Immune Organs
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
week 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
The primary lymphoid organs include the_____ ____ and then _____
bone marrow thymus
Where does Tcells originate from and where does it go to mature
originates from bone marrow and matures in the thymus.
The secondary lymphoid organs include the____and _____ ______
Lymph nodes, spleen, MALT
The thymus is located just above the___ and below the ____
heart, sternum
Which of the following is NOT considered a classical immune organ?
A) Bone marrow
B) Thymus
C) Skin
D) Spleen
Skin
What is the primary function of the spleen in the immune system?
A) To produce red blood cells
B) To filter blood and trap pathogens
C) To produce antibodies
D) To store iron
To filter blood and trap pathogens
What happens to T cells in the thymus during negative selection?
A) They are programmed to recognize pathogens
B) They are deleted if they bind too strongly to self-MHC
C) They become double positive
D) They leave the thymus and enter the bloodstream
They are deleted if they bind too strongly to self-MHC
Which of the following is a secondary lymphoid organ?
A) Bone marrow
B) Thymus
C) Spleen
D) Skin
Spleen
What is the role of dendritic cells in the immune system?
A) To produce antibodies
B) To present antigens to T cells
C) To destroy old blood cells
D) To circulate in the bloodstream
To present antigens to T cells
Where does hematopoiesis primarily occur in adults?
A. Thymus
B. Spleen
C. Bone marrow
D. Lymph nodes
Bone marrow
Which process eliminates T cells that strongly bind self-antigens?
A. Positive selection
B. Clonal expansion
C. Negative selection
D. Isotype switching
Negative selection
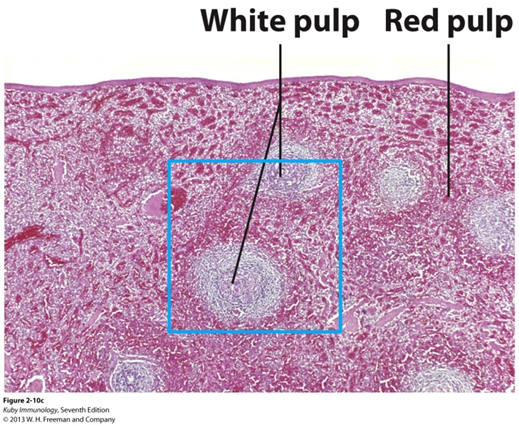
What is the function of white pulp in the spleen?
A. Phagocytosis of old red blood cells
B. Hematopoiesis
C. Site for lymphocyte activation and immune response.
D. Production of platelets
Site for lymphocyte activation and immune response.
What type of T cells emerge from thymic maturation?
A. CD19+ B cells
B. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
C. Natural killer cells
D. Plasma cells
CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
What happens to the thymus as a person ages?
A. It enlarges
B. It remains the same size
C. It involutes
D. It converts to lymph nodes
It involutes