatry is when offspring remain within their birth area throughout their lives, sharing the territory/home range of their parents.
Which types of animals commonly exhibit Natal Philopatry?
Natal Philopatry is found in various species, including birds and mammals, particularly female herd mammals.

What is one cost of Natal Philopatry related to competition?
Increased competition for resources such as food, nest sites, and mates occurs when offspring remain in their natal area.
How does inbreeding relate to Natal Philopatry?
Inbreeding can occur when offspring mate with close relatives, reducing the overall fitness of their offspring due to increased expression of recessive alleles.
What is mating suppression in the context of Natal Philopatry?
Adult breeders may suppress the reproduction of younger conspecifics in the area through various means, including chemical and behavioral methods.
What is one benefit of Natal Philopatry?
Staying in a familiar area can increase an animal's overall fitness by providing advantages in finding resources and avoiding predators.
What are the benefits of Natal Dispersal?
Benefits include decreased competition with relatives, reduced chance of inbreeding, and decreased chance of reproductive suppression.
What are some costs associated with Natal Dispersal?
Costs include increased exposure to new predators and the energy costs of travel, as well as the necessity for sufficient size and strength to leave the natal location.
What is the common trend regarding sex bias in Natal Dispersal?
In many species, males tend to disperse in mammals, while females typically disperse in birds.
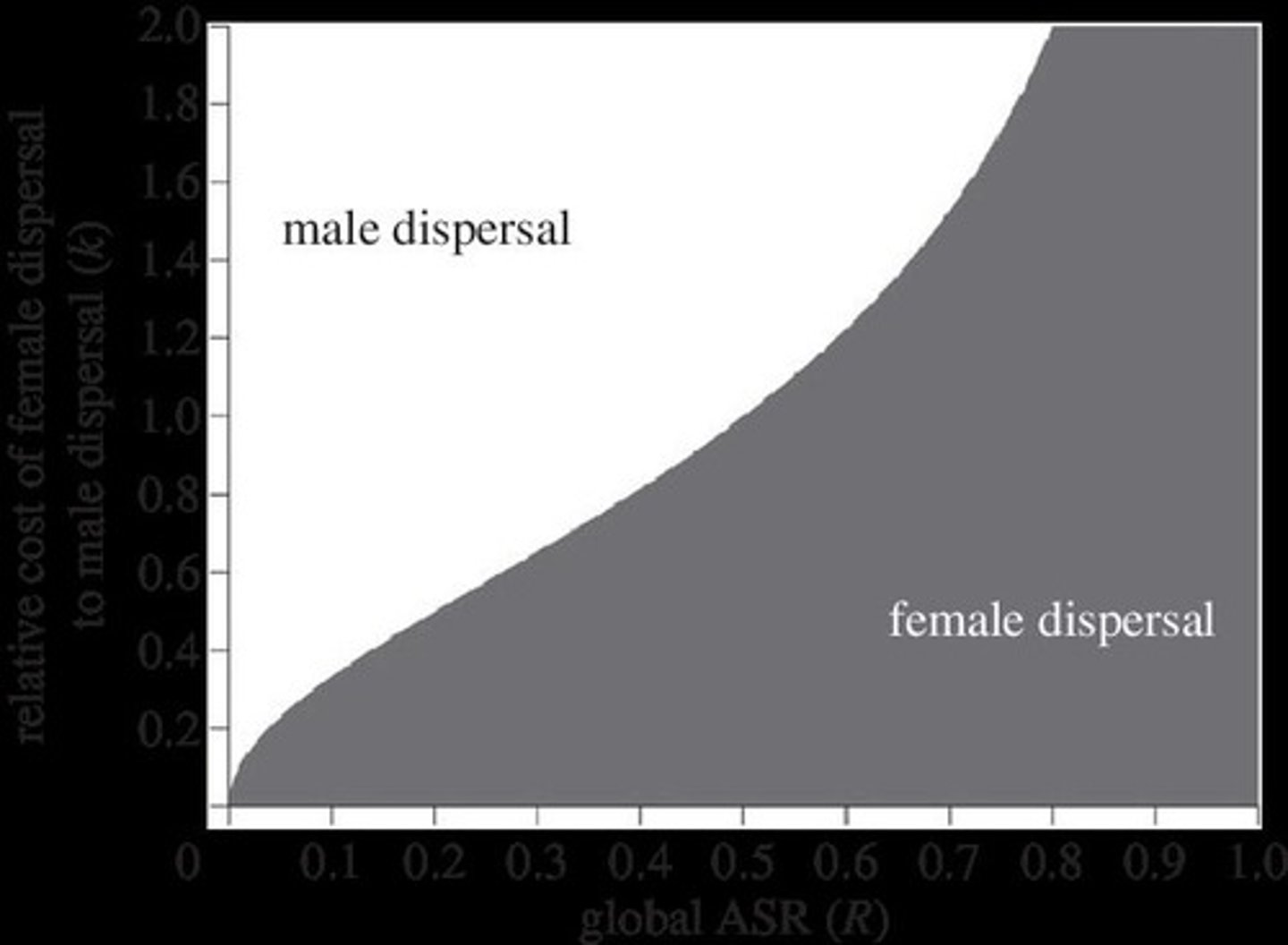
What factors influence whether a species exhibits sexually biased Natal Dispersal?
