anatomy 403: cardio 1
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
cardiovascular system
what does the heart do?
pump to drive circulation
cardiovascular system
what does the vasculature do?
vessels to transport blood
cardiovascular system
what does the blood do?
liquid connective tissue
cardiovascular system
what does the lymphatics?
vessels and organs to return excess intersitial fluid to venous return, and modulate immune responses
cardiovascular system
what are the functions of blood?
transportation, regulation, protection
functions of blood
transportation
____ (respiratory)
____ (digestive)
____ (digestive, respiratory, urinary)
_____ (endocrine) and cytokines
gases, nutrients, wastes, hormones
functions of blood
regulation
_____
_____
_____
pH, temperature, water balance
functions of blood
protection
_____
_____
immune, clotting
physical profile of blood
“thicker” than water
100.4 F
color: red-purple
typically 8%
____ liters
4-6
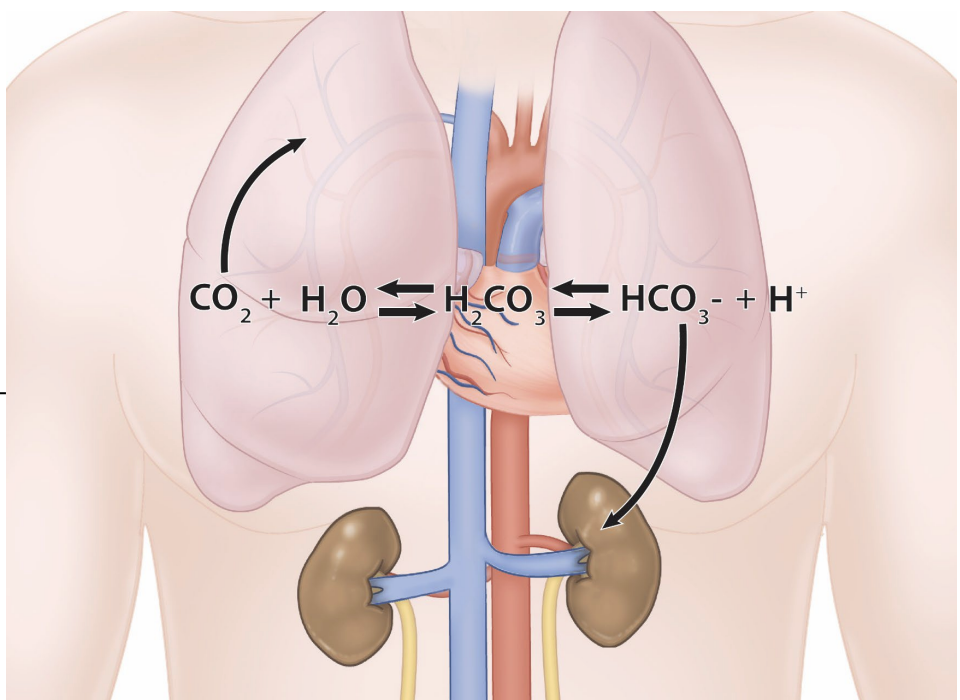
carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer
pH: 7.35-7.45
transportation of CO2
resist changes in pH
lungs clear: _____
tachypnea (>20 bpm)
bradypnea (<12 bpm)
kidneys clear: ______
CO2, H+ and HCO3-
carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer
what molecules do the lungs clear?
CO2
carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer
what molecules do the kidneys?
H+ and HCO3-
carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer
what is it called when you have > 20 breaths per minute?
tachypnea
carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer
what is it called when you have < 12 breaths per minute?
bradypnea
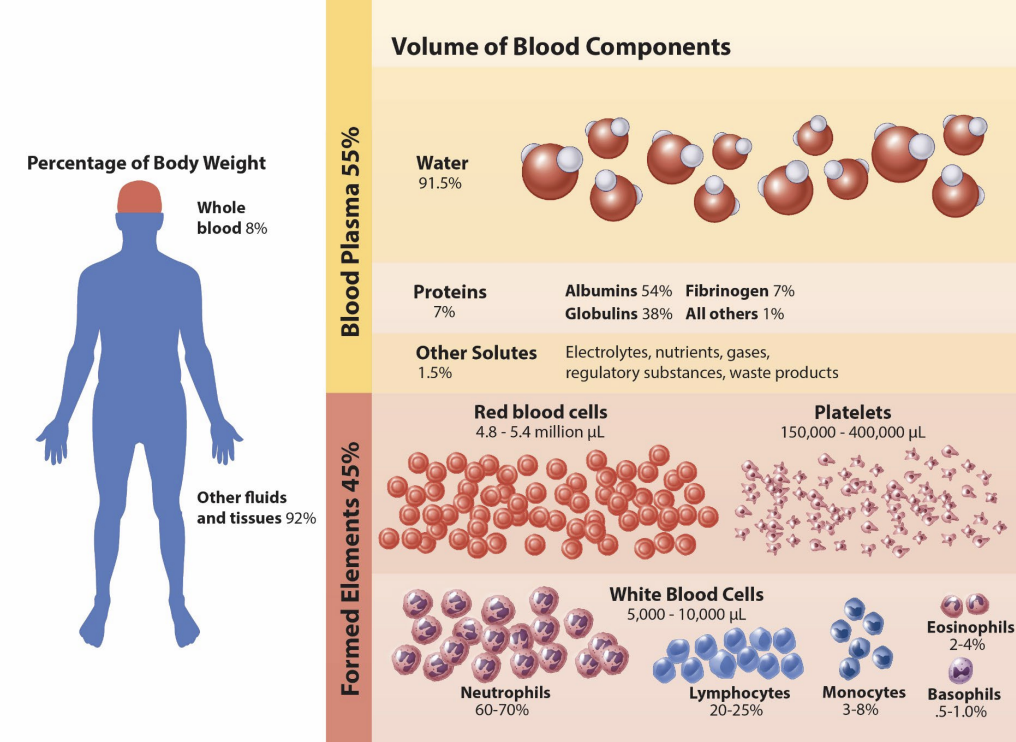
blood components
blood plasma (55%) is the _____
proteins, albumins, globulins, immunoglobulins, and fibrinogens are the _____
solvent, solution
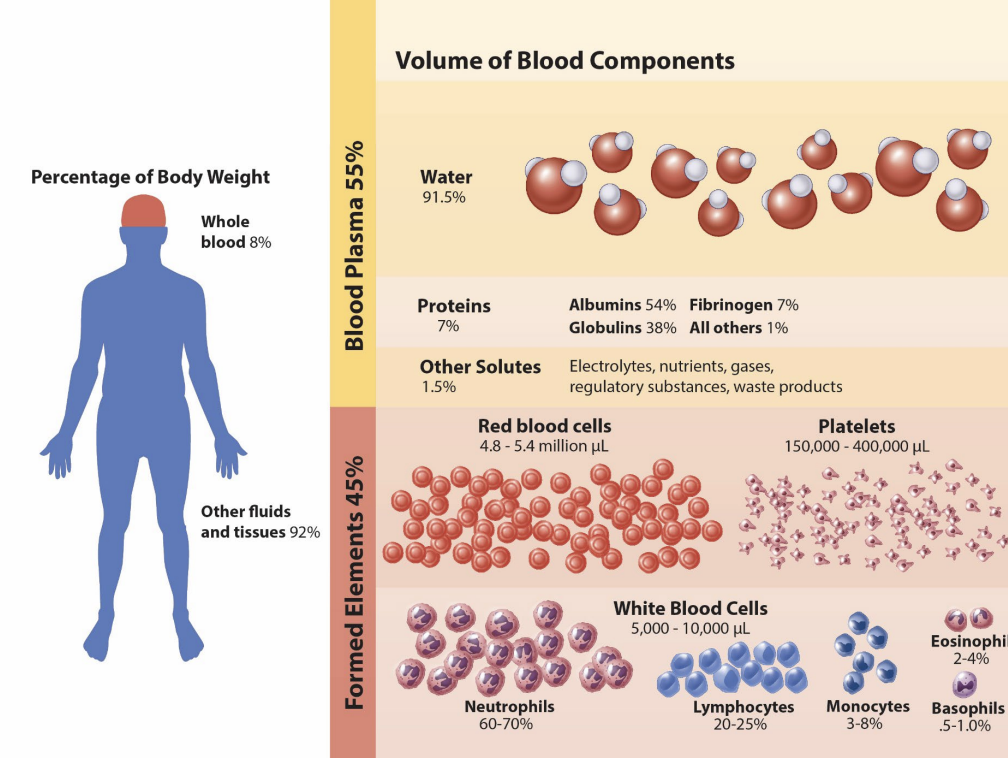
blood components
