Mixed flashcards
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
character USSF
Acts honestly and owns mistakes, integrity, highest standards accountable. This relates to USAF core value integrity
Commitment USSF
Set bold goals and learns fast, achieve audacious goals, 1% better daily, embrace challenges learn from experience and seek and offer feedback.This relates to the USAF core vale excellence in all we do.
Connection USSF
Foster safe and encouraging environment and seek and offer feedback.This relates to the USAF core vale service before self.
Courage USSF
smart risk, doing what right under pressure, innovate, speak up share ideas and thoughts.
Integrity USAF
Honesty, accountability( own up to your actions), courage, humility the absence of arrogance
Service before self USAF
Duty (Sacrifices), loyalty( preserve something bigger than self) and respect
Excellence in all we do USAF
Mission give 110%, Discipline and Teamwork, don’t cut corners. MDT
Problem solving
see it understand it and solve it for real
8 step PPSM
clarify | Identify and define the issue clearly Observe |
Break Down the Problem | Analyze, identify performance gaps |
Set Improvement Targets | Define goals/milestones for success |
Determine Root Causes | Discover what's really causing the problem DIG |
Develop Countermeasures | Create precautionary solutions |
See Countermeasures Through | carry out your solutions |
Confirm Results and Process | make sure the solution worked and the gap is closed |
Standardize Successful Processes | Lock in what works and apply it elsewhere |
Use when: Time allows for deep analysis, and the problem is process-based or recurring.
OODA Loop
Orient: analyze context and understand whats happening Decide: choose the best possible course of action Act: execute the decision quickly and effectively Fast fix used in tactical operations.
followership and leadership
Good Followers make a good leaders hand in hand
Federalism
shared powers between Federal government = Sets the rules for the whole country
State governments = Handle local issues
Enumerated Powers (Limited Government)
Rule book for the government
Separation of Powers & Checks and Balances
Legislative (makes laws), Executive (enforces laws), Judicial (interprets laws)
1st amendment
Freedom: of speech, religion and assembly
2nd amendment
Right to bear arms and maintain a militia
3rd amendment
Reject quartering of soldiers
4th amendment
Search and seizure protections need warrant
6-8th Amendment
Fair trials, legal process
10th Amendment
Rights & Powers: Any powers not given to the federal government by the Constitution belong to the states or the people. It helps limit federal control
UCMJ
Uniformed code of military justice (LAW)
MCM
Manual for Courts-Martial, detailing procedures and rules for military justice. (MCM shows you how)
Article 31 UCMJ
Service members rights
protection against self incrimination —right to remain silent, must be informed of offense, you don’t have to answer questions that could incriminate you.
rights for search and seizure protection—warrants required for personal property
right to legal counsel ( ADC).
Administrative actions (Non Punitive)
Correct with no formal punishment
Letters of Counseling (LOC) – A written notice to correct
Letters of Admonishment (LOA) – A stronger warning for repeated or serious concerns.
Letters of Reprimand (LOR) – A formal censure for violations of standards.
Records of Individual Counseling (RIC) – Documentation of verbal counseling sessions.
Unfavorable Information File (UIF) – An official record of disciplinary actions.
Preventative Action
Sets clear expectations and corrects behavior early to avoid serious issues. by training by educating feedback provide guidance, leadership example, and ensure clarity
Punitive Actions
formal punishment
Nonjudicial Punishment
-Article 15 – Handled by commander without court-martial Ex; Take pay or rank extra duties
Judicial Punishments?
Summary Court-Martial – Minor offenses
Special Court-Martial – Mid-level offenses
General Court-Martial – Most serious offenses
Responsibility of All Leaders
Comply with standards
Enforce standards
Never condone misconduct
Staff Judge Advocate (SJA)
Legal advisor to the commander.
Represents the Air Force and Space Force in legal matters.
Handles prosecution, legal reviews, and command-level legal support.
Area Defense Counsel (ADC)
Defends service members accused of misconduct
Provides independent legal representation (not tied to command)
Ensures fair treatment under military law
Victims’ Counsel (VC)
Supports victims of sexual assault or domestic violence
Advises them of their rights
May represent victims in certain court-martial proceedings
Professional relationships
standards of conduct and core values. Maintain respect while supporting mission effectiveness and proper military structure.
