Unit 1 AP Human Geography: The Power of Geovisualization
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Physical Geography
One of the two major divisions of systematic geography; the spatial analysis of the structure, processes, and location of Earth's natural phenomena such as climate, soil, plants, animals, and topography.

Human Geography
The study of the spatial variation in the patterns and processes related to human activity. They way in which humanity interacts with its immediate environment.
Spacial Analysis
The process of examining the locations, attributers and relationships of features in spacial data through overlay and nd other analytical techniques in order to address a question or gain useful knowledge.
Spacial Data
All of the information that can be tied to a specific location.
Quantitative Data
Data associated with mathematical models and statistical techniques used to analyze spatial location and association. Data that is backed up by information that has been formally collected.
Qualitative Data
Data associated with a more humanistic approach to geography, often collected through interviews, empirical observations, or the interpretation of texts, artwork, old maps, and other archives.

Reference Maps
Maps that show the absolute location of places and geographic features determined by a frame of reference, typically latitude and longitude.
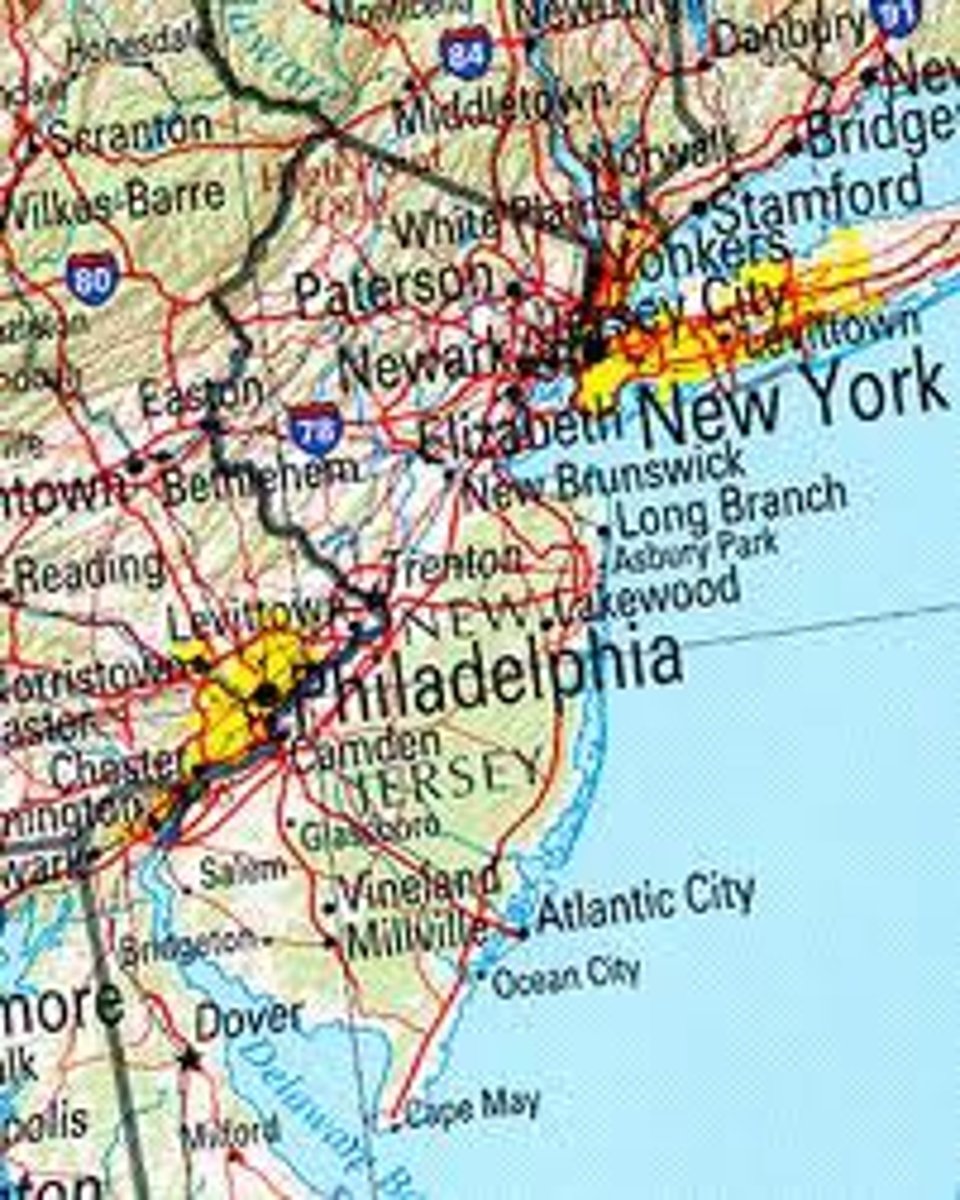
Road Map
Shows major highways, airports, cities, railroad tracks, and local points of interest, a reference map.
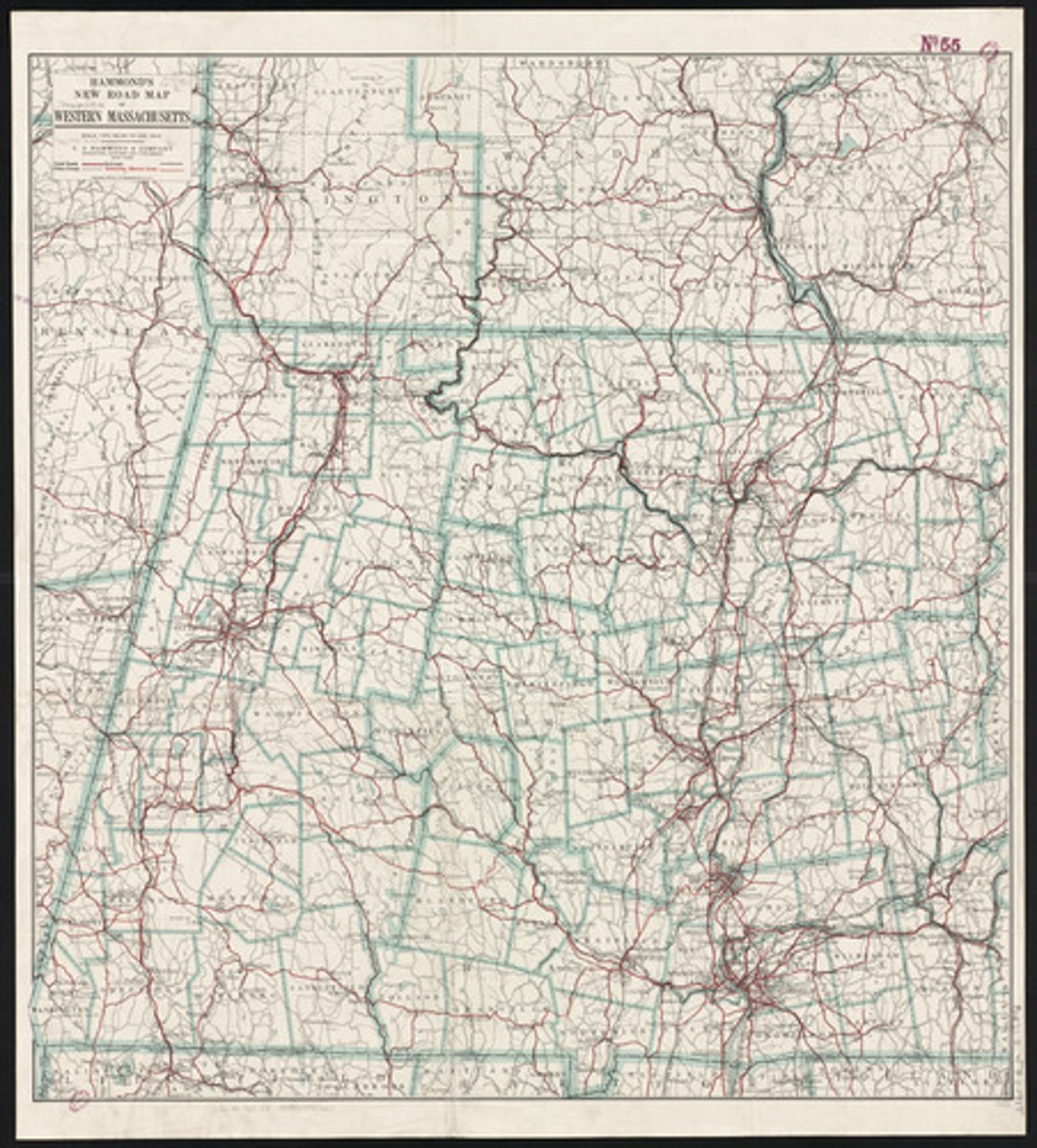
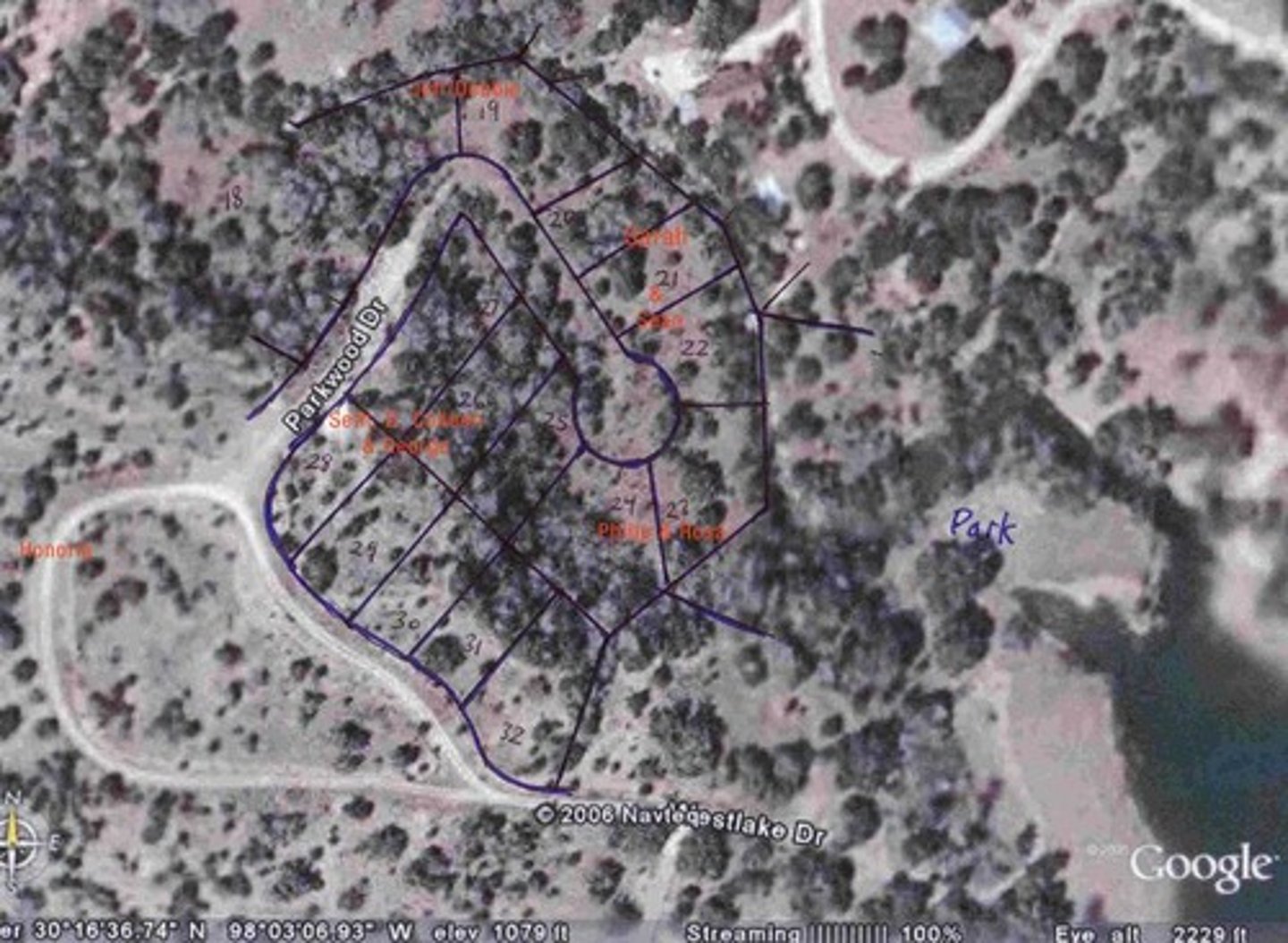
Plat Map
Detailed map illustrating the geographic boundaries of individual lots, a reference map.
Political Map
A map that shows man-made features such as boundaries, countries, and cities, a reference map.
Physical Map
A map that shows mountains, hills, plains, rivers, lakes, oceans, etc.
Locator Map
Used in books, newspapers, advertisements to show specific locations mentioned in the text. Allows a sense of space and location.
Thematic Maps
Maps that show the distribution, flow, or connection of one or more characteristics and are used to communicate data and information, show degree of an attribute, the pattern of its distribution, or its movement. - Relative locations.
Choropleth Map
A thematic map that uses tones or colors to represent spatial data as average values per unit area, different shades of a color, 1 data set measured.