Factors include inbreeding avoidance, local resource competition, local mate competition, and kin cooperation.
How does inbreeding influence sex bias in Natal Dispersal?
Sex bias may evolve to avoid genetic costs of inbreeding while maintaining species fitness by allowing one gender to remain in a well-adapted habitat.
What role does territory acquisition play in sex bias for Natal Dispersal?
The gender most involved in territory acquisition and defense is likely to stay home, gaining a competitive advantage through familiarity.
In bird species, which gender typically establishes and defends territory?
Males usually establish and defend territory, while fledged females disperse to find mates.
What is mate-defense polygyny?
A mating system where males compete for females rather than territories, leading to dispersal of young or losing males to seek mating opportunities.
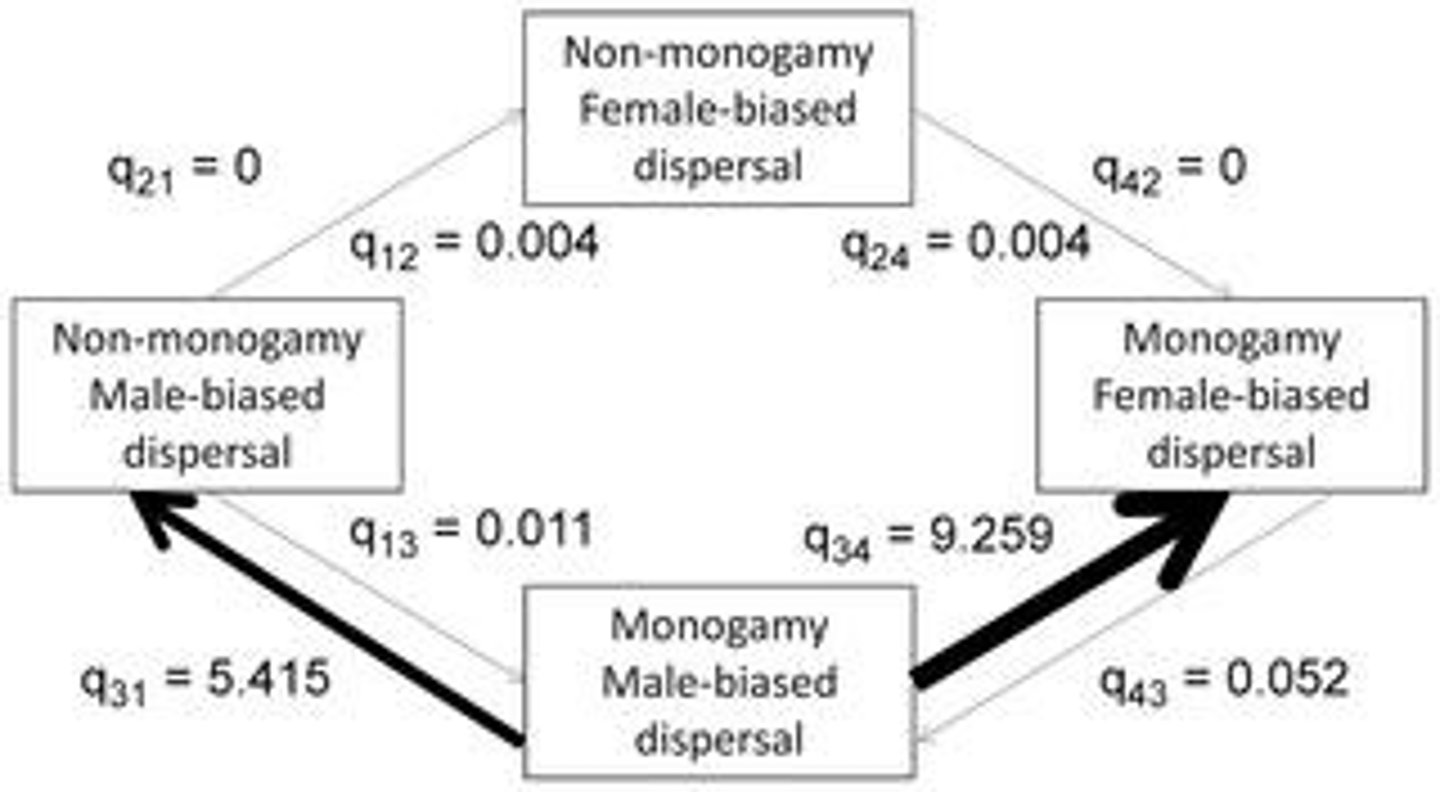
How does resource defense differ from mate-defense in terms of dispersal patterns?
In species that display resource defense, dispersal patterns may vary and not necessarily follow the trends seen in mate-defense species.
What determines which gender disperses in sexually biased Natal Dispersal?
Factors such as territory acquisition, breeding site choice, and the presence of the father influence which gender remains in the natal area.
What happens if the father is present when his female offspring mature?
If the father is present, he has first choice of the breeding site, leading to female dispersal to avoid inbreeding.
What is the advantage of philopatry over dispersal?
Philopatry is often seen as superior because it allows individuals to remain in a familiar and resource-rich environment.
What is the primary gender that typically disperses among mammals, according to the model discussed?
