Lecture 1 and 2 - Therapeutic Exercise Foundations
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
What does TBC stand for?
Treatment Based Classification (TBC)
In order to Navigate the TBCs, what do we classify patients based on?
Impairments (Muscle Weakness/Tightness, Joint Stiffness/Instability, Optimal Movement/Non-Optimal)
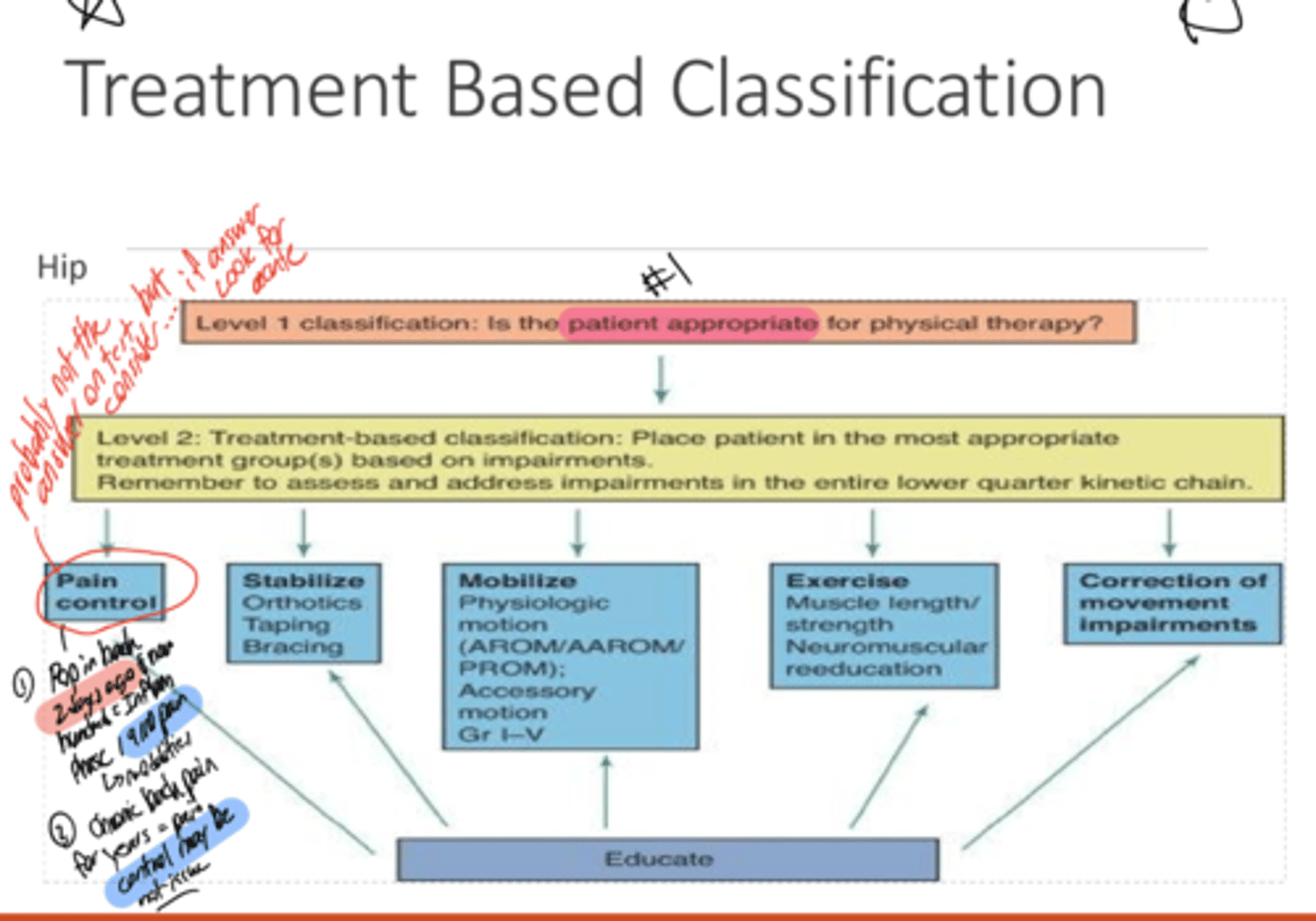
What are the Treatment Based Classifications? (5)
Pain Control
Stabilize
Mobilize
Exercise