______
erythrocytes (RBCs)
thrombocytes (platelets)
leukocuytes (WBCs)
formed elements
blood components
what are the three formed elements?
erythrocytes, thrombocytes, and leukocytes
formed elements
what are the leukocytes?
neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils
formed elements: blood smear
what are the 3 cell morphologies?
microcytic, normocytic, macrocytic
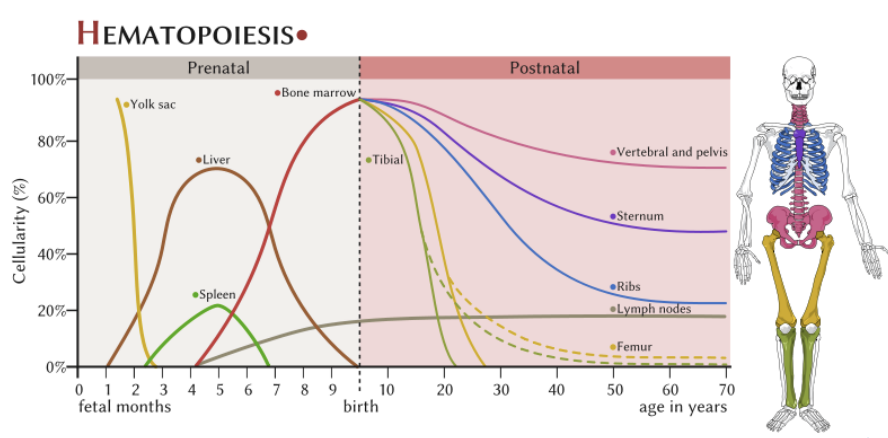
blood cell formation (hemopoiesis)
red bone marrow (hematopoietic connective tissue)
pluripotent stem cells
______: erythrocytes, thrombocytes, granular leukocytes, mast cells, and monocytes
______: agranular leukocytes (minus monocytes)
myeloid stem cells, lymphoid stem cells
cytokines
________
peptides or glycoproteins
act on surface membranes
different than hormones
auto—, para—, or endocrine actions
secreted by most ______ cells
_______ (different effect of different tissues)
ex) interleukin 4 (ILK-4)
B-cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation
T-cell proliferation
mast cell proliferation
may be pathologically dysregulated
hypercytokemia (cytokine storm)
inflammation, system shut down
small signaling molecules, nucleated, pleiotrophic
cytokines
cytokines are _________ of crossing plasma membrane
incapable
hemopoietic growth factors
hemopoietic cytokines
stimulate growth and/or development of blood ________
formed elements
hemopoietic growth factors
colony stimulating factors (CSFs) → myeloids
named for products on growth media
enhance myeloid stem cell _____ and differentiation
mitosis
hemopoietic growth factors
interleukins (ILs)
vast, diverse
mitosis and development of ______ cells
hemopoietic
hemopoietic growth factors
erythropoietin (EPO)
secreted in response to _____ (low oxygen)
erythrocytes
hypoxia
hemopoietic growth factors
thrombopoietin (TPO)
secreted in response to ______ damage
thrombocytes (platelets)
cellular
what are the hemopoietic growth factors?