Males typically disperse, as females usually nurse the young and males play little role in rearing.
What is an example of sex bias in natal dispersal?
It is partially based on local resource competition, affecting who has first choice of breeding sites.
What hypothesis suggests that competition for mates influences dispersal tendencies in mammals?
Local Mate Competition hypothesis.
How does the mating system affect dispersal pressure in mammals?
In polygynous species, males compete for mates, leading to higher dispersal pressure on males; in monogamous species, competition is roughly equal.
What is kin cooperation in the context of dispersal?
It refers to cooperation between family members that can make it beneficial to be philopatric, or staying in the natal area.
What is the relationship between social complexity and sex-biased dispersal?
The magnitude of sex-biased dispersal is predicted to increase with greater social complexity in species.
What are the three phases of habitat selection after dispersal?
Search, settlement, and residency.
What does the search phase in habitat selection involve?
The animal looks for a new habitat to settle into.
What occurs during the settlement phase of habitat selection?
The animal establishes its new territory or home range.
What is residency in the context of habitat selection?
Residency is when the animal has become established and lives in its new territory.
What factors do animals evaluate when selecting a new habitat?
Adequate resources, presence of conspecifics, and presence of other species.
How does the presence of conspecifics affect habitat selection?
Conspecifics can indicate the availability of necessary resources, but high density can lead to increased intraspecific competition.