Correction of Movement Impairments
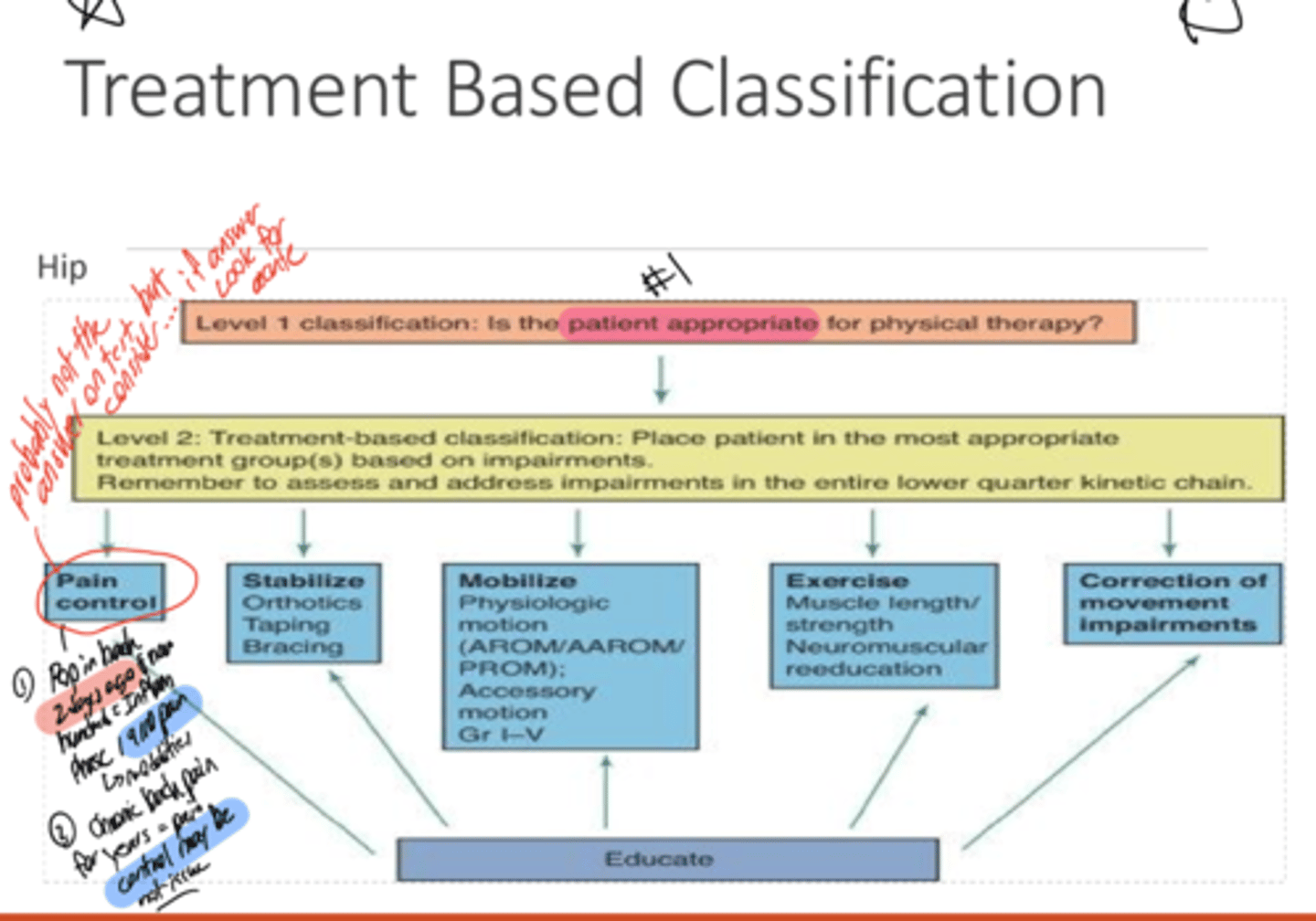
What 2 Main levels are the Rehabilitation Progression Pyramid Separated into?
Function Level (Skill --> Movements --> Synergies --> Balance and Gait --> Motor Function)
Impairment Level (Muscle Performance --> Sensory and Reflex integrity --> ROM and Muscle Length --> Joint Integrity and Mobility --> Posture --> Pain and inflammation)
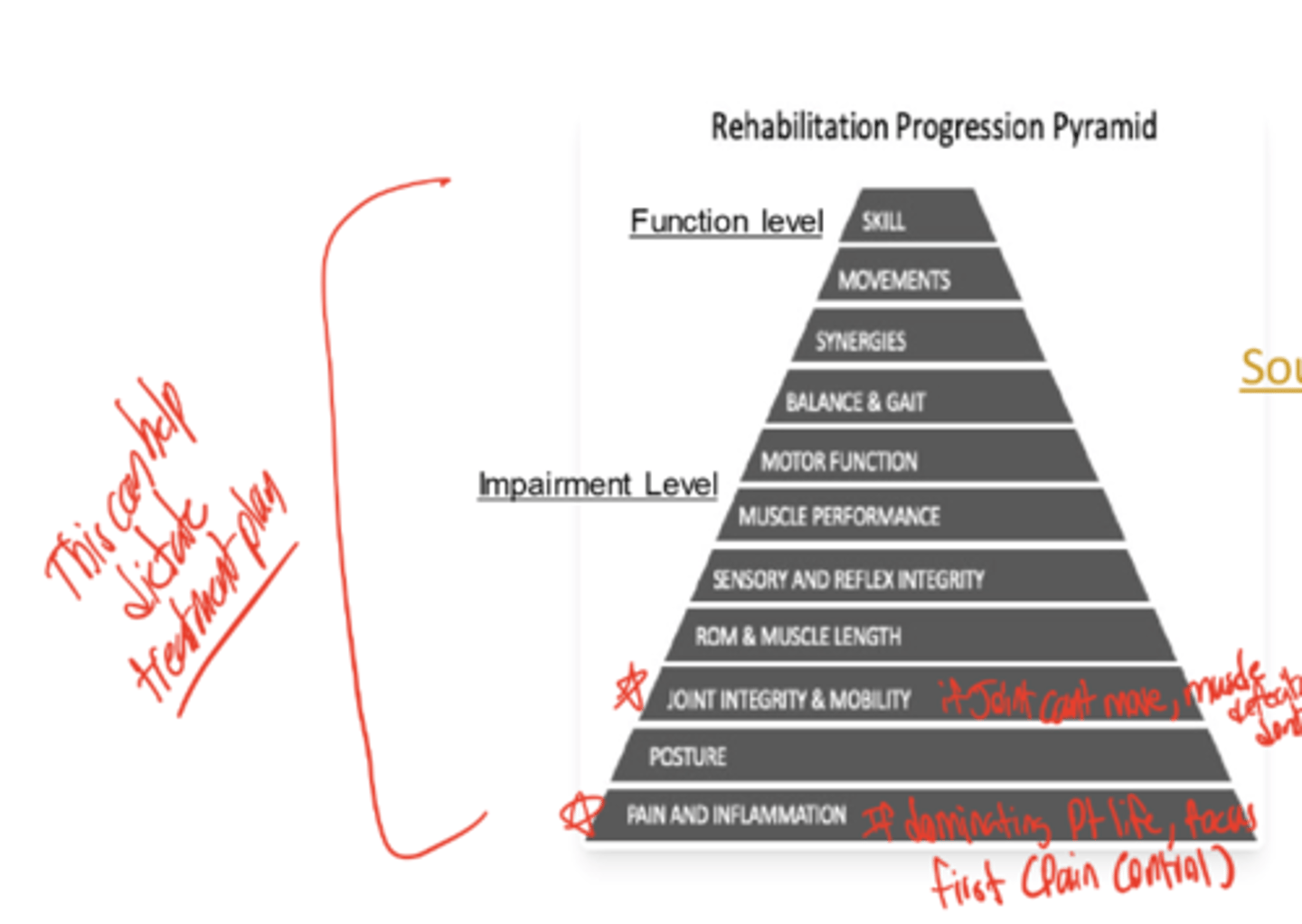
What is the First law of Thermodynamics?