hemopoietic cytokines, colony stimulating factors, interleukins, erythropoietin, and thrombopoietin
hemoatological malignancies
_______ (~30%)
bone marrow and leukocytes
immature WBCS or poorly developed
_______ (~56%)
lymphatic tissues
_______ (~14%)
bone marrow and plasma cells
leukemia, lymphoma, myelomas
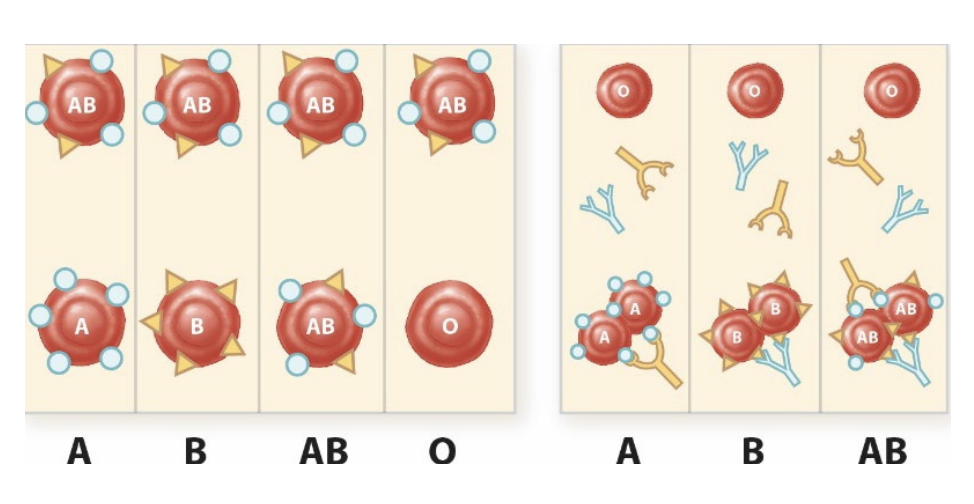
blood group systems
RBC surface “_____” (agglutinogens)
100 genetically identified, 36 recognized systems
ABO → A, B, AB, O
Rh
antigen
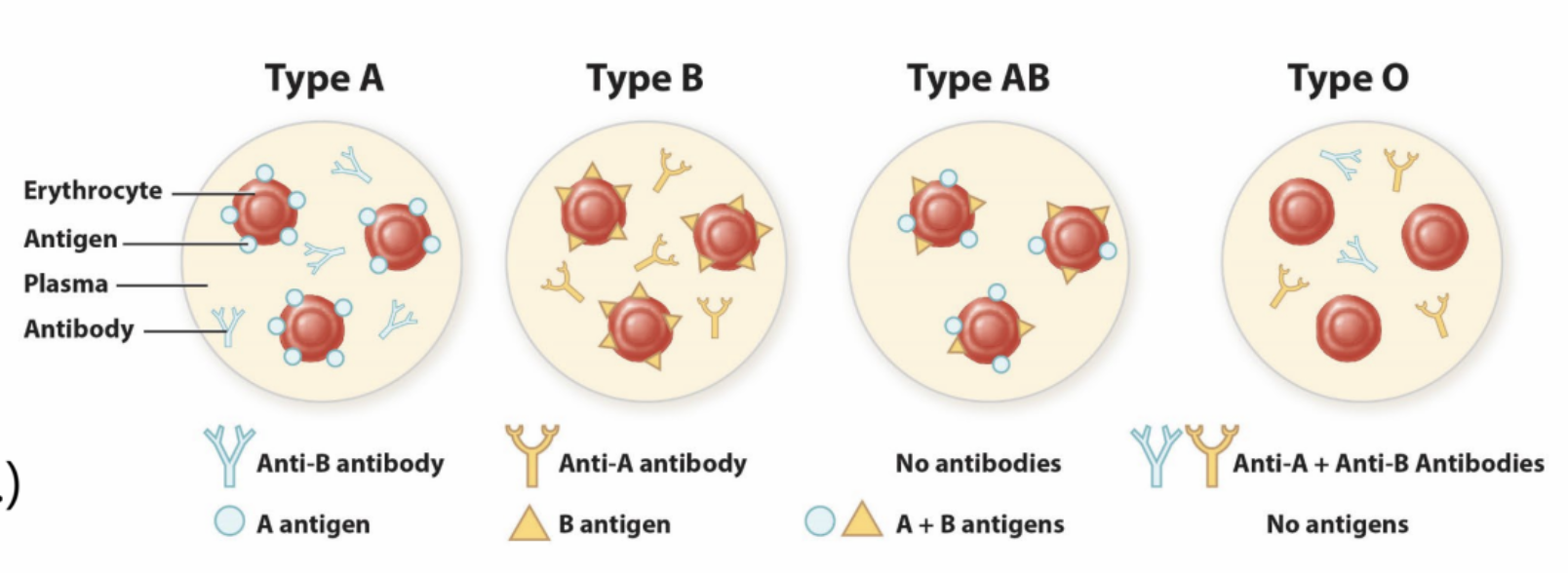
ABO
_______ agglutinogens (antigens)
~80% secretors (saliva, semen, etc.)