Fraternization
Fraternization is an unprofessional relationship between an officer and an enlisted member.
It undermines discipline, unit cohesion, and military credibility.
Can harm mission readiness and bring dishonor to those involved.
Marriage between an officer and an enlisted member is not considered fraternization.
Customs and courtesies must be upheld both on and off duty
Legal Consequences of UPRs
punishment under (UCMJ),
Article 92 – Failure to obey a lawful order or regulation
Article 133 – Conduct unbecoming of an officer
Article 134 – Conduct that brings discredit to the armed forces
Maximum Punishment:
Dismissal from service
Up to 2 years confinement
Critical thinking
is the process of carefully and objectively analyzing a subject or idea by:
Setting aside personal feelings, biases, or opinions to receive data driven answer
Focusing on facts, logic, and evidence
Statement
Methods for Evaluating Information
Presents information without trying to influence
Simply claims something
Can be either true or false
Fact
Can be verified or proven true
Subjective Claims
Subjective Claim: Truth depends on personal perspective
Example: “My favorite subject in school is science.”
the nine intellectual standards used in assessing one’s thinking
Clarity – Make information easy to understand. Memory Trick: Clear like glass.
Accuracy – Ensure facts are true and correct. Memory Trick: Accurate = Actual.
Precision – Get exact details, not vague ones. Memory Trick: Precision = Pinpoint.
Relevance – Stick to what matters for the topic. Memory Trick: Relevant = Related.
Depth – Go beyond the surface to explore complexity. Memory Trick: Depth = Dig Deeper.
Breadth – Consider different perspectives. Memory Trick: Breadth = Broader View.
Logic – Ensure ideas connect clearly. Memory Trick: Logic = Links that fit.
Significance – Focus on the most important details. Memory Trick: Significance = Spotlight.
Fairness – Keep reasoning balanced and unbiased. Memory Trick: Fair = Free from Bias.
SCARDBFLP OR CAP DR. BL SF
The Cognitive Domain is the mental battlefield
It’s where influence operations, propaganda, and critical thinking happen
Winning in this domain means protecting how people process truth and make decisions
“Cognitive attacks change how you think; disinformation feeds what you already believe
Cognitive Domain
Cognitive Domain Operations
It is the tools used to fight in that domain the action taken:
These are planned actions to influence, disrupt, protect, or exploit how people think. Target people’s will, beliefs, and psychology (village people tricking them with speakers)
Aim to influence decision-making and behavior
Used in military, political, or psychological strategies.
Includes:
📰 Disinformation
🎯 Propaganda
🤝 Influence campaigns
🛡 Counter-messaging
🛠 Think: “Cognitive operations are the actions used to win minds in the cognitive domain.”
Disinformation
Is the deliberate spread of false or misleading information to deceive or manipulate audiences.
relies on falsehoods to create chaos.
Both can shape outcomes in conflicts without direct warfare.
Example : A fake news article shared to stir fear
“Cognitive attacks change how you think; disinformation feeds what you already believe
Confirmation Bias
is when your brain only sees what it wants to see — you look for, believe, and remember things that support your existing beliefs, while ignoring or rejecting anything that goes against them.
Disinformation feeds confirmation bias to reinforce false beliefs
“Confirmation Bias = Comfort Bias”
Example in ActionImagine a team leader thinks a certain Airman is lazy.
Even when the Airman stays late or volunteers, the leader focuses on the one time they were late — and ignores the good behavior.