Energy CANNOT BE CREATED OR DESTROYED but TRANSFORMS from one state to another WITHOUT being depleted
What is Anabolism?
Is it Energy Storage or Release?
Give an Example
Creation of Large Molecules from Smaller Ones
Energy Storage
Glucose into Glycogen
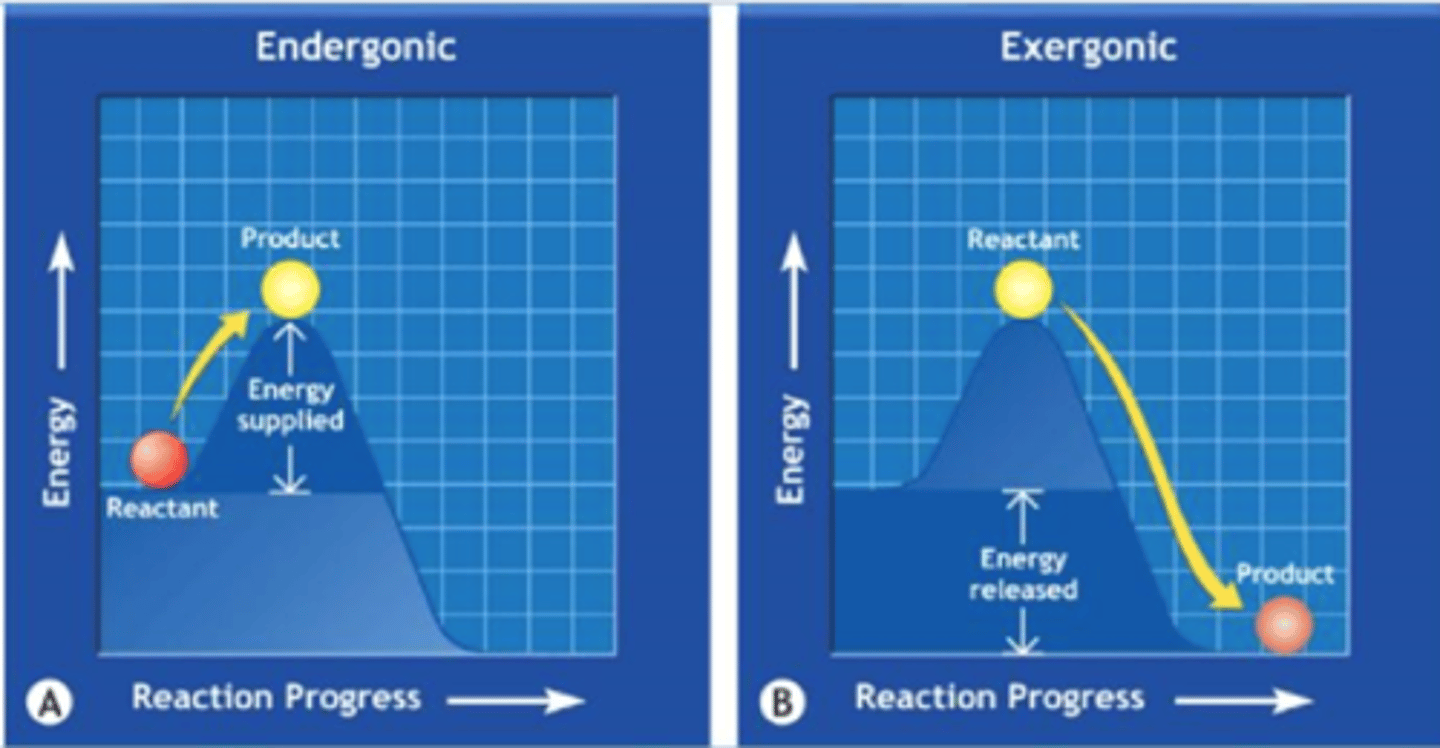
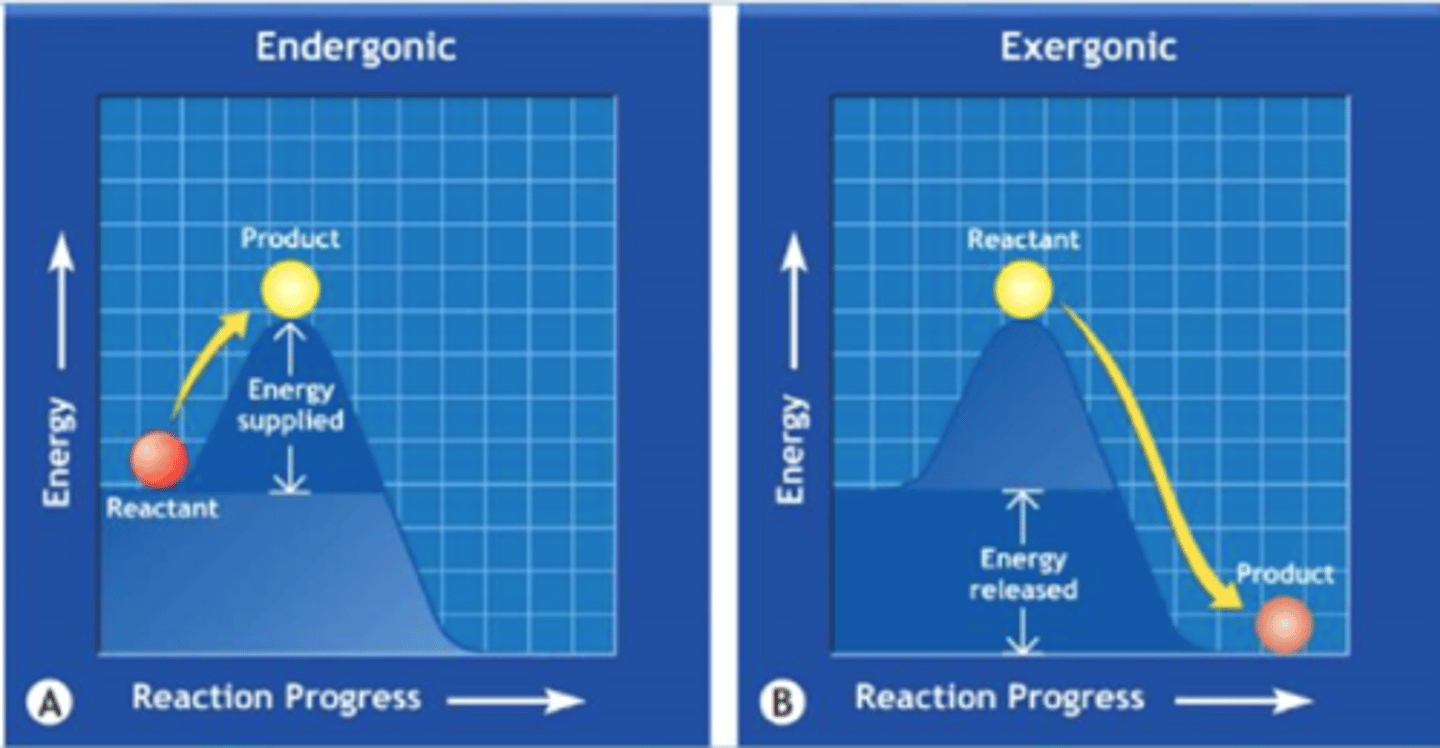