What is public information in habitat selection?
It refers to the information that animals gather about the reproductive success of conspecifics to determine the best nesting sites.
What are the two search strategies animals utilize when looking for new habitats?
The Comparison Tactic and the Sequential Search Tactic.
What does the Comparison Tactic involve?
Visiting several areas, revisiting eligible ones, and choosing the highest quality area.
What is the Sequential Search Tactic?
It involves evaluating an area for acceptance or rejection without returning to previously visited habitats.
What is Natal Habitat Preference Induction (NHPI)?
It is the influence of experience in the natal habitat on habitat selection, helping dispersers find suitable habitats more quickly.
What is migration in animals?
Migration is the relatively long-distance movement of individuals, usually on a seasonal basis.
Which animal groups exhibit migration?
Migration is found in birds, mammals, fish, reptiles, amphibians, insects, and crustaceans.
What can trigger migration in animals?
Triggers can include local climate, food availability, season, or mating reasons.
What factors can trigger animal migration?
Local climate, food availability, season of the year, or mating reasons.
What is true migration?
Movement that occurs annually or seasonally, or involves a major habitat change as part of an animal's life.
What characterizes Two Way Migration?
Involves leaving an area and returning later, often seen in long-living species like the Arctic Tern.
What is One Way Migration?
Migration that involves leaving the home range for a new location without returning, as seen in Pacific salmon.
Define Obligate Migration.
