Urethra
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is the urethra?
Tubular organ that serves as an outlet for urine from urinary bladder
What is the functional difference between the urethra in females and males?
Females: Only convey urine
Males: Carries urine, semen and seminal secretions
Urethral Sphincter
What
2 types
What: Muscles used to control exit of urine in urinary bladder
Types:
Internal urethral sphincter
External urethral sphincter
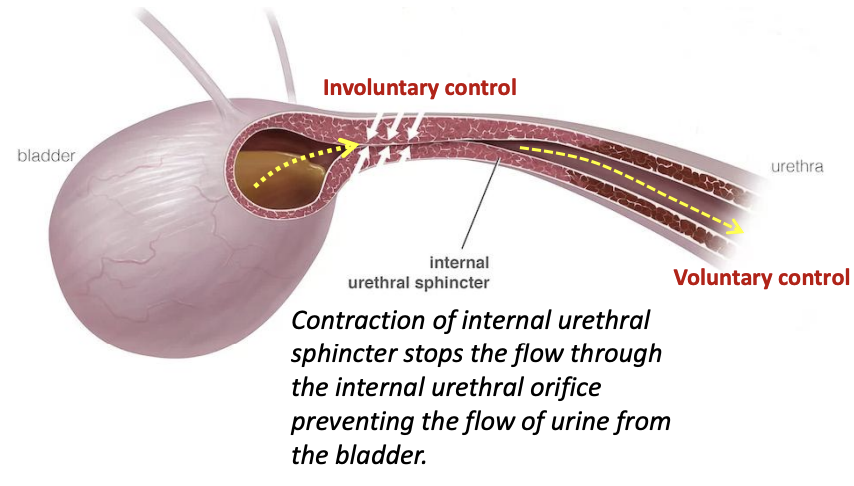
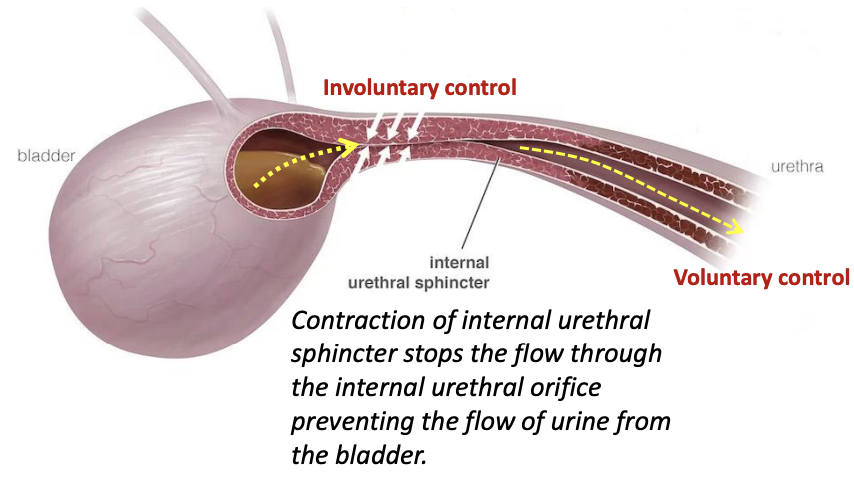
Urethral Sphincter: Internal Urethral Sphincter
Type of muscle
Location
Function
How it stops the flow of urine
Type of muscle: Smooth
Location: Continuous with detrusor muscle of bladder
Function: Regulates involuntary control of urine flow from bladder —> urethra
How it stops the flow of urine: Through contraction, stopping flow through the internal urethral orifice
Urethral Sphincter: External urethral sphincter
Type of muscle
Location
Function
Type of muscle: Striated urethralis muscle
Location: Distal third of urethra
Function: Provides voluntary control of urine flow from bladder —> urethra
Urinary Incontinence in Dogs
What
AKA
Clinical signs
Causes
#ffbb00
What: Loss of voluntary control of urination
AKA: Involuntary urine leakage