What is Endergonic Reactions?
is it Energy Storage or Release?
Reactions ABSORB OR STORE energy from surroundings
Energy Storage
What is Catabolism?
Is it Energy Storage or Release?
Give an Example
BREAKDOWN of large molecules into Smaller Molecules
Energy Release
Glycogen broken down into Glucose
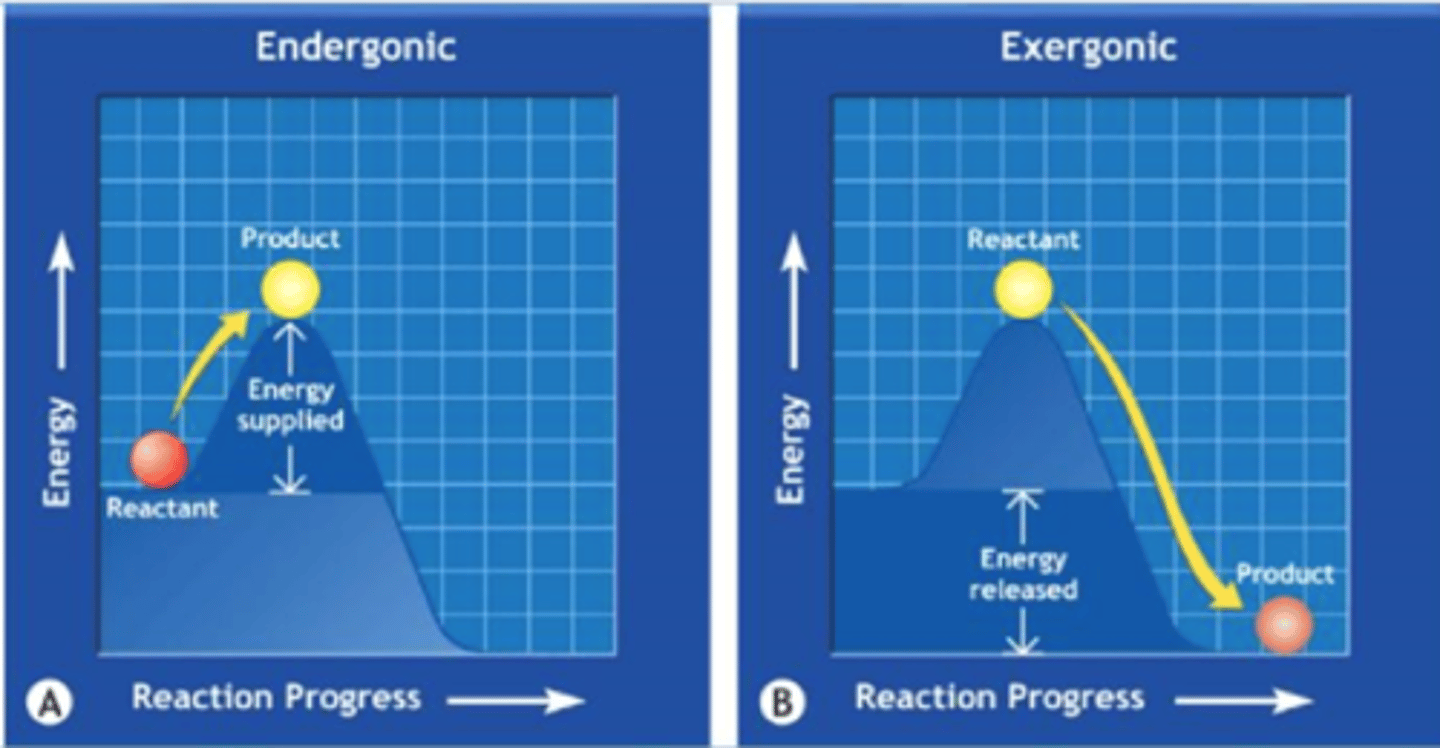
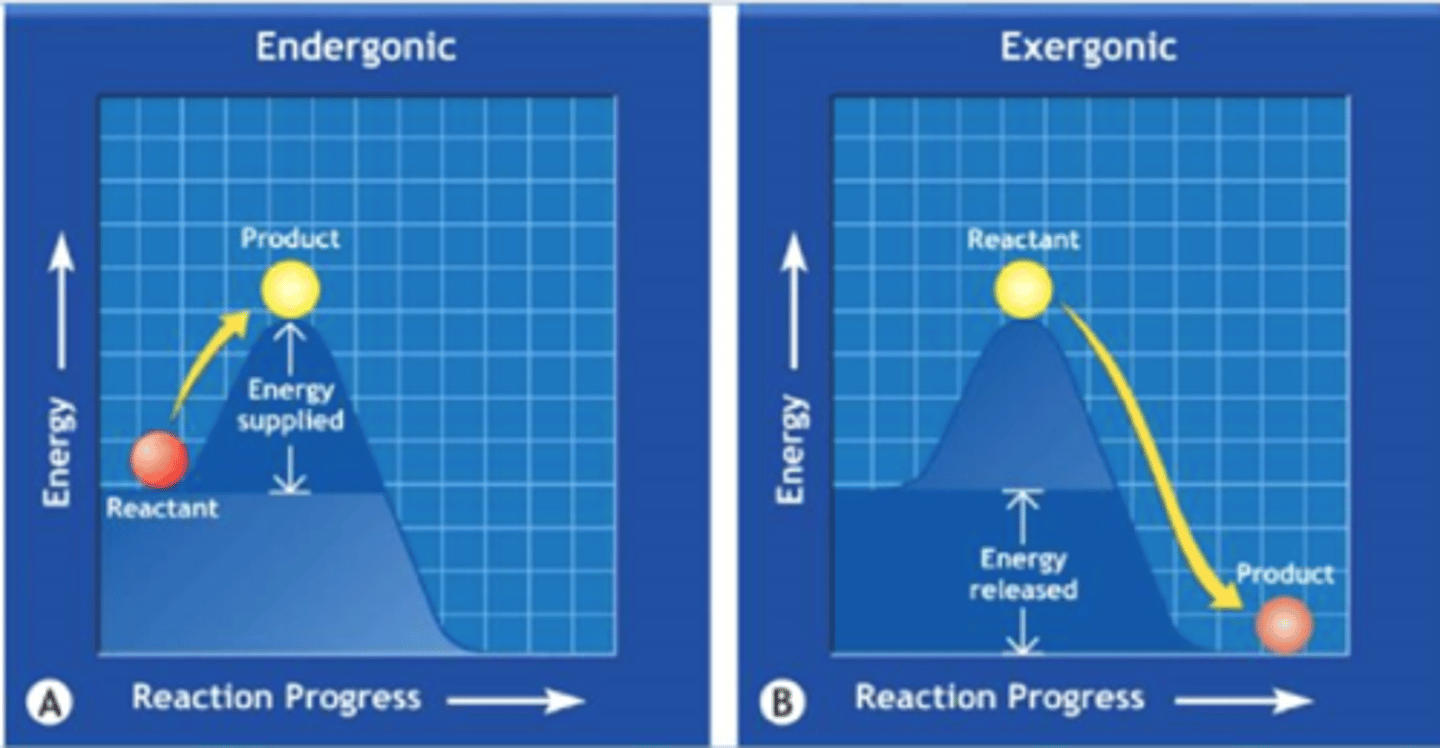
What is Exergonic Reactions?
is it Energy Storage or Release?
Physical or Chemical Reactions that RELEASES energy to surroundings
Energy Release
What process must occur in order for Muscles to keep contracting?
Hydrolysis
What is Hydrolysis?
What do you need?