_______ (antibodies, IgM) present in plasma
glycosphinogolipid, agglutinins
rh factor
Rh antigens = _________
maternal antibodies (mostly IgG, some IgM)
Rh- lacks D antibody
Rh+ has D antibody
integral membrane proteins
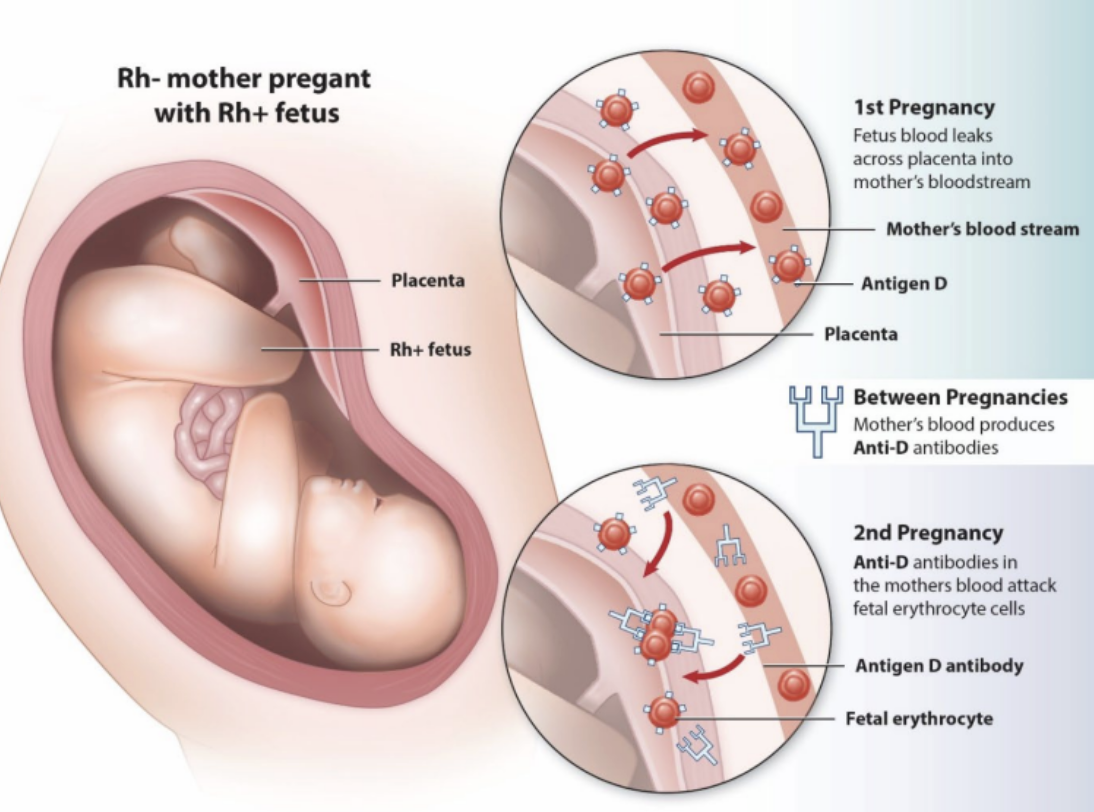
rh factor
hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)
____ fetus in an ____ mother
agglutinination and/or hemolysis
RhoGam is a 20th week intramuscular injection
Rh+, Rh-
rh factor - hemolytic disease of the newborn
1st pregnancy
fetus blood leaks across placenta into mother’s bloodstream
between pregnancy
mother’s blood produces ________
2nd pregnancy
mother’s blood attacks fetal erythrocyte cells
anti-D antibodies
red blood cells (erythrocytes)
4.8-5.4 million RBCs/uL
biconcave discs (d = 7-8 um)
hemoglobin (33% vs. 96% weight)
280 million molecules per RBC
13.5-17.0 g/dL
______ and lack _____
120 day life cycle
anucleate, mitochondria
oxygen
terminal proton acceptor in chemiosmosis (ATP)
necessary for active tissues
______: low oxygen in the blood
______: low oxygen in the tissues
hypoxemia, hypoxia
oxygen
what is hypoxemia?
low oxygen in the blood
oxygen
what is hypoxia?
low oxygen in the tissue
hemoglobin
____ protein
4 polypeptides (HbA = 2 alpha, 2 beta)
____
iron containing pigment
globin, heme
hemoglobin
what are the 3 types of binding for hemoglobin?
cooperative, competitive, and allosteric
hemoglobin
cooperative binding
1 O2 binds, the affinity increases for more O2 binding
O2
competitive binding
CO
allosteric binding
CO2 and H+
nitric oxide (NO)
binds ______ to hemoglobin
elsewhere
hemoglobin
what molecule is involved in cooperative binding?
O2
hemoglobin
what molecule is involved in competitive binding?
CO2
hemoglobin
what molecule is involved in allosteric binding?