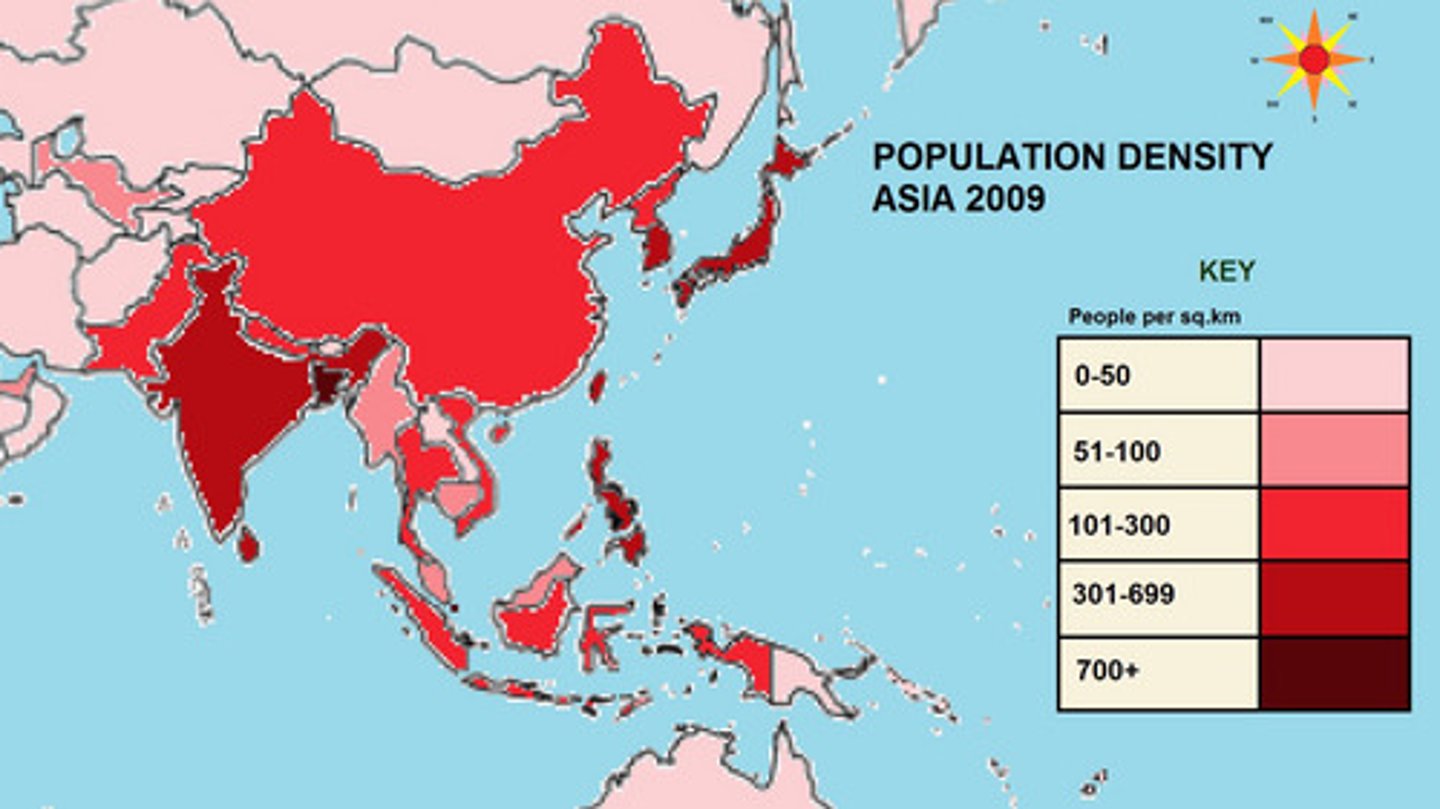
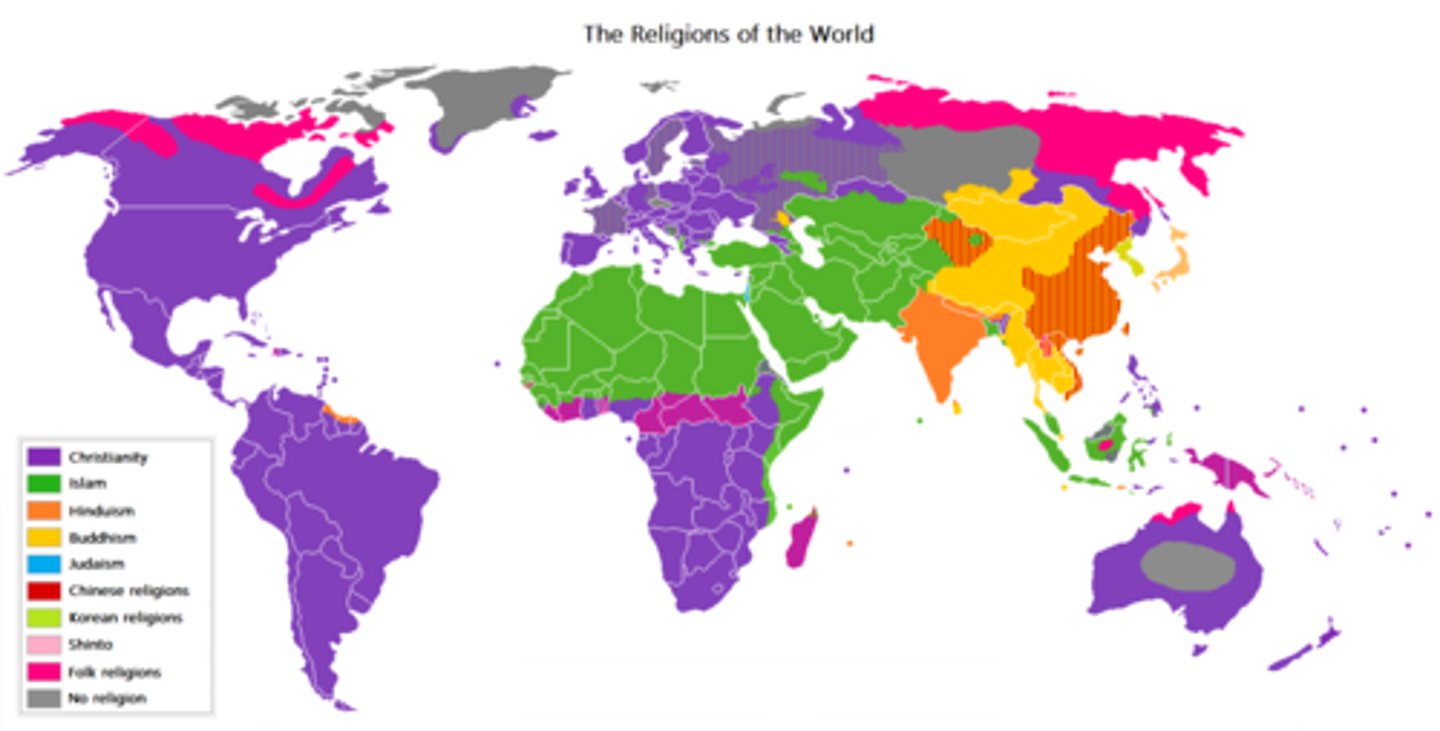
Categorical Map
Uses colors to show categories
(spacial data), more that one category of one subject being projected on the map like religion, biospheres, etc.
Isoline Map
Map displaying lines that connect points of equal value; for example, a map showing elevation levels.
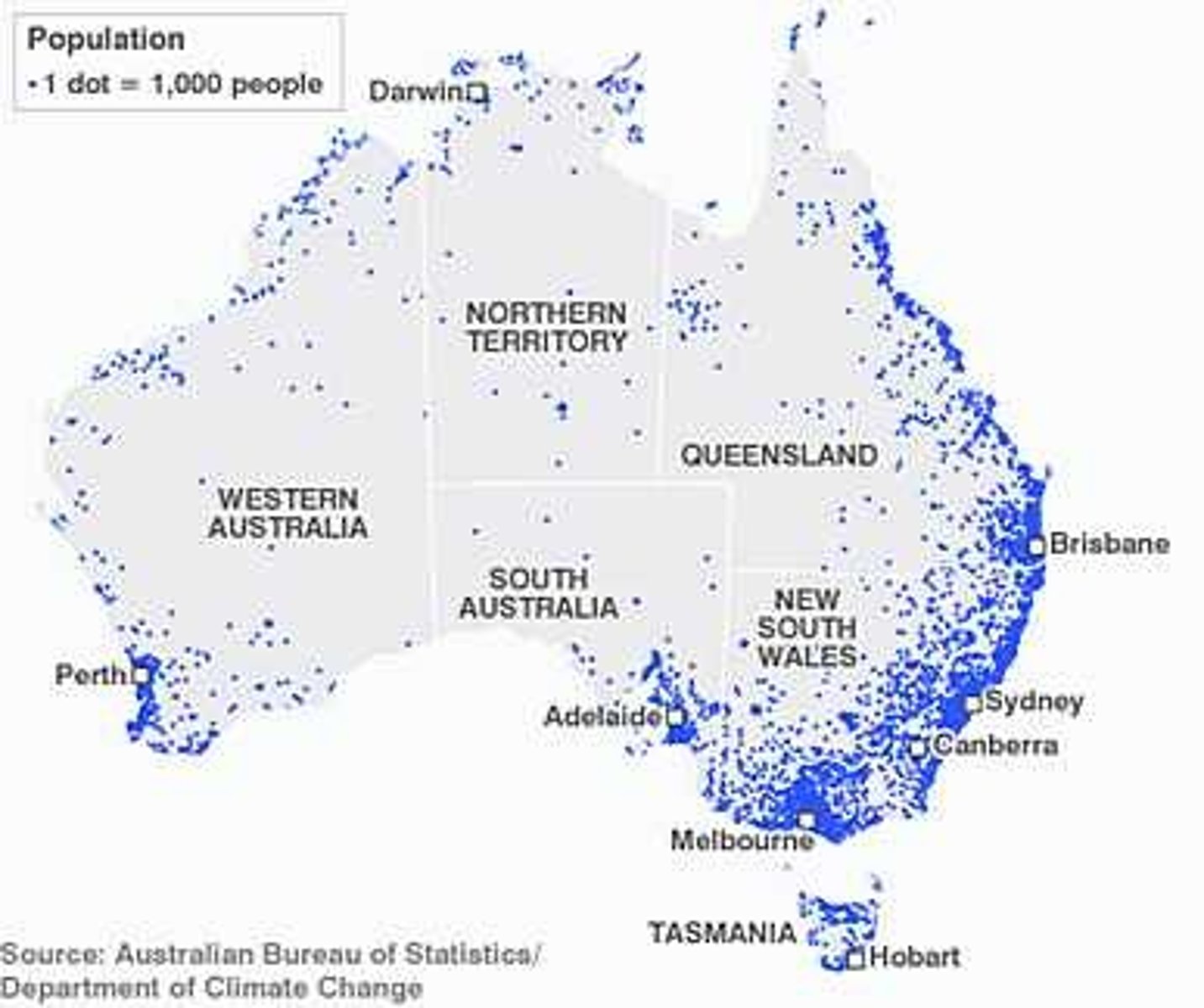
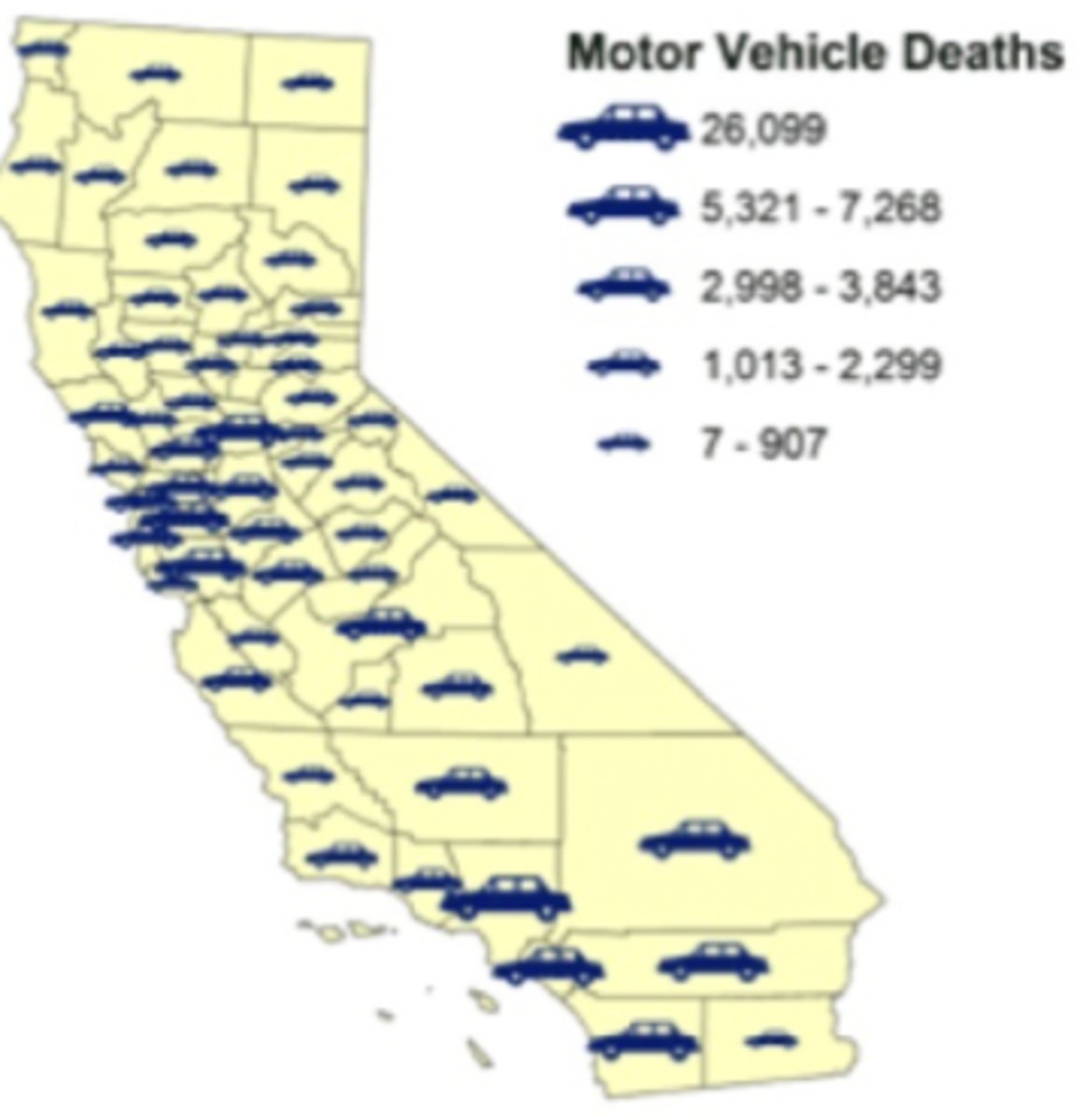
Dot Distribution Map
A map where dots/shapes are used to demonstrate the frequency or intensity of a particular phenomena.
Cartogram Map
A map in which the shape or size is distorted in order to demonstrate a variable such as travel, population or economic production. The larger the area the greater the value, the smaller the smaller the value.
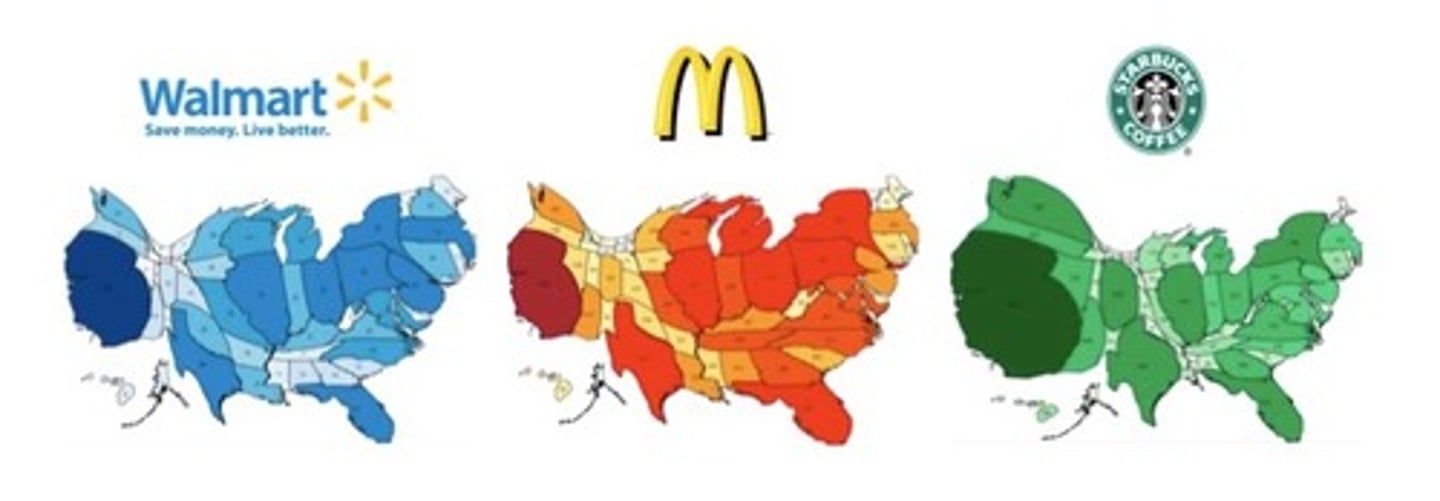
Graduated Symbol Map
A map with symbols that change in size according to the value of the attribute they represent.
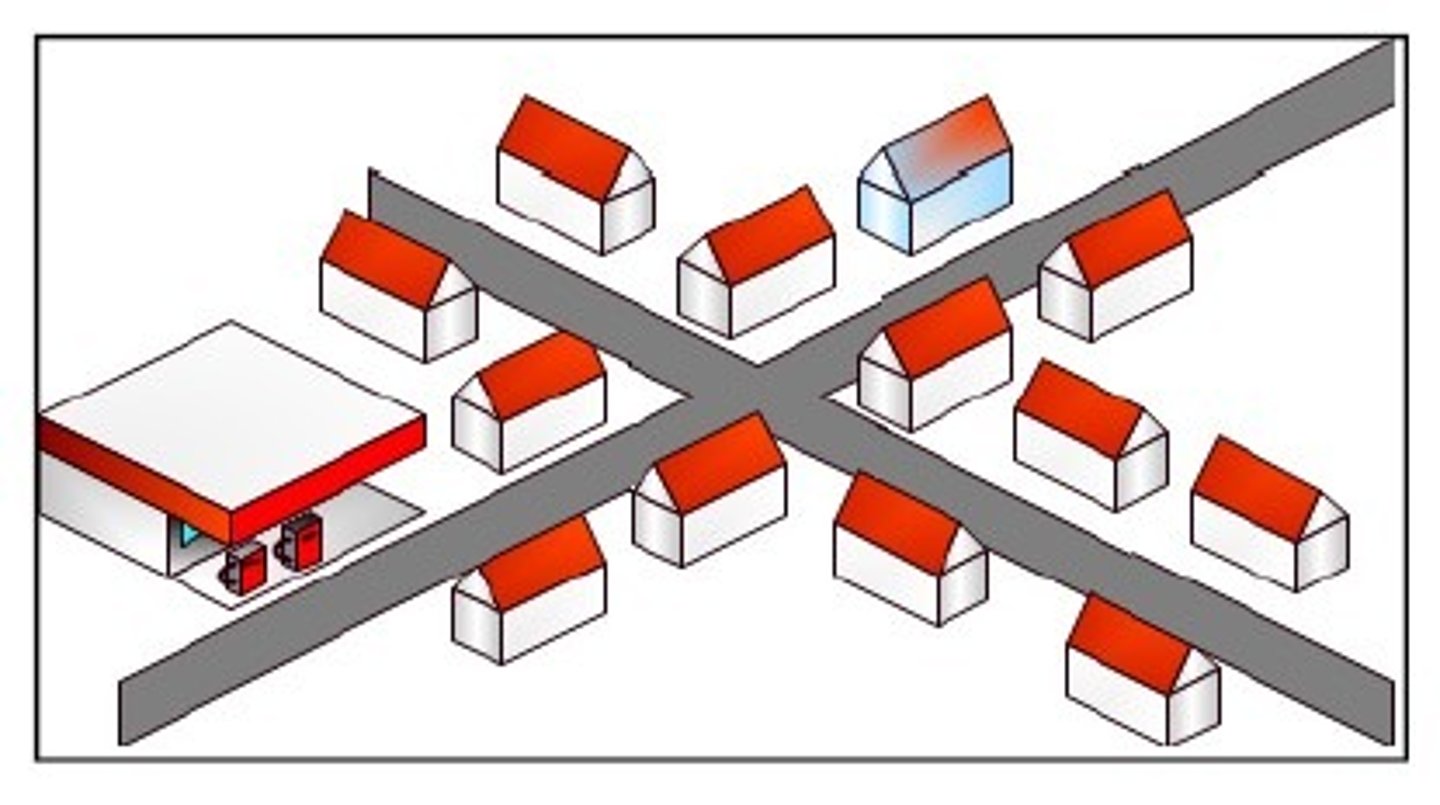
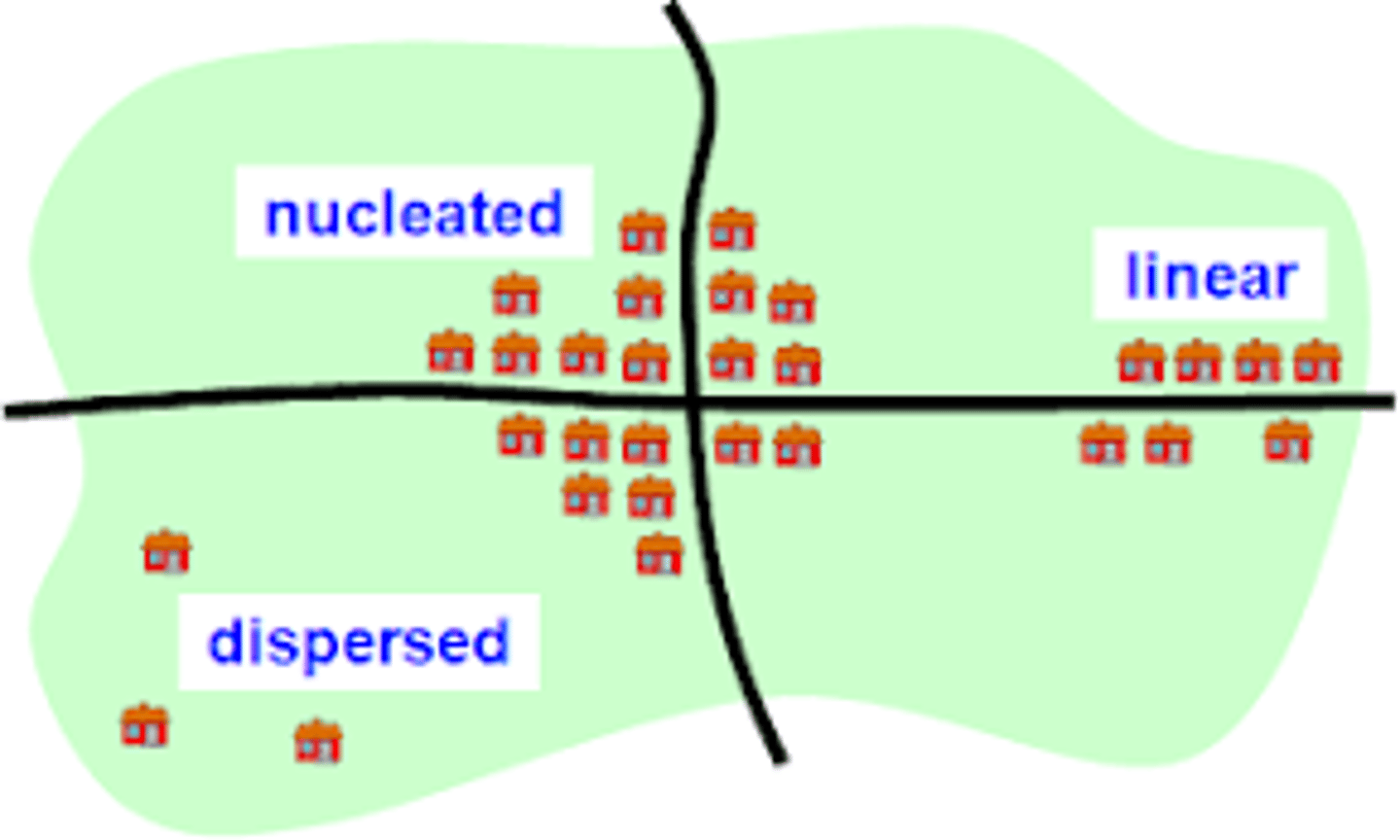
Clustered Phenomena
arranged in a group or concentrated area, a neighborhood, also nucleated
Linear Phenomena
arranged in a straight line, such as the distribution of towns along a railroad line, roads, rivers.