Clinical signs: Spotting or pooling of urine or dribbling of urine
Causes:
Neurological
Bladder storage dysfunction
Urethral disorder
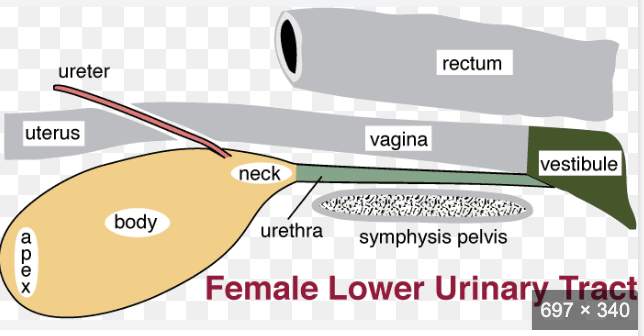
Female Urethra #ff00d1
Where does the it begin and end
Relationship between female urethra and bladder
Location in relation to reproductive tract
How does it exit the body
Anatomical term for the external opening
Where does the it begin and end:
Begins: Internal urethral orifice (at bladder neck)
Ends: External urethral orifice (in cranial vestibule)
Relationship between female urethra and bladder: Continuous with bladder and runs caudally from it
Location in relation to reproductive tract: Runs ventral to the reproductive tract along the pelvic floor
How does it exit the body: Passes obliquely through vaginal wall and opens ventrally at the junction between vagina and vestibule
Anatomical term for the external opening: External urethral orifice located on the floor of cranial vestibule
Male Urethra
Where does it begin and end
Consist of 2 parts
Carries
Where does it begin and end:
Begins: Internal opening at bladder neck
End: External opening at end of penis
Consist of 2 parts:
Pelvic part (further divided into preprostatic and prostatic part)
Penile part
Carries: Urine, semen and seminal secretions to the distal end of penis