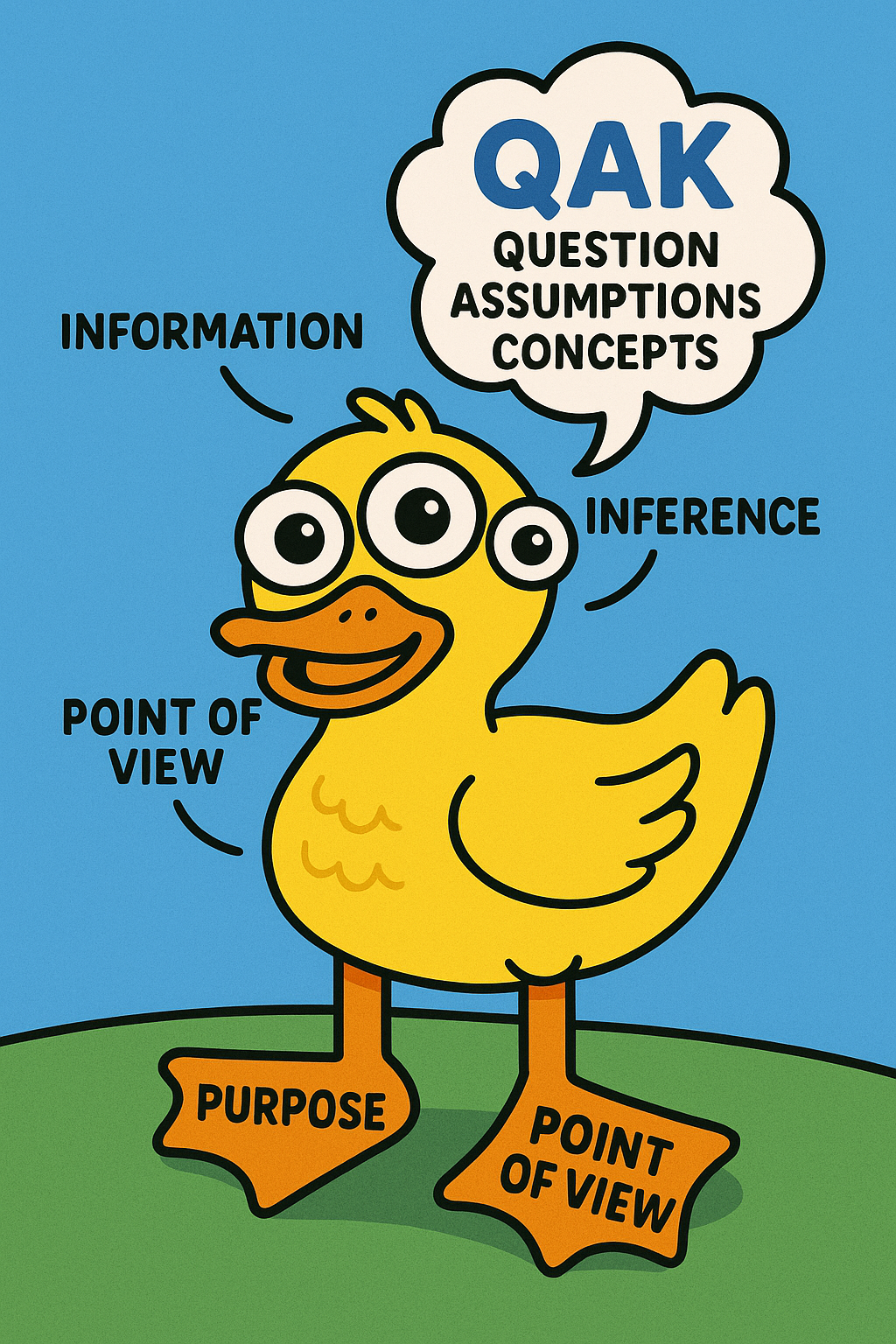
elements of reasoning that are used in the critical thinking process
Purpose – Identify your goal behind the thought process. Memory Trick: No purpose? No point.
Question at Issue – Focus on the actual question being asked. Memory Trick: Question the question.
Points of View – Consider multiple perspectives. Memory Trick: POV = Put On Variations.
Information – Ensure data is accurate, clear, and fair. Memory Trick: No info = No insight.
Concepts and Ideas – Understand the key ideas shaping your thoughts. Memory Trick: Concepts = Core Ideas.
Assumptions – Recognize beliefs influencing your thinking. Memory Trick: Assumptions = Automatic Thoughts.
Implications – Consider possible outcomes of a decision. Memory Trick: Implications = If… then…
Inferences – Draw conclusions based on evidence. Memory Trick: Inferences = In-between the lines.
common thinking errors that can lead to faulty training:
System 1 Thinking is the part of your brain that:
Works fast and automatically
Uses your habits, past experiences, and gut feelings
Makes decisions without you even realizing it
You see someone smile → You smile back instantly
You read “2 + 2” → You instantly know it’s “4”
You hear your name → You turn your head right away
“System 1 = Snap Reaction!”