Dispersed Phenomena
Spread out over a large area, such as the distribution of large malls in a city.
Circular Phenomena
Equally spaced from a central point, forming a circle, such as the distribution of the homes of people who shop at a particular store.
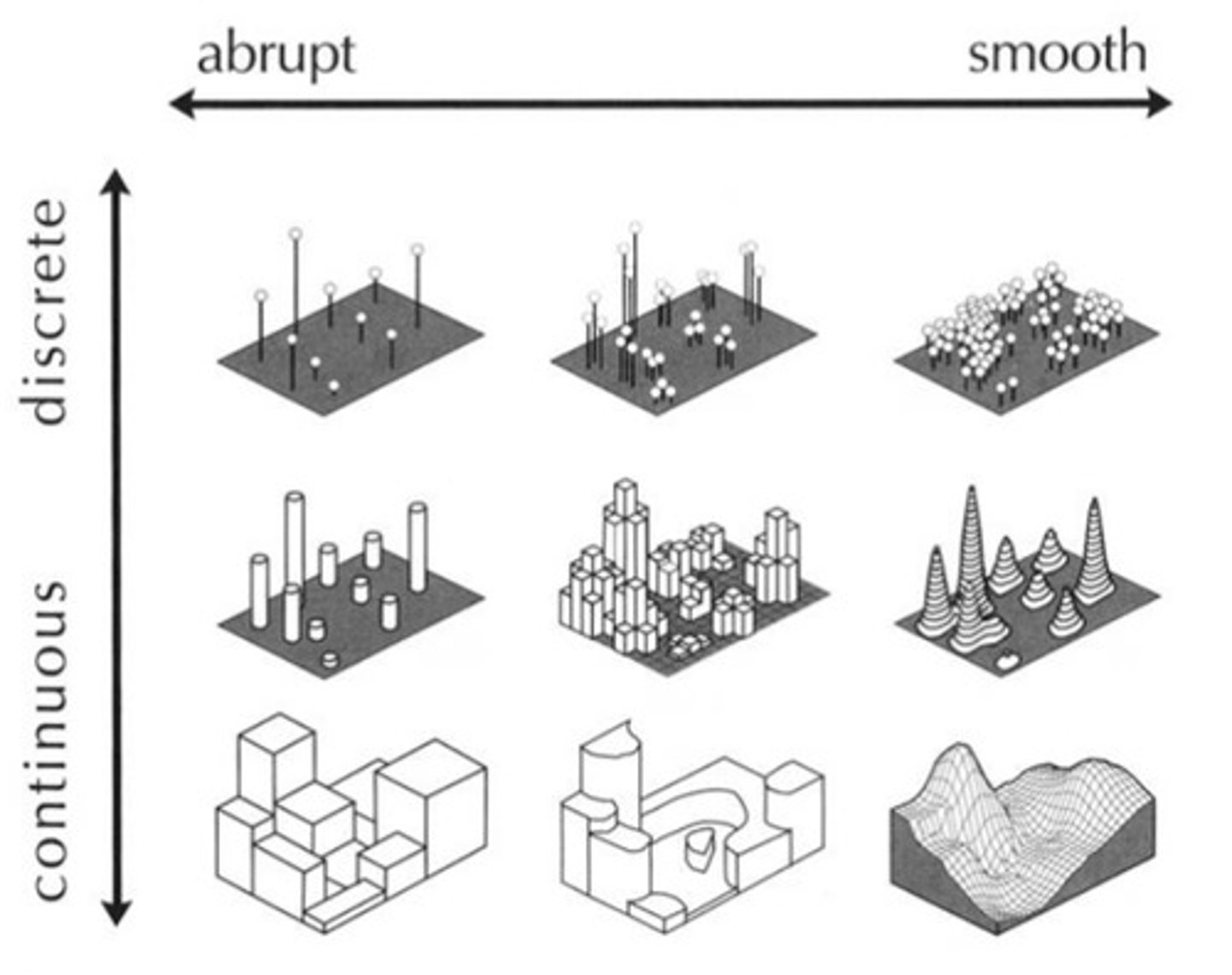
Geometric Phenomena
in a regular arrangement, such as the squares formed by roads in the midwest.