CO2, H+, NO
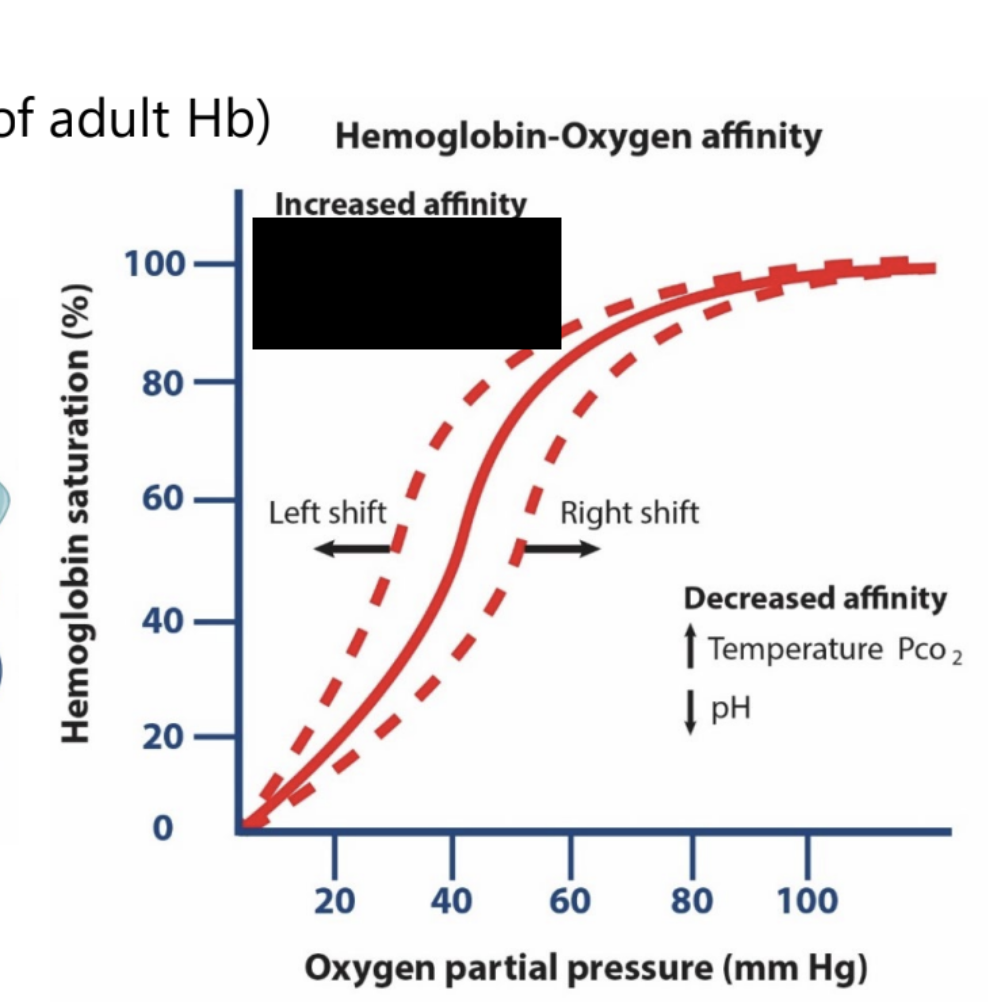
hemoglobin: hemoglobin-oxygen affinity
increased affinity is associated with what changes in the sigmoidal curve?
decreased temperature, decreased PCO2, and increased pH
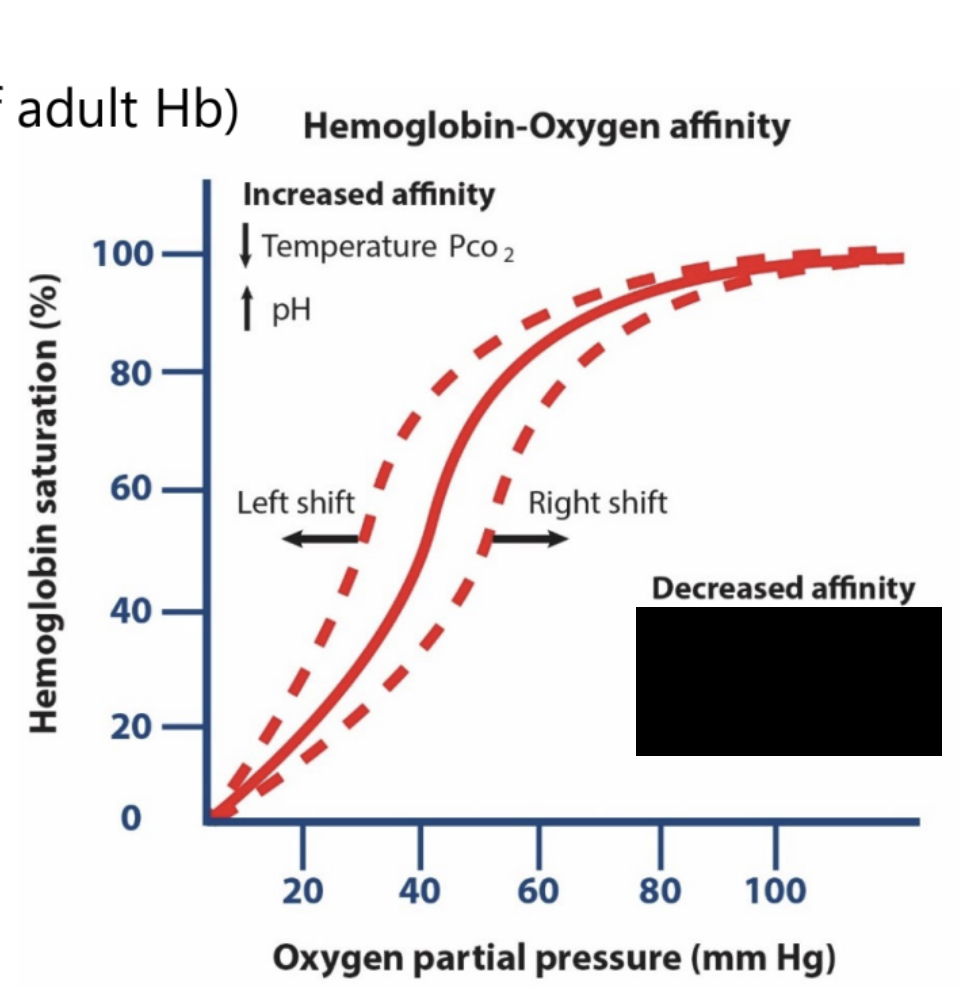
hemoglobin: hemoglobin-oxygen affinity
decreased affinity is associated with that changes in the sigmoidal curve?