Breakdown of 1 ATP molecule to create energy
Water
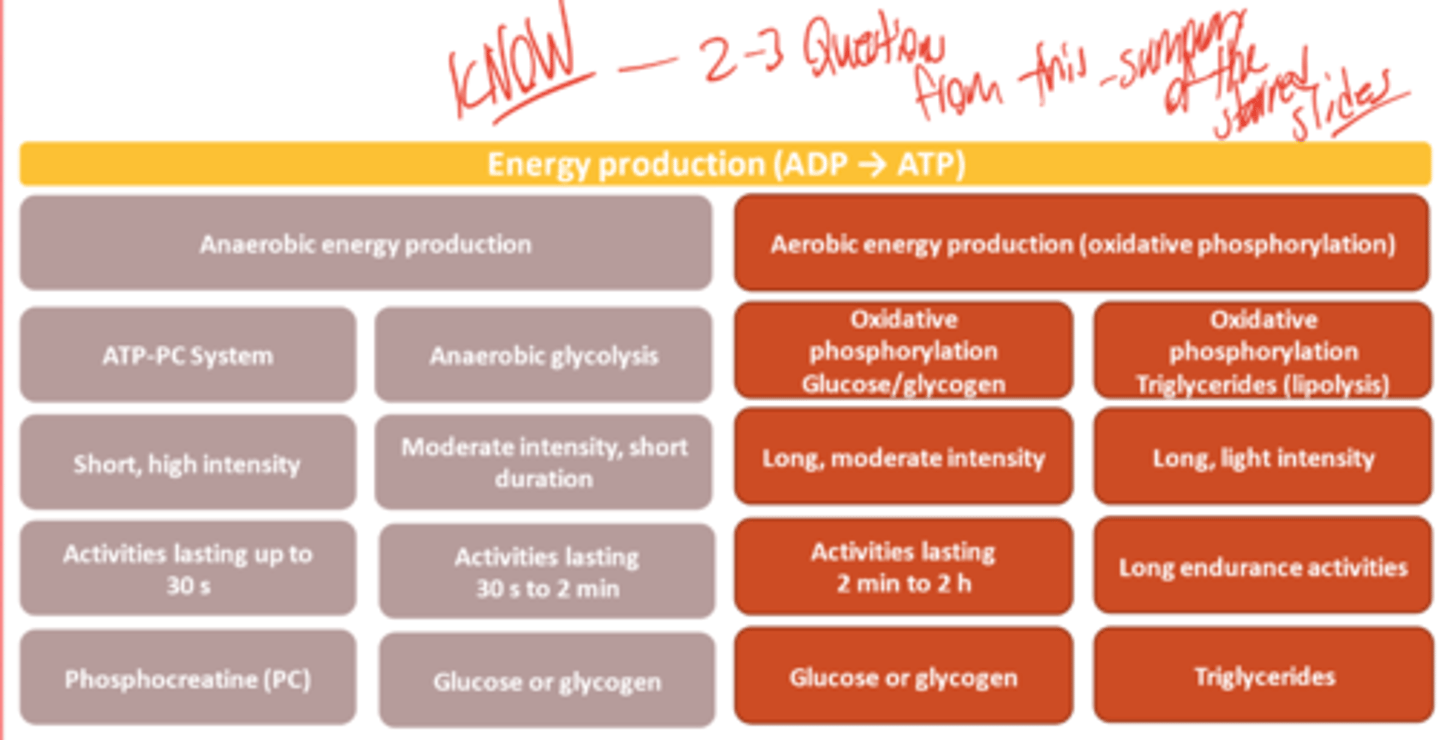
What are the 3 Biological Energy Systems?
Are they Anaerobic or Aeorobic?
Phosphagen System (Anaerobic)
Glycolysis (Anaerobic)
Oxidative System (Aerobic)
For the Phosphagen System
Anaerobic or Aerobic?
Where does it occur?
What intensity of exercise is it used for?
How much energy is created?
How long is it active for?
Anaerobic
Sarcoplasm
Short-term high intensity activities
LIMITED amount of energy
<30 seconds ALL OUT muscular effort
For Glycolysis
Anaerobic or Aerobic?
Where does it occur?
What nutrient gets broken down for create ATP?
How long is it active for?
How much energy is created?
Anaerobic
Sarcoplasm
Carbohydrates (Glycogen STORED in muscles, Glucose DELIVERED in blood)
30 seconds - 2 minutes
Larger amounts, but MADE SLOWER than Phosphagen System
For the Oxidative Phosphorylation
Anaerobic or Aerobic?
Where does it occur?
What nutrients gets broken down for create ATP?
How long does Glycogen/Glucose energy active for?
What activities is this system used for?
Aerobic
Mitochondria
Fats (1st), Carbs (2nd), Protein (3rd)
2min to 2 hours
Long Endurance activities
What are the muscle fiber types?
Do they have high or low oxidative activity, glycolytic activity, and ATPase activity?
Type 1: Slow Twitch (Oxidative Phosphorylation, High Oxidative, LOW ATPase activity)
Type 2a: Fast Twitch Oxidative (High Glycolytic Capacity, High Oxidative Capacity, High ATPase activity)
Type 2b: Fast Twitch Glycolytic (Low Oxidative, High Glycolytic Activity, High Myosin ATPase Activity)
What muscles contain slow oxidative fibers?
Postural muscles due to low force from them
When are type 2a fibers recruited?
POWER activities that require MULTIPLE repetitions
How resistant to fatigue are type 2a muscle fibers?
Relatively resistant
Which fibers are the "middle ground" fibers?
Why?
Type 2a
They are still slow to fatigue like type 1 but can still fatigue fast at the same time like type 2b fibers
How resistant to fatigue are type 2b muscle fibers?
Poor!
Fatigue rapidly
When are type 2b muscle fibers recruited?
High intensity, short duration exercises such as FULL EFFORT SPRINTS
Muscle force is related to what other physiological aspect of muscles?
Cross Sectional Diameter
Muscle Strength is related to what physiological aspect of myscles?
Diameter
Since muscle fiber diameter helps dictate strength, what should occur first before strengthening? (usually)
Hypertrophy
What percentage of intensity should adults train at in order to increase muscle fiber cross sectional area and force production?
60-70%
When it comes to muscle architecture, what does is the relationship between force and cross sectional area?
They are DIRECTLY proportional!
What is the relationship between velocity and excursion (distance traveled) between muscles?
They are proportional to the length of the muscle!
What are muscles with SHORTER fibers and LARGER cross sectional areas designed for?
GIve an Example
FORCE
Glutes
What are the muscles with LONG fibers designed for?
Excursion and velocity!
Movement!
What is the definition of torque?
Ability of force to produce rotation
What is the definition of Force?
Ability to change a state of rest or motion of an object
What is the definition of a Moment Arm?
Length between joint access and line of force acting on the joint
What is the torque formula?
Torque = force x moment arm
What is the length tension relationship?