Random Phenomena
No order, no pattern of distribution of position like that the distribution of pet owners in a city.
Four-Level Analysis
Systematic way to study geographic phenomena looking at comprehension, identification, explanation, and prediction. A very important approach to spacial thinking, think like a GEOGRAPHER!!
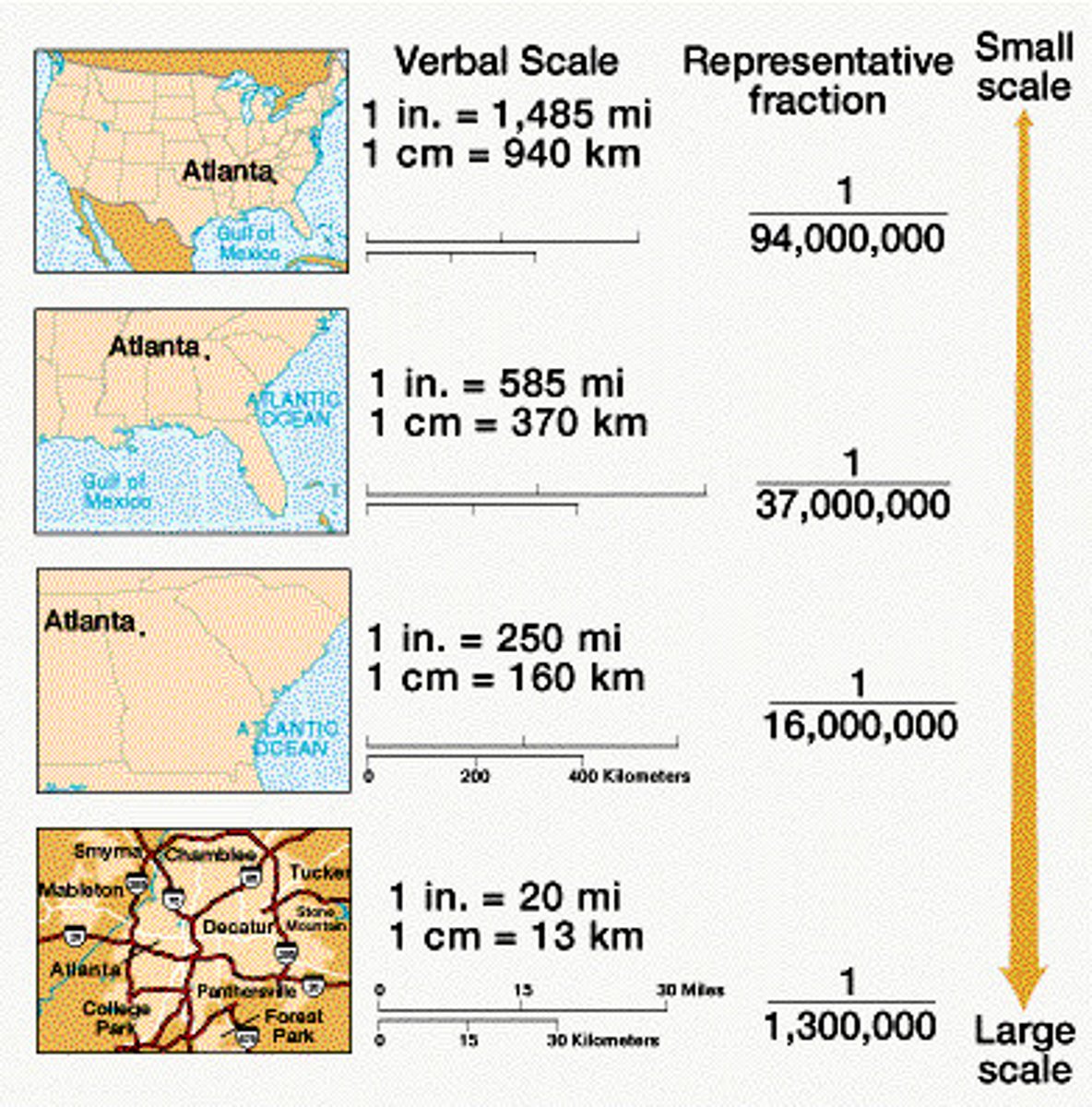
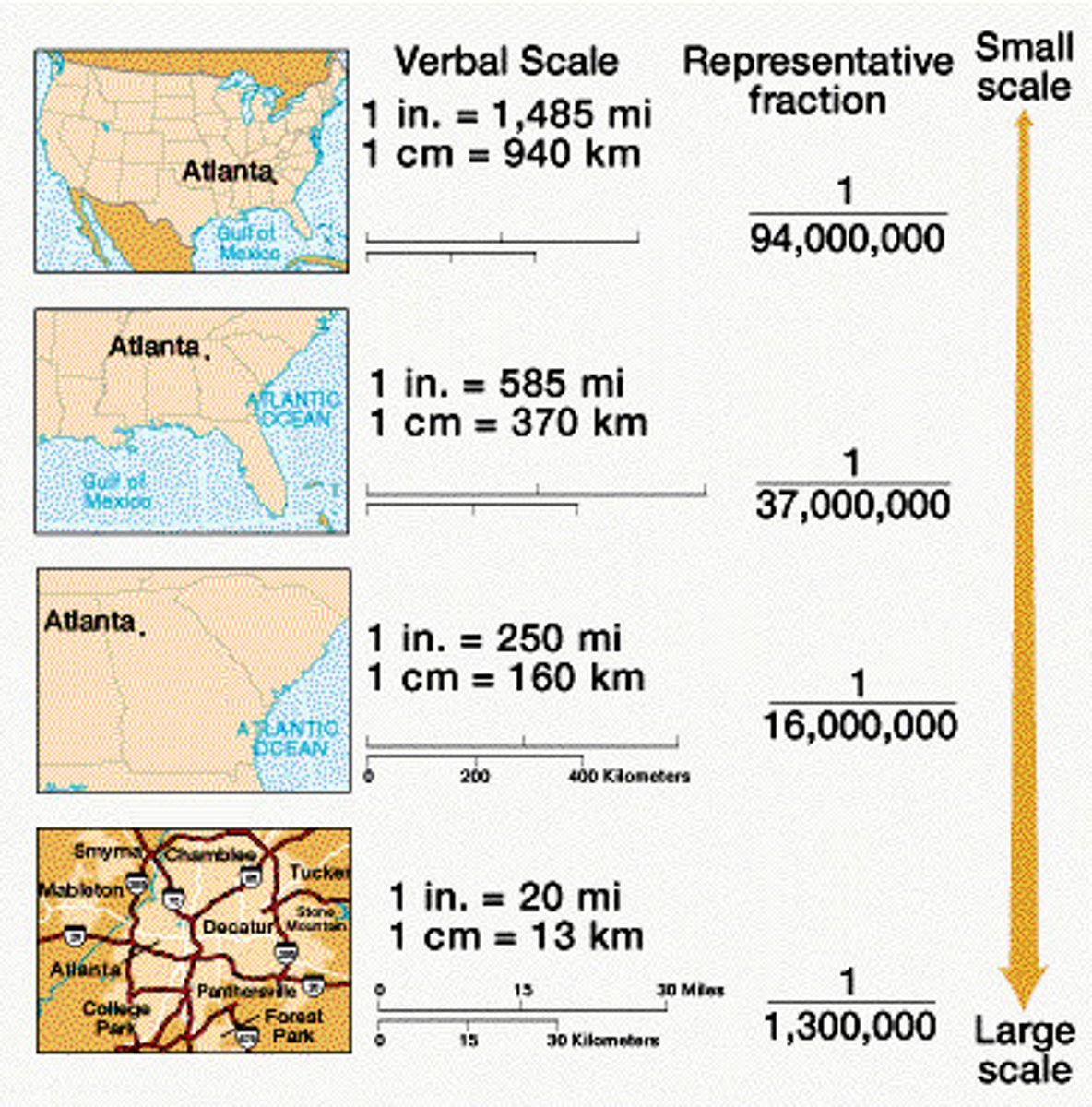
Scale Analysis
A scale that determines what is being studied based on the size of the area being examined. Zoom into an area on a map = large scale, zoom out is small scale.
Relative Location (Situation)
The location of a place relative to other places. This can be perceptual.