increase temperature, increased PCO2, and decreased pH
hemoglobin: hemoglobin-oxygen affinity
increased affinity is associated with what shift for the sigmoidal curve?
left shift
hemoglobin: hemoglobin-oxygen affinity
decreased affinity is associated with what shift for the sigmoidal curve?
right shift
carbon monoxide poisoning
hemoglobin affinity for ____ much greater than for O2
250x more affinity
CO
erythropoiesis
erythropoietin (EPO)
development in adults:
______ (peritubular interstitial cells - fibroblasts)
takes ~10 days to adjust to altitude change
development in fetus:
______ (perisinusoidal cells)
driven by hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) and (EP)
kidneys, liver
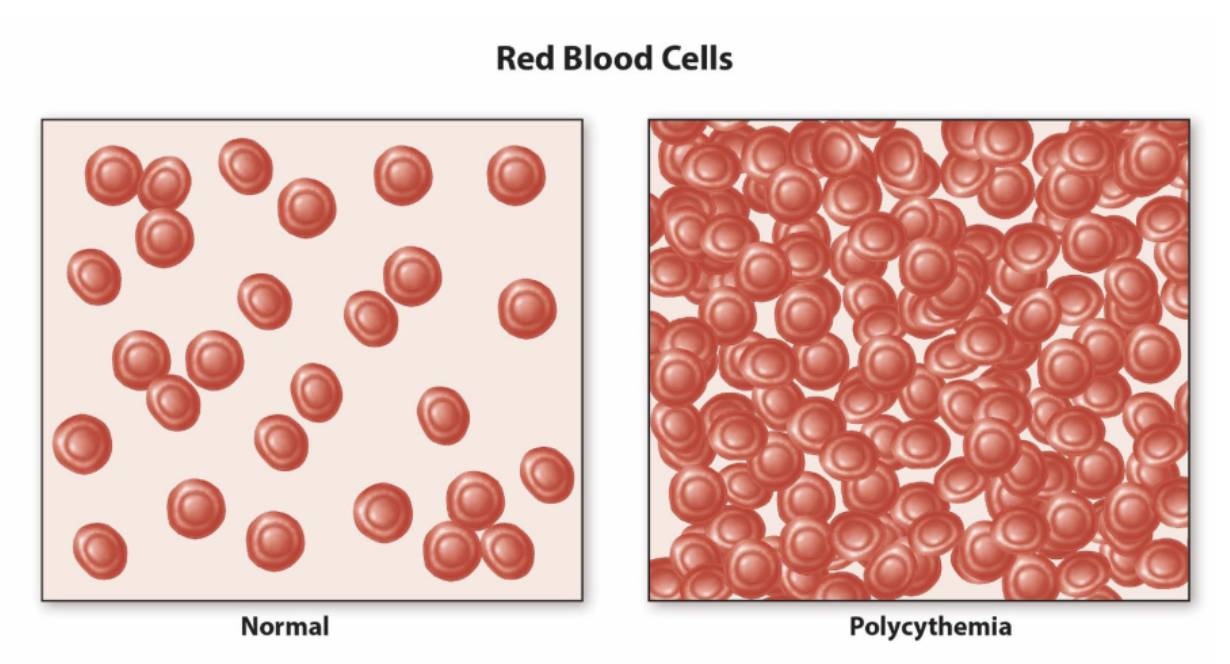
blood doping
_______ EPO
transfusions
homologous
autologous
natural blood doping
______ risk
spontaneous clotting
exogenous, polycythemia
hematocrit
percentage of RBCs of total blood volume
______ < [40-50%] < ______
RBCs or plasma volume
hemorrhage, dehydration, menstruations, etc.
critical
<15% → cardiac failure
>60% → spontaneous clotting
anemia, polycythemia
anemia
_____ oxygen carrying capacity of the blood, decreased hematocrit
various types:
iron-deficiency anemia
megaloblastic anemia (inadequate B12 intake)
hemolytic anemia
aplastic anemia
microcytic anemia
reduced
anemia
what two types of anemia have direct issues with hemoglobin?