Ability of a muscle to create force depending on the length of the muscle
What can cause changes to the length tension relationship? (2)
Postural Malalignment
Immobilization
Define Positional Strength
Lengthened muscles that might be interpreted as weak even though they are capable of producing tension at a better range
What are the factors that affect muscle performance? (8)
Fiber type
Fiber diameter
Muscle size
Force-velocity relationship
Training Specificity
Neurological Adaptation
Muscle Fatigue
Muscle Soreness
What is the timeframe for Neurologic Adaptation?
2-4 Weeks
When it comes to Muscle Fatigue, what is resistive exercises limited to?
Form Fatigue
Wolfs law is adaptation of what tissue type?
Bone
David's law is adaptation of what tissue type
Soft tissue
Rapid increases in strength after introduction of new exercises is due to what?
Neurological Adaptation and Motor Learning
What can interfere with proper nervous system control?
Bad instruction
Bad monitoring
Define Muscle Fatigue
Defined as reversible decrease in contractile strength that occurs after long lasting or repeated muscular activity
What can muscle fatigue lead to?
Injury!
What type of muscle contractions can cause DOMS?
When does this occur?
For how long?
Eccentric Contraction
2 Days Later
7 Days
What is important to understand about "Work" during Isometric contractions?
There is NO work being performed
Work = Force x DISTANCE
What are the characteristics of Isometric Contractions?
Static
No Joint Movement
No muscle length changes
Important for function
Isometric Contractions are important to maintain strength during _____________
Immobilization
Isometric Exercises are good for what type of purposes?
Strengthening weak points in ROM
Muscle Re-Ed Purposes
Stabilization Programs
Isometrics should be done cautiously with people who have what condition?
HTN
Cardiovascular Disease
In concentric contractions internal force is greater or less than external force?
Greater
In eccentric contractions internal force is greater or less than external force?
Less
Compared to concentric contractions, what are advantages eccentric contractions have over concentric?
More tension and LOWER metabolic cost
Important for functional movement pattern (decelerate limbs)
Most energy efficient form
Develop greatest tension in muscle actions
What are some advantages to manual resistance?
Individualized resistance (can meet the patients needs)
Isometric or dynamic
ROM can be controlled
More joint stabilization
Direct patient interaction
What are some disadvantages to manual resistance?
Subjective resistance
Lack of independence/HEP
Limited by strength of PT
increased PT labor and time
For exercise frequency, how many times should dynamic exercises be performed?
Every other day
For exercise frequency, how many times should Isometric exercises be performed?
Several times per day
For exercise frequency, how many days a week is optimum to improve?
3 days per week
For exercise frequency, how many days a week is optimum to maintain?
2 Days per week
Intensity of exercise dosage is based around what?
1 RM
What intensity should Hypertrophy be performed?
70-85%
What intensity should Power be performed?
0-60% Lower Body
30-60% Upper Body
What intensity should Strength be performed?
60-70%
What intensity should Endurance be performed?
<70%
What is the process for establishing a 1RM?
Detail it
1. Warm up
Perform 6-10 reps of a weight of 50% your 1RM
Rest 1-5 Minutes (until 100% recovered)
2. Increase the Weight
Do 3 reps of around 80% your 1RM
Rest 1-5 Minutes (until 100% recovered)
3. Do Heaviest lift
Increase load and do 1 Rep and increase weight till technique is compromised
Once highest weight achieved = your 1RM
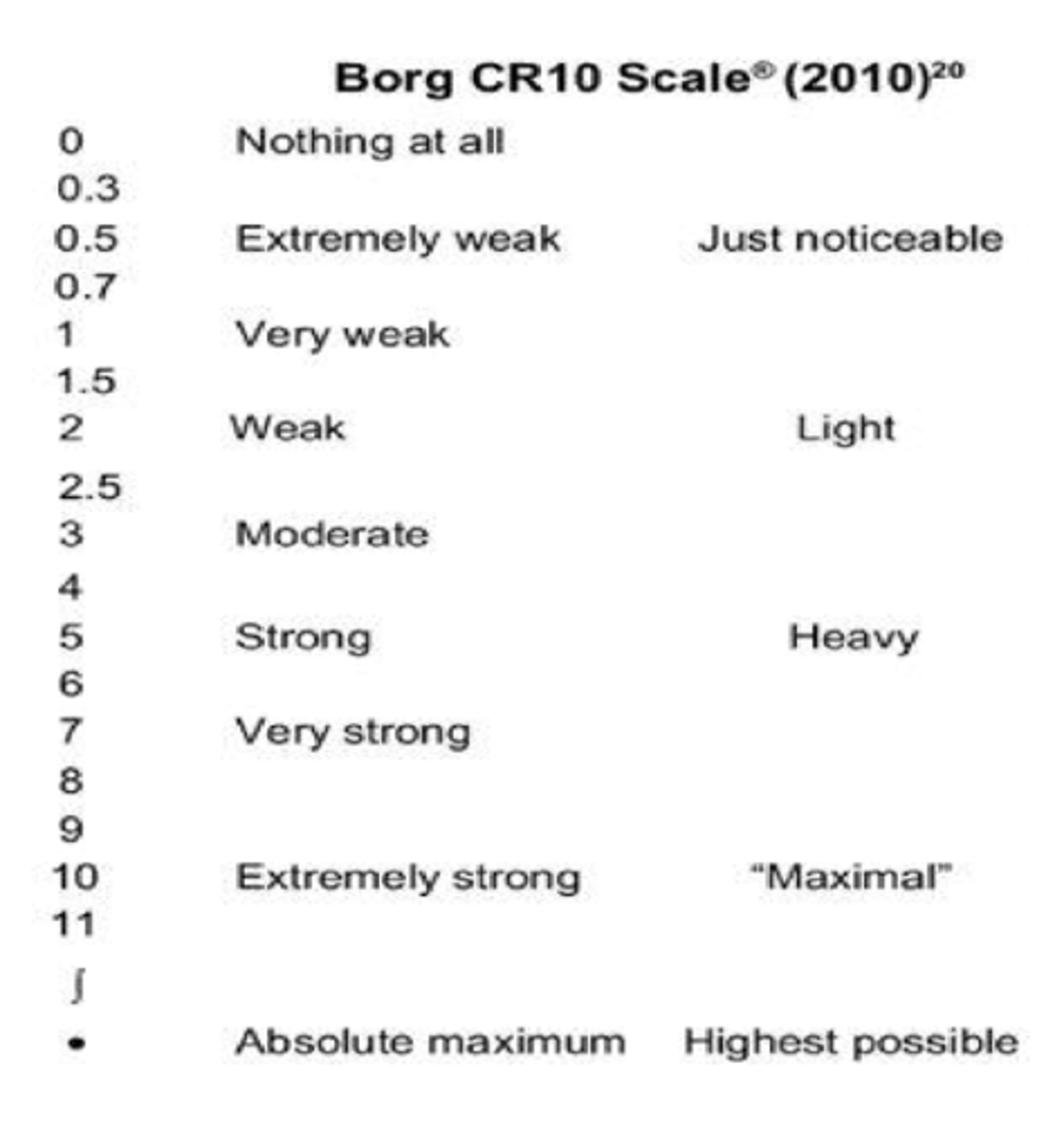
For establishing intensity using the Borg Scale, how do we do it?