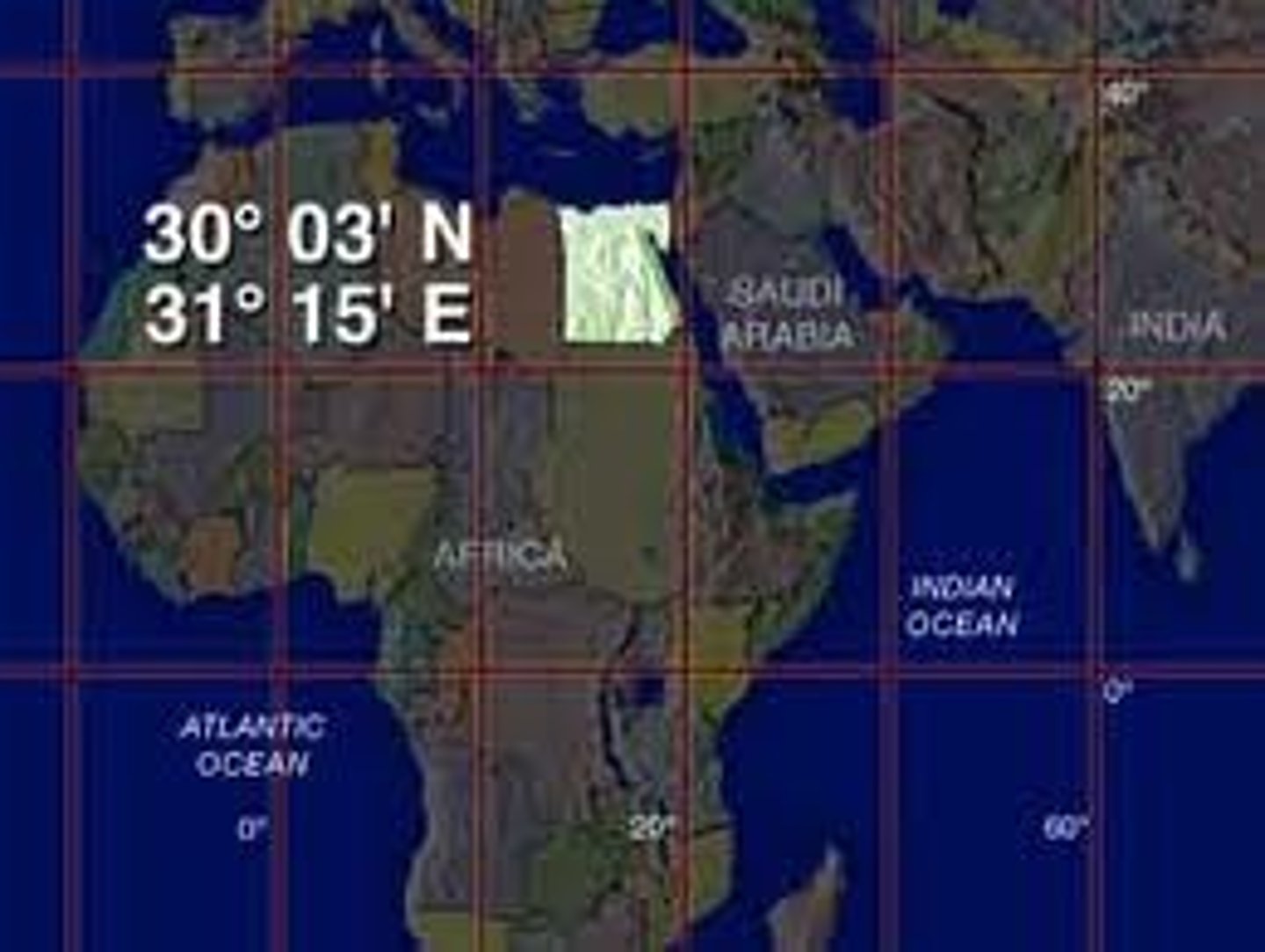
Absolute Location
Exact location of a place on the earth described by global coordinates, longitude and latitude!
Remote Sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods, ie: geothermal data, seismic activity projections.
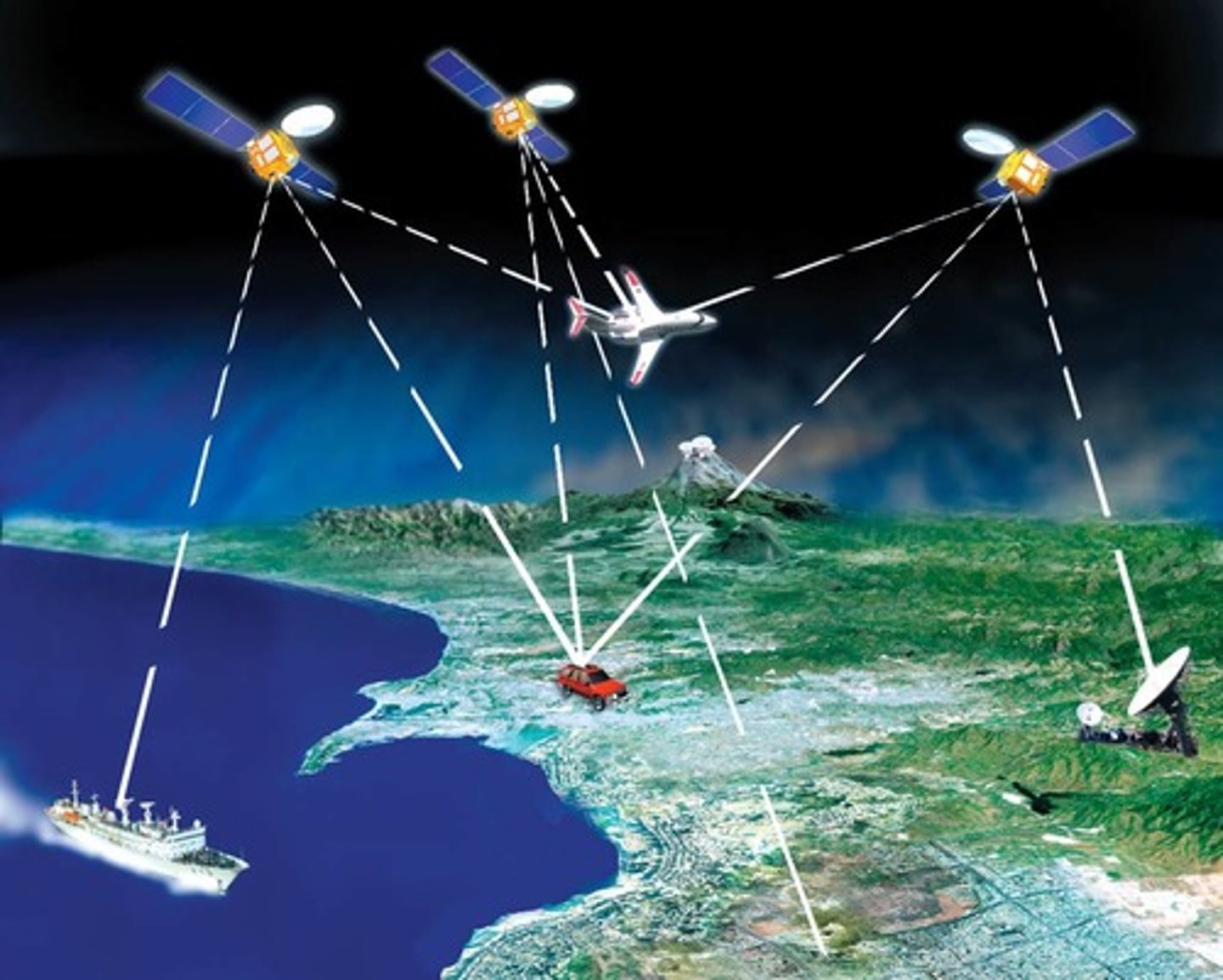
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
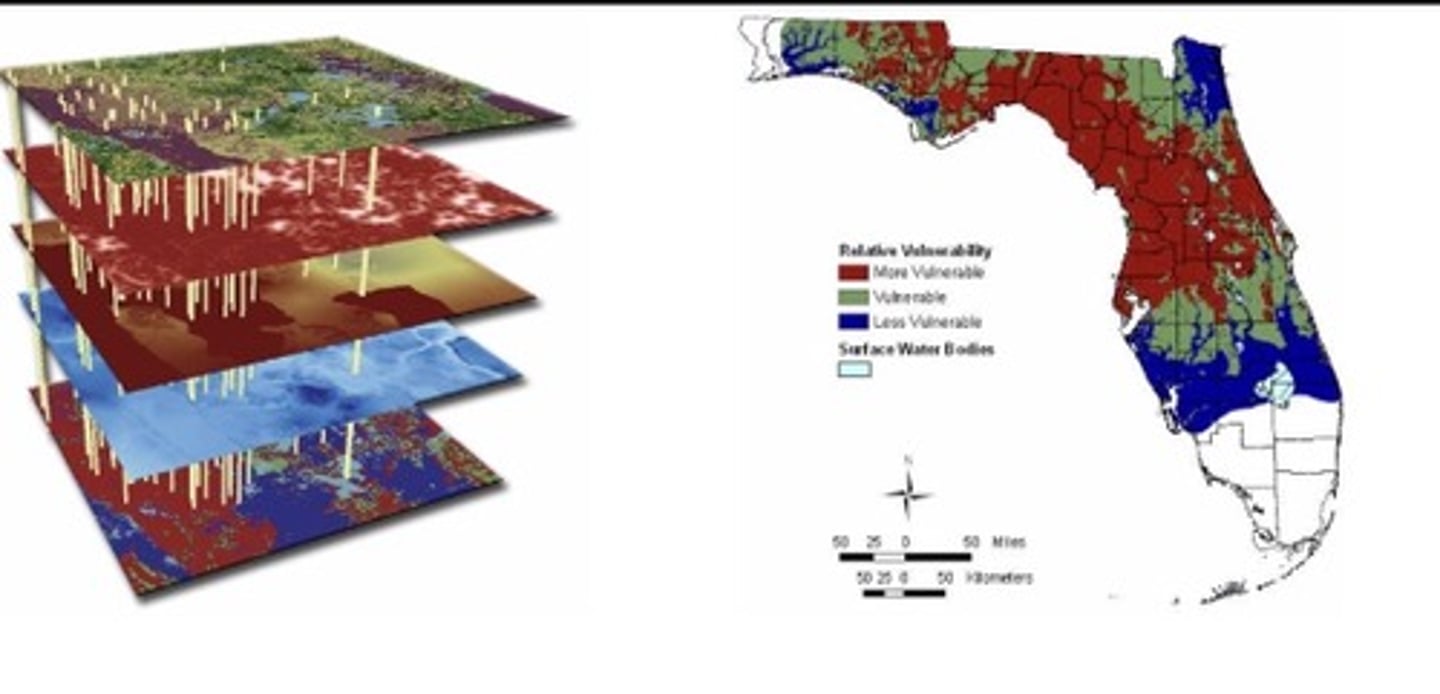
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
Place
A specific point on Earth distinguished by specific human and physical characteristics.