A migration that individuals must undertake, such as the annual migration of wildebeest.
What is Facultative Migration?
Migration where individuals can choose whether to migrate or not, like sexually mature Pacific salmon.
What is Complete Migration?
When all individuals in a population migrate.
What is Partial Migration?
When some individuals migrate while others do not, which can include differential migration based on age or sex.
What is Multigenerational Migration?
A migration that takes more than one generation to complete, such as the migration of Monarch butterflies.
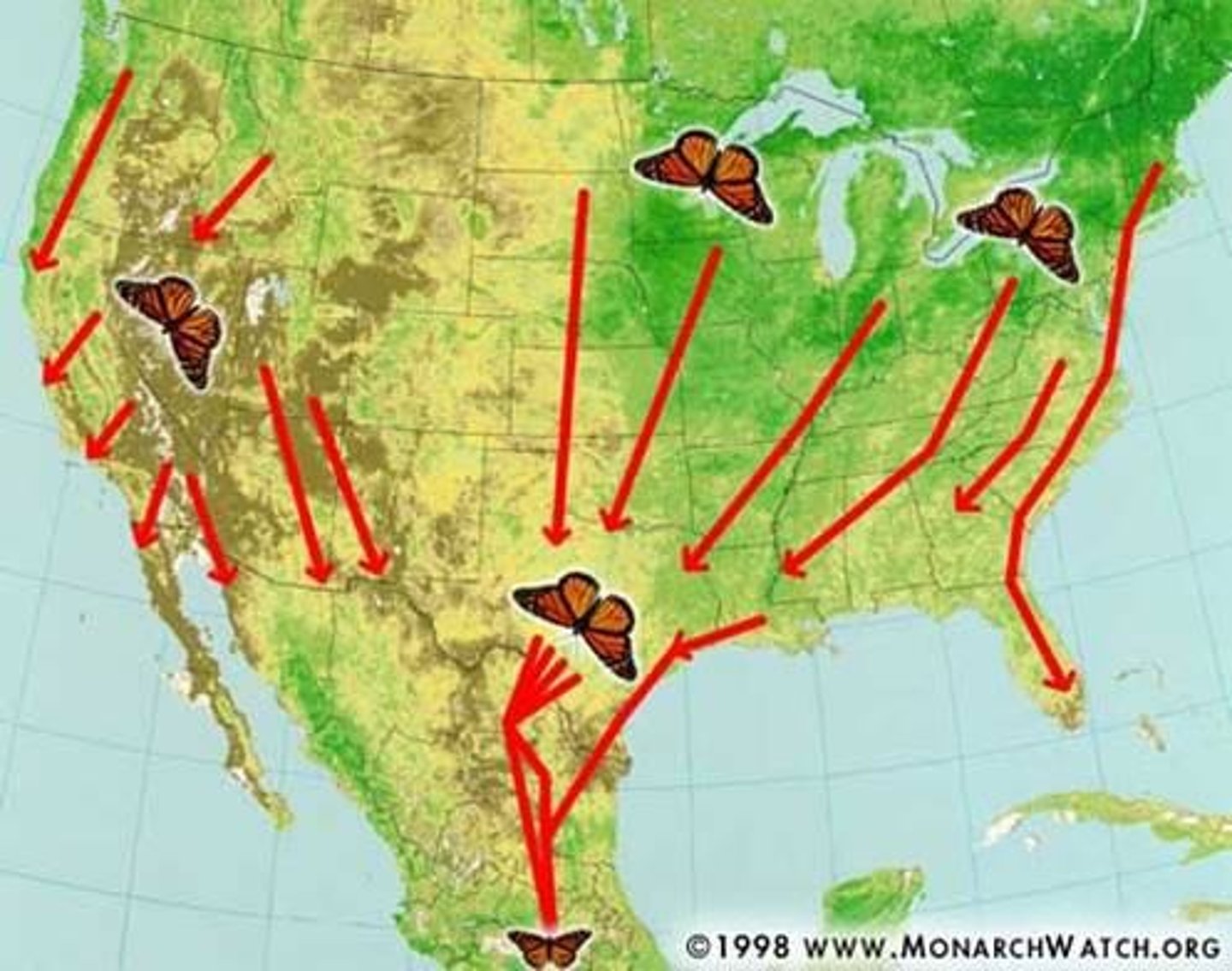
What are Daily Migrations?
Regular migrations that occur within a 24-hour period, like vertical migrations of oceanic species.
What are irregular migrations?
Non-cyclical migrations that can occur due to famine, overpopulation, or other pressures, sometimes referred to as Irruptions.
What are the energy costs associated with migration?
Migration can require large amounts of energy, and many species may not eat or reduce eating while migrating.
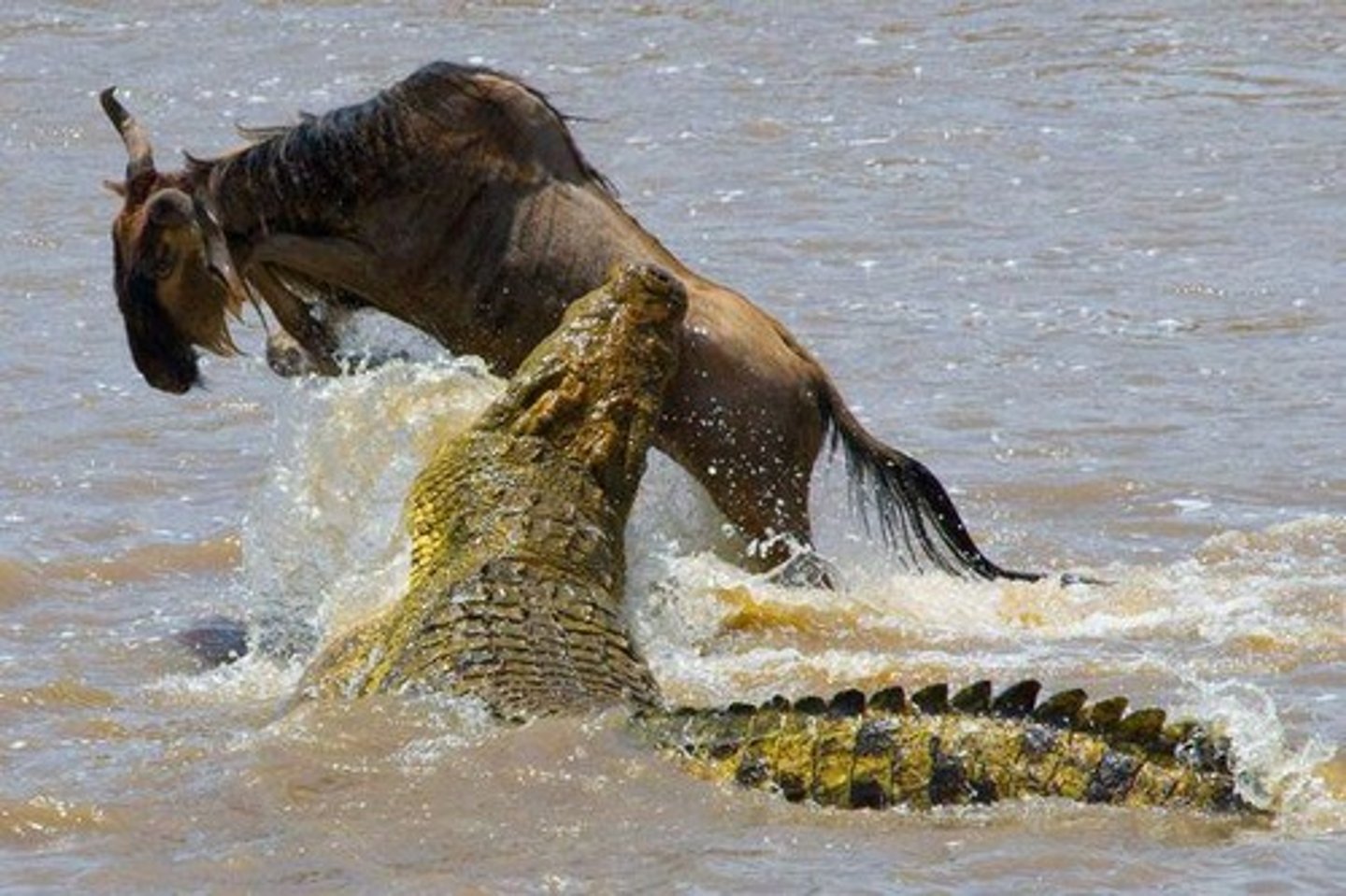
How does migration expose animals to predation?
Migrants may be targeted by predators that wait for them to enter their range, such as Nile crocodiles waiting for wildebeest.

What weather-related risks do migrants face?
Migrants can be adversely affected by shifts in weather, such as early frost or snowstorms that can kill migrating species.
What types of terrains can migrants encounter?
Migrants may cross inhospitable terrains like large bodies of water or deserts, and face obstacles such as mountain ranges or human-made structures.
What are the benefits of migration regarding resource availability?