iron-deficiency and megaloblastic anemia
anemia
megaloblastic anemia
inadequate ___ intake
pernicious anemia (stomach cannot produce intrinsic factor)
B12
anemia
hemolytic anemia
_____ rupture
plasmalemma
anemia
aplastic anemia
_______ destruction
red bone marrow
anemia
microcytic anemia
____ RBCs
small
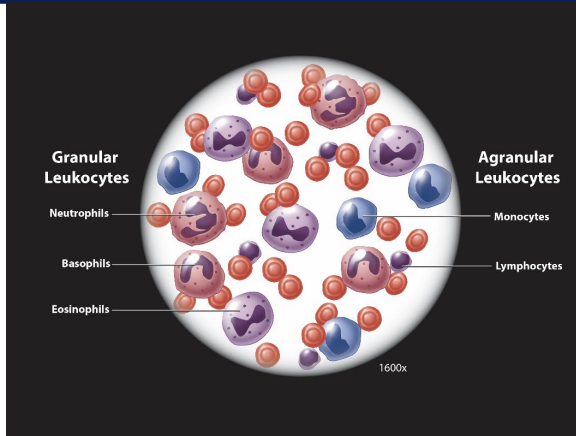
white blood cells (leukocytes)
granular vs. agranular
phagocytosis
chemotaxis and emigration
attracted to/moving toward _____ signal
chemical
white blood cells (leukocytes)
what are granular leukocytes?
basophils, eosinophils, neutrophils
white blood cells (leukocytes)
what are agranular leukocytes?
monocytes and lymphocytes
development
hematoxylin and eosine (H and E staining)
H (basic; blue)
____ and ____
E (acidic; red)
______
nuclei, granules, cytoplasm
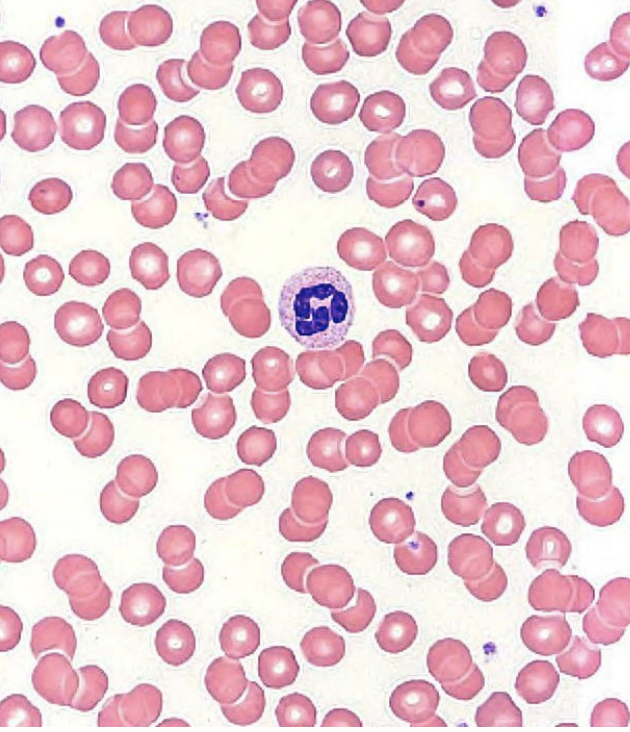
granular leukocytes: neutrophils
no strong dye attraction
2-5+ lobed nuclei
polymorphonuclear leukocytes (polys)
found in blood and tissues
life span: < 1 week
phagocytic and chemotaxic
degranulation
____ and ____
pus
~60% of WBCs (abundant)
lysozyme (bactericidal), non-specific granules
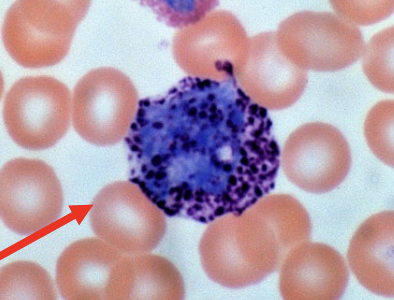
granular leukocytes: basophils
absorb basic stain → blue-purple
2 lobed nuclei
granules obscure nuclei
life span: 1-2 years
chemotaxic
degranulation
_____, _____, and _____
stimulate the formation of IgE on mast cells
anaphylaxis
allergies and ectoparasites
ticks
>1% of WBCs (least abundant)
histamine, heparin, and serotonin
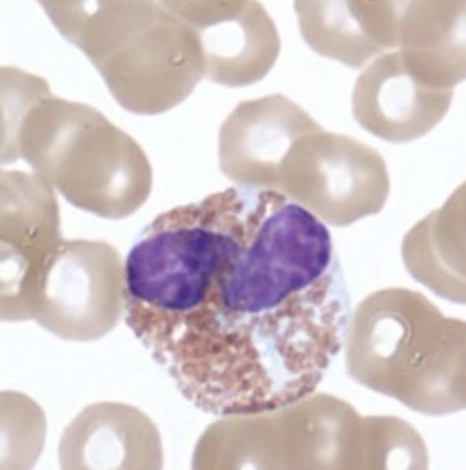
granular leukocytes: eosinophils
absorb eosin stain (acidic) → red/orange
2-3 lobed nuclei
granules do not obscure nuclei
life span < 2 weeks
phagocytic (limited)
chemotaxic
degranulation (enzymes)
_______ and _______
major basic protein
kills endoparasites
~3% of WBCs
histaminidase and leukotrienes
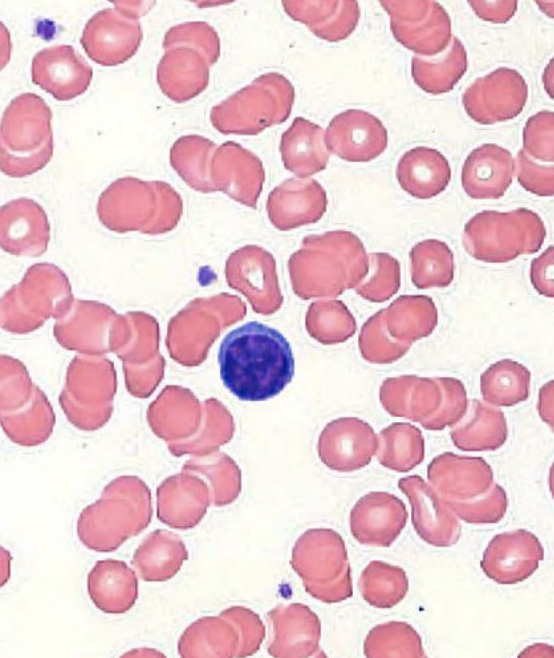
agranular leukocytes: lymphocytes
nuclei round or indented and stain dark
cytoplasm stains blue
acquired immunity
T cells → helper, cytotoxic, suppressor
B cells → plasma cells
innate immunity
natural killer cells
never _______
small (90%) vs. large (10% lymphocytes)
~25% of WBCs
phagocytic
agranular leukocytes: lymphocytes
what cells are part of acquired immunity?