It's like your brain is on autopilot.
System 1 Thinking
System 2 Thinking
common thinking errors that can lead to faulty training
Slow and Smart
System 2 Thinking is the part of your brain that:
Works slowly, carefully, and deliberately
Needs focus and effort
Is used for solving new, difficult, or unfamiliar problems
Not looking at a pattern—need to use critical thinking to break info down (slow and deliberate)
It’s like your brain puts on glasses and says, “Let me think this through.” like doing your taxes buying a new car. you do this a lot G
Common Thinking Errors
Asking the wrong questions – Poor phrasing can mislead discussions. Right question = right direction.
Deflection – Shifts focus away from the original intent.
Thinking too quickly – Leads to mistakes. Slow down to think better.
Stereotypes – Create biases and snap judgments. Stereotypes = shortcut errors.
Halo effect
you let one good thing about a person influence your opinion about everything else they do — even if it’s not related. One good trait = total assumption.
Exampler: supervisor is really good at PT so you thinkThey’re automatically a great leader
Trust their decisions more
Overlook their weaknesses in other areas like paperwork or planning
Even if they’re not good at everything, that one strong trait (PT skills) casts a “halo” over the rest.
Belief Perseverance
Sticking to your belief even after it's proven wrong
We see what we believe, not what’s real.
Example:
You believe an Airman is lazy.
They show you their perfect attendance and performance record —
but you still think they’re lazy..
value judgment
Based on contributions or skills. Value = what you do.
The consistency principle
Principles of Moral Reasoning
Apply the same standards to all cases. Same rule, same judgment.
example
An Airman is late to formation, and they get corrected.
But then, your friend is late… and you say “It’s fine, don’t worry about it.”
That’s inconsistency — applying rules only to some.
To be , you'd:
✅ Correct both fairly — no favorites
✅ Hold yourself to the same standardthat is being consistent
Missing Information
this is a sources of conflict communication factors
When facts are left out, people make assumptions, leading to misunderstandings and misalignment. Memory Trick: No info = Instant friction.
rewards
sources of conflict Structural Factors
Rewards
Competing for rewards like promotions or recognition can create rivalry. • Fosters a "me vs. you" environment. 🧠 Memory Trick: “Rewards = Race mode.”
Resource Inter-dependence
sources of conflict
People must share time, money, and manpower.
Conflict arises when everyone’s needs are high, but resources are limited.
🧠 Memory Trick: “Sharing stress = Tug-of-war.”
Competing:
Thomas-Kilmann represent how someone handles conflict.
Competing: my way or no way
AFNC Approach The AF applies styles to real problem-solving situations.
INSIST:
Task Orientation: High
people orientation Low
Forcing your solution; not cooperative
🧠 Memory Trick: “Compete = Command”
Think: “I’m in charge!” – pushes forward even if others resist AFNC MEMORY TRICK: I EAT SPICY CHICKEN CURRY
avoiding
Thomas-Kilmann represent how someone handles conflict.
Avoiding
· Style: Not cooperative, not assertive
· Nickname: Evades conflict entirely
· Problem-Solving Term: Evade
· AFNC Approach The AF applies styles to real problem-solving situations.: Avoid (Passive)
· 🧠 Memory Trick: “Avoid = Vanish”
· Think: “If I don’t look at it, it’ll go away.”
compromising
· Thomas-Kilmann represent how someone handles conflict.
compromising
· Style: Kind of cooperative, kind of assertive
· Nickname: Only get some of what you want
· Problem-Solving Term: Settle
· AFNC Approach The AF applies styles to real problem-solving situations. Compromise (Middle-ground)
· 🧠 Memory Trick: “Compromise = Cut in the middle”
· Think: “We both lose a little, but move on.”
