13 (p1). substance-use disorders
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
substance-use disorders (SUDs)
involve self-administration of any of the 10 substances that alters mood, perception, or brain functioning, resulting in substance abuse or substance dependence
psychological dependence
the subjective feeling of needing the substance to adequately function
physical dependence
when the body adapts to the substance’s constant presence
tolerance
requiring more of the substance to experience an effect once obtained at a lower dose
withdrawal
an adverse physiological symptom that occurs when consumption of a used substance is ended abruptly and is thus removed from the body
criteria for all SUDs + the 4 groupings of the 11 symptoms
an adolescent must show 2 or more significant clinical signs of distress for at least 12 months
impaired control (1-4)
social impairment (5-7)
risky use (8-9)
pharmacological criteria (10-11)
what is the most prevalent substance used/abused by adolescents?
alcohol
how does age at onset influence SUD development?
we have an adolescent sensitive period that encourages the dev of risk-taking traits, but they can lead to vulnerability to drug use, which can cause neurobiological changes that further increase risk of SUDs
what is a strong predictor of subsequent alcohol abuse/dependence
alcohol use before age 14
4 categories of causes for SUDs
personality and developmental factors
family history
family functioning
peer involvement
examples of personality and developmental factors
significant adjustments in sleep-wake cycle during adolescence alters reward-related brain functions
critical neurocognitive abilities, like executive functioning and inhibitory control, are impaired by sleep difficulties → increased risk-taking and sensation-seeking
perceiving oneself to be physically older than same-age peers
striving for adult social roles
how connected they feel to their school community
family-based approach to treatment
seek to modify negative interactions btwn family members, improve communication btwn members, and develop effective problem-solving skills to address areas of conflict
multisystemic therapy (MST)
involves intensive intervention that targets family, peer, school, and community systems - ESPECIALLY effective in the treatment of SUDs among delinquent adolescents
parents have step-by-step guidelines for implementing contingency management to control adolescent substance use: familiar cognitive-behavioral interventions like behavioral contacts and contingencies to reinforce abstinence, as well as ways to overcome common roadblocks to treatment
motivational interviewing (MI)
a patient-centered and directive approach that addresses the ambivalence and discrepancies btwn a person’s current values and behaviors and their future goals
Life Skills training
emphasizes building drug-resistance skills, personal and social competence, and altering cognitive expectancies around substance use
SUD in early remission
none of the criteria have been met for at least 3 months but for less than 12 months (w the exception of "craving”)
SUD in sustained remission
none of the criteria have been met at any time during a period of 12 months or longer (w the exception of “craving”)
mild, moderate, and severe criteria
mild - presence of 2-3 symptoms
moderate - 4-5
severe - 6+
CAGE questionnaire + score
C - have you felt you should cut down on your drinking?
A - have people annoyed you by criticizing your drinking?
G - have you ever felt bad or guilty abt your drinking?
E - have you ever had a drink first thing in the morning to steady your nerves or get rid of a hangover?
“yes” = 1 point
0 pts - low risk
1 pt - possible concern, warrants further discussion
2+ pts - indicates a likely alcohol problem; further assessment recommended
3-4 pts - high likelihood of alcohol dependence
CRAFFT questionnaire + when it’s used + scores
used if there’s a problematic pattern of use in 12 months
C - have you ever ridden in a car driven by someone (including yourself) who was high or had been using alcohol or drugs?
R - do you ever use alcohol or drugs to relax, feel better abt yourself, or fit in?
A - do you ever use alcohol or drugs while you’re alone?
F - do you ever forget things you did while using alcohol or drugs?
F - do your family or friends ever tell you that you should cut down on your drinking or drug use?
T - have you ever gotten into trouble while you were using alcohol or drugs?
“yes” = 1 pt
0 - low risk
1 - medium risk; brief intervention and continued monitoring recommended
2+ - high risk; further assessment and possible referral to treatment needed
3 developmental pathways that predict SUDs according to the biopsychosocial model
the enhanced reinforcement pathway
the negative affect pathway
the deviance-prone pathway
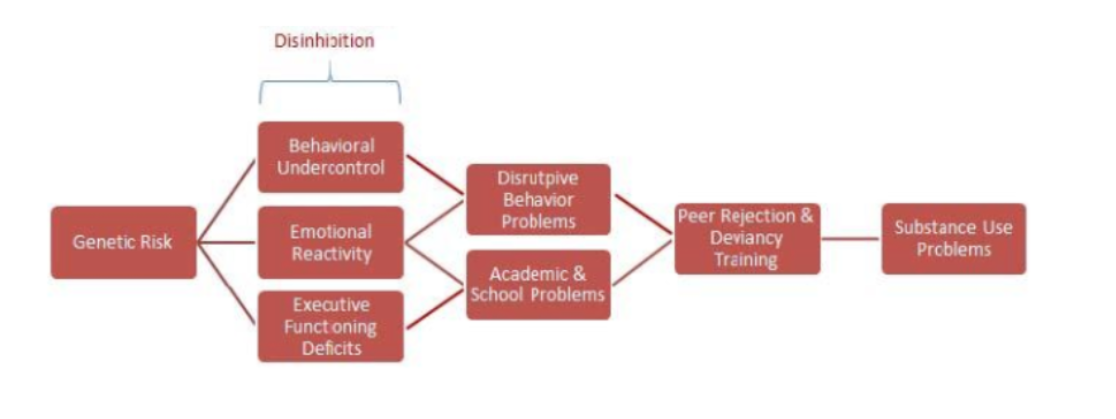
describe the deviance-prone pathway
describe the negative affect model

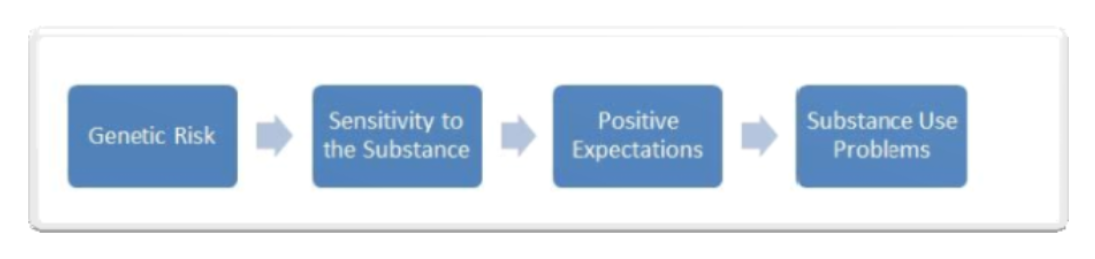
describe the enhanced reinforcement pathway
DARE
school-based program that increases children’s knowledge of substance use problems
primary prevention programs
attempt to stop the problem before it starts via education
secondary prevention programs
attempts to treat the disorder/risk factors that are already there