Perform 2 Reps of a resistance
If those 2 reps measure a 5-6 on the Borg Scale = the weight that will be used for 12-15 reps
What is the set range for Endurance Training?
2-4 Sets
What is the set range for Hypertrophy Training?
1-3 Sets
What is the set range for Strength Training?
1-3 Sets
What is the set range for Power Training?
1-3 Sets
What is the rep range Hypertrophy?
8-12 Reps
What is the rep range Endurance?
10-25 Reps
What is the rep range for Strength?
8-12 Reps
What is the rep range Power?
3-6 Reps
What are the rest intervals for Hypertrophy?
1-3 Minutes
What are the rest intervals for Strength?
1-2 Minutes
What are the rest intervals for Power?
2-3 Minutes
What are the rest intervals for Endurance?
30-60 Seconds
What is the importance of muscles and "overload"?
Define it
In order for muscles to improve the muscle has to be overloaded
Definition: Applying resistance to a tissue that they are used to
For patients, what is the proper way to sequence exercises?
1. Specifically isolate impaired muscles
2. Begin from Isometric to Multi Joints
3. Begin with slow --> Fast Speeds
For General Strength (Non Patients), what is the proper way to sequence exercises?
1. Large muscle groups before small
2. When training ALL major muscle groups ALTERNATE between Upper and Lower body activities
3. When training upper and lower body parts on DIFFERENT DAYS, SWITCH between Agonist and Antagonist Exercises
4. Multi Joint BEFORE Single Joint "activities"
5. When training INDIVIDUAL muscle groups, train HIGHER intensity exercises BEFORE lower intensity exercises
When designing an exercise program, what should it based around?
The TBC (treatment based classification)
Interval Training is used mainly for what metabolic system?
Anaerobic or Aerobic?
Anaerobic.....BUT CAN be aerobic depending on how you train it
What is Interval Training?
Training of bursts of SHORT intense activity then LONGER intervals of short activity
What is Circuit Training?
Sessions of exercise done by completing 8-15 stations that are completed in sequence of one another
When it comes to Neurological Changes and Biomechanical changes, do they occur before or after the 4-8 Week mark?
Neurological = Before (2-4 Weeks)
Biomechanical = After
What are the guidelines for exercise with pain?
Pain should be <2/10 and no greater than >5/10 (Ideally want 0-10)
Pain should NOT return after 1 Hour of exercise
Pain should NOT increase the next morning
Exercise should be adjusted depending on pain response
What should resistive training focus on the most when it comes to Preadolescent Kids?
(11 Years old in girls, 13 years only in boys)
Neurological Aspect in training
What should resistive training focus on the most when it comes to Adolescent Kids?
(12-18 year old girls , 14-18 year old boys)
Similar to Preadolescent
BE DONE WITH PROPER INSTRUCTION, SUPERVISION, AND SAFE PROGRESSION
What age range is strength potential the highest?
18-30
For Middle Aged people, how much exercise is needed to POSITIVELY affect strength?
2 Hours+ a week
A little bit of training makes a big difference between ACTIVE AND INACTIVE
For Advanced Aged people, how can exercise affect Joints?
Can PREVENT or moderate symptoms of degeneration
What tissues require adequate length to allow for full ROM of articular surfaces for Joint Mobility?
Interposed tissue
Joint Capsule
Ligaments
Tendons
Muscles
Bursae
Fascia, Skin
Decreased mobility can lead to what disorders/pathologies?
Trauma to soft tissue
Surgery (joint replacements)
Joint Disease (Osteoarthritis)
Prolonged Immobilization
Neuromuscular Disease
Immobilization has what effects on Muscle? (4)
Muscle fiber atrophy
Functional loss IS GREATER than muscle mass loss
Decreased electrical activity
Increased CT, subcutaneous fat
Remobilization has what effects on Muscle AFTER immobilization? (1)
Longer the immobilization requires longer rehab
Immobilization has what effects on Tendons?
(2)
Decreased collagen, water, GAGs, Stiffness, Tissue weight, Elastic Stiffness
Increased Synthesis and degradation of collagen
Remobilization has what effects on Tendons?
(3)
Improvement of tensile strength and energy absorption
Facilitations normal gliding and soft tissue relationships
PREVENTS scar tissue formation