Migration can lead species from areas with low seasonal resources to areas with high seasonal resources, like American robins migrating south in winter.

How can migration benefit reproductive success?
Many migratory species travel to areas with better resources for raising young, such as Gray whales calving in coastal Hawaiian waters.
How does migration reduce predation effects?
If predators cannot follow migrants, the chances of survival for individuals increase.
How can migration reduce interspecific competition?
Migrating to less densely populated areas can reduce competition for resources during critical life cycle points.
What is piloting in animal navigation?
The ability of an animal to find its way using landmarks, which can be visual, olfactory, or magnetic.
How do black rhinoceroses navigate their territory?
They memorize their home territory to allow for rapid movement despite having poor vision.
What navigational method do salmon use to find their natal streams?
Olfaction.
What is compass orientation in animal navigation?
The ability of an animal to find its way without using landmarks, relying on an external reference system.
What can serve as an external reference system for compass orientation?
Magnetic fields, the stars, or the sun.
What happens to an animal using compass orientation if it is displaced?
It will end up in the wrong location based on its set angle of reference.
What is vector navigation?
An inherited program that tells an animal the compass direction to head in and for how long to travel.
How was vector navigation demonstrated in blackcap warblers?
Offspring of two populations with different migration destinations migrated to a point between the two adult populations' destinations.