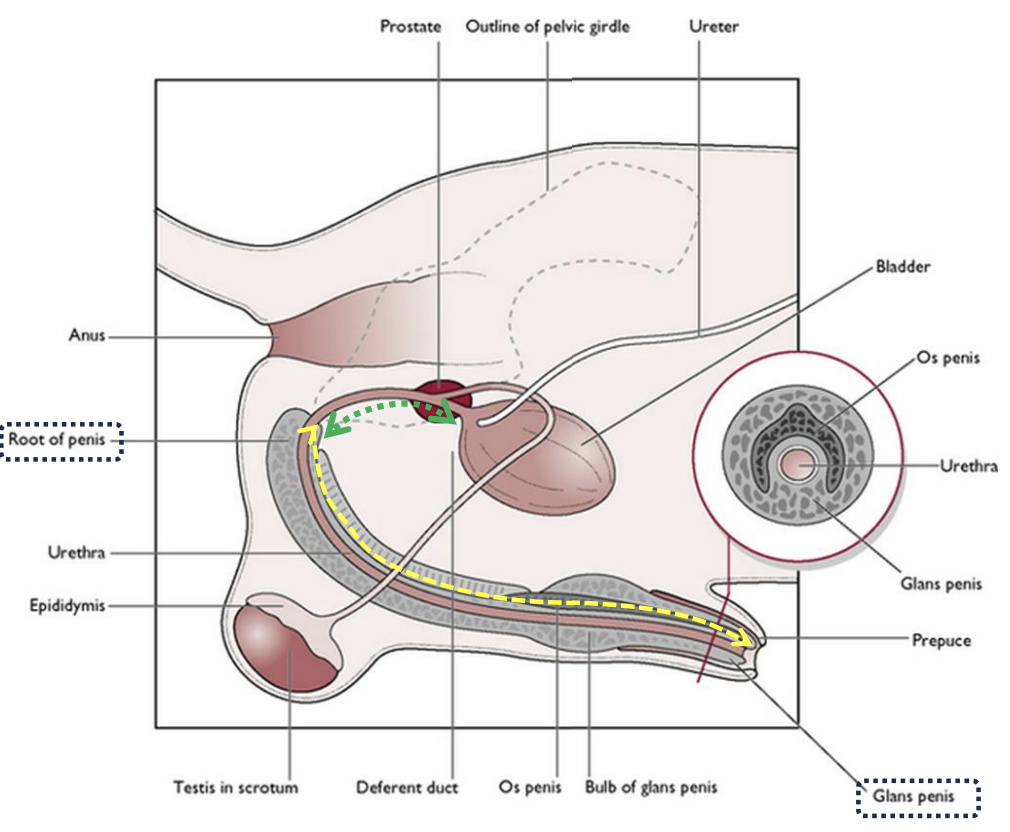
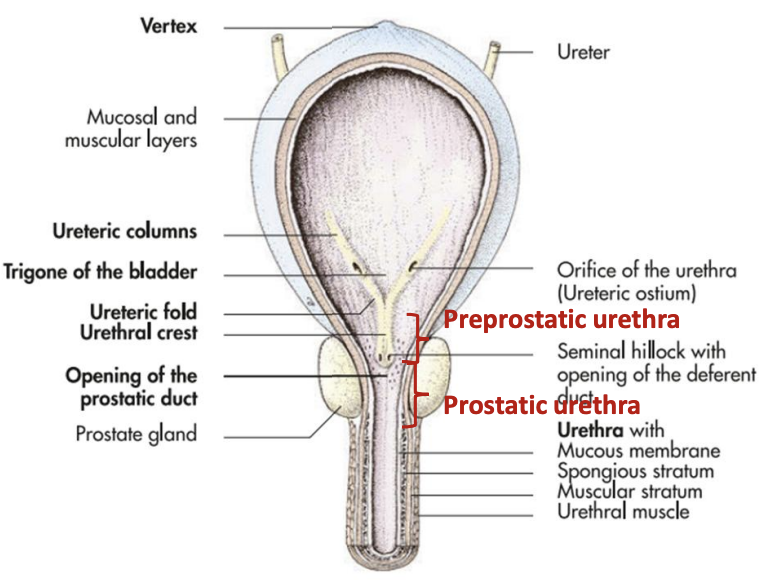
Male Urethra: Pelvic Part
Preprostatic part
Long or short
Where it begins and ends
Prostatic part
Passes through
Preprostatic part:
Long or short: Short
Where it begins and ends:
Begins: Internal opening of urethra
Ends: Seminal hillock with openings of deferent ducts
Prostatic part:
Passes through: Prostate glands
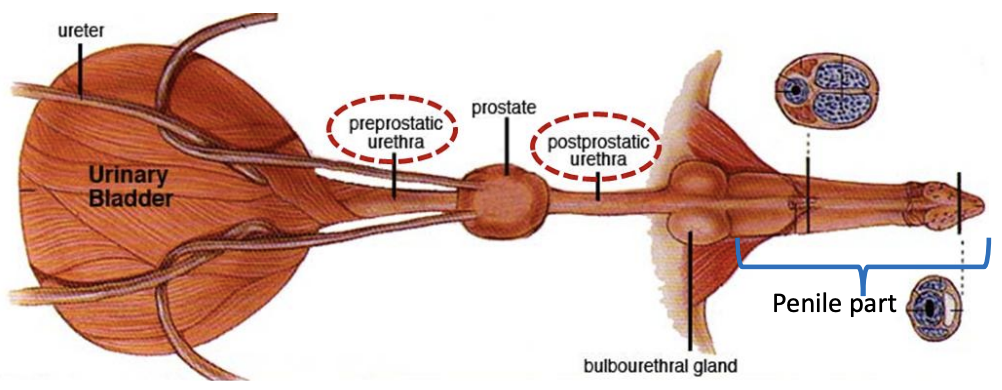
Male Urethra: Prostate gland
Shape
Location
Divides the urethra into
Shape: Spherical
Location: Between preprostatic urethra and postprostatic urethra
Divides the urethra into:
Preprostatic
Prostatic: Surrounded dorsolaterally by prostate gland
Postprostatic: Runs from body of prostate gland to the root of penis (paired bulbourethral glands also present in cats here)
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease
Describes conditions affecting
Causes
Types
Which gender at greater risk
Symptoms
Describes conditions affecting: Bladder or urethra of cats
Causes: Physical conditions and behavioural disorders
Types: Non-obstructive and obstructive types
Which gender at greater risk: Males due to their narrower urethra
Symptoms:
Difficulty and pain when urinating
Increased urination
Blood in urine