Location
Identifies where specific phenomena are located either on a grid system or relative to another location.

Site
This is used to refer to PLACE, characteristics at an immediate location ie: soil type, climate, labour force, types of structures.

Situation
This is used to refer to PLACE, refers to the location of a place relative to its surroundings and connectivity to other places.

Sense of place...
As per human beings an idea of PLACE as seen through their own perspective and personal beliefs. London will be perceived differently by someone who lives there vs. someone who is visiting.

Toponyms
The name given to a portion of Earth's surface, place names.
Time-Space Compression
The rapid innovation of communication and transportation technologies associated with globalization that transforms the way people think about space and time. All due to technological innovation.

Spacial Interaction
The impact of distance determined by contact, movement and the flow of things between locations allowing for increased connection.
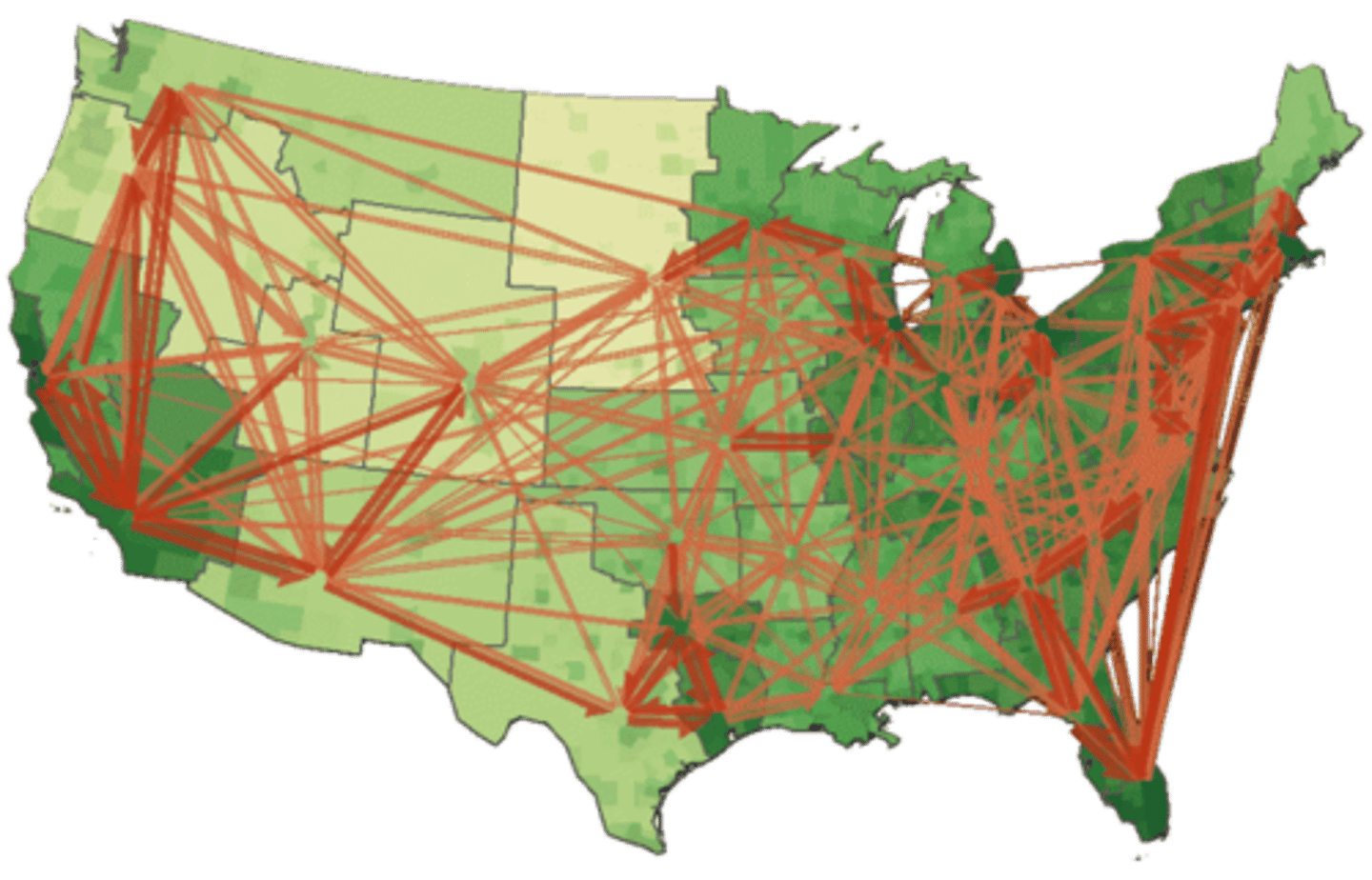
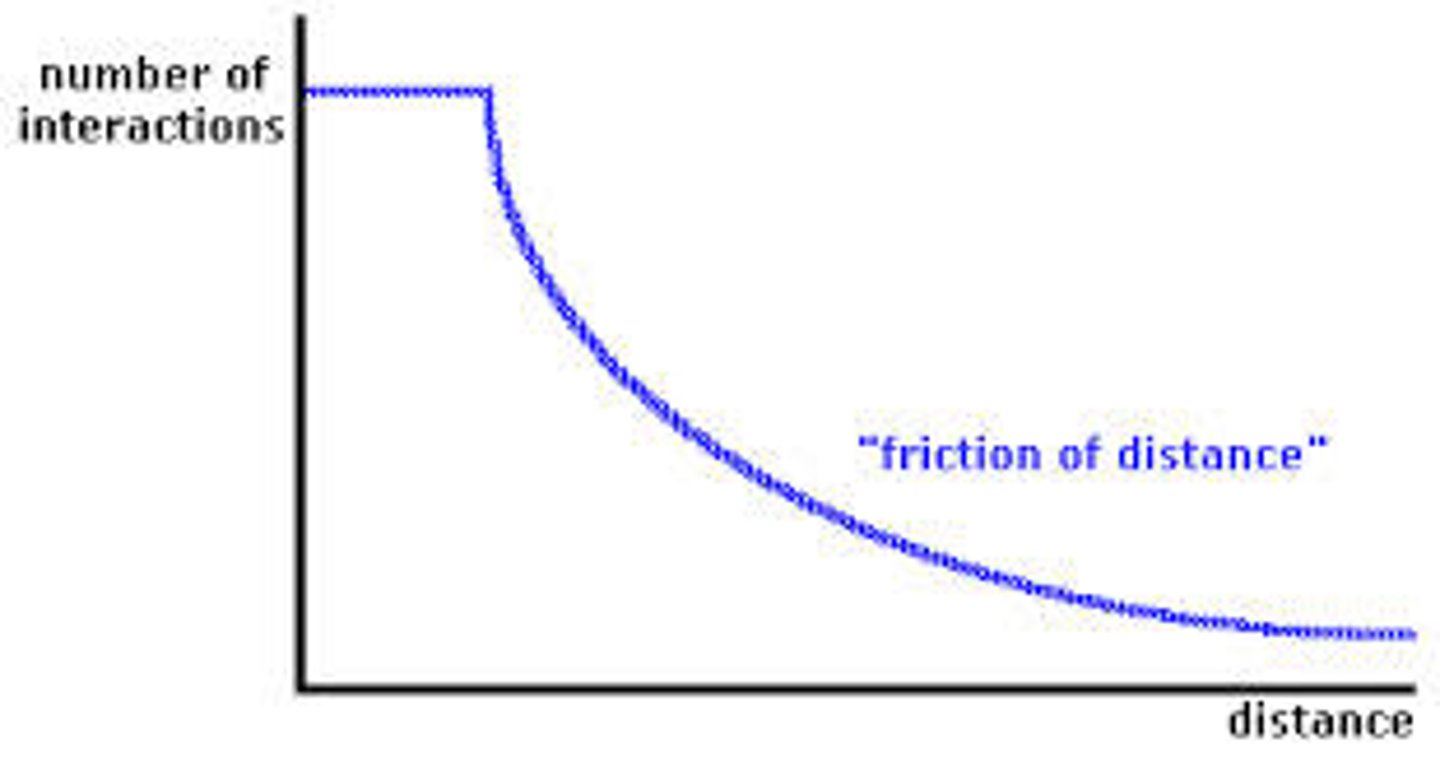
Friction of Distance/Distance of Decay
The idea that when things are farther apart they tend to be less connected. However, globalization and GPS/GIS have reduced the influence of physical distance.
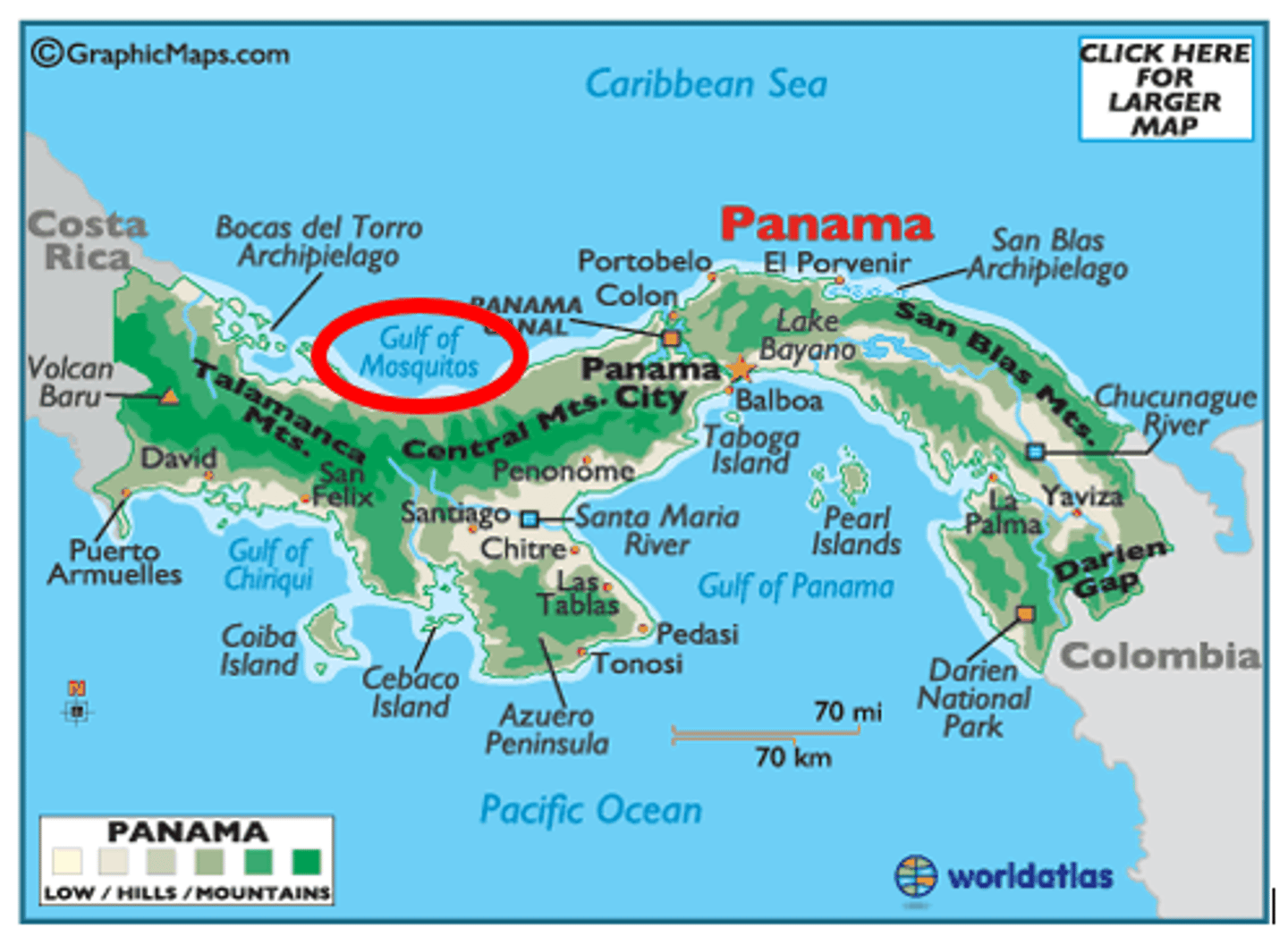
Spacial Association
When 2 or more phenomena are related or associated with one another. For instance many malaria cases in one location is associated with lots of mosquitos in the location and monsoon rains in the location, 3 phenomena.
Renewable Natural Resources
Theoretically are unlimited and will not be depleted based on use by people, wind, heat from the sun.
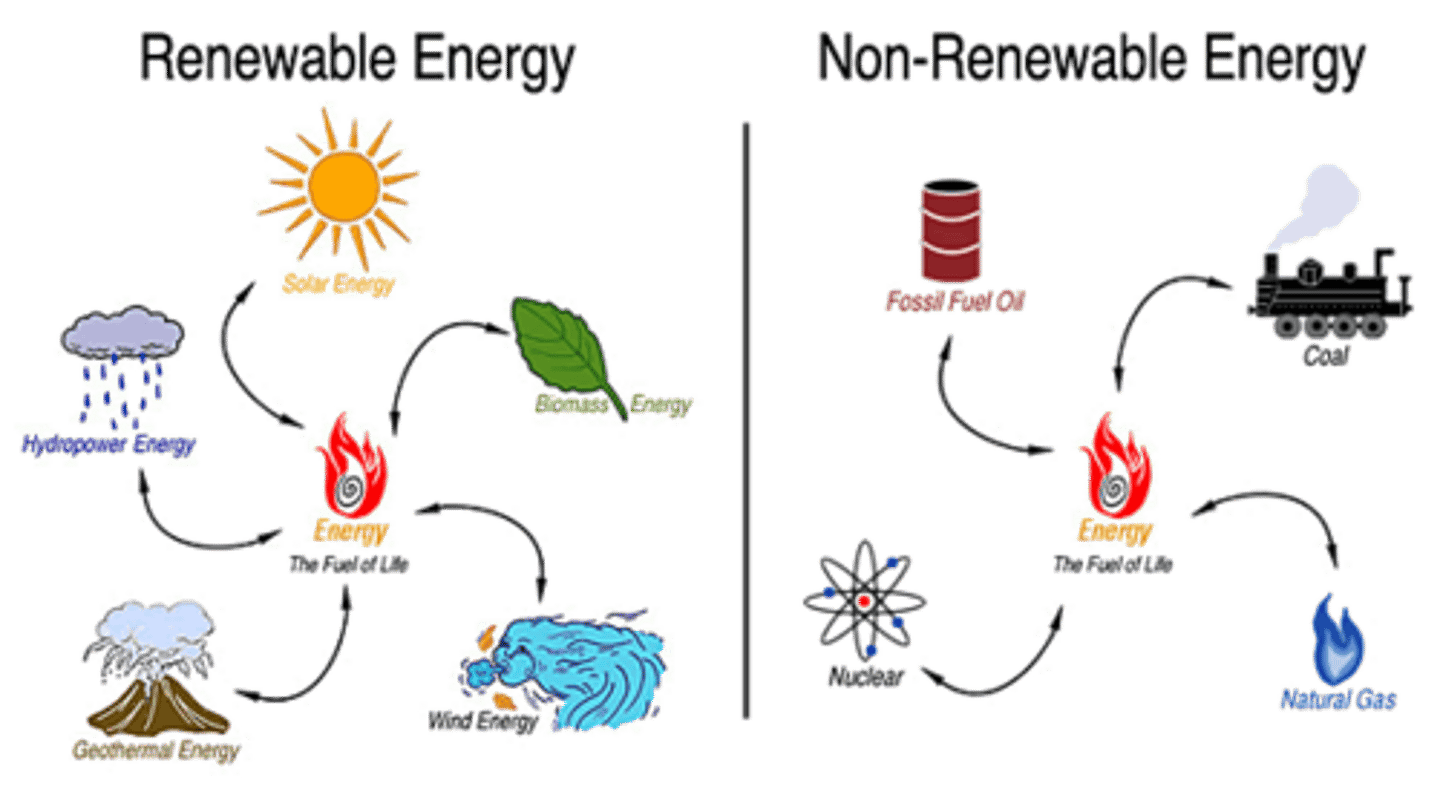
Non-renewable Resources
A resource that cannot be reused or replaced easily (ex. gems, iron, copper, fossil fuels).
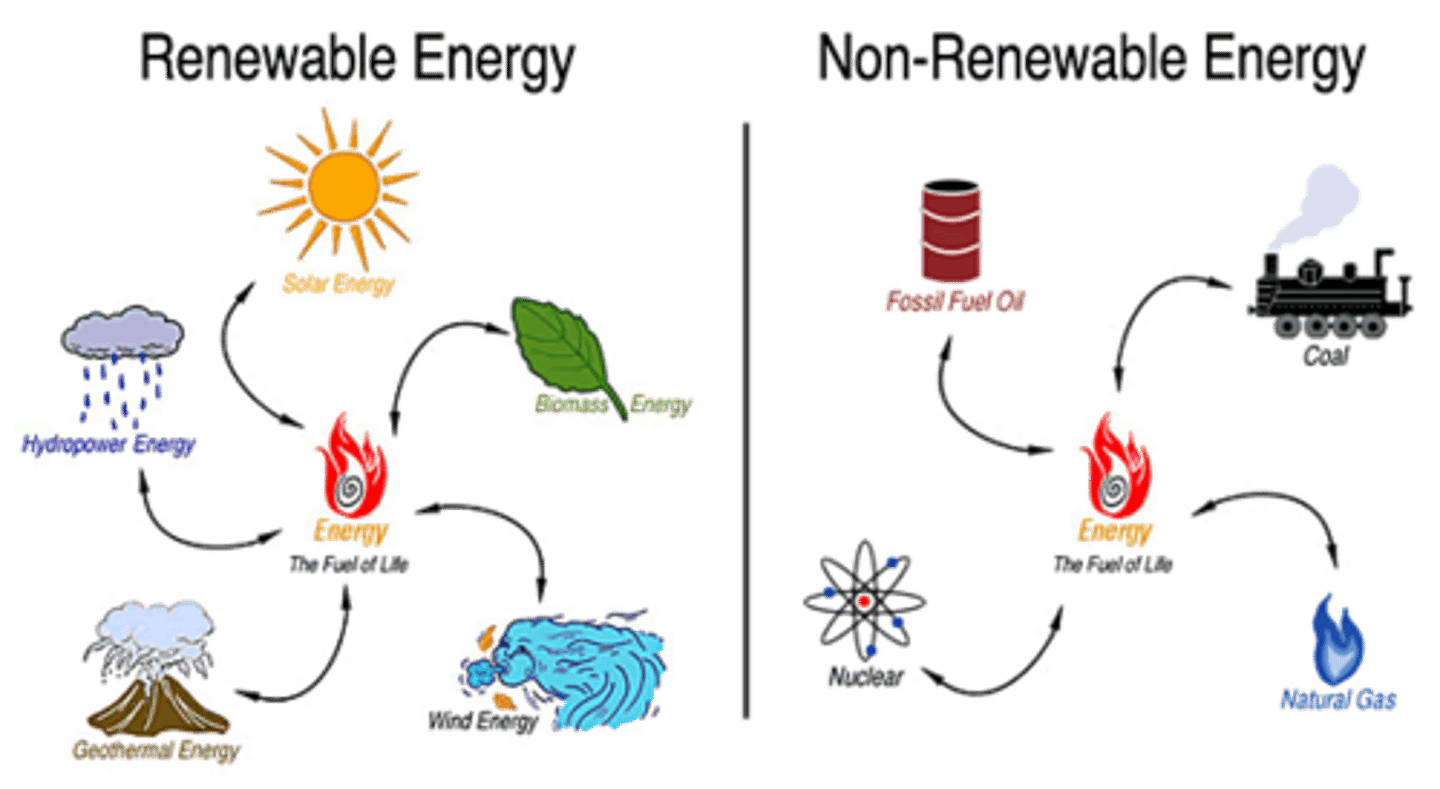
Sustainability
The use of Earth's renewable and nonrenewable natural resources in ways that do not constrain resource use in the future.