What is path integration in animal navigation?
The process by which an animal integrates information on the direction and duration of each leg of an outward journey to return home.
What is true navigation?
An animal's ability to maintain or establish a reference to a goal without using landmarks, also known as homing.
Which animals are known for their ability to true navigate?
Homing pigeons, certain migratory birds, sea turtles, and spiny lobsters.
What is a notable example of a long migratory flight?
Bar-tailed Godwits flying 11,000 km from Alaska to New Zealand.
What are common themes in animal orientation systems?
The use of multiple cues, a hierarchy of systems, and transfer of information among various systems.
How do animals use visual cues for navigation?
By recognizing landmarks that can be stored in memory for later journeys.
What is an example of an animal using visual landmarks?
Digger wasps use visual landmarks to navigate back to their burrows.
How do sand fleas navigate using celestial cues?
They can navigate using the position of the sun, requiring an internal clock to account for the sun's movement.
What experiment demonstrated the sun compass in sand fleas?
Sand fleas were acclimatized to an artificial day/night cycle and then placed in natural sunlight to observe their navigation.
What is the role of an internal clock in navigation by the sun?
It helps animals maintain their circadian rhythm and adjust for the sun's movement in the sky.
What environmental factor do sand fleas use to determine their heading?
Sunlight and their internal clock.
How do sand fleas behave when placed in natural sunlight?
They move roughly 180° in the wrong direction, up the beach instead of down to the sea.
What did Karl von Frisch discover about honeybees?
Bees can identify the direction and range to a food source using a waggle dance.
What is the purpose of the waggle dance performed by honeybees?
To signal the range and direction of a food source relative to the sun.
How do bees navigate back to food sources on overcast days?
They use polarized light to determine the sun's position when it is blocked.
What happens to sunlight as it passes through the atmosphere?
It becomes polarized by particles and water molecules in the air.
What are the two ways polarized light can be used for orientation?
As an axis for orientation and to determine the sun's position when it is blocked.
Which celestial cue do some birds use for navigation?
Stars and the night sky.
What did experiments with warblers in a planetarium demonstrate?
They oriented themselves towards the south and maintained orientation with respect to displayed stars.
What do birds need to navigate by stars?
A built-in ability to read star patterns and an accurate time-of-day clock.
Which animals are sensitive to the Earth's magnetic field?
Mammals like blind mole rats and birds such as pigeons.
How do homing pigeons use magnetic field information?
They rely on it along with other navigational cues, especially when the sun is not visible.
What did William Keeton's research on homing pigeons reveal?
Time-shifted pigeons could not orient correctly on sunny days but could on overcast days.
What are the advantages of using magnetic fields for orientation?
They provide consistent orientation year-round and are useful when visual or celestial cues are limited.
What is the Earth's magnetic field's relationship with the solar wind?
It extends from the Earth's inner core to where it meets the solar wind.
What is the angle of inclination in relation to the Earth's magnetic field?
It is the angle that the magnetic force line makes with the horizon.
Which animals use the angle of inclination as a compass?
Some amphibians, reptiles, and birds.
What is the polarity of the Earth's magnetic field?
The magnetic south pole is negative, and the magnetic north pole is positive.
How do some animals use polarity as a compass?
They can distinguish north from south based on magnetic polarity.
What behavior do cows and wild deer exhibit in relation to the Earth's magnetic field?
They tend to align their bodies north-south while relaxing.
What effect do high voltage power lines have on animal alignment?
Animals do not align their bodies north-south when under high voltage power lines.
What are the two types of inclination in the Earth's magnetic field?
Poleward, where lines of force are steepest, and equatorward, where lines of force are parallel to the Earth's surface.
What tool allows animals to determine their direction towards the pole or equator?
The inclination compass.
Which animal species are known to respond to small differences in the intensity of the magnetic field?
Bees, sea turtles, alligators, and homing pigeons.
How do many animal species use the Earth's magnetic field?
They use it as a magnetic compass to obtain directional information.