Accommodating
Thomas-Kilmann represent how someone handles conflict.
accommodating
· Style: Very cooperative, not assertive
· Nickname: Gives in to others
· Problem-Solving Term: Comply
· AFNC Approach The AF applies styles to real problem-solving situations: Accommodate (Yield)
· 🧠 Memory Trick: “Accommodate = All yours”
· Think: “You win, I’ll step back.”
·
Collaborating
Thomas-Kilmann represent how someone handles conflict.
collaborating
· Style: Very cooperative, very assertive
· Nickname: Wants the best for each other
· Problem-Solving Term: Cooperate
· AFNC Approach The AF applies styles to real problem-solving situations:: Collaborate (Integrate)
· 🧠 Memory Trick: “Collaborate = Combine to Climb”
· Think: “We both rise by working together.”
What is the role of Doctrine in the USAF?
GUIDEBOOK! EXPLAINS WHAT WE BELIEVE! Helps the Air Force use airpower smartly and effectively. Shows how Airmen fit into the joint team. Guides planning, training, and missions. ‘How to fly, fight, and win — smartly."
What is the role of Doctrine in the USSF?
Teaches Guardians how to think and operate in space. Helps protect satellites, comms, and space systems. Supports the entire military with space capabilities. “Think like a space warfighter.”
Why does Doctrine matter?
It gives everyone a shared way of thinking. Helps make good decisions in complex situations. Doctrine provides direction and purpose.
USAF Core Functions Air Superiority
Control the skies to prevent enemy air advantage.
Example: Operation Desert Storm – ensured U.S. dominance of Iraqi airspace.
Memory Cue: 🛡 “We own the sky.”
USAF Core Functions ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, Reconnaissance)
Purpose: Collect and share info to support decisions and missions.
Example: Operation Unified Response – helped assess Haiti earthquake damage.
Memory Cue: 👀 “Knows before you go.”
USAF Core Functions Rapid Global Mobility
Purpose: Transport forces and supplies quickly anywhere on Earth.
Example: Operation Just Cause – quickly airlifted troops into Panama.
Memory Cue: ✈ “Anywhere, anytime.”
USAF Core Functions Global Strike
Purpose: Deliver precise, lethal power globally to deter or defeat.
Example: Operation Deliberate Force – targeted airstrikes in Bosnia.
Memory Cue: 💣 “Strike fast. Strike far.”
USAF Core Functions Command and Control (C2)
Purpose: Direct, coordinate, and manage air, space, and cyber forces.
Example: Operation Odyssey Dawn – coordinated NATO air operations in Libya.
Memory Cue: 🧠 “Control the chaos.
USSF Core Competencies Space Security
Purpose: Protect U.S. and allied space assets and maintain freedom in space.
Memory Cue: 🛡 “Stay free. Stay ready.”
USSF Core Competencies Combat Power Projection
Purpose: Deliver offensive/defensive space capabilities in support of warfighting.
Memory Cue: 🎯 “Space boosts the fight.”
USSF Core Competencies Provide Independent Options
Purpose: Offer unique space capabilities that can shape military outcomes on their own.
Think: Giving commanders more tools that don’t rely on ground or air forces.
Memory Cue: 📡 “Options only space can provide
USSF Core Competencies Ensure Space Mission Assurance
Purpose: Make sure our space systems are reliable, secure, and always working.
Think: Redundancy, backups, and hardening systems against threats.
Memory Cue: 🔒 “Mission ready. Always.”
USSF Core Competencies Enhance Space Mobility and Logistics
Purpose: Develop ways to maneuver, refuel, and repair in space.
Think: Future of space operations—freedom of movement and support.
Memory Cue: 🚀 “Move. Maintain. Sustain.”
Barries to problem solving to overcome:
Emotion, biases stereotype attitude
Identify the purpose of the AFFORGEN and SPAFORGEN :
sustainable, capacity driven model for presenting forces to Joint force commanders (JFCs)
Why do we need AFFORGEN?
Enable operational preparedness and readiness recovery while ensuring a predictable and sustainable force offering
How does the AFFORGEN work?