T and B cells
agranular leukocytes: lymphocytes
what cells are part of innate immunity?
natural killer cells
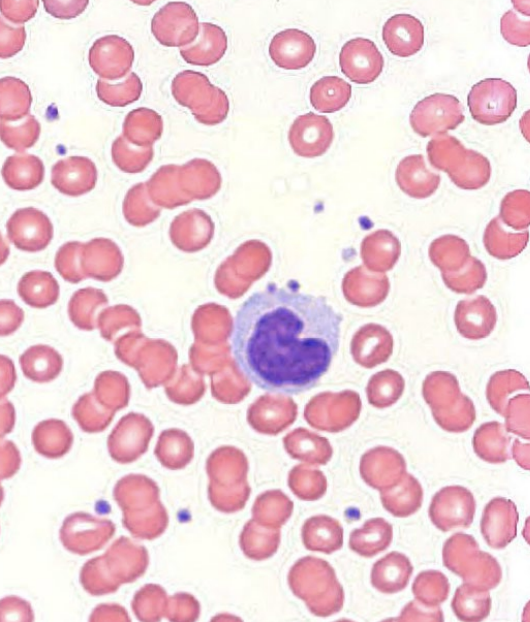
agranular leukocytes: monocytes
U-shaped nuclei
life span: < 3 days in blood, months in tissues
_____ in tissues
fixed or wandering
_____ (skin, mucosa)
antigen presenting cells
innate → adaptive
~10% of WBCs
macrophages, dendritic cells
differential white blood cell count
what is leukocytosis?
high white blood cell count
differential white blood cell count
what is leukopenia?
low white blood count
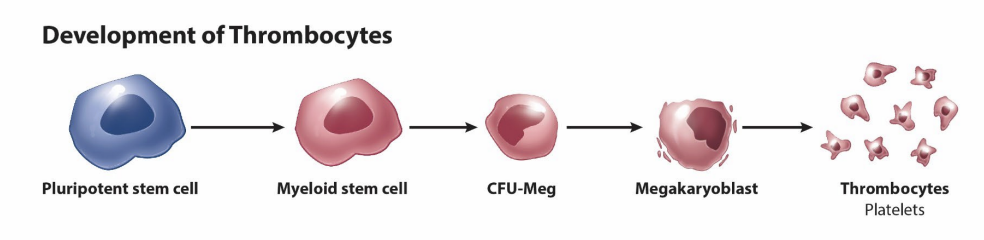
platelets (thrombocytes)
pieces of cytoplasm
anucleate
derived from _______
50 um in diameter
polypoid
proplatelets into marrow sinusoids → platelets
thrombopoietin (TPO)
150-400 k/uL
life span: 8-10 days
macrophages in spleen
megakaryocytes
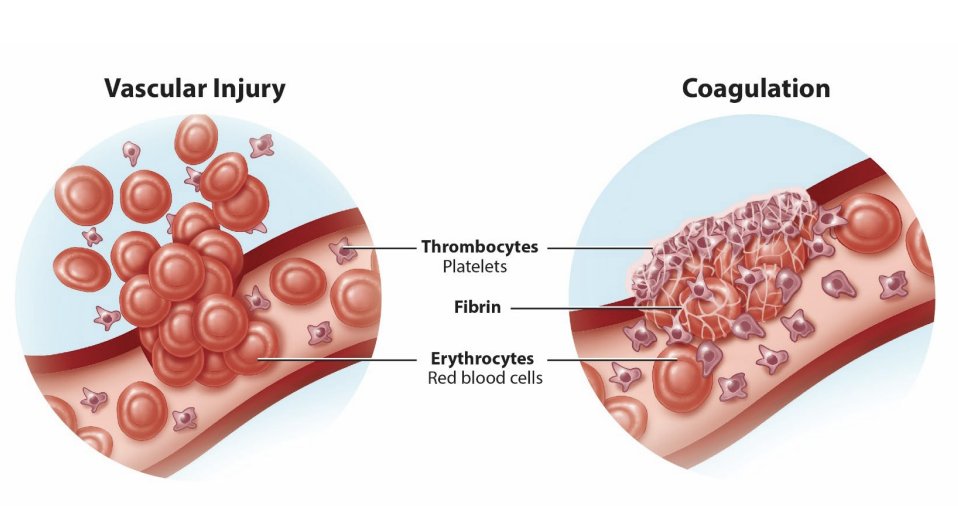
platelets (thrombocytes)
coagulation
______
soluble (in presence of vascular injury) → insoluble (mesh-like network)
platelet activation
contact with ______ and von Willebrand
fibrin
immune responses
inflammation
secrete cytokines
_______
fibrin, collagen, antibacterial