land use
the ways in which people use a particular area of Earth's surface; for example, for farming, development, or preservation.

Built Environment
Part of the physical landscape that represents material culture; the landscape created by humans.

Cultural Ecology
How humans adapt to their environment.
Environmental Determinism
The view that the natural environment has a controlling influence over various aspects of human life including cultural development.

Possibilism
The physical environment may limit some human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to their environment.

Geographic Scale (Relative Scale)
Refers to the amount of territory that the map represents.
Global, World Regional, National, National Regional, Local, State, County etc. Also referred to as aggregation.
Region
An area of Earth distinguished by a distinctive combination of cultural and physical features.
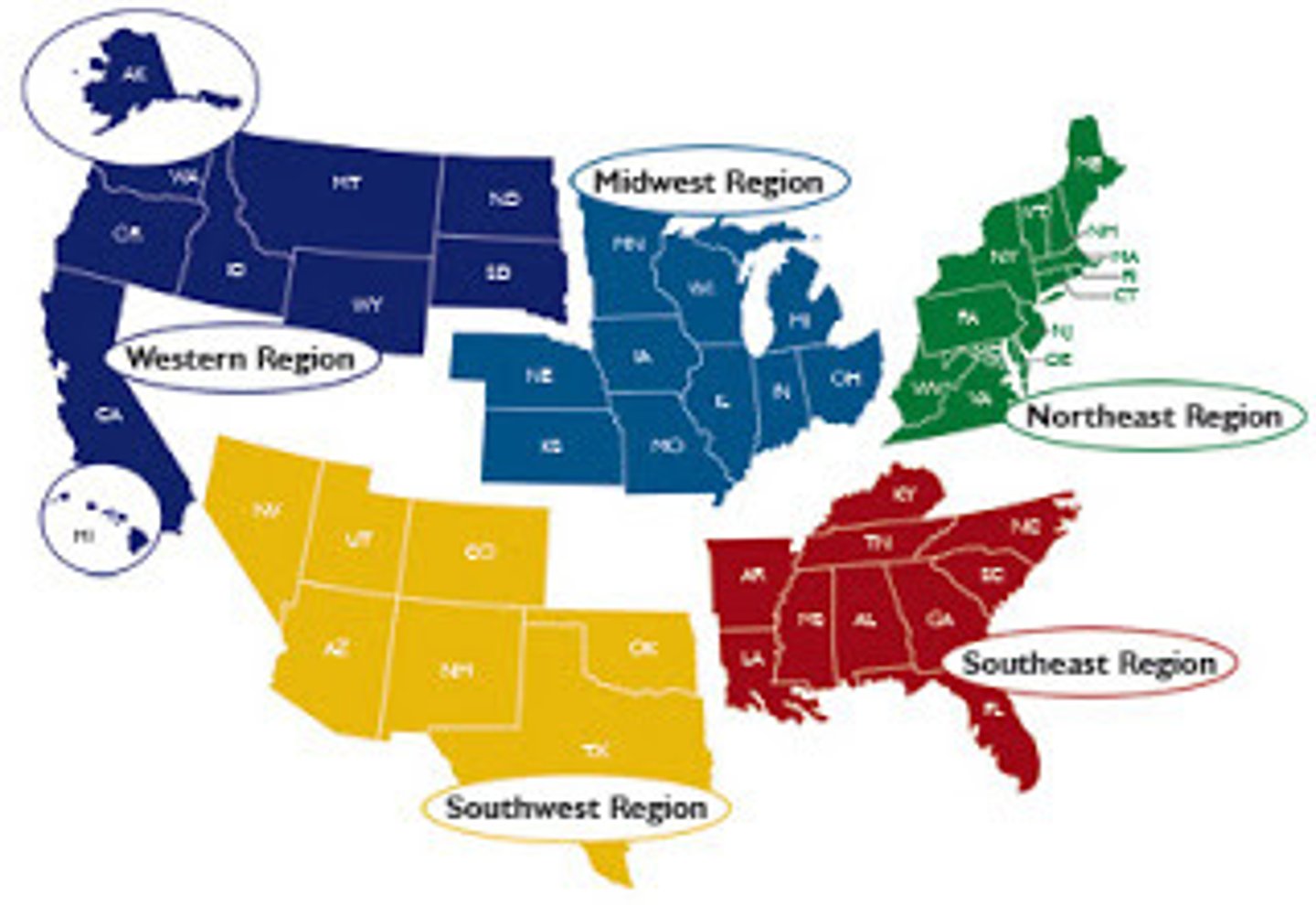
Formal Region
Also Uniform or Homogeneous Region, a regions united by 1 or more traits/characteristics.
Functional Region
Also a Nodal Region, a region that is united by an activity, united by networks of communication, transportation or other interactions.
Perceptual Region
Also a Vernacular Region
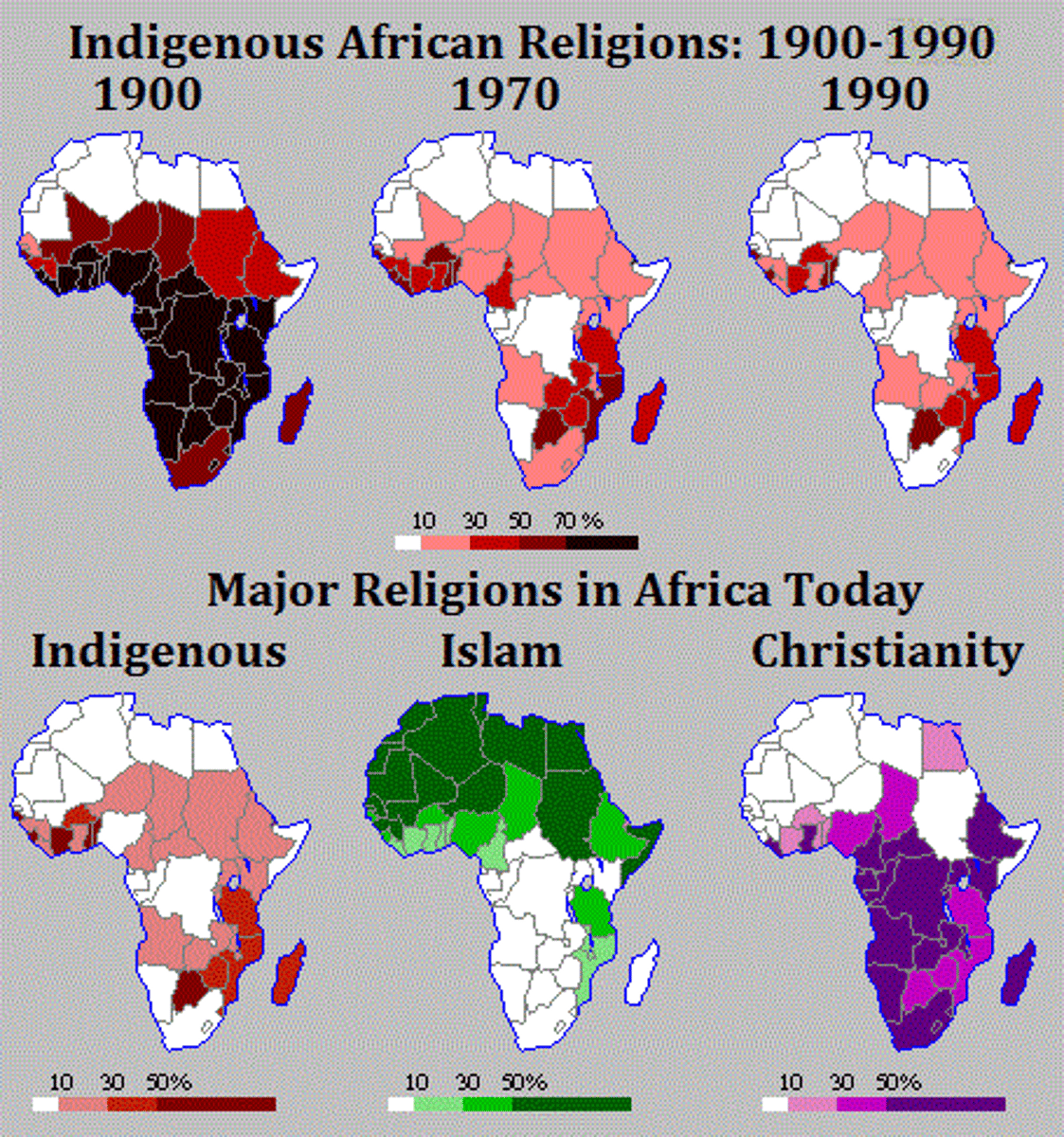
Transitional Region (Sub-Region) Boundaries
A sub region that exhibits characteristics of both/multiple regions, they is no sharp boundary/divide. North Africa and Saharan Africa both exhibit Islam, Christianity and Animist religions culturally and the is also a blending of these faiths, syncretism.
Overlapping Region (Sub-Region) Boundaries
This can be quite perceptual, this is when a place can be part of more than 1 region. Brazil is as its own contained but can be part of South America, Latin America the western hemisphere.
Contested Regional (Sub-Region) Boundaries
This occurs when man-made boundaries are disputed politically. Kashmir, Crimea, Taiwan, even the idea of the Statue of Liberty, is she a Jersey Girl or a New Yorker?.
Syncretism
The unification or blending of opposing people, ideas, or practices, frequently in the realm of religion. For example, when Christianity was adopted by people in a new land, they often incorporate it into their existing culture and traditions, polytheism and allowing the saints to represent the theology of multiple Gods.

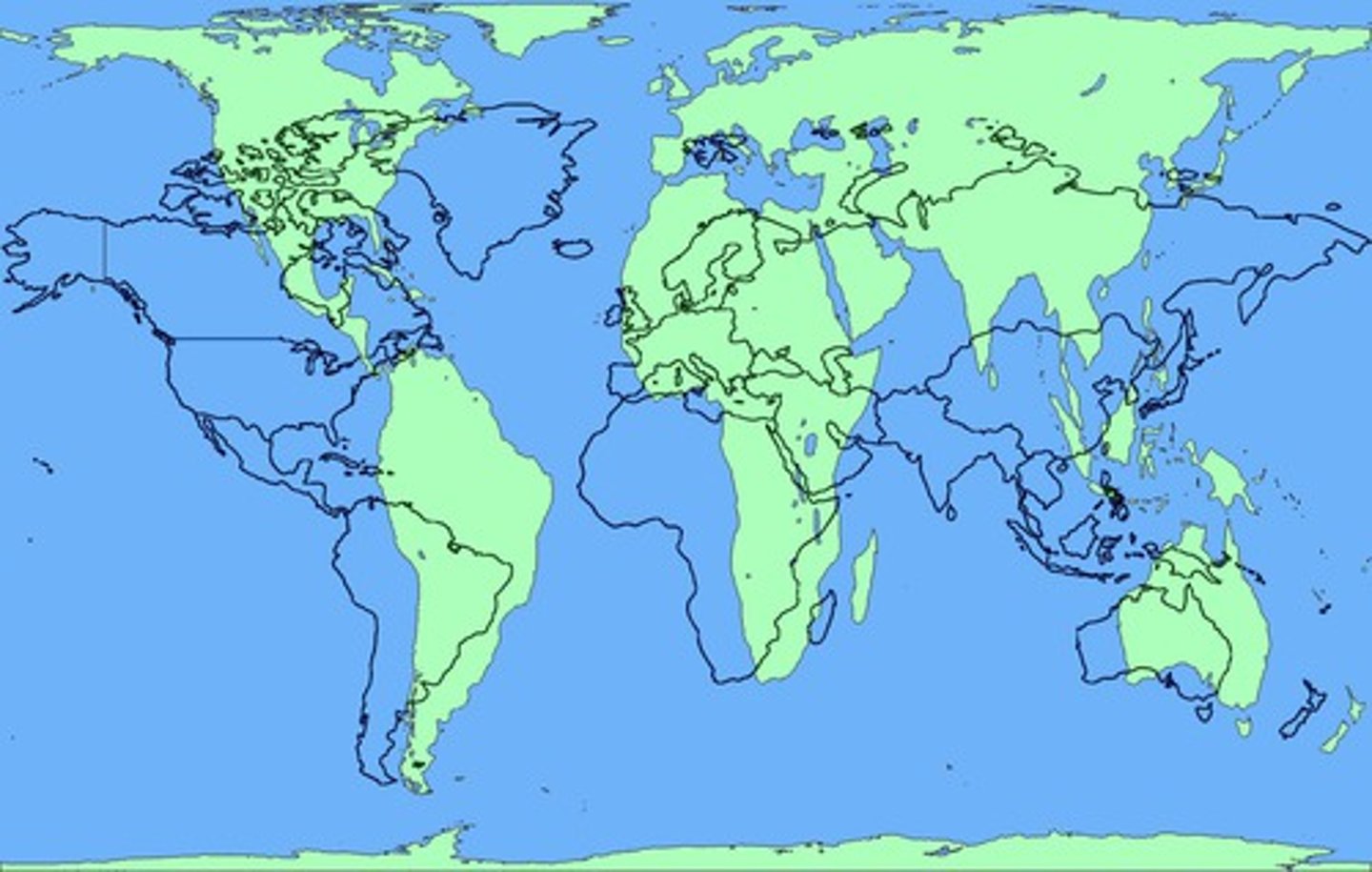
Mercator Map Projection
Accurately shows shape and direction, but distorts distance and size of land masses, Greenland as large as Africa this is not accurate. Mercator projections outlines in black.
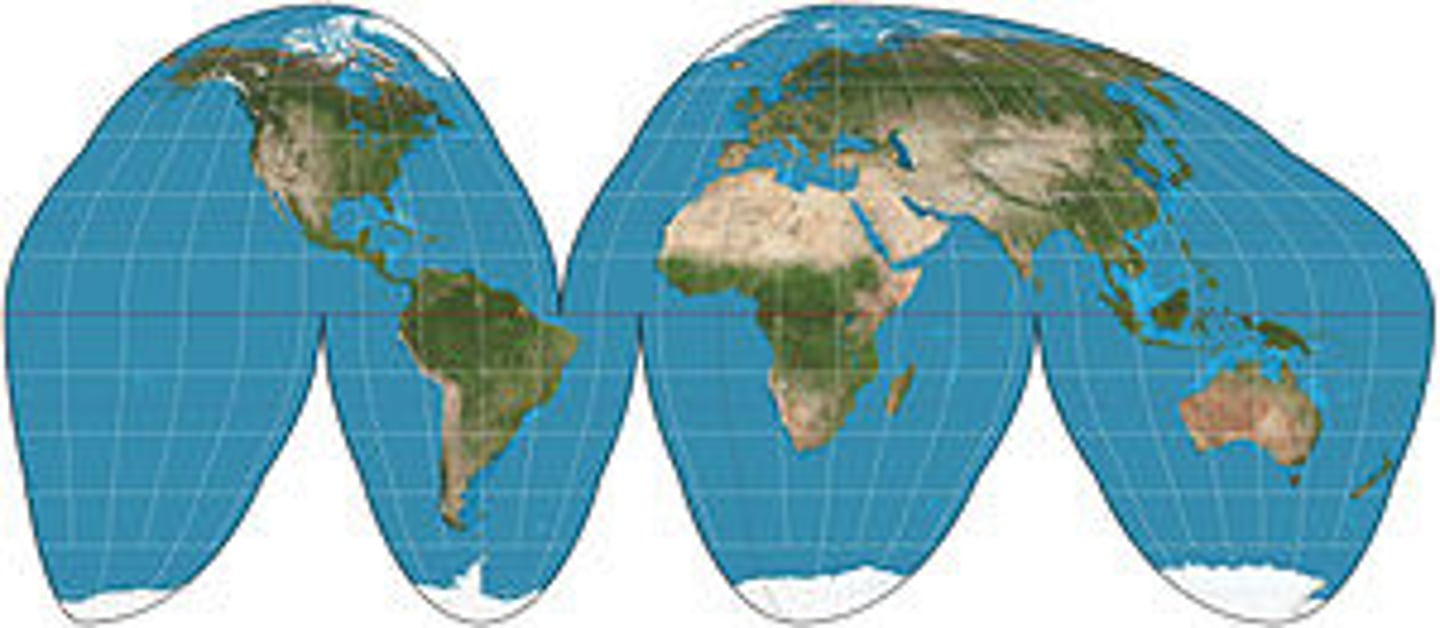
Goode-Homolosine Map Projection
Avoids shape distortion and the restrictions of a rectangular map by creating "interruptions" in the map's continuity. Useless for navigation, interrupted make lines of logitude point in different directions.
Robinson Map Projection
A map projection that does not distort the area of water to landmass as much, but whose direction does not hold as true.