Based on 3 principles:readiness, predictability, and sustainability
the fisrt rotational phase of readiness in the AFFORGEN cycle
Reset – After deployment: reconnect with family, rebuild the team, recover.
the 2nd rotational phase of readiness in the AFFORGEN cycle
Prepare – Train hard to build up unit readiness.
the third rotational phase of readiness in the AFFORGEN cycle
Ready – Complete certifying events to prove the unit is mission-ready.
the fourth rotational phase of readiness in the AFFORGEN cycle
4.Commit – Ready for deployment or actively deployed.
Why It Matters AFFORGEN
Predictability – You’ll know when your unit might deploy—helps planning and quality of life.
Sustainability – Keeps the cycle going long-term without burning people out.
SPAFORGEN: Space Force Generation Model : Prepare Phase
Guardians train, upgrade skills, take professional military education, and focus on resilience. Think of it as sharpening the sword.
SPAFORGEN: Space Force Generation Model : Ready Phase
Advanced training kicks in—large-scale exercises, squadron validations, and mission rehearsals. This is where Guardians prove they’re ready for real-world ops.
SPAFORGEN: Space Force Generation Model: Commit Phase
Guardians are either deployed or actively supporting missions. They’re now fully mission-ready and executing operations.
SPAFORGEN creates a predictable cycle HOW MANY PHASES? THEY DEPLOY HOW?
Most Guardians are employed in place, not physically deployed like other services.
SPAFORGEN is how the U.S. Space Force organizes, BY?
standardized battle rhythm has 3 phases
Organizational Culture vs Organizational Climate
Culture = Long-term, deep beliefs, values, and traditions; it's the foundation.
Climate = Day-to-day mood and attitude in the unit; it changes more easily. Attitudes, perceptions, short-term, adjustable
🧠 Culture = personality / Climate = mood
What are some ways to build a positive organizational climate? Building a Positive Organizational Climate?
Safe & Secure:
Provide a safe space—physically and emotionally (trust, respect, no fear).
High Standards:
Expect more than the bare minimum. Push for growth and excellence.
Feedback Tools:
Use DEOCS to check unit morale and make improvements with results.
Little Things Matter:
Every action by a leader matters (even a simple “thanks”!)
How do you change an organizational climate for the better?
Address the Unit
• Share DEOCS results honestly
Implement Changes
• Explain changes and their mission impact
Inspire Action
• Communicate goals and energize the team
Reinforce Good Behavior
• Support effort and lead by example
DEOCS stands for Defense Equal Opportunity Climate Survey.
confidential survey that asks Airmen (and all DoD personnel) about how they feel in their unit — things like:
Morale
Trust in leadership
Leaders use DEOCS results to understand the climate of their unit and make it better
SOB 1: What is the 1st Stages of Team Growth?
Forming
🧠 “Getting to know each other”
Everyone’s polite and unsure of their role
You’re figuring out where you fit in
The team is learning its mission and tasks
Leader acts like a Director to set the tone and explain the mission.
SOB 1: What is the 2nd Stages of Team Growth?
Storming
🧠 “Rough patch”
People start disagreeing or clashing
Stress from slow progress, confusion
Arguments over how to do things
Leader becomes a Coach to calm the chaos and help resolve issues.
SOB 1: What is the 3rd Stages of Team Growth?
Norming
🧠 “Team starts clicking”
Team members trust each other
Rules and routines are set
People work together and get things done
Leader acts as a Collaborator, building confidence and teamwork.
SOB 1: What is the 4th Stages of Team Growth?
Performing
🧠 “We got this”
The team is confident and working well
Problems get solved fast
Everyone knows their role and respects each other
The leader becomes a Visionary, planning ahead and developing future leaders.
SOB 2: What do Leaders and Followers Do to Build a Good Team?
What does a Director do (Forming)
Leader: Gives direction, sets expectations
Follower: Learns roles, listens, adjusts
Coach (Storming)
Leader: Resolves conflict, encourages input
Follower: Speaks up, stays respectful
Collaborator (Norming)
Leader: Delegates, builds confidence
Follower: Owns tasks, supports teammates
Visionary (Performing)
Leader: Plans ahead, grows future leaders
Follower: Improves, helps others grow
Types of Leadership
Laissez-Faire = “L for Lazy”
Laissez-Faire = Let it happen (leader disappears)
Think: “L for Lazy Leader” → doesn’t lead, doesn’t care
🛑 AVOID IT!